Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1,2,3 : by Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 1
Uploaded by
Rupesh Nidhi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views7 pagesThis document discusses key concepts in C programming including hierarchy of operations, associativity of operators, the history of C, and compiling and running a C program. It explains that hierarchy of operations determines the order calculations are performed based on operator precedence. Associativity refers to how operators of the same priority are handled from left to right or right to left. The history section gives a brief overview of the origins and development of the C language. Finally, it outlines the basic steps to compile a C program into an executable file.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chap1,2,3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses key concepts in C programming including hierarchy of operations, associativity of operators, the history of C, and compiling and running a C program. It explains that hierarchy of operations determines the order calculations are performed based on operator precedence. Associativity refers to how operators of the same priority are handled from left to right or right to left. The history section gives a brief overview of the origins and development of the C language. Finally, it outlines the basic steps to compile a C program into an executable file.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views7 pagesChapter 1,2,3 : by Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 1
Uploaded by
Rupesh NidhiThis document discusses key concepts in C programming including hierarchy of operations, associativity of operators, the history of C, and compiling and running a C program. It explains that hierarchy of operations determines the order calculations are performed based on operator precedence. Associativity refers to how operators of the same priority are handled from left to right or right to left. The history section gives a brief overview of the origins and development of the C language. Finally, it outlines the basic steps to compile a C program into an executable file.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
Chapter 1,2,3…
By Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 1
Hierarchy of operations
The priority or precedence in which the operations in an arithmetic statement are performed is
called the hierarchy of operations.
Note that 6 / 4 gives 1 and not 1.5
because 6 and 4 both are integers and
therefore 6 / 4 must evaluate to an
integer. Similarly 5 / 8 evaluates to zero,
since 5 and 8 are integers and hence 5 / 8
must return an integer value.
By Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 2
Associativity of Operators
Ø When an expression contains two operators of equal priority the tie
between them is settled using the associativity of the operators.
Ø All operators in C have either Left to Right associativity or Right to Left
associativity.
Ø Let us understand this with the help of a few examples.
vConsider the expression a = 3 / 2 * 5 ; Here there is a tie
between operators of same priority, that is between / and *. This tie
is settled using the associativity of / and *. Both enjoy Left to Right
associativity. Therefore firstly / operation is done followed by *.
vConsider a = b = 3 ; Here both assignment operators have the
same priority. So order of operations is decided using associativity
of = operator. = associates from Right to Left. Therefore, second = is
performed earlier than first =.
By Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 3
Associativity of Operators…
By Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 4
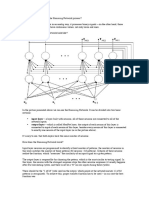
History of C
By Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 5
Overview of C program
By Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 6
Compiling and Running a program
Ø Compiler translates source program
into another representation or file
with extension .o called object
file.(e.g. sample.o)
Ø Linking is the process of putting
together other program files and
functions that are required by the
program
Ø And finally the compiled and linked
program is called executable object
code and stored as extension of .out
(e.g. sample.out)
By Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 7
You might also like
- Critical Path Method: Farrokh Alemi, PH.DDocument40 pagesCritical Path Method: Farrokh Alemi, PH.DAli Kamel100% (2)
- Answer Key Python Class 7Document4 pagesAnswer Key Python Class 7Divtej SinghNo ratings yet
- CB72504 Warhammer Age of Sigmar Roleplay - Soulbound - Shadows in The Mist - Anvilgard Map (2021-04-19)Document1 pageCB72504 Warhammer Age of Sigmar Roleplay - Soulbound - Shadows in The Mist - Anvilgard Map (2021-04-19)Lleman0% (1)
- IMF and World Bank AssignmentDocument5 pagesIMF and World Bank AssignmentAmazing worldNo ratings yet
- Electronic Device and CircuitDocument124 pagesElectronic Device and CircuitRupesh NidhiNo ratings yet
- A New Method For Improving The RQD Determination of Rock Core in BoreholeDocument9 pagesA New Method For Improving The RQD Determination of Rock Core in BoreholeKevin RiosNo ratings yet
- Specification Requirements For Conveyor Pulleys and ShaftsDocument15 pagesSpecification Requirements For Conveyor Pulleys and Shaftsjonodo8967% (3)
- Machine Learning TutorialDocument149 pagesMachine Learning TutorialRupesh NidhiNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocument19 pagesCustomer Relationship ManagementAshok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Earth Magnetometer ProjectDocument17 pagesEarth Magnetometer ProjectMario Ariel VesconiNo ratings yet
- Computer Science NotesDocument3 pagesComputer Science NotesBiplap HomeNo ratings yet
- Perl Assignment OperatorsDocument6 pagesPerl Assignment OperatorslhltkphjfNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Experiment No. 3Document17 pagesWorksheet - Experiment No. 3chlorine169No ratings yet
- Principal of Programming Short NotesDocument35 pagesPrincipal of Programming Short NoteskumarabhiNo ratings yet
- Brief Note of C++ CHDocument91 pagesBrief Note of C++ CHsetegnNo ratings yet
- Mostly Asked FAQ's PythonDocument6 pagesMostly Asked FAQ's PythonViraja AmbatapudiNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document27 pagesModule 2shahany habeebNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1665129622681 6984059836935141680Document27 pagesOrca Share Media1665129622681 6984059836935141680Subodh DevkotaNo ratings yet
- 3CS4 OOPS Unit 2Document32 pages3CS4 OOPS Unit 2niworah679No ratings yet
- BPUT MCA 2007 - 2009 Solved QuestionsDocument11 pagesBPUT MCA 2007 - 2009 Solved Questionsdnayak3821396No ratings yet
- Aspects of Applicative Programming For Parallel ProcessingDocument8 pagesAspects of Applicative Programming For Parallel ProcessingprettyhatNo ratings yet
- Unit - I (2 Marks)Document9 pagesUnit - I (2 Marks)sharmilakumari sNo ratings yet
- Compilers and Translation Learning PortfolioDocument5 pagesCompilers and Translation Learning PortfolioChristopher Edward PhiferNo ratings yet
- Introduction To C++ Inheritance: CS107L Handout 05 Autumn 2007 October 26, 2007Document27 pagesIntroduction To C++ Inheritance: CS107L Handout 05 Autumn 2007 October 26, 2007usman33_15No ratings yet
- CS343 2008 SectiondDocument7 pagesCS343 2008 SectiondMfanwekhaya DubeNo ratings yet
- APLC DocumentationDocument24 pagesAPLC DocumentationAnuja SharmaNo ratings yet
- CS101-Topic 114Document6 pagesCS101-Topic 114Ahmad FarazNo ratings yet
- Presentation PoorvDocument27 pagesPresentation PoorvKartikeySinghNo ratings yet
- CITS 3242 Programming Paradigms: Introduction To Functional ProgrammingDocument17 pagesCITS 3242 Programming Paradigms: Introduction To Functional ProgrammingManpreet Singh BudhailNo ratings yet
- Lab-10 Functions in Python: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLab-10 Functions in Python: ObjectivesFarrukh AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 NotesDocument26 pagesModule 5 NotesDency SanganiNo ratings yet
- Expressions and Assignment StatementsDocument25 pagesExpressions and Assignment StatementsAlia MaitahNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CS3353 - C Programming and Data StructuresDocument6 pagesUnit 1 CS3353 - C Programming and Data StructuresKokila SNo ratings yet
- Csi 07Document25 pagesCsi 07Mai Cao Thị ThanhNo ratings yet
- SG2 Elective 4Document12 pagesSG2 Elective 4katernalism04No ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Functional and Imperative Programming Languages (10 Marks)Document7 pagesCompare and Contrast Functional and Imperative Programming Languages (10 Marks)Mridul Kumar BoruahNo ratings yet
- C AnsDocument12 pagesC Anssurendra_chauhan_2No ratings yet
- Cscc24 Midterm NotesDocument5 pagesCscc24 Midterm NotesDeveloperAtWorkNo ratings yet
- Csi 07Document25 pagesCsi 07dangvodich07No ratings yet
- Introduction To ReferencesDocument16 pagesIntroduction To ReferencesJeremy PhoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CompilerDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Compilerakhtar abbasNo ratings yet
- PPL FinalDocument31 pagesPPL Finalproject6.checkNo ratings yet
- Semantics: Computer Programming Value Variable Name Imperative Statements OperatorDocument7 pagesSemantics: Computer Programming Value Variable Name Imperative Statements OperatorNeshad PrettyNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document16 pagesSession 1the477577No ratings yet
- Object - Oriented Programming: Concepts of OopsDocument10 pagesObject - Oriented Programming: Concepts of OopsHarsha PaniaNo ratings yet
- Chap09 1473751047 598107Document54 pagesChap09 1473751047 598107Le Duc PhiNo ratings yet
- 21csc203p-App - Unit 4Document85 pages21csc203p-App - Unit 4jhaa98676No ratings yet
- Classes Ass Op OverloadDocument6 pagesClasses Ass Op OverloadCasey PerdidoNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument19 pagesFunctionsjosephramsingculanNo ratings yet
- Howland J.E. - Functional Programming and The J Programming Language-Department of Computer Science (2005)Document23 pagesHowland J.E. - Functional Programming and The J Programming Language-Department of Computer Science (2005)Gulrez MNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Elements of Programming: C MP Sing PR GramsDocument29 pages1.2 Elements of Programming: C MP Sing PR Gramskp88No ratings yet
- Control FlowDocument9 pagesControl FlowAli ShahNo ratings yet
- Class - XI Subject: Computer ScienceDocument38 pagesClass - XI Subject: Computer ScienceSaksham Kumar GargNo ratings yet
- Analysis & Design of AlgorithmsDocument14 pagesAnalysis & Design of AlgorithmsHarshit kumar sinhaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence LabDocument20 pagesArtificial Intelligence LabBulmi HilmeNo ratings yet
- Functional Languages: Historical OriginsDocument6 pagesFunctional Languages: Historical OriginsAli ShahNo ratings yet
- Lci Manual: 1 SyntaxDocument9 pagesLci Manual: 1 SyntaxtuNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1: Title: Study of Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument20 pagesAssignment No.1: Title: Study of Object Oriented ProgrammingSports ClubeNo ratings yet
- 15-411 Compiler Design: Lab 3 Fall 2009Document8 pages15-411 Compiler Design: Lab 3 Fall 2009Smile GaffoorNo ratings yet
- C++ Notes-1Document39 pagesC++ Notes-1kuchipudi durga pravallikaNo ratings yet
- Programming Paradigms: A Must Know For All ProgrammersDocument4 pagesProgramming Paradigms: A Must Know For All ProgrammersZunaira TahirNo ratings yet
- Operators and Expressions: Prof. Rajiv Kumar IIM KashipurDocument12 pagesOperators and Expressions: Prof. Rajiv Kumar IIM KashipurRajat SinghNo ratings yet
- DR M. Arifur Rahman: PHY-206 CpnaDocument13 pagesDR M. Arifur Rahman: PHY-206 CpnaMuheb BullahNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Programming: Lab Practical Week 1 ObjectiveDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Programming: Lab Practical Week 1 ObjectiveAli KhanNo ratings yet
- DR M. Arifur Rahman: PHY-206 CpnaDocument13 pagesDR M. Arifur Rahman: PHY-206 CpnaMuheb BullahNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms ModuleDocument53 pagesDesign and Analysis of Algorithms Moduledawit8030No ratings yet
- Pointers Concise InstructionDocument3 pagesPointers Concise InstructionrickenjusNo ratings yet
- Python Important Questions and AnswersDocument82 pagesPython Important Questions and Answerssiva kesavNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Using Computer: by Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 1Document19 pagesProblem Solving Using Computer: by Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 1Rupesh NidhiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Computer Software and Programming Languages: by Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 1Document14 pagesOverview of Computer Software and Programming Languages: by Er. Rupesh Kumar Nidhi 1Rupesh NidhiNo ratings yet
- Hierarchical Sentence Level Attention TransformerDocument1 pageHierarchical Sentence Level Attention TransformerRupesh NidhiNo ratings yet
- Hamming NetworkDocument2 pagesHamming NetworkRupesh NidhiNo ratings yet
- Structure: Recurrent Artificial Neural Network John Hopfield Content-Addressable Memory BinaryDocument2 pagesStructure: Recurrent Artificial Neural Network John Hopfield Content-Addressable Memory BinaryRupesh NidhiNo ratings yet
- Abelardo Rodríguez, Ann Kendall (2001)Document14 pagesAbelardo Rodríguez, Ann Kendall (2001)Alexander J. SicosNo ratings yet
- Chat GPT-GM QualityDocument2 pagesChat GPT-GM QualitypkguptaqaqcNo ratings yet
- mt4 GuideDocument24 pagesmt4 GuideGeorge PruteanuNo ratings yet
- Mico Paulo S. Caballero - Let Us Practice MoreDocument3 pagesMico Paulo S. Caballero - Let Us Practice MoreMico Paulo CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Admiral Markets Uk LTD Client Complaints Handling ProcedureDocument3 pagesAdmiral Markets Uk LTD Client Complaints Handling ProcedureTensonNo ratings yet
- Air of Fredoom - Infinity History of Corruption in BoliviaDocument315 pagesAir of Fredoom - Infinity History of Corruption in BoliviaParavicoNo ratings yet
- Order LetterDocument13 pagesOrder LetterdellaNo ratings yet
- Rural Marketing - Project ShaktiDocument12 pagesRural Marketing - Project ShaktiMonisha HenryNo ratings yet
- LM78S40 Switching Voltage Regulator Applications: National Semiconductor Application Note 711 March 2000Document17 pagesLM78S40 Switching Voltage Regulator Applications: National Semiconductor Application Note 711 March 2000Pravin MevadaNo ratings yet
- Labor Law Bar Exam 2012 ResearchDocument9 pagesLabor Law Bar Exam 2012 ResearchMalaybalaycity TiktokchallengeNo ratings yet
- GPS System Limitations: Known Geographic & Weather Related LimitationsDocument1 pageGPS System Limitations: Known Geographic & Weather Related LimitationsVaibhav PooniaNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 2Document13 pagesProgress Test 2Enrique GarciaNo ratings yet
- LT825Document3 pagesLT825dhanushkaran456No ratings yet
- SRF Foundation Brief Profile 30-03-19Document6 pagesSRF Foundation Brief Profile 30-03-19AbishaNo ratings yet
- Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, BhopalDocument2 pagesMaulana Azad National Institute of Technology, BhopalNiteshNarukaNo ratings yet
- SLO County Citizens Homeless Commission ReportDocument16 pagesSLO County Citizens Homeless Commission ReportNick WilsonNo ratings yet
- gp30mpc 150Document27 pagesgp30mpc 150locomotoras.slpNo ratings yet
- Zombie: Survival GuideDocument25 pagesZombie: Survival Guideapi-462582713No ratings yet
- Jalosjos v. COMELECDocument9 pagesJalosjos v. COMELECshhhgNo ratings yet
- Experiment4 DoxDocument9 pagesExperiment4 Doxsajith100% (1)
- YZF-R7 Owners Manual 2023sDocument100 pagesYZF-R7 Owners Manual 2023sSedatNo ratings yet
- H2H Connectivity Guide V7.3Document78 pagesH2H Connectivity Guide V7.3Roshan MadusankaNo ratings yet
- Djimon Hounsou CADocument101 pagesDjimon Hounsou CAlolita damienNo ratings yet