Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 4 - Enzymes & Metabolism
Uploaded by
Grace Leung0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views4 pagesChapter 4 - Enzymes & Metabolism
Uploaded by
Grace LeungCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Suggested answers to Exercise and Reading to
learn
Ch 4 Enzymes and metabolism
Exercise
Multiple-choice questions (p. 4-20)
1 B 2 C 3 B
4 D 5 A 6 C
Short questions (p. 4-21)
7 a True 1m b False; some enzymes work outside cells 1m c False; enzymes are proteins
1m d True 1m
8 a Any one from:
Volume of trypsin / enzyme solution / number of drops of enzyme added
Concentration of trypsin solution / albumin solution
Volume of buffer / number of drops of buffer added
Diameter / size of wells
Depth / volume of agar in each dish / diameter / size of dish 1m b i 6 + 9 + 8 + 11 / 4 = 8.5
1m ii Any one from: 1m
To give reliable results
To give more representative results
To minimize effects of atypical / freak results or errors / mistakes
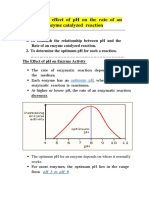
iii As pH increases / it becomes more alkaline, the activity of trypsin increases.
OR 0.5m
As pH decreases / it becomes more acidic, the activity of trypsin decreases.
0.5m
Trypsin has the greatest activity /works best at pH 9. 0.5m
OR
The optimum pH for trypsin is at 9. 0.5m c A — Buffer at pH 4
B — Buffer at pH 9
C — Buffer at pH 7
OR
Boiled trypsin and buffer at pH 4, pH 7 and pH 9
OR
Water and buffer at pH 4, pH 7 and pH 9 (1m for all correct answers or no mark)
9 HKALE Biology 2004 I Q4 Main
concept:
1. name of inhibitor
2. evidence for deduction based on the graph / description of the enzymatic activity observed.
3. explanation of inhibitory action.
e.g. 1
1. non-competitive inhibitor / allosteric inhibitor (name)
2. inhibitory action of inhibitor cannot be overcome by increased substrate concentration
(deduction) OR lowers enzymatic activity irrespective of substrate concentration
(description).
3. because inhibitor does not bind to the active site (explanation). e.g. 2
1. irreversible inhibitor (name)
2. lowers enzymatic activity irrespective of substrate concentration (description).
3. binds to enzyme permanently / forms a covalent bond with enzyme (explanation).
Structured questions (p. 4-22)
10 a The rate of reaction increases when the polyphenol oxidase concentration increases.
1m b Rate of reaction = 1/18 = 0.056 1m
From the graph, the enzyme concentration is around 1.15%. 1m c Use boiled enzyme in the
tube. 1m d The enzyme does not work in acidic medium. / The enzyme is denatured in
acidic medium. 1m e The colour change becomes faster at start 0.5m as enzyme activity
increases with temperature. 0.5m
When temperature becomes too high, no further colour change will be observed
0.5m as the enzyme is denatured. 0.5m f The rate of
reaction drops / stops if all active sites of the enzymes are blocked. 1m The inhibitor
competes with normal substrate for active sites. 1m
11 HKCEE Biology 2003 I Q3b
(b) (i) The catalase in the paper disc broke down hydrogen peroxide, releasing oxygen.
When the amount of oxygen evolved reached a certain level, the oxygen bubbles
buoyed up the disc to the surface of the hydrogen peroxide solution. (ii) (1)
pH Rate of reaction (S-1)
3 <0.01
5 0.02
7 0.05
9 0.05
11 0.04
(2)
(iii) (1) any value between 7 and 9 (or any value read from the graph drawn)
(2) Repeat the experiment using hydrogen peroxide solutions with smaller pH
intervals between 7 and 9.
(iv) The catalase activity would be similar to that of the previous investigation
because catalase is not denatured at 4°C and it can become active again at room
temperature.
Essay (p. 4-23)
12 Enzymes are biological catalysts, speeding up metabolic reactions without being used.
1m
Enzymes can be reused. Enzyme molecules return to its original form after completing the
reaction. 1m
Enzymes are required in relatively small amount because enzymes remain unchanged in the
reaction. 1m
Enzymes are proteins. They are easily denatured by high temperatures and extreme values of
pH. 1m
The actions of enzymes are specific. Each enzyme catalyses only one type of reaction.
1m
Examples of enzyme application:
Biological washing powder, papain in meat tenderizers, enzyme to coagulate milk to
produce cheese, enzyme to modify the starch in bread, enzymes to break down plant cell
wall in fruit juices, enzymes to remove hairs from hides 1m
Advantages of using enzymes in the above applications:
Enzymes are specific in action. This reduces the production of unwanted products. 1m
Enzymes are efficient in small amounts. This lowers the cost of production. 1m
Many enzymes work at moderate conditions. Extreme conditions such as high temperatures and
pressures are not required. 1m
Communication max 3m
Reading to learn (p. 4-24)
1 Buchner observed that the yeast extract had changed the sugar solution into alcohol.
1m
2 Certain enzymes in yeasts catalyse the conversion of sugar to alcohol. They could work
inside or outside living cells. 1m
3 Buchner’s discovery was important in opening up a new area of research, i.e. enzymes
working outside living cells. 1m
Many commercial products (e.g. cheese) rely on application of enzymes which work under this
condition. 1m
You might also like
- Flashcards Paper 1Document43 pagesFlashcards Paper 1emilysacre123No ratings yet
- Enzymes LolsDocument39 pagesEnzymes LolsA FloraldeNo ratings yet
- Act 3 Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity PH and Inhibitors PDFDocument3 pagesAct 3 Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity PH and Inhibitors PDFGezem GigantoNo ratings yet
- Enzymes LolsDocument38 pagesEnzymes LolsThon JustineNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument4 pagesEnzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseKhurt RogandoNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Book ExerciseDocument3 pagesCH 4 - Book ExerciseHarry LeungNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Action Testing Catalase Activity Lab ReportDocument4 pagesEnzyme Action Testing Catalase Activity Lab ReportAnthony100% (3)
- BL NurBio Activity 7 - Factors Affecting Enzymes Activity Revised (SY-2023-2024) - EditedDocument6 pagesBL NurBio Activity 7 - Factors Affecting Enzymes Activity Revised (SY-2023-2024) - EditedDouble DeckerNo ratings yet
- Ezra BiochemDocument5 pagesEzra Biochemyayayaniza100% (2)
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymescosmosstars304No ratings yet
- Enzymes Lab Report - Activty 8Document6 pagesEnzymes Lab Report - Activty 8JengNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Enzyme ActivityDocument34 pagesFactors Affecting Enzyme ActivitySharifah Nurain0% (1)
- The Effects of PH and Temperature On The Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument9 pagesThe Effects of PH and Temperature On The Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseMoira Mochie C. BasilioNo ratings yet
- Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactionsDocument2 pagesEnzymes catalyze biochemical reactionsCaithlyn KirthleyNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Post Lab With EADocument30 pagesEnzymes Post Lab With EAKezia Anne BaguioNo ratings yet
- Pepsin Enzyme Activity LabDocument4 pagesPepsin Enzyme Activity LabDebrah DebbieNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument7 pagesEnzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseMaria Christina Paine80% (5)
- ENZYMESDocument4 pagesENZYMESjpkaomeNo ratings yet
- Activity 20 25Document8 pagesActivity 20 25wangshannahNo ratings yet
- ENCARNACION, Jericho P - OrgChemLab - ExperimentNo18 (Incomplete)Document4 pagesENCARNACION, Jericho P - OrgChemLab - ExperimentNo18 (Incomplete)Jericho EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Enzyme ActivityDocument7 pagesExperiment 2 - Enzyme ActivityFatimatuzzahra' Binti Hardiyono FISNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab ReportDocument15 pagesEnzyme Lab ReportJessa Marie UseroNo ratings yet
- Enyzmatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument6 pagesEnyzmatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseGio Punsalan50% (2)
- Running Head: Effect of PH On Amylase Activity 1Document5 pagesRunning Head: Effect of PH On Amylase Activity 1Faye BaliloNo ratings yet
- Biochem Expt 6Document5 pagesBiochem Expt 6SEAN JODI M. COSEPENo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument9 pagesEnzymesramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- 1. Enzyme2. Active site 3. Enzyme-substrate complex4. CatalystDocument10 pages1. Enzyme2. Active site 3. Enzyme-substrate complex4. CatalystNushrat KaziNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Lab ReportDocument7 pagesEnzymes Lab ReportMemorie BrownNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: What Are Enzymes? Types of Reactions A) Anabolic ReactionDocument3 pagesEnzymes: What Are Enzymes? Types of Reactions A) Anabolic ReactionKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Bio 1500Document3 pagesBio 1500Paige DarbonneNo ratings yet
- Effect of PH On Invertase ActivityDocument4 pagesEffect of PH On Invertase ActivityToni Sy Encinares100% (2)
- Protein Quantification Using Hartree-Lowry AssayDocument4 pagesProtein Quantification Using Hartree-Lowry AssayHuyen Tram NguyenNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Factors Affecting Enzymes ActivityDocument5 pagesEnzymes Factors Affecting Enzymes ActivityDanniele YtingNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-12-09 at 08.23.07Document9 pagesScreenshot 2021-12-09 at 08.23.07ro shresthaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biological CatalystsDocument9 pagesEnzymes: Biological CatalystsChamzelleNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM LAB - Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument6 pagesBIOCHEM LAB - Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseIsmael Cortez100% (2)
- The Effect of PH On The Rate of An Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionDocument12 pagesThe Effect of PH On The Rate of An Enzyme Catalyzed ReactionMechAttackNo ratings yet
- Chem 132.2 Experiment 7Document6 pagesChem 132.2 Experiment 7Genry TanNo ratings yet
- Formalreport INVERTASEDocument2 pagesFormalreport INVERTASEyamsytron50% (4)
- LAB EXERCISE: Enzymes II-AmylaseDocument6 pagesLAB EXERCISE: Enzymes II-AmylaseBasem AbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Factors That Affect Enzyme ActionDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Factors That Affect Enzyme ActionYealshaday BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Mahmal BiologyhlDocument13 pagesMahmal Biologyhlapi-663908086No ratings yet
- Enzymatic Activity of Salivary Amylase Formal ReportDocument7 pagesEnzymatic Activity of Salivary Amylase Formal ReportKatrina Lee Gagan100% (2)
- Enzyme and Digestion WrittenDocument7 pagesEnzyme and Digestion WrittenJamielle Fuentes EliseoNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument4 pagesEnzymatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseRoy Ruby Caberoy100% (1)
- Effect of Temperature and pH on Salivary Amylase ActivityDocument11 pagesEffect of Temperature and pH on Salivary Amylase ActivityAmberValentineNo ratings yet
- Determination of Enzyme Activity Through Glucose Using Picric Acid Method, PH and Temperature (2EMT - Group 1, 2010)Document6 pagesDetermination of Enzyme Activity Through Glucose Using Picric Acid Method, PH and Temperature (2EMT - Group 1, 2010)Mary ChristelleNo ratings yet
- Biological Catalysts: IGCSE Biology (Cambridge)Document40 pagesBiological Catalysts: IGCSE Biology (Cambridge)송준혁No ratings yet
- (Bio 024) Biochemistry Lab Activity 8 Factors Influencing Enzyme ActionDocument3 pages(Bio 024) Biochemistry Lab Activity 8 Factors Influencing Enzyme ActionAnandu RajNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - GB1 - LABDocument4 pagesEnzymes - GB1 - LABChristian Jayvon LalunaNo ratings yet
- Liver LabDocument6 pagesLiver Labtensai-sama100% (5)
- The Effect of pH on Enzyme ActivityDocument12 pagesThe Effect of pH on Enzyme ActivityAb AbNo ratings yet
- S.3 Biology Chapter 5Document85 pagesS.3 Biology Chapter 5Fung Shan CheungNo ratings yet
- Effect of pH & Temp on Enzyme ActivityDocument4 pagesEffect of pH & Temp on Enzyme ActivityTSHIRELETSO KOLAAGANONo ratings yet
- Determining Enzyme ActivityDocument8 pagesDetermining Enzyme ActivityNesha VincentNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 2021Document6 pagesEnzymes 2021lowkeydeadNo ratings yet
- Formal Lab Report 1 Bio115LDocument11 pagesFormal Lab Report 1 Bio115LAllyra LiquiganNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit InstructionsDocument3 pagesAlkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit InstructionsLinh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsFrom EverandThe Total Synthesis of Natural ProductsJohn ApSimonNo ratings yet
- Detecting the environment answers and explanationsDocument5 pagesDetecting the environment answers and explanationsGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Coordination in HumansDocument5 pagesChapter 16 - Coordination in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Reproduction in HumansDocument4 pagesChapter 13 - Reproduction in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Growth & DevelopmentDocument4 pagesChapter 14 - Growth & DevelopmentGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Human movement and muscle contractionDocument7 pagesHuman movement and muscle contractionGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Nutrition in HumansDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Nutrition in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Food & HumansDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Food & HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Curvas de Absorción-Extracción Mineral Bajo Un Sistema Aeropónico para CrisantemoDocument8 pagesCurvas de Absorción-Extracción Mineral Bajo Un Sistema Aeropónico para CrisantemojrcorreacNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells - New AdvancesDocument251 pagesElectrochemical Cells - New AdvancesIamangel10100% (1)
- SUPACDocument33 pagesSUPACroh12100% (4)
- Food Chemistry: A A A BDocument10 pagesFood Chemistry: A A A BOSWALDO ALEXIS VARGAS VALENCIANo ratings yet
- Hypochlorite Production General Information: 740 E. Monroe Road, St. Louis, MI 48880Document43 pagesHypochlorite Production General Information: 740 E. Monroe Road, St. Louis, MI 48880کبری ادریس رسولNo ratings yet
- Percentage and Profit Loss Problems Solved Step-by-StepDocument45 pagesPercentage and Profit Loss Problems Solved Step-by-Stepsmruti paridaNo ratings yet
- Ambigard - 2K Waterproof Coating For ConcreteDocument4 pagesAmbigard - 2K Waterproof Coating For ConcreterudrabirNo ratings yet
- Grafico de Propiedades Grafico de Propiedades: Temperatura TemperaturaDocument16 pagesGrafico de Propiedades Grafico de Propiedades: Temperatura TemperaturaMaileth Carolina Anillo ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Exercise AlkaneDocument17 pagesExercise Alkanerudi_zNo ratings yet
- PDS Stopaq Subsea Intermediate Wrap V3 enDocument1 pagePDS Stopaq Subsea Intermediate Wrap V3 enAndyNo ratings yet
- 1074 PDF C02Document116 pages1074 PDF C02mih4iNo ratings yet
- Slump TestDocument4 pagesSlump TestJec SepradoNo ratings yet
- BAKER Drilling - Products Fluid End Expandable Parts PDFDocument56 pagesBAKER Drilling - Products Fluid End Expandable Parts PDFAnonymous GjCOVlgNo ratings yet
- Aoac971 20Document1 pageAoac971 20Jhon Alexander Rincon ReinaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Auditing and Assurance Services A Systematic Approach 11th Edition Messier Test BankDocument36 pagesFull Download Auditing and Assurance Services A Systematic Approach 11th Edition Messier Test Bankzickshannenukus100% (33)
- Lecture-1. Introduction To Pharmacology-1Document26 pagesLecture-1. Introduction To Pharmacology-1AbdulahiNo ratings yet
- SATA Changing and Maintenance of Spray GunsDocument1 pageSATA Changing and Maintenance of Spray Gunsmrn215No ratings yet
- Freezing Point Depression LabDocument6 pagesFreezing Point Depression LabErryn BardNo ratings yet
- NutriMost Coconut Oil LiteratureDocument2 pagesNutriMost Coconut Oil LiteratureTheophilus TyavNo ratings yet
- Textile Finishing: Shrinkagecontrol: Fabric ScienceDocument18 pagesTextile Finishing: Shrinkagecontrol: Fabric ScienceAnushka Singh100% (2)
- GIZ Manual On IHWM Module 6bDocument8 pagesGIZ Manual On IHWM Module 6bAlberto CamachoNo ratings yet
- Development of A Biosensor Using Photobacterium Spps For The Detection of Environmental PollutantsDocument3 pagesDevelopment of A Biosensor Using Photobacterium Spps For The Detection of Environmental PollutantsSbisNo ratings yet
- 13t 86 Western BentoniteDocument5 pages13t 86 Western BentoniteCharlie ChongNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Reduction ReactionDocument18 pagesOxidation Reduction ReactionDean Brando Mansinadez CincoNo ratings yet
- Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Enantiopure L-Benzofuranyl- and L-Benzobthiophenyl AlaninesDocument12 pagesChemoenzymatic Synthesis of Enantiopure L-Benzofuranyl- and L-Benzobthiophenyl AlaninesabdullahkhanduNo ratings yet
- 02-781 Protection of SW SystemsDocument28 pages02-781 Protection of SW SystemsHattar MNo ratings yet
- 18.08.22 - OSR - STAR CO-SC - Jee - Adv - 2020 - P1 - GTA-12 (P1) - QPDocument19 pages18.08.22 - OSR - STAR CO-SC - Jee - Adv - 2020 - P1 - GTA-12 (P1) - QPYuva AkhilNo ratings yet
- Ravenol Usvo TechnologyDocument5 pagesRavenol Usvo TechnologymindsNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetDocument6 pagesLab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetMd Afif AbrarNo ratings yet
- Astm D3242Document6 pagesAstm D3242Difany tsabitaNo ratings yet