Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic: Bacterial Meningitis and Its Prevention Description/ Overview: Materials/ Equipment: General Objective
Uploaded by
Dannah Bullianday0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
244 views5 pagesOriginal Title
health teaching plan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
244 views5 pagesTopic: Bacterial Meningitis and Its Prevention Description/ Overview: Materials/ Equipment: General Objective
Uploaded by
Dannah BulliandayCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Level II AACUP Accredited
Topic: Bacterial Meningitis and its Prevention
Description/ Overview:
Materials/ Equipment:
Visual aid
General Objective:
After 10 minutes of health teaching, the patient will be able to define bacterial meningitis, its symptoms, and preventions.
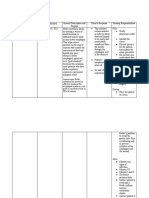
Objectives Learning Content Teaching Strategy Time Evaluation and
Allotment Assessment Tool
(in minutes)
Patient/ Significant other will be able to:
COGNITIVE: Definition of Meningitis
1. Describe meningitis particularly “Meningitis” means inflammation of the Discussion with 1 minute Question and
bacterial meningitis. visual aid Answer
meninges. The meninges are tissues that
cover the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis
may happen for many reasons. The most
common causes of meningitis are infections
with bacteria and viruses. Bacterial
meningitis can be quite severe and may Discussion with
result in brain damage, hearing loss, visual aid (leaflet)
learning disability, or death. The disease
can also cause permanent disabilities such
as hearing loss, brain damage, seizures or
amputation.
2. Trace the route of transmission of the Question and
diesease Transmission 1 minute Answer
Bacterial meningitis is transmitted through
air droplets and direct contact with anyone
already infected with the disease. The
infection is spread through close contact
with oral secretions, such as shared drinks, Discussion with
utensils and cigarettes, through coughing, visual aid (leaflet)
or through intimate contact such as kissing.
3. Enumerate the symptoms of the 1 minute Question and
Symptoms and when to seek Medical Care
disease and know when to seek medical Answer
care. Early symptoms of meningitis may include:
High fever
Rash
Vomiting
Severe headache
Neck stiffness
Lethargy
Nausea
Sensitivity to light
Because the infection progresses rapidly,
you should seek immediate medical care if
2 or more of these symptoms occur at the
same time.
4. Recognize the treatment for bacterial Discussion 1 minute Question and
Treatment
meningitis. Answer
Bacterial meningitis can be treated with a
number of effective antibiotics. It is
important, however, that treatment be
started early in the course of the disease.
Appropriate antibiotic treatment should
reduce the risk of fatal meningitis to below
15%
AFFECTIVE:
5. Realize the severity of the possibility
of transmission of the disease. Is it Contagious? Discussion 1 minute Question and
Yes, some forms of bacterial meningitis are Answer
contagious. The bacteria are spread
through the exchange of respiratory and
throat secretions (i.e., coughing, kissing).
People in the same residential unit, day
care center, or anyone with direct contact
with an infected person's oral secretions
would be considered to be at increased risk
of acquiring the infection. People who
qualify as close contacts of a person with
meningitis should receive antibiotics to
prevent them from getting the disease.
Fortunately, none of the bacteria that cause
meningitis are as contagious as things like
the common cold or the flu.
6. Choose and select the appropriate 1 minute Question and
kind of vaccination for the prevention of Prevention: Vaccines Discussion with Answer
Meningitis. visual aid
Vaccines are the most effective way to
protect against certain types of bacterial
meningitis. There are vaccines for 3
types of bacteria that can cause
meningitis:
Meningococcal vaccines help
protect against N. meningitidis
Pneumococcal vaccines help
protect against S. pneumoniae
Hib vaccines help protect against
Hib
PSYCHOMOTOR: Prevention: Avoid the Spread of Disease Reporting with Return
5. Demonstrate practices to avoid the You cannot get meningitis from casual Visual Aid 2 minutes Demonstration
spread of the disease. contact, such as by breathing the air that an
infected person has breathed. These
bacteria do not live long outside the human
body. But you can get it from close or
prolonged contact with an infected person.
The bacteria that cause meningococcal
meningitis live in the back of the nose and
throat and are carried by 10% to 25% of the
population.
Good personal hygiene can help prevent
the spread of disease:
Don't share food, glasses, water
bottles, or eating utensils.
Don't share tissues or towels.
Don't share lip gloss or lipstick.
Wash hands often with soap and
water.
Remember: A person with bacterial
meningitis can remain contagious for about
24 hours after starting antibiotics. If a
person with meningitis has exposed your
teen to the disease, ask the doctor whether
it is necessary to take antibiotics. Doing this
for a few days may help prevent your teen
from getting the disease.
Meningitis Prevention: Enhance the Reporting with
Visual Aid
6. Create a healthier ways to enhance Immune System
the immune system for the prevention of Keeping the immune system healthy helps
Meningitis. prevent susceptibility to a wide range of
diseases. It may also help prevent infection
by the viruses and bacteria that cause
meningitis. This is just one more reason
your teen may benefit from:
Eating a well-balanced diet, rich in Question and
vegetables and fruits Answer
Getting enough sleep
Exercising regularly
Avoiding cigarettes, drugs, and
alcohol
References:
https://www.webmd.com/children/vaccines/prevent-meningitis-tips-protect-your-teen
https://www.sfcdcp.org/infectious-diseases-a-to-z/meningococcal-disease/
https://www.brown.edu/campus-life/health/services/promotion/general-health-physical-health/meningitis
https://www.cdc.gov/meningitis/bacterial.html
You might also like
- Final FRCA exam MCQ-SBAs –February 2012Document9 pagesFinal FRCA exam MCQ-SBAs –February 2012Suhas Kapse100% (2)
- CSA Revision Notes: For TheDocument37 pagesCSA Revision Notes: For TheOphthalmology PLUSNo ratings yet
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- NPIDocument13 pagesNPIJohndelle Banlasan HernanNo ratings yet
- Laguna State Polytechnic University: College of Nursing and Allied Health A.Y. 2021-22 PurposeDocument4 pagesLaguna State Polytechnic University: College of Nursing and Allied Health A.Y. 2021-22 PurposeKristine Louise JavierNo ratings yet
- Bag technique nursing careDocument2 pagesBag technique nursing careDanz KieNo ratings yet
- Teen Mother Newborn Care GuideDocument34 pagesTeen Mother Newborn Care GuideYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Buddy WorksDocument3 pagesBuddy WorksJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Patient With PNEUMONIA (Geriatrics)CHRISTIE MONTANO0% (1)
- NURSING DIAGNOSIS (2) On Pregnant Woman Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING DIAGNOSIS (2) On Pregnant Woman Knowledge Deficitanon_168410816No ratings yet
- LFDDocument3 pagesLFDVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- NCP .Postoperative.Document5 pagesNCP .Postoperative.Jerome GazmenNo ratings yet
- AB Critical Thinking ExercisesDocument4 pagesAB Critical Thinking ExercisesAhmad BaolayyanNo ratings yet
- Resource UnitDocument5 pagesResource UnitEthel Marie OlvezNo ratings yet
- Nursing care plan for patient with meningiomaDocument3 pagesNursing care plan for patient with meningiomaShaira TillahNo ratings yet
- NCP For Parent and Child PDFDocument3 pagesNCP For Parent and Child PDFMariana Mikaela AlagarNo ratings yet
- Name: Ma. Princess P. Seril DATE: DECEMBER 5, 6, 8, 9-2011 GROUP: 53 Area: Alimannao Rhu Clinical Instructor: Evelyn C. Cristobal, RNDocument2 pagesName: Ma. Princess P. Seril DATE: DECEMBER 5, 6, 8, 9-2011 GROUP: 53 Area: Alimannao Rhu Clinical Instructor: Evelyn C. Cristobal, RNRoshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Case Study Peralta (Drug N NCP)Document10 pagesCase Study Peralta (Drug N NCP)Trisha Cruise100% (1)
- Now, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingDocument2 pagesNow, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingShyla ManguiatNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic AcidDocument2 pagesTranexamic AcidIrish Ivy VibethNo ratings yet
- Mothers' Experiences of Premature Infants in the NICUDocument4 pagesMothers' Experiences of Premature Infants in the NICUMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonia PatientDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Pneumonia PatientvonNo ratings yet
- Cesarean Delivery: A Reading OnDocument4 pagesCesarean Delivery: A Reading OnAnge MinguitoNo ratings yet
- Virtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsDocument7 pagesVirtual Clinical Duty Daily RequirementsEdgie FabreNo ratings yet
- NPI Inference Remark/AnalysisDocument1 pageNPI Inference Remark/AnalysisAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityJayson OlileNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan CapDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan Capalexander abasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FeverDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan Feverbharat singhNo ratings yet
- Assessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkyaw100% (1)
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Ampicillin Drug Study GuideDocument3 pagesAmpicillin Drug Study GuideAlyssa Mae DumularNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument3 pagesNCP FormatAl Bhert Timbal MagbalotNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareDocument15 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pain Management and Self-CareKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument1 pageDisturbed Sleep PatternHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument1 pageLeadershipchoobiNo ratings yet
- Manage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisDocument4 pagesManage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisYeni PuspitaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPJoseph Dableo ParreñoNo ratings yet
- NCP Knowledge Deficient FPDocument2 pagesNCP Knowledge Deficient FPDayanaj OngNo ratings yet
- Fdar NCPDocument3 pagesFdar NCPjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Proper home visit proceduresDocument2 pagesProper home visit procedureslea mae andoloyNo ratings yet
- NCP For Ulnar SurgeryDocument5 pagesNCP For Ulnar SurgeryjiloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07No ratings yet
- HTP Ineffective BreathingDocument3 pagesHTP Ineffective BreathingShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Nursing care plan for post-operative patientDocument3 pagesNursing care plan for post-operative patientAya BolinasNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Active Fluid Volume LossMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPAriaNo ratings yet
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationErika Mae MananganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanCaracel Cabrera SobionoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorists and their Major ContributionsDocument22 pagesNursing Theorists and their Major ContributionsG a i l R i c h w e l lNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Education for an Underweight InfantDocument2 pagesNutrition Education for an Underweight InfantYzobel Phoebe ParoanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Application QuestionsDocument2 pagesClinical Application QuestionsCathrine Mae RamilNo ratings yet
- Head Nurse: General ObjectiveDocument10 pagesHead Nurse: General Objectiveeihjay-bravo-8041No ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocument2 pagesNCP Disturbed Body ImageDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Duavent Drug Study - CunadoDocument3 pagesDuavent Drug Study - CunadoLexa Moreene Cu�adoNo ratings yet
- AmikacinDocument1 pageAmikacinMuhammad ArsalanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndeoendentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndeoendentDiane Sarino CabonceNo ratings yet
- Journal ReadingDocument3 pagesJournal ReadingroseonabreezeNo ratings yet
- EsophagomyotomyDocument3 pagesEsophagomyotomySamVelascoNo ratings yet
- Lesssion Plan MENINGITISDocument16 pagesLesssion Plan MENINGITISISLAMIC KNOWLEDGE BASED ON TRULY HADISNo ratings yet
- Prevent Bacterial Meningitis With VaccinesDocument9 pagesPrevent Bacterial Meningitis With VaccinesAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument2 pagesDrug Study ParacetamolDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmoxiclavDocument2 pagesDrug Study AmoxiclavDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GrilinctusDocument2 pagesDrug Study GrilinctusDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesDrug Study LevofloxacinDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Summary of Iv and MedsDocument1 pageSummary of Iv and MedsDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Symptoms, Previous Treatment and Result, Social and Vocational Responsibilities)Document1 pageSymptoms, Previous Treatment and Result, Social and Vocational Responsibilities)Dannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan: Get Plenty of Rest. Stay in Bed If You CanDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan: Get Plenty of Rest. Stay in Bed If You CanDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of Systems: Prefers Darkened Room and Is Easily Irritated, and NauseatedDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of Systems: Prefers Darkened Room and Is Easily Irritated, and NauseatedDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Reconstructive Surgery - Volume 2Document318 pagesGynecology Reconstructive Surgery - Volume 2Bharti Pant GahtoriNo ratings yet
- 2012 Infant Mortality ReportDocument52 pages2012 Infant Mortality ReportSusie CambriaNo ratings yet
- 2A - Zahirah Rahmadian Budiman - PROBLEMS WITH PAINDocument5 pages2A - Zahirah Rahmadian Budiman - PROBLEMS WITH PAINZahirah BudimanNo ratings yet
- TNM Ca de MamaDocument4 pagesTNM Ca de MamaacademiaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Drug AbuseDocument2 pagesNature of Drug AbuseColin GosbertNo ratings yet
- Emergency Assistance Plan by TW 12oct21Document7 pagesEmergency Assistance Plan by TW 12oct21Than WinNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Audit Into The Success Rate of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Analgesia in General Dental PracticeDocument4 pagesA Clinical Audit Into The Success Rate of Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Analgesia in General Dental PracticeGina CastilloNo ratings yet
- GE Logiq 400 500 Probe GuideDocument2 pagesGE Logiq 400 500 Probe GuideNesakkumaren SivakumaranNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils and Low-Intensity Electromagnetic Pulses in The Treatment of Androgen-Dependent AlopeciaDocument10 pagesEssential Oils and Low-Intensity Electromagnetic Pulses in The Treatment of Androgen-Dependent AlopeciaHuman ResourcesNo ratings yet
- MS2 - Neurologic Disorder My ReportDocument30 pagesMS2 - Neurologic Disorder My ReportNeil Lansang BallobanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Practices and Physiological EffectsDocument9 pagesElectrical Safety Practices and Physiological EffectsSmr OnlyNo ratings yet
- The Delirium Rating Scale (DRS)Document12 pagesThe Delirium Rating Scale (DRS)Cristian SolísNo ratings yet
- TaurodontDocument14 pagesTaurodontHameed WaseemNo ratings yet
- Unit 55Document7 pagesUnit 55Antara BiswasNo ratings yet
- 1 Dental Caries PDFDocument38 pages1 Dental Caries PDFmayang putriNo ratings yet
- Scedosporium Apiospermum Keratomycosis in A DogDocument4 pagesScedosporium Apiospermum Keratomycosis in A DogDavid Argüelles AndradeNo ratings yet
- (Book 4) Collins Parker, Mia - PCOS Nutrition - A Complete PCOS Diet Book With 4 Week Meal Plan and 4 Week Fitness Exercise Plan To Reduce Weight and Prevent Diabetes. PCOS Causes, Symptoms and HolDocument134 pages(Book 4) Collins Parker, Mia - PCOS Nutrition - A Complete PCOS Diet Book With 4 Week Meal Plan and 4 Week Fitness Exercise Plan To Reduce Weight and Prevent Diabetes. PCOS Causes, Symptoms and HolAndreea Daniela100% (4)
- Aquagenic Palmoplantar Keratoderma With Dorsal Hand Involvement in An Adolescent FemaleDocument2 pagesAquagenic Palmoplantar Keratoderma With Dorsal Hand Involvement in An Adolescent FemaleTher RayNo ratings yet
- 2004 NEJM Photosensitivity NEJ 2004Document7 pages2004 NEJM Photosensitivity NEJ 2004Alma EscobarNo ratings yet
- 43THYROID II 2021 ThyroiditisDocument29 pages43THYROID II 2021 ThyroiditisRaju ThapaNo ratings yet
- 9 Steam InhalationDocument2 pages9 Steam InhalationKen Morales Alcantara100% (1)
- Perineum RepairDocument5 pagesPerineum RepairYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- Physical Exercise and PsychologicalDocument10 pagesPhysical Exercise and Psychologicalbodeadumitru9261100% (1)
- Nursing ChecklistDocument6 pagesNursing Checklistapi-380053762No ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (Pih)Document56 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension (Pih)shandi23100% (5)
- Vet Surgery, Anesthesia & ImagingDocument4 pagesVet Surgery, Anesthesia & ImagingAndika Budi Kurnianto0% (1)
- Doctors - Dermatologists Area Phone: Tuesday, 13 November 2007 13:51Document18 pagesDoctors - Dermatologists Area Phone: Tuesday, 13 November 2007 13:51pinakindpatelNo ratings yet