Professional Documents
Culture Documents
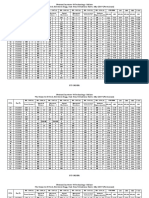
Sample 4272
Sample 4272
Uploaded by
Goran WnisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sample 4272
Sample 4272
Uploaded by
Goran WnisCopyright:
Available Formats
BASIC
ELECTRONICS
(For Engineering Students)
By
J.B. Gupta
B.Sc. (Elec. Engg.); C. Eng. (I);
F.I.E. (India); M.I.S.T.E.
S.K. KATARIA & SONS®
Publisher of Engineering and Computer Books
4885/109, Prakash Mahal, Dr. Subhash Bhargav Lane,
Opposite Delhi Medical Association, Daryaganj, New Delhi-110002
Phone : +91-11-23243489, 23269324; Telefax : +91-11-23243489
e-mail : katariabooks@yahoo.com; katariabook@gmail.com
Website : www.skkatariaandsons.com
Published By:
S.K. Kataria & Sons®
4885/109, Prakash Mahal, Dr. Subhash Bhargav Lane,
Opposite Delhi Medical Association, Daryaganj, New Delhi-110002
Phone : +91-11-23243489, 23269324; Telefax : +91-11-23243489
e-mail : katariabooks@yahoo.com; katariabook@gmail.com
Head Office:
Opp. Clock Tower, Ludhiana (Pb.)
Phone: 2726401
Edited By : Rajeev Manglik
B.E. (Elec.) Pb. Univ.
Rohit Manglik
B.E. (Elec.) Univ. of Roorkee
© ALL RIGHTS STRICTLY RESERVED
STATUTORY WARNING
Information contained in this book has been obtained by the author from sources believed to be reliable and are correct
to the best of his knowledge. Every effort has been made to avoid errors and omissions and ensure accuracy. Any error or
omission noted may be brought to the notice of the publisher which shall be taken care of in the forthcoming edition of this
book. However, neither the publisher nor the author guarantee the accuracy or completeness of any information published
herein, and neither the publisher nor author take any responsibility or liability for any inconvenience, expenses, losses or
damage to any one resulting from the contents of the book.
The book is meant for educational and learning purposes and there is no attempt on the part of publisher/author to
render engineering and other professional services. If such services are required, the assistance of an appropriate
professional should be sought.
The author of the book has taken all possible care to ensure that the contents of the book do not violate any
existing copyright or other intellectual property rights of any person in any manner whatsoever. In the event, the author
has been unable to track any source and if any copyright has been inadvertently infringed, the facts may be brought
to the notice of the publisher in writing for corrective action.
Send all correspondence to : M/s S.K. Kataria & Sons, New Delhi
Email: katariabooks@yahoo.com
First Edition: August 2008; Second Edition: 2009-2010; Reprint: 2011; Reprint: 2012; Reprint: 2013;
Reprint: 2014
Price: ` 295/-
Laser Typesetting by : Printed at :
AISA ENTERPRISES New A.S. Offset Printers
PREFACE TO THE SECOND EDITION
T he primary aim of presenting this book is to meet the needs of first year students of
degree engineering (all branches) studying in Engineering Colleges affiliated to the
University of Technology of MP. The subject matter has been presented in an easy compre-
hensive manner, logical sequence using simple language and to give a detailed exposition of
the fundamentals.
The book consists of 16 chapters providing a comprehensive coverage of course as
prescribed by University of Technology of MP for first year students for the course ‘Basic
Electronics’. A large number of worked-out examples, theoretical exercises and numerical
problems, all of degree standard, have been included in the text. The solution to illustrative
examples covering almost all subtopics of various chapters makes the entire presentation
easy to follow. Selected exercises and numerical problems with answers given at the end of
each chapter help the students in evaluating their understanding of the subject. Highlights
given at the end of almost each chapter help the students in refreshing their knowledge
while short answer type questions with answers help them in preparing for viva-voce/
practical examinations and interviews.
A large number of objective questions (multiple-choice, true/false and fill-in the blanks
types) has been given at the end of the book. These questions have been designed to bring
out the hidden aspects and also to test the knowledge, understanding and application aspect
of learning. The questions will certainly help the students to score better in their regular as
well as competitive examinations.
Every care has been taken to eliminate misprints, omissions and errors but it is too much to
expect that no inaccuracy/misprint/error has crept in and the authors would be grateful to the
readers for bringing to their notice any such errors/misprints/omissions they may come across
while going through the book.
The authors shall feel satisfied if the book meets the needs of the students for whom it is
meant. Suggestions and criticism for the improvement of the book shall be welcomed.
The authors will like to thank all the Scientists, Engineers, Authors and Publishers whose
works and text have been the source of enlightenment, inspiration and guidance to us in the
presentation.
Lastly, but not the least, the authors are thankful to their publishers for bringing out the book
in such a short period and for pricing it moderately despite heavy cost of paper and printing.
August 2009 Authors
OTHER USEFUL BOOKS
J.B. Gupta A Course in Electrical Technology
J.B. Gupta Basic Electrical Engineering [A Course in Electrical Technology Vol. 1]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Machines [A Course in Electrical Technology Vol. 2]
J.B. Gupta Electronics Engineering [A Course in Electrical Technology Vol. 3]
J.B. Gupta Theory and Performance of Electrical Machines
[DC Machines, AC Machines and Polyphase Circuits]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Machines-I [DC Machines]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Machines-II [AC Machines]
J.B. Gupta Electronic Devices and Circuits
J.B. Gupta Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering and Electronics
J.B. Gupta A Course in Electrical Power
[Generation & Economic Considerations; Transmission & Distribution;
Switchgear & Protection; Utilization of Electrical Power & Electric Traction]
J.B. Gupta Generation and Economic Considerations [Electrical Power Systems Vol. 1]
J.B. Gupta Transmission and Distribution [Electrical Power Systems Vol. 2]
J.B. Gupta Switchgear and Protection [Electrical Power Systems Vol. 3]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Power Systems [Vol. 1 of A Course in Electrical Power]
J.B. Gupta Utilization of Electrical Power and Electric Traction [Vol. 2 of A Course in Electrical Power]
J.B. Gupta A Course in Electrical and Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation
J.B. Gupta Question Bank in Electrical Engineering
J.B. Gupta An Integrated Course in Electrical Engineering [Objective Questions With Answers & Notes]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Installation Estimating & Costing
J.B. Gupta Elements of Electrical Engineering & Electronics
J.B. Gupta Electrical and Electronics Engineering [Rajasthan Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Engineering [1st/2nd Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Science [G.G.S.I.P. Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering [Pb. Technical University]
J.B. Gupta Basic Electrical Engineering [1st/2nd Semester Rajiv Gandhi Technical Univ., MP]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Technology [M.D. Univ; G.J. Univ. and Kurukshetra Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Science [Amity Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Basic Electronics [Electronics Engineering]
J.B. Gupta Electronics Engineering [1st/2nd Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Basic Electronics [1st/2nd Semester Rajiv Gandhi Technical Univ., MP]
J.B. Gupta Electromechnical Energy Conversion [M.D. Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Engineering Materials and Semiconductor Devices [M.D. Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Measurements and Measuring Instruments
J.B. Gupta Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation [3rd Semester Pb. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation [3rd Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electronic Devices and Circuits [3rd Semester Pb Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electrical Machines [4th Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electrical and Electronics Engineering Materials [4th Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Semiconductor Materials and Devices [4th Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electromechanical Energy Conversion-I [4th Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Energy Conversion [4th Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Analog Electronics [4th Semester Pb Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Analog Integrated Circuits [5th Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Pulse and Digital Switching Circuits [5th Semester Pb Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Linear Integrated Circuits [5th Semester Pb Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electromechanical Energy Conversion-II [5th Semester U.P. Technical Univ.]
J.B. Gupta Electronics Measurement and Instrumentation [5th Semester M.D. Univ.]
CONTENTS
UNIT–I : ELE CTR
ELECTR ONIC COMPONENT
CTRONIC COMPONENTSS ............................................................ 1—157
1. PASSIVE COMPONENTS ............................................................................... 3 1 9
1.1. Introduction ............................................................................................................................................. 3
1.1.1. Active Components ................................................................................................................. 3
1.1.2. Passive Components ............................................................................................................. 3
1.2. Resistors ................................................................................................................................................ 3
1.3. Inductors .............................................................................................................................................. 10
1.4. Capacitors ........................................................................................................................................... 11
1.5. Chassis and Ground ........................................................................................................................... 18
■ Highlights ......................................................................................................................................... 18
■ Exercises ......................................................................................................................................... 18
■ Short Answer Type Questions With Answers .................................................................................. 19
■ Problems ......................................................................................................................................... 19
2. BASIC SEMICONDUCTOR AND P-N JUNCTION THEORY ........................ 2 0 6 6
2.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... 20
2.2. Structure of an Atom ............................................................................................................................ 20
2.3. Electron Orbits and Energy Levels ...................................................................................................... 21
2.4. Electron Volt ......................................................................................................................................... 22
2.5. Current Density .................................................................................................................................... 23
2.6. Semiconductor Materials ..................................................................................................................... 23
2.7. Energy Bands in Solids ....................................................................................................................... 24
2.8. Conduction in Solids .......................................................................................................................... 26
2.9. Drift and Diffusion Currents ................................................................................................................ 27
2.9.1. Drift Current ........................................................................................................................... 27
2.9.2. Diffusion Current ................................................................................................................... 28
2.10. Atomic Bonds ...................................................................................................................................... 28
2.11. Intrinsic Semiconductors .................................................................................................................... 29
2.11.1. Production of Holes and Free Electrons .............................................................................. 31
2.11.2. Carrier Generation and Recombination .............................................................................. 31
2.11.3. Conduction in Intrinsic Semiconductors .............................................................................. 32
2.11.4. Effects of Heat and Light on Conductivity of Intrinsic Semiconductors .............................. 33
2.11.5. Fermi Level in an Intrinsic Semiconductor .......................................................................... 33
2.12. Extrinsic Semiconductors ................................................................................................................... 34
2.12.1. Terms Used in Extrinsic Semiconductors ........................................................................... 38
2.12.2. Effect of Temperature on Extrinsic Semiconductors ........................................................... 38
2.12.3. Charge Carriers .................................................................................................................... 38
2.12.4. Majority and Minority Charge Carriers .................................................................................. 39
2.13. Mass Action Law ................................................................................................................................. 39
2.14. Charge Densities in an Extrinsic Semiconductor ............................................................................. 39
2.15. Conductivity of Metals ......................................................................................................................... 40
2.16. Conductivity of Semiconductors ......................................................................................................... 42
2.17. Fermi Level in an Extrinsic Semiconductor ....................................................................................... 46
2.18. Basic Structure of P-N Junction .......................................................................................................... 48
2.19. Space Charge at a Junction ................................................................................................................ 50
2.20. P-N Junction as a Diode ..................................................................................................................... 51
2.20.1. Forward Biasing .................................................................................................................... 51
2.20.2. Reverse Applied Bias .......................................................................................................... 52
2.21. Metal Semiconductor Junctions ......................................................................................................... 52
2.21.1. Short-Circuited and Open-Circuited P-N Junction .............................................................. 53
2.21.2. Large Forward Voltages ........................................................................................................ 53
2.21.3. Bulk Resistance .................................................................................................................... 53
2.21.4. Energy Band Structure of an Open-Circuited P-N Junction ................................................ 54
2.21.5. Volt-Ampere Characteristics of P-N Junction ....................................................................... 55
2.21.6. Important Terms Often Used in P-N Junction ...................................................................... 56
■ Highlights ......................................................................................................................................... 57
■ Exercises ......................................................................................................................................... 60
■ Short Answer Type Questions With Answers .................................................................................. 61
■ Problems ......................................................................................................................................... 66
3. JUNCTION DIODES .......................................................................................... 6 7 8 7
3.1. Introduction .......................................................................................................................................... 67
3.2. Diode Failure Modes and Ohmmeter Check .................................................................................... 68
3.3. Junction Breakdown ........................................................................................................................... 68
3.4. Ideal Diode .......................................................................................................................................... 70
3.5. Current Components in a P-N Diode ................................................................................................ 70
3.6. Quantitative Theory of P-N Diode Currents ....................................................................................... 71
3.6.1. Diffusion Length .................................................................................................................... 72
3.6.2. Forward Currents .................................................................................................................. 72
3.6.3. Reverse Saturation Current .................................................................................................. 73
3.6.4. Volt-Ampere Characteristic ................................................................................................... 73
3.6.5. Determination of Diode Characteristics .............................................................................. 74
3.7. Temperature Dependence of P-N Diodes .......................................................................................... 76
3.8. Diode Resistance ............................................................................................................................... 77
3.9. Real Diode .......................................................................................................................................... 80
3.9.1. Piecewise Linear Diode Characteristic ............................................................................... 81
3.10. DC Load Lines .................................................................................................................................... 82
3.11. P-N Diode Applications ...................................................................................................................... 83
■ Highlights ......................................................................................................................................... 84
■ Exercises ......................................................................................................................................... 85
■ Short Answer Type Questions With Answers .................................................................................. 86
■ Problems ......................................................................................................................................... 87
4. SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES ........................................................................ 88122
4.1. Introduction .......................................................................................................................................... 88
4.2. Zener Diodes ...................................................................................................................................... 88
4.3. Zener Diode Applications ................................................................................................................... 91
4.4. Tunnel Diode ....................................................................................................................................... 97
4.5. Pin Diode ........................................................................................................................................... 100
4.6. Varactor Diode ................................................................................................................................... 101
4.6.1. Varactor Diode in Tuning Circuit ......................................................................................... 103
4.7. Point Contact Diode .......................................................................................................................... 104
4.8. Step Recovery Diode ........................................................................................................................ 105
4.9. Fast-Recovery Diodes ...................................................................................................................... 106
4.10. Schottky Diode .................................................................................................................................. 106
4.11. Backward Diodes .............................................................................................................................. 108
4.12. Power Diodes ................................................................................................................................... 108
4.12.1. Basic Structure .................................................................................................................... 109
4.12.2. Diode Characteristics ......................................................................................................... 109
4.12.3. Types of Power Diodes ........................................................................................................ 111
4.12.4. Power Diode Ratings ........................................................................................................... 111
4.13. Varistors or Voltage Dependent Resistors (VDRs) .......................................................................... 111
4.14. Photodiode ......................................................................................................................................... 112
4.15. Light Emitting Diode (LEDs) ............................................................................................................. 113
■ Highlights ....................................................................................................................................... 116
■ Exercises ....................................................................................................................................... 116
■ Short Answer Type Questions With Answers ................................................................................ 119
■ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 121
5. BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS (BJTS) ........................................ 123157
5.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................................................ 123
5.2. Transistor Terminals ........................................................................................................................ 124
5.3. Transistor Action ............................................................................................................................... 124
5.3.1. Unbiased Transistor ........................................................................................................... 124
5.3.2. Operation of Transistor ....................................................................................................... 126
5.4. Transistor Biasing ............................................................................................................................ 128
5.4.1. Different Operating Conditions For a Transistor ............................................................... 128
5.5. Important Points Regarding Working of Transistors ..................................................................... 130
5.6. Transistor Current Components ...................................................................................................... 131
5.7. Current Amplification Factors ........................................................................................................... 133
5.8. Relationship Between α and β ................................................................................................................... 133
5.9. Base Spreading Resistance ............................................................................................................ 135
5.10. Transistor Circuit Configurations ..................................................................................................... 135
5.11. Common Base (CB) Configuration ................................................................................................. 135
5.11.1. Characteristics of Common Base Configuration .............................................................. 136
5.12. Common Emitter (CE) Configuration ............................................................................................... 139
5.12.1. Characteristics of Common Emitter Configuration ........................................................... 141
5.13. Common Collector (CC) Configuration ........................................................................................... 144
5.14. Comparison of Characteristics of Transistors In Different Configurations ................................... 145
5.15. Transistor as an Amplifier ................................................................................................................ 146
5.16. Transistor Load Lines ...................................................................................................................... 147
5.16.1. DC Load Line ...................................................................................................................... 147
5.16.2. Quiescent Point ................................................................................................................... 147
5.16.3. AC Load Line ....................................................................................................................... 148
5.17. Standard Notations For Voltages and Currents .............................................................................. 150
5.18. Transistor Packaging ....................................................................................................................... 151
■ Highlights ....................................................................................................................................... 152
■ Exercises ....................................................................................................................................... 153
■ Short Answer Type Questions With Answers ................................................................................ 154
■ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 157
UNIT–II : BASIC ELE CTR
ELECTR ONIC CIR
CTRONIC CUIT
CIRCUIT
CUITSS .................................................. 159—246
6. RECTIFIERS .................................................................................................. 161193
6.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................................................ 161
6.2. Half-Wave Rectifiers ......................................................................................................................... 162
6.3. Full-wave Rectifiers .......................................................................................................................... 168
6.3.1. Centre-Tap Full-Wave Rectifier ........................................................................................... 168
6.3.2. Bridge Rectifier .................................................................................................................... 169
6.3.3. Circuit Analysis .................................................................................................................... 169
6.3.4. Merits and Demerits of Full-Wave Rectifiers Over Half-Wave Rectifiers .......................... 172
6.3.5. Merits and Demerits of Bridge Rectifiers Over Centre-Tap Rectifiers .............................. 172
6.3.6. Comparison Between Half-Wave, Centre-Tap and Bridge Rectifiers .............................. 173
6.4. Filter Circuits ..................................................................................................................................... 175
6.4.1. Series Inductor Filter ........................................................................................................... 176
6.4.2. Shunt Capacitor Filter ......................................................................................................... 177
6.4.3. Choke-Input or L-Section Filter ........................................................................................... 180
6.4.4. Capacitor-Input or π-Filter ................................................................................................... 182
6.4.5. Salient Features of L-Section and p-Filters ....................................................................... 183
6.4.6. R-C Filters ........................................................................................................................... 183
6.5. Bleeder Resistor ............................................................................................................................... 186
6.6. Voltage Regulation ............................................................................................................................ 187
6.7. Rectifier Specifications ..................................................................................................................... 187
■ Highlights ....................................................................................................................................... 189
■ Exercises ....................................................................................................................................... 190
■ Short Answer Type Questions With Answers ................................................................................ 191
■ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 193
7. ELECTRICAL WAVE FILTERS .................................................................... 194209
7.1. Introduction ......................................................................................................................................... 194
7.2. Decibel and Neper ............................................................................................................................. 194
7.3. Classification of Filters ...................................................................................................................... 195
7.4. Passive filters ..................................................................................................................................... 197
7.5. Low-Pass filters ................................................................................................................................. 197
7.5.1. Low-Pass R-C Filter Circuit ................................................................................................ 197
7.5.2. Low-Pass R-L Filter Circuit ................................................................................................ 199
7.5.3. Inverted L-Type Filter Circuit ................................................................................................ 199
7.5.4. T-Type Filter Circuit .............................................................................................................. 199
7.5.5. π-Type Filter Circuit .............................................................................................................. 199
7.6. High-Pass Filters ............................................................................................................................... 200
7.6.1. High-Pass R-C Filter Circuit ............................................................................................... 200
7.6.2. High-Pass R-L Filter Circuit ................................................................................................ 202
7.6.3. Inverted L-Type Filter Circuit ................................................................................................ 202
7.6.4. T-Type Filter Circuit .............................................................................................................. 202
7.6.5. π-Type Filter Circuit .............................................................................................................. 202
7.7. R-C Band-pass Filter ......................................................................................................................... 203
7.8. R-C Band-stop (or Band-Elimination) Filter ..................................................................................... 203
7.9. Band-Pass and Band-Stop Resonant Filter Circuits ....................................................................... 204
7.9.1. Series Resonant Band-Pass Filter Circuit ........................................................................ 204
7.9.2. Parallel Resonant Bandpass Filter Circuit ........................................................................ 205
7.9.3. Series Resonant Band-Stop Filter ..................................................................................... 205
7.9.4. Parallel Resonant Band-Stop Filter ................................................................................... 206
7.10. Qualitative Evaluation of Filter Types ................................................................................................ 207
■ Highlights ....................................................................................................................................... 207
■ Exercises ....................................................................................................................................... 208
■ Short Answer Type Questions With Answers ................................................................................ 208
■ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 209
8. BJT AMPLIFIERS ......................................................................................... 21 0246
8.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................................................ 210
8.2. Transistor Amplifier Practical Circuit ................................................................................................ 211
8.2.1. Emitter Bypass Capacitor ................................................................................................... 212
8.2.2. AC Ground ........................................................................................................................... 212
8.3. Phase Reversal ................................................................................................................................ 212
8.4. Load Line Analysis ........................................................................................................................... 214
8.5. Amplifier Gains .................................................................................................................................. 217
8.5.1. Graphical Determination of Voltage and Current Gains ................................................... 218
8.6. AC Emitter Resistance ..................................................................................................................... 219
8.7. Hybrid Parameters ............................................................................................................................. 219
8.8. Two-Port Devices and The Hybrid Model .......................................................................................... 220
8.8.1. Hybrid Parameters or h-Parameters ................................................................................. 220
8.8.2. Hybrid Model ........................................................................................................................ 222
8.9. Transistor Hybrid Model .................................................................................................................... 223
8.10. Typical Values of h-Parameters For a Transistor ............................................................................. 225
8.11. Transistor Amplifier Circuit Performance in h-Parameters ............................................................. 225
8.12. Simplified Common Emitter Hybrid Model ....................................................................................... 230
8.12.1. Generalized Approximate Model ........................................................................................ 231
8.13. Transistor Biasing ............................................................................................................................ 231
8.14. Selection of Operating Point ............................................................................................................. 232
8.15. Analysis of A CE Transistor Amplifier Using h-Parameters ........................................................... 234
8.16. Analysis of A CB Transistor Amplifier Using h-Parameters ........................................................... 237
8.17. Analysis of A CC Transistor Amplifier Using h-Parameters ........................................................... 240
8.18. Classification of Amplifiers ............................................................................................................... 243
■ Highlights ....................................................................................................................................... 243
■ Exercises ....................................................................................................................................... 244
■ Short Answers Type Questions With Answers .............................................................................. 245
■ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 246
UNIT–III : MEASURING INS TR
INSTR UMENT
TRUMENT
UMENTSS ..................................................... 247—300
9. CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE ................................................................ 249272
9.1. Introduction ........................................................................................................................................ 249
9.2. Block Diagram of A General Purpose CRO ..................................................................................... 249
9.3. Cathode Ray Tube ............................................................................................................................ 250
9.4. Focusing Device ............................................................................................................................... 253
9.4.1. Electrostatic Focusing ........................................................................................................ 253
9.4.2. Electromagnetic Focusing .................................................................................................. 255
9.5. Basic Controls .................................................................................................................................. 258
9.6. Basic Oscilloscope Patterns ............................................................................................................ 262
9.7. Measurement of Phase Difference .................................................................................................. 265
9.8. Measurement of Frequency of a Voltage Signal .............................................................................. 267
9.9. Measurement of Voltage and Current .............................................................................................. 269
■ Highlights ....................................................................................................................................... 269
■ Exercises ....................................................................................................................................... 271
■ Short Answer Type Questions With Answers ................................................................................ 271
■ Problems ....................................................................................................................................... 272
10. ELECTRONIC METERS .............................................................................. 273300
10.1. Introduction ......................................................................................................................................... 273
10.1.1. Accuracy ............................................................................................................................... 273
10.1.2. Precision .............................................................................................................................. 273
10.1.3. Resolution ........................................................................................................................... 274
10.1.4. Sensitivity ............................................................................................................................. 274
10.2. Errors .................................................................................................................................................. 274
10.2.1. Gross Errors ........................................................................................................................ 274
10.2.2. Systematic Errors ................................................................................................................ 274
10.2.3. Random Errors ................................................................................................................... 274
10.3. Analog Multimeter .............................................................................................................................. 275
10.4. Permanent magnet moving coil meter ............................................................................................. 275
10.4.1. PMMC as a DC Ammeter .................................................................................................... 276
10.4.2. PMMC as a DC Voltmeter .................................................................................................... 278
10.4.3. PMMC as Ohmmeter ........................................................................................................... 279
10.4.4. PMMC as AC Voltmeter ....................................................................................................... 279
10.4.5. PMMC as AC Current Meter ................................................................................................ 280
10.5. Multimeter or AVOmeter ..................................................................................................................... 280
10.6. Electronic Multimeter (OR VOM) ........................................................................................................ 283
10.7. Demerits of Analog Multimeters ....................................................................................................... 285
10.8. Digital Voltmeters (DVMs) .................................................................................................................. 286
10.9. Digital Multimeters (DMMs) ............................................................................................................... 286
10.10. Characteristics of Digital Meters ....................................................................................................... 287
10.11. LCR Meters ........................................................................................................................................ 289
10.12. Q Meter ............................................................................................................................................. 289
10.12.1. Measurement of Low Impedance Components ............................................................... 291
10.12.2. Measurement of High Impedance Components .............................................................. 292
10.12.3. Errors ................................................................................................................................... 293
Basic Electronics
Publisher : S K Kataria and Sons
ISBN : 978819069194 9 Author : J.B. Gupta
( KATSON )
Type the URL : http://www.kopykitab.com/product/4 272
Get this eBook
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- DatasheetDocument409 pagesDatasheetmicpreamp100% (1)
- Undertaking Code of Conduct by StudentsDocument1 pageUndertaking Code of Conduct by StudentsKunalNo ratings yet
- Know All About-CLATDocument36 pagesKnow All About-CLATKunalNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology::Silchar 4th Semester B.Tech Mechanical Engg. EXTRA LOAD Tabulation Sheet, MAY 2018Document4 pagesNational Institute of Technology::Silchar 4th Semester B.Tech Mechanical Engg. EXTRA LOAD Tabulation Sheet, MAY 2018KunalNo ratings yet
- Bengaluru To Guwahati Ch42Qn: Indigo 6E-119Document2 pagesBengaluru To Guwahati Ch42Qn: Indigo 6E-119KunalNo ratings yet
- Guwahati To Bengaluru Pk6Umi: Air Asia I5-1983Document2 pagesGuwahati To Bengaluru Pk6Umi: Air Asia I5-1983KunalNo ratings yet
- Ticket 3441358762-1Document2 pagesTicket 3441358762-1KunalNo ratings yet
- Notice: National Institute of Technology SilcharDocument2 pagesNotice: National Institute of Technology SilcharKunalNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Silchar B.Tech. 2nd Semester Tabulation (ELECTRICAL) 2017 Batch, Extra Load Exam Held in May 2019 (PROVISIONAL)Document1 pageNational Institute of Technology Silchar B.Tech. 2nd Semester Tabulation (ELECTRICAL) 2017 Batch, Extra Load Exam Held in May 2019 (PROVISIONAL)KunalNo ratings yet
- Received With Thanks ' 14,115.00 Through Payment Gateway Over The Internet FromDocument1 pageReceived With Thanks ' 14,115.00 Through Payment Gateway Over The Internet FromKunalNo ratings yet
- Received With Thanks ' 14,115.00 Through Payment Gateway Over The Internet FromDocument1 pageReceived With Thanks ' 14,115.00 Through Payment Gateway Over The Internet FromKunalNo ratings yet
- Applicant Name Application No. Course Receipt No Date Payment Mode Instrument No Bank SL No Description AmountDocument1 pageApplicant Name Application No. Course Receipt No Date Payment Mode Instrument No Bank SL No Description AmountKunalNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Silchar 8Th Sem B.Tech Civil Engg. End Sem Tabulation Sheet, May-2019 (Provisional)Document6 pagesNational Institute of Technology Silchar 8Th Sem B.Tech Civil Engg. End Sem Tabulation Sheet, May-2019 (Provisional)KunalNo ratings yet
- Some Properties of Non-Linear Dynamic Systems AreDocument42 pagesSome Properties of Non-Linear Dynamic Systems AreKunalNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. Course Structure & Syllabus, Electrical Engineering Department, N.I.T. SilcharDocument55 pagesB. Tech. Course Structure & Syllabus, Electrical Engineering Department, N.I.T. SilcharKunalNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology::Silchar 4th Semester B.Tech Electrical Engg. End Sem Tabulation Sheet, May 2019 (Provisional)Document4 pagesNational Institute of Technology::Silchar 4th Semester B.Tech Electrical Engg. End Sem Tabulation Sheet, May 2019 (Provisional)KunalNo ratings yet
- Assign 3 FullDocument26 pagesAssign 3 FullKunalNo ratings yet
- V CurveDocument6 pagesV CurveKunalNo ratings yet
- What Is ConsciousnessDocument1 pageWhat Is ConsciousnessKunalNo ratings yet
- 117av - Automotive Electrical and Autotronics PDFDocument8 pages117av - Automotive Electrical and Autotronics PDFvenkiscribd444No ratings yet
- B.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualDocument87 pagesB.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualSwastika sainNo ratings yet
- RHRP840, RHRP850, RHRP860: Package FeaturesDocument4 pagesRHRP840, RHRP850, RHRP860: Package Featuresbruno barbosaNo ratings yet
- Qfet Qfet Qfet Qfet: FQP55N10Document8 pagesQfet Qfet Qfet Qfet: FQP55N10andreanuovoNo ratings yet
- 10 True Repair Case Histories of LCD Monitors Volume I PDFDocument58 pages10 True Repair Case Histories of LCD Monitors Volume I PDFMar DocdorNo ratings yet
- Presentation Major Project FINALDocument20 pagesPresentation Major Project FINALReena MishraNo ratings yet
- SUD40N06-25L: Vishay SiliconixDocument6 pagesSUD40N06-25L: Vishay SiliconixFahd AfifiNo ratings yet
- Diode Process Fabrication - Oswaldo IsaiDocument3 pagesDiode Process Fabrication - Oswaldo IsaiOswaldo GuerreroNo ratings yet
- AOD408 N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor: Features General DescriptionDocument4 pagesAOD408 N-Channel Enhancement Mode Field Effect Transistor: Features General DescriptionLudmila MilaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Assignment #2 2 PDFDocument5 pagesElectronics Assignment #2 2 PDFKhairi SalehNo ratings yet
- EXP-1Document8 pagesEXP-1Parthiv IjardarNo ratings yet
- Suniva Suniva Opt330 72 4 100 Silver Mono Solar Panel Specs PDFDocument2 pagesSuniva Suniva Opt330 72 4 100 Silver Mono Solar Panel Specs PDFJean Miguel BacaniNo ratings yet
- Bundelkhand University, Jhansi B. Tech. (Food Tech.) I SemesterDocument51 pagesBundelkhand University, Jhansi B. Tech. (Food Tech.) I SemesterAnupNo ratings yet
- MD-D02 Installation Manual v02 - 200514 - EnglishDocument4 pagesMD-D02 Installation Manual v02 - 200514 - EnglishMladin DorianNo ratings yet
- MMUP Sample Questions - ELEDocument29 pagesMMUP Sample Questions - ELEAbdul Rahman A R63% (8)
- SampleDocument11 pagesSampleRishab kumarNo ratings yet
- MDQ18N50GDocument6 pagesMDQ18N50GFrancisco PérezNo ratings yet
- Conectores RexhrothDocument36 pagesConectores RexhrothBilly ZununNo ratings yet
- Electronic SwitchesDocument28 pagesElectronic Switchesgame masterNo ratings yet
- MDI5N40/MDD5N40: N-Channel MOSFET 400V, 3.4 A, 1.6Document7 pagesMDI5N40/MDD5N40: N-Channel MOSFET 400V, 3.4 A, 1.6Francisco RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Frequency Modulation and Demodulation Trainer ST2203 Operating PDFDocument63 pagesFrequency Modulation and Demodulation Trainer ST2203 Operating PDFManojSarma100% (1)
- 20MEP-155 - Workshop Practice Sample Viva Questions With AnswersDocument12 pages20MEP-155 - Workshop Practice Sample Viva Questions With AnswersVerbala RastogiNo ratings yet
- BTS 410 E2 Fonte CDMDocument16 pagesBTS 410 E2 Fonte CDMPaulo SilvaNo ratings yet
- 01 Relays PDFDocument110 pages01 Relays PDFŽarko MočnikNo ratings yet
- Matlab KhánhDocument9 pagesMatlab KhánhTrần Thanh TiếnNo ratings yet
- Pioneer djm-250mk2 Mixer Exploded View and Parts ListDocument13 pagesPioneer djm-250mk2 Mixer Exploded View and Parts ListOktay YuseinNo ratings yet
- MDP2N60/MDF2N60: N-Channel MOSFET 600V, 2.0A, 4.5Document8 pagesMDP2N60/MDF2N60: N-Channel MOSFET 600V, 2.0A, 4.5Erroz RosadiNo ratings yet
- An 6076Document16 pagesAn 6076Celso CastroNo ratings yet
- Diod RectifierDocument35 pagesDiod RectifierRizalNo ratings yet