Professional Documents
Culture Documents
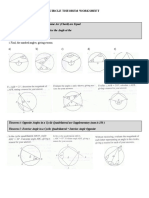
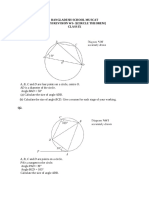
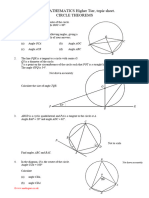
GCSE Circle Theorems (40
Uploaded by
Mohd Uvais0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views6 pagesOriginal Title
9-proof-of-circle-theorems
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views6 pagesGCSE Circle Theorems (40
Uploaded by
Mohd UvaisCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Name: ___________________________
GCSE (1 – 9)
Proof of Circle Theorems
Instructions
• Use black ink or ball-point pen.
• Answer all questions.
• Answer the questions in the spaces provided
– there may be more space than you need.
• Diagrams are NOT accurately drawn, unless otherwise
indicated.
• You must show all your working out.
Information
• The marks for each question are shown in brackets
– use this as a guide as to how much time to spend on each
question.
Advice
• Read each question carefully before you start to answer it.
• Keep an eye on the time.
• Try to answer every question.
• Check your answers if you have time at the end
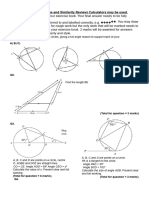
1 B
C
A
A, B and C are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O.
Prove that angle AOC is twice the size of angle ABC.
You must not use any circle theorems in your proof.
(Total for Question 1 is 4 marks)
2
B
O
C
A, B and C are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O.
AOC is a diameter of the circle.
Prove that angle ABC is 90°
You must not use any circle theorems in your proof.
(Total for Question 2 is 4 marks)
3
B
C
O
D
A
A, B, C and D are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O.
Prove that angle ABD and angle ACD are equal.
(Total for Question 3 is 2 marks)
4
B
C
A, B, C and D are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O.
Prove that angle ABC and angle ADC add to 180°
(Total for Question 4 is 4 marks)
5
A
O B
D C E
A, B and C are points on the circumference of a circle, centre O.
DCE is a tangent to the circle.
Prove that angle BCE and angle BAC are equal.
(Total for Question 5 is 4 marks)
You might also like
- 6 Circle TheoremsDocument16 pages6 Circle Theoremsaishwaryagoel08No ratings yet
- Name: - : InstructionsDocument16 pagesName: - : Instructionsinvestigation offcerNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged WatermarkDocument16 pagesIlovepdf Merged WatermarkSheikh Mohammad ForhadNo ratings yet
- SU1 Circle TheoremsDocument1 pageSU1 Circle TheoremsPlonkerNo ratings yet
- 6 Igcse Circle TheoremsDocument18 pages6 Igcse Circle Theorems4sqsmq2856No ratings yet
- Name: - : InstructionsDocument8 pagesName: - : InstructionsNeysa FariaNo ratings yet
- Circle-Theorems QuestionsDocument25 pagesCircle-Theorems QuestionsjasmineNo ratings yet
- Higher Unit 16 Topic Test: NameDocument23 pagesHigher Unit 16 Topic Test: NameTanvir ButaNo ratings yet
- Math10 - Q2 - Week 4Document20 pagesMath10 - Q2 - Week 4Venice Gwyn ChavezNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems Worksheet MWDocument6 pagesCircle Theorems Worksheet MWColdblood 3000No ratings yet
- Circle Theorem WorksheetDocument5 pagesCircle Theorem WorksheetConroy ColeNo ratings yet
- Find, The Marked Angles, Giving Reason: A) B) C) D) E) : Circle Theorem Worksheet Exercise 1 - Introductory QuestionsDocument5 pagesFind, The Marked Angles, Giving Reason: A) B) C) D) E) : Circle Theorem Worksheet Exercise 1 - Introductory QuestionsConroy ColeNo ratings yet
- G7 Math Q3 Week 7 Circle and Related Segments and AnglesDocument41 pagesG7 Math Q3 Week 7 Circle and Related Segments and AnglesROSEMARIE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Topic 13-Symmetric Properties of TangentsDocument15 pagesTopic 13-Symmetric Properties of TangentsIndah KartikasariNo ratings yet
- Ying Wa Girls' School Mathematics Test 3 Secondary 4 MathematicsDocument10 pagesYing Wa Girls' School Mathematics Test 3 Secondary 4 MathematicsShelbyNo ratings yet
- ဒသမတန္း အခန္း (၈) mathDocument17 pagesဒသမတန္း အခန္း (၈) mathZakir Amad 32No ratings yet
- 9 Vectors PDFDocument8 pages9 Vectors PDFCiaoNo ratings yet
- Circle Basics Part 1Document19 pagesCircle Basics Part 1Felix HorseradaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Handout #4: 1 ProblemsDocument6 pagesGeometry Handout #4: 1 ProblemsWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Q3 Week 7Document9 pagesMath 7 Q3 Week 7clemence enree ocampoNo ratings yet
- Circles: Circle. This Distance Is Called The Radius of The CircleDocument29 pagesCircles: Circle. This Distance Is Called The Radius of The CircleEjay InocNo ratings yet
- LP 140317 Y11 Circle Thms 1Document4 pagesLP 140317 Y11 Circle Thms 1Redzuan SaidiNo ratings yet
- Circles CBSE Class 9 WorksheetDocument11 pagesCircles CBSE Class 9 Worksheetmaria100% (1)
- Lecture 4 circle Geometry part-2 Abhay mahajan_230806_170926Document13 pagesLecture 4 circle Geometry part-2 Abhay mahajan_230806_170926Nihal NihalNo ratings yet
- Name: - : InstructionsDocument8 pagesName: - : InstructionsKhasimNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Assignment, 2023Document21 pagesYear 10 Assignment, 2023gamerthee32No ratings yet
- CIRCLE THEOREM MATH REVISIONDocument7 pagesCIRCLE THEOREM MATH REVISIONEhan FFNo ratings yet
- Ch11D 1. in The Figure, O Is The Centre of The Circle. PQ and RQ Are The Tangents To The CircleDocument3 pagesCh11D 1. in The Figure, O Is The Centre of The Circle. PQ and RQ Are The Tangents To The Circle子美No ratings yet
- Circles: A Set of Points in A Plane Having An Equal Distance From A Fixed PointDocument23 pagesCircles: A Set of Points in A Plane Having An Equal Distance From A Fixed PointJasper SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 11a Circle Theorems B - H - Question PaperDocument7 pages11a Circle Theorems B - H - Question Paperzakaraya0No ratings yet
- CircleDocument6 pagesCircleDarkNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Lesson 1 With NotesDocument3 pagesMod 5 Lesson 1 With NotesLakshmiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10.3 Arcs of A CircleDocument16 pagesLesson 10.3 Arcs of A CircleJyoti KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Geometry Grade-11 12Document10 pagesGeometry Grade-11 12jhdmss100% (1)
- Inscribe Angle and Chords of and Tangent of A Circle: TopicDocument7 pagesInscribe Angle and Chords of and Tangent of A Circle: TopicOiro Kram YakNo ratings yet
- Geometry Handout #7: 1 ProblemsDocument6 pagesGeometry Handout #7: 1 ProblemsWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- Geometry H Circle Theorems v2 1Document9 pagesGeometry H Circle Theorems v2 1gopi undavalliNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems and Circle Geometry (H)Document22 pagesCircle Theorems and Circle Geometry (H)Maria Khin YadanarNo ratings yet
- AS/A Level Mathematics The Equation of A Circle: Mathsgenie - Co.ukDocument3 pagesAS/A Level Mathematics The Equation of A Circle: Mathsgenie - Co.ukMuhammadShabbirNo ratings yet
- 11b Circle theorems B_H_Mark Scheme v2Document7 pages11b Circle theorems B_H_Mark Scheme v2samuel.oliver-sherryNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument3 pagesCircle Theoremstaliahspence123No ratings yet
- Angle Chasing - Junior: Thanom Shaw March 31 & April 1, 2021Document5 pagesAngle Chasing - Junior: Thanom Shaw March 31 & April 1, 2021BobNo ratings yet
- Circle - Theorems NewDocument23 pagesCircle - Theorems NewAromaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Galois 10 Contest ProblemsDocument4 pages2017 Galois 10 Contest Problemsmichelle tanNo ratings yet
- FjtfjyfyjDocument8 pagesFjtfjyfyjdshsj djkdghsdgysudNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Geometry (Pythagoras and Trigonometry with Algebra Recap) Follow Up WorksheetDocument4 pagesYear 9 Geometry (Pythagoras and Trigonometry with Algebra Recap) Follow Up WorksheetLynxNo ratings yet
- Name: - For Form: 4 - Mathematics Pre-Test# (2circle Theorem)Document2 pagesName: - For Form: 4 - Mathematics Pre-Test# (2circle Theorem)Mark VelasquezNo ratings yet
- GCSE Practice Math EquationDocument3 pagesGCSE Practice Math EquationAditya RathiNo ratings yet
- 22 11 22 Tmom1Document20 pages22 11 22 Tmom1BPM NalagarhNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremsDocument11 pagesCircle Theorems0nesstess0No ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Tool - Circle Geometry ConceptsDocument14 pagesFormative Assessment Tool - Circle Geometry ConceptsReygie Fabriga100% (3)
- Circles, Tangent-Chord Theorem, Intersecting Chord Theorem and Tangent-Secant TheoremDocument11 pagesCircles, Tangent-Chord Theorem, Intersecting Chord Theorem and Tangent-Secant TheoremStefanie BargoNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths Cbse Circles NotesDocument11 pagesClass 9 Maths Cbse Circles Notesdinesh_kp7647No ratings yet
- Circle Theorem Part 1Document4 pagesCircle Theorem Part 1saishaalva777No ratings yet
- BG10M (Chap - Circles)Document1 pageBG10M (Chap - Circles)Md AfrozNo ratings yet
- The BEST Thing About Circle Geometry IsDocument12 pagesThe BEST Thing About Circle Geometry IsbalachandarNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry - Tangents: ProblemsDocument1 pagePlane Geometry - Tangents: ProblemsevkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Jism 10 MathsDocument8 pagesJism 10 MathsJismon MathewNo ratings yet
- Circle and Related Terms 1Document15 pagesCircle and Related Terms 1John Angel Baring100% (1)
- VehicleVerification28!07!2019 20-09-36Document1 pageVehicleVerification28!07!2019 20-09-36Sujith Raj SNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Information Technology Design and Manufacturing, KancheepuramDocument21 pagesIndian Institute of Information Technology Design and Manufacturing, KancheepuramMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- MIT18 02SC PB 3 CombDocument2 pagesMIT18 02SC PB 3 CombMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- STP Mathematics 9 Sample ChapterDocument19 pagesSTP Mathematics 9 Sample ChapterMohd Uvais100% (2)
- Joint Admission Test For Masters: Information BrochureDocument64 pagesJoint Admission Test For Masters: Information BrochureSwarnadeep BagchiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Higher Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesDocument16 pagesMathematics Higher Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Lelm 501Document28 pagesLelm 501Ahana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- MA Handbook of Information 2019Document24 pagesMA Handbook of Information 2019Shreya MondalNo ratings yet
- Gls Int Macro PDFDocument1,018 pagesGls Int Macro PDFJoab Dan Valdivia CoriaNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Document1 pageTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Mohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- Lelm 504Document11 pagesLelm 504Vaibhav Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - ANSWERS - Analysis and Approaches HL - Sixth Edition - IBID 2019Document138 pagesMathematics - ANSWERS - Analysis and Approaches HL - Sixth Edition - IBID 2019Mohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- C4 A Level Maths Algebra Questions AQA OCR Edexcel MEIDocument2 pagesC4 A Level Maths Algebra Questions AQA OCR Edexcel MEIMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- MA Handbook of Information 2019Document24 pagesMA Handbook of Information 2019Shreya MondalNo ratings yet
- Lelm 503Document19 pagesLelm 503Aniket SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Graphing Class X Activities for GeometryDocument26 pagesGraphing Class X Activities for GeometrymsujoyNo ratings yet
- Maths Lab BookDocument30 pagesMaths Lab BookAhana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Eco Masters Course ScheduleDocument3 pagesEco Masters Course ScheduleMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- Igidr Admission Notice 2020-21Document2 pagesIgidr Admission Notice 2020-21Shoaib AshrafNo ratings yet
- 9 Velocity Time GraphsDocument8 pages9 Velocity Time GraphsElephant CastleNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions: Memory TipsDocument5 pagesInverse Trigonometric Functions: Memory TipsMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- Class X For Hosting UpdatedDocument3 pagesClass X For Hosting UpdatednavneezNo ratings yet
- XII ECONOMICS SAMPLE PAPER 2020-21Document10 pagesXII ECONOMICS SAMPLE PAPER 2020-21akankasha thakurNo ratings yet
- Advanced Identities ReviewDocument5 pagesAdvanced Identities ReviewMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- C2 A Level Maths Curve Sketching Questions AQA OCR Edexcel MEIDocument3 pagesC2 A Level Maths Curve Sketching Questions AQA OCR Edexcel MEIMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- C3 A Level Maths Functions Questions AQA OCR Edexcel MEIDocument4 pagesC3 A Level Maths Functions Questions AQA OCR Edexcel MEIMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- Admission Notice 2021 WebsiteDocument2 pagesAdmission Notice 2021 WebsiteMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- C2 A Level Maths Calculus Questuons AQA OCR Edexcel MEIDocument5 pagesC2 A Level Maths Calculus Questuons AQA OCR Edexcel MEIMohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- 8MA0 - 01 Pure MathematicsDocument48 pages8MA0 - 01 Pure MathematicsRishiraj DasNo ratings yet
- Easy Extra Marks Teachers - EASY Marks NCERT Exemplar Problems Solutions Physics CDocument345 pagesEasy Extra Marks Teachers - EASY Marks NCERT Exemplar Problems Solutions Physics CSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Ranon, Lyan Anacleto Q M12 PMDocument7 pagesRanon, Lyan Anacleto Q M12 PMHan NahNo ratings yet
- Complete Igcse Physics PPT CompilationDocument185 pagesComplete Igcse Physics PPT CompilationKareem Elhag100% (4)
- Barbeador PHILIPS HQ6920Document7 pagesBarbeador PHILIPS HQ6920GiovaniNo ratings yet
- Review Analytic GeometryDocument10 pagesReview Analytic GeometryGerard GuangcoNo ratings yet
- EMF Measurement Report - HPCL-T1 - JAN 2020Document4 pagesEMF Measurement Report - HPCL-T1 - JAN 2020Prasad GoreNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document17 pagesChap 1Esiyak MengeshaNo ratings yet
- 10th STD Science Periodic Classification of Elements Lesson Plan Eng Version 2017-18Document1 page10th STD Science Periodic Classification of Elements Lesson Plan Eng Version 2017-18Bandenawaz M NNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit and Overcurrent Protection of IGCT-based Three-Level NPC InvertersDocument7 pagesShort Circuit and Overcurrent Protection of IGCT-based Three-Level NPC InvertersReza GhasemiNo ratings yet
- W2DU - Analisys Coaxial DipoleDocument14 pagesW2DU - Analisys Coaxial DipolebyponsNo ratings yet
- An Alternative Mathematical Model For Special Relativity Guy Tsabary and Aviv CensorDocument17 pagesAn Alternative Mathematical Model For Special Relativity Guy Tsabary and Aviv CensorYotam KatzirNo ratings yet
- Inkjet Nozzle Simulation Using Level Set MethodDocument18 pagesInkjet Nozzle Simulation Using Level Set MethodNEHA THAKUR 1982605No ratings yet
- Ignition System: Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and EducationDocument53 pagesIgnition System: Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and EducationQuân ĐoànNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Fhwa Nhi 07 071 Earth Retaining Strucutures June 2008 Without SolutionsDocument711 pagesVdocuments - MX Fhwa Nhi 07 071 Earth Retaining Strucutures June 2008 Without SolutionsShivanan SinghNo ratings yet
- Electronicbekm 2023Document159 pagesElectronicbekm 2023Bekir MouradNo ratings yet
- Diagnosti ControladorDocument198 pagesDiagnosti ControladorMONTACARGAS AVS100% (1)
- Landmark Discoveries P Block 2016 July 25 Elias FinalDocument59 pagesLandmark Discoveries P Block 2016 July 25 Elias FinalSahil MalhanNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Plant Balance Sections 5-6 Scrubber and Grinding Mill Equipment SelectionDocument22 pagesMaintenance Plant Balance Sections 5-6 Scrubber and Grinding Mill Equipment SelectionJr.JeanNo ratings yet
- Glider Aerobatics ManualDocument36 pagesGlider Aerobatics ManualmichetraviNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Dome Roof InstallationDocument7 pagesAluminium Dome Roof Installationmuhammad.younisNo ratings yet
- Mec 201 04 Aug 20Document18 pagesMec 201 04 Aug 20hemanth singhNo ratings yet
- Product and Performance Task: Basic CalculusDocument23 pagesProduct and Performance Task: Basic CalculusYvez Vyanka CastilloNo ratings yet
- Direct VariationDocument44 pagesDirect VariationMary Ann Rasco100% (1)
- A10 A Pid Va 718602 201Document1 pageA10 A Pid Va 718602 201zhangNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagram - : Dr. Aneela Wakeel 02-01-2018Document42 pagesPhase Diagram - : Dr. Aneela Wakeel 02-01-2018Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- SohanDocument7 pagesSohanShuvayan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Maryland Boiler Safety:: Compressed Air TanksDocument2 pagesMaryland Boiler Safety:: Compressed Air TanksMohammed YcfssNo ratings yet
- FCC Crystal Phonon ModelingDocument4 pagesFCC Crystal Phonon ModelingLuis SerranoNo ratings yet
- Easun Reyrolle 2TJM70 (20110307) PDFDocument2 pagesEasun Reyrolle 2TJM70 (20110307) PDFshashirajNo ratings yet
- Enabling Assessment 2.1 Intoduction To MicrosDocument4 pagesEnabling Assessment 2.1 Intoduction To MicrosAvrick GoNo ratings yet
- Q3 Science 5 Periodical Test Questions No HeadingDocument4 pagesQ3 Science 5 Periodical Test Questions No HeadingWea Joy Mantolino-MasNo ratings yet