Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 16 - Coordination in Humans
Uploaded by
Grace Leung0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
69 views5 pagesChapter 16 - Coordination in Humans
Uploaded by
Grace LeungCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Suggested answers
Ch 16 Coordination in humans
Exercise
Multiple-choice questions (p. 16-29)
1 A 2 A 3 D
4 A 5 C 6 B
Short questions (p. 16-30)
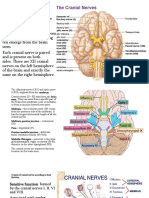
7 a Cerebral hemisphere / cerebrum / cerebral cortex / left hemisphere 1m b i 1
SSA helps select or identify correct words from past experience or memory
/ understand the language / process written words. 1m
2 It sends nerve impulses to muscles of the mouth and face to form words.
1m
3 It receives impulses from the eyes / optic nerve 1m and
passes impulse to visual association area. 1m ii B Speech association
area A 1m
8 Endocrine glands produce hormones which diffuse directly into the blood. 1m Exocrine
glands release their secretions through ducts. 1m
For example, salivary glands secrete saliva through salivary ducts into the mouth 1m
while pancreas secretes insulin directly into the blood. 1m
Structured questions (p. 16-30)
9 HKCEE Biology 2006 I Q3
2. A. * cerebellum (1)
It is for coordinating the activities of muscles in maintaining body balance (1)
B. Z protects Y from mechanical damage (1)
C. Drawing of different neurones (D):
correct position of cell bodies (½), presence of 2 synapses only (½)
*Labels (L): receptor / nerve ending, sensory neurone, interneurone, motor neurone,
effector / biceps / muscle (any four) 4 x (½)
Correct pathway (P): Indicate the direction of nerve impulse transmission OR direction
can be identified from the label(s) of the component (1)
Total: 7 marks
10 HKCEE Biology 2004 I Q2c
(b) (i) Receptor: taste buds / smell receptor (1)
Effector: salivary glands (1)
(ii) (light) → light sensitive cells relay neurone in brain
sensory neurone motor neurone
muscle of iris → (contraction of iris muscle / pupil constriction) (3) (iii)
(1) Cerebrum (1)
(2) The responses can be controlled voluntarily. )
They are not stereotyped. ) any two (1,1)
They need to be learned. )
11 HKCEE Human Biology 2004 I Q2c
Essays (p. 16-31)
12 Nerve impulses are electrical messages transmitted along nerve fibres at high speed. 1m
When a nerve impulse arrives the ending of an axon, it stimulates the ending to release
neurotransmitters. 1m
The neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse 1m and stimulate the dendron of the next
neurone to generate a nerve impulse to continue the transmission. 1m Importance:
This ensures nerve impulses travel in one direction only. 1m
Most neurones have more than one synapse, so neurones can communicate with many
other neurones. 1m
Complex network of neurones enables nervous system to achieve coordination that
involves many receptors and effectors. 1m
Communication 1m
13 HKALE Biology 2004 II Q5a
Reading to learn (p. 16-32)
1 The cerebral cortex lacks receptors that detect pain. 1m
No nerve impulses can be generated to give the sensation of pain. 1m
2 Doctors stimulate specific areas in the cerebral cortex 1m
and observe the effects of the stimulation on the patient. 1m
3 Left cerebral hemisphere 1m
You might also like
- Anatomy Physiology NotesDocument20 pagesAnatomy Physiology Notesanshul kushwaha100% (1)
- PRMO Test Series DiscountDocument19 pagesPRMO Test Series Discountsudhir singh100% (3)
- Ruach Ha Kodesh or Holy Religious SpiritDocument10 pagesRuach Ha Kodesh or Holy Religious Spiritharsan100% (1)
- Cranial Nerves: Origin, Components and FunctionsDocument14 pagesCranial Nerves: Origin, Components and FunctionsluckyNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE VESSEL Handbook - Eugene F. Megyesy 12th 2001Document501 pagesPRESSURE VESSEL Handbook - Eugene F. Megyesy 12th 2001vamcodong71% (7)
- Basic Science Js3 LESSON NOTESDocument47 pagesBasic Science Js3 LESSON NOTESAdio Babatunde Abiodun Cabax80% (5)
- Formulas by LufkinDocument1 pageFormulas by LufkinSebastianCicognaNo ratings yet
- 2011 Mena Annual Reportv1Document73 pages2011 Mena Annual Reportv1Yasmeen LayallieNo ratings yet
- "A Study Consumer Satisfaction Towards Royal Enfield BikesDocument72 pages"A Study Consumer Satisfaction Towards Royal Enfield BikesKotresh Kp100% (1)
- T2-1 MS PDFDocument27 pagesT2-1 MS PDFManav NairNo ratings yet
- bk2 - ch16 - Sug Ans - eDocument2 pagesbk2 - ch16 - Sug Ans - enonameNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Coordination in Humans: ExerciseDocument9 pagesCH 16 Coordination in Humans: ExerciseyanaaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - I: Biology XDocument5 pagesWorksheet - I: Biology XDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Coordination Nervous System Transduction ProcessDocument17 pagesCoordination Nervous System Transduction ProcessNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- Final Neurologic AssessmentDocument72 pagesFinal Neurologic AssessmentNico MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Axon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyDocument6 pagesAxon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyshashwatthegamerytNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Nervous System #2 Physiology: Neurons: Dendrites The SomaDocument2 pagesWorksheet Nervous System #2 Physiology: Neurons: Dendrites The SomaHAA-BEENo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 8 The Nervous System: Structure of A NerveDocument5 pagesWork Sheet 8 The Nervous System: Structure of A NerveJapet Floyd AlipioNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment ReviewerDocument10 pagesHealth Assessment ReviewerZLKASMdlasmNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Bio Combined End of Topic B10Document3 pagesAQA GCSE Bio Combined End of Topic B10Mahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- E Learning FinalsDocument7 pagesE Learning Finalsnorma BernardoNo ratings yet
- BG3 Unit 5-6 Exercises CORRECTEDDocument10 pagesBG3 Unit 5-6 Exercises CORRECTEDAndreesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Stimuli and ResponsesDocument19 pagesChapter 1 - Stimuli and ResponsesFlorence EweNo ratings yet
- Control & Coordination Part - 1Document35 pagesControl & Coordination Part - 1Dance is LifeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System1Document76 pagesNervous System1ahmed jeylaaniNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Education Presentation Presentation in Dark Green White Corporate Clean StyleDocument20 pagesBiodiversity Education Presentation Presentation in Dark Green White Corporate Clean StyleHasna AlzakryNo ratings yet
- Volume 10Document26 pagesVolume 10sequeirachris24No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemShaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- Theme: Management and Continuity of LifeDocument10 pagesTheme: Management and Continuity of LifeAnonymous 7pn3HEbYLNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument3 pagesCoordination and ResponseclintonbogololephojaneNo ratings yet
- 179 Anatomy Nervous System 1Document55 pages179 Anatomy Nervous System 1Ralph NilloNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Aam Amarullah, M.PD Biology and Health Program Center For Foundation Studies (CFS)Document67 pagesLecturer: Aam Amarullah, M.PD Biology and Health Program Center For Foundation Studies (CFS)Universal DiscoveringNo ratings yet
- STUDY GUIDE - Finalterm IIDocument7 pagesSTUDY GUIDE - Finalterm IIDavid MolinaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous Systemvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous Systemkmakabe78No ratings yet
- 2484 Act1 021324Document3 pages2484 Act1 021324pasil.chapNo ratings yet
- Coordination in the human bodyDocument9 pagesCoordination in the human bodyEdgar LeungNo ratings yet
- 2804 Ans 2 20Document42 pages2804 Ans 2 20Maria JanticNo ratings yet
- anaphy-lab-disc-7 (2)Document44 pagesanaphy-lab-disc-7 (2)BSLMS1D - Depasupil, Laurice Ann A.No ratings yet
- Biology All Chapters F4Document83 pagesBiology All Chapters F4Mohamed Abuukar AbdukadirNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For RLE 101Document9 pagesReviewer For RLE 101ZLKASMdlasmNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesControl and CoordinationShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- NEUROLOGICAL ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVESDocument75 pagesNEUROLOGICAL ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVESHarper EppsNo ratings yet
- Y10 Co Ordination and ResponseDocument88 pagesY10 Co Ordination and ResponseelizabethNo ratings yet
- Brain NeuroanatomyDocument227 pagesBrain NeuroanatomyNkechukwu OgakwuNo ratings yet
- Nervous System OrganizationDocument15 pagesNervous System OrganizationKristine AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Goals of the Special Senses Lab ActivitiesDocument14 pagesGoals of the Special Senses Lab ActivitiessylNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Physiology: DR - Mustafa Al-Shehabat MSC, PHDDocument33 pagesThe Nervous System Physiology: DR - Mustafa Al-Shehabat MSC, PHDمحمد السنجلاويNo ratings yet
- SHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022Document16 pagesSHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022kailaskrishnaushusNo ratings yet
- THE-NERVOUS-SYSTEM_CO-LAPTOP-UVPUU78A (1)Document29 pagesTHE-NERVOUS-SYSTEM_CO-LAPTOP-UVPUU78A (1)renztheoapuliNo ratings yet
- Nervous System IIDocument33 pagesNervous System IIGeorgette TouzetNo ratings yet
- CH-21 Neural Control and Coordination.......Document16 pagesCH-21 Neural Control and Coordination.......Irmin HasanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemKin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemDeejay BeekayNo ratings yet
- Brain Reflexes, Regions, FunctionsDocument4 pagesBrain Reflexes, Regions, FunctionsmeeraNo ratings yet
- B1 2.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesB1 2.1 The Nervous Systemsjc22No ratings yet
- GA&E 10 - Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesGA&E 10 - Peripheral Nervous SystemSu ZikaiNo ratings yet
- CoordiantionDocument56 pagesCoordiantionvijayp22No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School SecunderabadDocument13 pagesDelhi Public School SecunderabadVedant SinghalNo ratings yet
- Bio Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesBio Control and CoordinationR.Pearlsis SophiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: AP BiologyDocument65 pagesThe Nervous System: AP BiologyaiswiftNo ratings yet
- Mini-Lectures 1 - 3 Biological Psychology 2023 03 08Document40 pagesMini-Lectures 1 - 3 Biological Psychology 2023 03 08eeNo ratings yet
- Nervous System PracticeDocument14 pagesNervous System Practicealyaziahalkaabi19No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Body Coordination 2.1 Body CoordinationDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Body Coordination 2.1 Body CoordinationMarcia PattersonNo ratings yet
- Detecting the environment answers and explanationsDocument5 pagesDetecting the environment answers and explanationsGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Growth & DevelopmentDocument4 pagesChapter 14 - Growth & DevelopmentGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Reproduction in HumansDocument4 pagesChapter 13 - Reproduction in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Nutrition in HumansDocument6 pagesChapter 6 - Nutrition in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Human movement and muscle contractionDocument7 pagesHuman movement and muscle contractionGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Enzymes & MetabolismDocument4 pagesChapter 4 - Enzymes & MetabolismGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Food & HumansDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Food & HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Movement of Substances Across Cell MembraneGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- ErgonomicsDocument15 pagesErgonomicsdtmNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte 8simlh - Rev 3.02Document32 pagesGigabyte 8simlh - Rev 3.02Denis MartinsNo ratings yet
- Acer Aspire 4535 (Compal LA-4921P) PDFDocument57 pagesAcer Aspire 4535 (Compal LA-4921P) PDFMustafa AkanNo ratings yet
- National School Building Inventory FormsDocument12 pagesNational School Building Inventory FormsAnonymous w7r911SD91% (11)
- Consumer Notebook Price List For September 2010Document4 pagesConsumer Notebook Price List For September 2010Anand AryaNo ratings yet
- Basic Load (Individual) Veterinarian Field PackDocument3 pagesBasic Load (Individual) Veterinarian Field PackJohn MillerNo ratings yet
- Clone CDDocument2 pagesClone CDavk.oracleNo ratings yet
- Berkowitz Et Al (2010) - Skills For Psychological Recovery - Field Operations GuideDocument154 pagesBerkowitz Et Al (2010) - Skills For Psychological Recovery - Field Operations GuideRita CamiloNo ratings yet
- The Greatest Showman PDFDocument22 pagesThe Greatest Showman PDFMJ RecordNo ratings yet
- LUMIX G Camera DMC-G85HDocument9 pagesLUMIX G Camera DMC-G85HnimodisNo ratings yet
- Manjit Thapp ResearchDocument24 pagesManjit Thapp ResearchDough RodasNo ratings yet
- Self-Sustainable Village: Dharm Raj Jangid 16031AA015Document2 pagesSelf-Sustainable Village: Dharm Raj Jangid 16031AA015Dharm JangidNo ratings yet
- Results and DiscussionsDocument13 pagesResults and DiscussionsEdpher Leo SindolNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Study ScheduleDocument2 pagesPediatrics Study ScheduleNatnaelNo ratings yet
- Direct Marketing: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument30 pagesDirect Marketing: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinJunaid KhalidNo ratings yet
- Research 10 Mod2Document28 pagesResearch 10 Mod2Fernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- 02.casebook - BLDG Repairs & Maint - Chapter 1 - 2011 (Water Seepage)Document13 pages02.casebook - BLDG Repairs & Maint - Chapter 1 - 2011 (Water Seepage)Hang kong TseNo ratings yet
- The Secret Science of Shaktipat - Guide To Initiation 13 September 2020Document77 pagesThe Secret Science of Shaktipat - Guide To Initiation 13 September 2020Patrick JenksNo ratings yet
- OlayDocument36 pagesOlayrachit.chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design and Linux System AdministrationDocument47 pagesCompiler Design and Linux System AdministrationGouri ShankerNo ratings yet
- RRT LH: Gt'R:Ut (TLDocument75 pagesRRT LH: Gt'R:Ut (TLkl equipmentNo ratings yet
- Fee Structure 2023-2024Document10 pagesFee Structure 2023-2024Emmanuel NjogellahNo ratings yet
- Pag-IBIG Employer Enrollment FormDocument1 pagePag-IBIG Employer Enrollment FormDarlyn Etang100% (1)