Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCU GTD SQ - Achondo, Carlos
Uploaded by
Doc Achondo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pages1. Complete moles have diffuse swelling of the chorionic villi throughout the placenta with trophoblastic proliferation but no embryonic development. Partial moles have less extensive swelling of chorionic villi in a scalloped pattern and presence of an embryo/fetus and placental membranes.
2. Risk factors for a molar pregnancy include extremes of maternal age. Risk factors for malignant transformation include a large for dates uterus.
3. A 25 year old woman diagnosed with a complete molar pregnancy would have it evacuated through suction curettage.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Complete moles have diffuse swelling of the chorionic villi throughout the placenta with trophoblastic proliferation but no embryonic development. Partial moles have less extensive swelling of chorionic villi in a scalloped pattern and presence of an embryo/fetus and placental membranes.
2. Risk factors for a molar pregnancy include extremes of maternal age. Risk factors for malignant transformation include a large for dates uterus.
3. A 25 year old woman diagnosed with a complete molar pregnancy would have it evacuated through suction curettage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesMCU GTD SQ - Achondo, Carlos
Uploaded by
Doc Achondo1. Complete moles have diffuse swelling of the chorionic villi throughout the placenta with trophoblastic proliferation but no embryonic development. Partial moles have less extensive swelling of chorionic villi in a scalloped pattern and presence of an embryo/fetus and placental membranes.
2. Risk factors for a molar pregnancy include extremes of maternal age. Risk factors for malignant transformation include a large for dates uterus.
3. A 25 year old woman diagnosed with a complete molar pregnancy would have it evacuated through suction curettage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
MANILA CENTRAL UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
DEPARTMENT OF OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
PATHOLOGIC OBSTETRICS
GTD Short Quiz
Dr. Milagros T. Jocson
NAME: Carlos D. Achondo Jr.
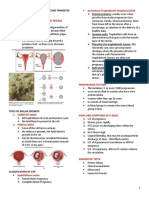
1.2. Describe the difference between Complete H. Mole and Partial H. Mole regarding the FF:
Complete Mole Partial Mole
1. Degree of involvement of the placenta
2.Presence or absence of embryonic development:
Complete Mole Partial Mole
Degree of placental There is diffuse The hydropic
involvement swelling of chorionic chorionic villi is less
villi (edematous extensive and more
chorionic villi) localized producing a
Also there is scalloping pattern of
trophoblastic edematous villi.
proliferation
Presence or absence No fetal or placental There is presence of
of embryonic membranes embryo/fetus and
development placental membranes
3. Identify 1 risk factor for H Mole: Extremes of maternal age
4. Identify 1 risk factor for malignant transformation of H Mole: Large for dates uterus
5. 25 y/o G2P0 diagnosed with Complete H Mole. What will be the mode of evacuation? Suction Curettage
6. What is meant by Plateauing titer of bHCG titer post molar evacuation?
The serum bHCG post molar evacuation regresses but it is insufficient, quantitatively, the
regression or the drop oof bHCG is only less than 10% for a 3 week period.
7-10. Describe histologic characteristics of the ff:
7. Invasive Mole: The presence of hyperplastic cytotrophoblast and syncitiotrophoblast with villous
stroma within the myometrium and or in the metastatic lesions.
8. Choriocarcinoma: It also has cyto and syncitiotrophoblast but without villous stroma.
9. PSSTT: The hyperplastic layer is the intermediate trophoblast that was the previous site where the
placenta implants, called chorionic frondosum.
10. ETT: this arises from intermediate trophoblast as well but unlike in PSTT which came from the
previous placental site implantation, it came from the chorionic levae.
You might also like
- Vesicular Mole: Dr. Mohammed Abdalla Egypt, Domiat G. HospitalDocument32 pagesVesicular Mole: Dr. Mohammed Abdalla Egypt, Domiat G. HospitalPrathibha GuruguriNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument23 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseasemmamloukNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument7 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Tumor Trofoblas GestasionalDocument14 pagesTumor Trofoblas GestasionalTriyoga PramadanaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument6 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseEvan100% (1)
- OB - Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (JCR)Document5 pagesOB - Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (JCR)gellie gellesNo ratings yet
- Int J Clin Oncol 2000 p71Document8 pagesInt J Clin Oncol 2000 p71Handris SupriadiNo ratings yet
- Case Study H MOLEDocument11 pagesCase Study H MOLEmaori_martinez82% (11)
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument2 pagesHydatidiform MoleMonisha RaviNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ayman - GTDand GTN - NotesDocument34 pagesProf. Ayman - GTDand GTN - NotesThekra AlmosaedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PathologyDocument54 pagesChapter 4 Pathologykristinenidoy.mdNo ratings yet
- Vesicular Mole: Dr. Mohammed Abdalla Egypt, Domiat G. HospitalDocument32 pagesVesicular Mole: Dr. Mohammed Abdalla Egypt, Domiat G. Hospitalmadmax500No ratings yet
- Clinical Gynecologic Oncology (Ninth Edition)Document32 pagesClinical Gynecologic Oncology (Ninth Edition)Brandon MachainNo ratings yet
- OB M02 Ch2.1 GTD GTNDocument10 pagesOB M02 Ch2.1 GTD GTNDeshi SportsNo ratings yet
- An Update On Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument9 pagesAn Update On Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseFellita Ratri ANo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument53 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Diseaseahmad danil fatahNo ratings yet
- Kehamilan MolaDocument88 pagesKehamilan MolaYhanna UlfianiNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument43 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseHoney May Rollan VicenteNo ratings yet
- Letter To The EditorDocument2 pagesLetter To The EditorLuthfia WardhaniNo ratings yet
- بیماری تروفوبلستیک بارداریDocument44 pagesبیماری تروفوبلستیک بارداریrazvanNo ratings yet
- Artigo The Pathology of Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument9 pagesArtigo The Pathology of Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseSarah Saene da Silva NoiaNo ratings yet
- Molar Pregnancy: Presented byDocument87 pagesMolar Pregnancy: Presented bysanjay kashyapNo ratings yet
- H MolepcdplDocument55 pagesH MolepcdplCrisha SaguidNo ratings yet
- Trophoblastic and Pregnancy: DiseasesDocument6 pagesTrophoblastic and Pregnancy: DiseasesKonstantinos PapadakisNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaDocument18 pagesGestational Trophoblastic NeoplasiaTanuj sai kumarNo ratings yet
- 3RD TrimesterDocument7 pages3RD TrimesterAmethystNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (Neha Martin Msc. NSG 2nd Year)Document13 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease (Neha Martin Msc. NSG 2nd Year)Gunu SinghNo ratings yet
- Histological Diagnosis of Hydatidiform Moles: Histological Changes of Complete and Partial Moles AreDocument8 pagesHistological Diagnosis of Hydatidiform Moles: Histological Changes of Complete and Partial Moles AreClareen JuanicoNo ratings yet
- Case Study H MOLEDocument11 pagesCase Study H MOLEHomework PingNo ratings yet
- Case 10Document5 pagesCase 10irma suwandi sadikinNo ratings yet
- Molarpregnancy 160623022400Document89 pagesMolarpregnancy 160623022400BHAKTI KASHYAPNo ratings yet
- GTD MolaDocument8 pagesGTD MolaNurul AslamiahNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument17 pagesHydatidiform MoleRitamariaNo ratings yet
- S&M Cystadenoma, H MoleDocument35 pagesS&M Cystadenoma, H MoleShefali GoyalNo ratings yet
- GTD Case StudyDocument9 pagesGTD Case StudyZnarf Izlah Sadanreb100% (1)
- Jurnal Mola HidatidosaDocument8 pagesJurnal Mola HidatidosaDebby SofianaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease AtrashDocument24 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease Atrashaschubeke736No ratings yet
- 10.1515 - Med 2019 0098Document4 pages10.1515 - Med 2019 0098fansofiuNo ratings yet
- UFA-Referat II GTNDocument47 pagesUFA-Referat II GTNHeldasari SianturiNo ratings yet
- CP Hydatidiform MoleDocument13 pagesCP Hydatidiform Molesweetheart_joannieNo ratings yet
- GTD For Year 3Document25 pagesGTD For Year 3Hasanah NurmirafudinNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform Mole: AuthorsDocument7 pagesHydatidiform Mole: AuthorsIdo KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument4 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseasePrincess PlateroNo ratings yet
- Vesicular MoleDocument27 pagesVesicular MolePadmaNo ratings yet
- Molar Pregnancy - Case PresentationDocument7 pagesMolar Pregnancy - Case Presentationアンナドミニク100% (1)
- Invasive Molar Pregnancy and MRI: What Every Radiologist Must KnowDocument51 pagesInvasive Molar Pregnancy and MRI: What Every Radiologist Must Knowmelchi santander go100% (1)
- Fournier 2011Document9 pagesFournier 2011Nofi NurinaNo ratings yet
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument58 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseJalajarani SelvaNo ratings yet
- Vesicular MoleDocument46 pagesVesicular Moledhisazainita0% (1)
- Ijgo 13877Document8 pagesIjgo 13877rutujaNo ratings yet
- Molar Pregnancy (Hydratiform Mole)Document5 pagesMolar Pregnancy (Hydratiform Mole)Sampat KumawatNo ratings yet
- 6th Lecture Embryogenesis 2nd Week-8thDocument28 pages6th Lecture Embryogenesis 2nd Week-8thHussein Al Saedi100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Tarct Infection in ChildrenDocument4 pagesAcute Respiratory Tarct Infection in ChildrenDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Section 3: Neurologic Critical CareDocument7 pagesSection 3: Neurologic Critical CareDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Section 3: Neurologic Critical CareDocument7 pagesSection 3: Neurologic Critical CareDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Chap 30 - Renal Control of Acid-BaseDocument11 pagesChap 30 - Renal Control of Acid-BaseDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Low Back PainDocument9 pagesLow Back PainDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- The External Eye Structures Include The Eyelids and Surrounding Tissues, Conjunctiva, Lacrimal Apparatus, Cornea, and Anterior ChamberDocument2 pagesThe External Eye Structures Include The Eyelids and Surrounding Tissues, Conjunctiva, Lacrimal Apparatus, Cornea, and Anterior ChamberDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Clinics Breech Delivery - MVNDocument31 pagesClinics Breech Delivery - MVNDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Gyne Keme ReviewDocument63 pagesGyne Keme ReviewDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Pedia-Pulmo Flupped SGDDocument1 pagePedia-Pulmo Flupped SGDDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Quiz DM in Pregnancy - ACHONDODocument1 pageQuiz DM in Pregnancy - ACHONDODoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- INTERPROFESSIONAL COLLABORATION IN HEALTHCARE-AchondoDocument1 pageINTERPROFESSIONAL COLLABORATION IN HEALTHCARE-AchondoDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- H MoleDocument71 pagesH MoleDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Universal Health Care-StudentsDocument72 pagesUniversal Health Care-StudentsDoc AchondoNo ratings yet
- Volcano Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesVolcano Lesson Planapi-294963286No ratings yet
- Small Business and Entrepreneurship ProjectDocument38 pagesSmall Business and Entrepreneurship ProjectMădălina Elena FotacheNo ratings yet
- CO 101 Introductory Computing CO 102 Computing LabDocument17 pagesCO 101 Introductory Computing CO 102 Computing Labadityabaid4No ratings yet
- Rwamagana s5 Mathematics CoreDocument4 pagesRwamagana s5 Mathematics Coreevariste.ndungutse1493No ratings yet
- Listening Tests 81112Document13 pagesListening Tests 81112luprof tpNo ratings yet
- Analysis of MMDR Amendment ActDocument5 pagesAnalysis of MMDR Amendment ActArunabh BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Multibody Dynamics Modeling and System Identification For A Quarter-Car Test Rig With McPherson Strut Suspension PDFDocument122 pagesMultibody Dynamics Modeling and System Identification For A Quarter-Car Test Rig With McPherson Strut Suspension PDFnecromareNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 I - Prefix and Suffix TestDocument10 pagesQuiz 2 I - Prefix and Suffix Testguait9No ratings yet
- List of Bird Sanctuaries in India (State-Wise)Document6 pagesList of Bird Sanctuaries in India (State-Wise)VISHRUTH.S. GOWDANo ratings yet
- EvolutionCombatMedic 2022Document17 pagesEvolutionCombatMedic 2022smith.kevin1420344100% (1)
- p7000 Series PDFDocument592 pagesp7000 Series PDFtony445No ratings yet
- YhhjjDocument52 pagesYhhjjSam CunananNo ratings yet
- MSDS Formic AcidDocument3 pagesMSDS Formic AcidChirag DobariyaNo ratings yet
- Routine Maintenance For External Water Tank Pump and Circulation Pump On FID Tower and Rack 2017-014Document5 pagesRoutine Maintenance For External Water Tank Pump and Circulation Pump On FID Tower and Rack 2017-014CONVIERTE PDF JPG WORDNo ratings yet
- Mongodb TutorialDocument106 pagesMongodb TutorialRahul VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Dash8 200 300 Electrical PDFDocument35 pagesDash8 200 300 Electrical PDFCarina Ramo LakaNo ratings yet
- LMSTC Questionnaire EFFECTIVENESS IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF LUCENA MANPOWER SKILLS TRAINING CENTER BASIS FOR PROGRAM ENHANCEMENTDocument3 pagesLMSTC Questionnaire EFFECTIVENESS IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF LUCENA MANPOWER SKILLS TRAINING CENTER BASIS FOR PROGRAM ENHANCEMENTCriselda Cabangon DavidNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Vectors. - . in A Nutshell: AT Patera, M Yano October 9, 2014Document19 pagesMatrices and Vectors. - . in A Nutshell: AT Patera, M Yano October 9, 2014navigareeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Ms Ss1a W QP Jun13Document20 pagesAqa Ms Ss1a W QP Jun13prsara1975No ratings yet
- Resa Auditing Theorydocx - CompressDocument64 pagesResa Auditing Theorydocx - CompressMaeNo ratings yet
- Distance SortDocument6 pagesDistance SortAI Coordinator - CSC JournalsNo ratings yet
- Steve Jobs TalkDocument3 pagesSteve Jobs TalkDave CNo ratings yet
- Geopolymer Book Chapter1 PDFDocument37 pagesGeopolymer Book Chapter1 PDFDick ManNo ratings yet
- PP Checklist (From IB)Document2 pagesPP Checklist (From IB)Pete GoodmanNo ratings yet
- Team 6 - Journal Article - FinalDocument8 pagesTeam 6 - Journal Article - FinalAngela Christine DensingNo ratings yet
- DXFtoGerberConversionGuide Rev2!12!10 13Document8 pagesDXFtoGerberConversionGuide Rev2!12!10 13Tomasz BarwińskiNo ratings yet
- GSE v. Dow - AppendixDocument192 pagesGSE v. Dow - AppendixEquality Case FilesNo ratings yet
- Ict's - 2022 - Mentorship - Summarized - Thread - by - Trader - Theory - Sep 22, 22 - From - RattibhaDocument11 pagesIct's - 2022 - Mentorship - Summarized - Thread - by - Trader - Theory - Sep 22, 22 - From - RattibhaChristiana OnyinyeNo ratings yet
- Wps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawDocument1 pageWps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawAli MoosaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 OutlineDocument3 pagesChapter 10 OutlineFerrari75% (4)