Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 16 Coordination in Humans: Exercise
Uploaded by
yanaaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 16 Coordination in Humans: Exercise
Uploaded by
yanaaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch 16 Coordination in humans
Exercise
Multiple-choice questions (p. 16-33)
1 A 2 D 3 A 4 A
5 C 6 C 7 B 8 B
9 B 10 C 11 A
Short questions (p. 16-35)
12 HKALE Biology 2009 I Q1
13 HKCEE Biology 2008 I Q2
(a) to harbour more neurones/nerve cells (cell bodies/interneurons; NOT cell/ brain cells) 1
(b) Y:*medulla oblongata/medulla 1
It acts as the reflex centre for some reflex actions
OR It controls involuntary actions 1
(correct function with wrong examples 1)
Correction function with examples of reflex and involuntary action mixed up 1
One correct example instead of function 1)
(c) Motor area 1
(d) Sensory area 1
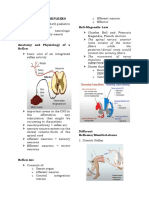
14 a Correct drawing to show dendron of sensory neurone starts at receptor and travels through dorsal
root; cell body is drawn inside dorsal root ganglion and axon enters grey matter of spinal cord 1
b Muscle 1
c Reflex action produces fast response / protects the body from danger / protects the body from
damage. 1
d Reflex arcs connect with other neurones to transmit nerve impulses to the brain. 1
15 HKDSE Biology 2013 IB Q1
Structured questions (p. 16-36)
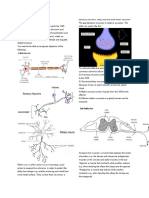
16 a P: mitochondrion 1
Q: nucleus 1
R: myelin sheath 1
b i By diffusion 1
from a high concentration to a low concentration. 1
ii The chemicals may change the shape of the active sites of the enzymes, 1
or bind to the active sites of the enzymes. 1
Neurotransmitter molecules cannot bind to the active sites of the enzymes. 1
The breaking-down reaction of the neurotransmitter molecules cannot be catalysed. 1
17 a The cerebral hemisphere is the site for intelligence / sight / hearing / enables us to think / make
decisions / have memories / controls voluntary actions. 1
The cerebellum coordinates muscular movements / maintains body balance. 1
b Death may result. 1
Part C controls involuntary actions / controls breathing / heart beat. 1
c Spinal cord 1
There will be no impulses below the cut-position / at the lower body. /
There will be no sensation below the cut-position. /
There will be paralysis below the cut-position.
(any 2) 1×2
Essay (p. 16-36)
18 HKDSE Biology Practice Paper 2012 IB Q12
Reading to learn (p. 16-37)
1 The chicken would have bled to death due to a lack of oxygen carried by the blood. 1
2 The medulla oblongata is the reflex centre for many reflex actions in the head. 1
It also controls involuntary actions such as breathing and heart beat. 1
3 No 1
It is because the chicken had lost its cerebrum, which is the site for thinking and making decisions.
1
Ch 17 Movement in humans
Exercise
Multiple-choice questions (p. 17-26)
1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A
5 C
Short questions (p. 17-26)
6 HKALE Biology 2010 II Q5b
7 HKDSE Biology 2013 IB Q2
(a) type of joint: hinge joint*
Example in our body: elbow joint/knee joint (2 m)
(b) A binds bones together
And prevents the dislocation f bones during movement
B attaches muscles to bones
And transmits the pulling force produced by muscle contraction (4 m)
8 a Structures Q and S 2
b i Structure P / tendon transmits the pulling force generated by muscle contraction to bones. 1
ii Structure P / tendon is inelastic / does not stretch. 1
c One piece of structure R / muscle moves the joint in one direction, and the second one is needed to
move the joint in the opposite direction. /
One piece of structure R / muscle bends the joint, and the second one is needed to straighten the
joint. 2
9 HKDSE Biology Sample Paper IB Q6
6. (a) Upon the arrival of nerve impulses, the nerve ending release a neurotransmitter (3)
(1) / a chemical
which diffuses across the gap between the nerve ending and the muscle fibre
(1)
the neurotransmitter / chemical will stimulate the membrane of muscle cells
(1), resulting in muscle contraction
(b) The joint serves as the fulcrum (1) of the lever system, which allows the (2)
movement of adjoining bones relative to one another (1)
10 HKALE Biology 2007 I Q6
Structured questions (p. 17-28)
11 a Hip bone 1
b i Blood cells 1
ii It is lighter / stronger per unit mass. /
It requires less energy to move around. /
Fewer minerals are needed to form it.
(any 2) 1×2
c i To reduce friction. / As a shock absorber. 1
ii
Difference Bone Cartilage
1 Rigid / not flexible Flexible
2 Heavy Light
3 Contains marrow No marrow
4 Contains calcium No calcium
phosphate phosphate
5 Internal blood No internal blood
vessels vessels / has
external blood
vessels
6 Attached to Not attached to
muscles muscles
(any 3) 1×3
iii To allow bone to increase in length / to grow. 1
iv Rib attachment to sternum / in trachea / ear / pinna / intervertebral disc / nose (any 2) 1×
2
12 HKALE Biology 1998 II Q1a, c
1. (a) Left (½) cerebral cortex (½) initiates impulse (½)that travels along a
neurone ½). Synapse(½)with inter-neurone(½)at the spinal cord (½).
(max.5)
Synapse with a motor neurone (½). Efferent motor impulse (½) exits the
spinal cord via the ventral root (½), reaches the muscle(½).
(c) synovial gap(½):a space between the upper arm and lower arm bones so
(1½)
that bending can occur (1)
synovial membrane (½):secretes the synovial fluid (½). (1)
synovial fluid (½): cushioning effect during movement (½). (1)
minimize friction / serves as lubricant so that motion can occur
(½)
smoothly (½)
cartilage at ends of bones (½): smooth surface (½)to minimize friction
(1½)
(½)during movement
ligaments binding the two bones(½):connect the 2 bones in place (½),
(1½)
prevents dislocation (½)
(max.5)
13 HKCEE Biology 2009 I Q7a–b
Essay (p. 17-28)
14 Bones are made up of living cells and minerals. /
Minerals make the bones hard. /
Compact bone forms the outer shell of all bones and the shafts in limb bones. /
It provides great strength for supporting the weight of the body. /
The shafts of limb bones are filled with yellow bone marrow. /
Spongy bone is found at the heads of limb bones. /
It is porous to help absorb shock and resist stress. /
The cavities are filled with red bone marrow, which produces blood cells. /
Blood vessels run along bones. Blood supplies oxygen and nutrients to bone cells and removes waste
from them.
(any 8) 1×8
Communication 3
Reading to learn (p. 17-29)
1 Calcium phosphate 1
2 The bones in the right arm of the tennis player are more frequently under stress than the bones in the
left arm. 1
Bone cells secrete more minerals to strengthen the bones in the right arm. 1
3 They can do exercise daily 1
to keep their bones under stress. 1
Ch 18 Homeostasis
Exercise
Multiple-choice questions (p. 18-15)
1 A 2 B 3 B 4 C
5 C
Short questions (p. 18-16)
6 HKDSE Biology Sample Paper IB Q11a
11. (a) (1) hormone A (1) (3)
when the blood glucose level drops from the normal level to 40 mg per
100 mL, the rate of hormone B secretion remains at a low level (1)
but the rate of hormone A secretion increases (1)
(2) * glucagon (1) (3)
it promotes the conversion of glycogen into glucose in the liver (1)
so as to increase the blood glucose level (1) when it is below the normal
value
(b) Any two of the following: (2)
eat smaller portions of food but more frequently (1)
reduce the intake of food with high sugar content (1) / eat complex
carbohydrates
take regular exercise (1)
frequent monitoring of blood glucose level (1)
take appropriate medication (1)
7 HKALE Biology 2008 I Q7
Structured question (p. 18-16)
8 HKCEE Biology 2008 I Q8b
Essay (p. 18-16)
9 Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable / relatively constant internal environment. /
Homeostasis involves negative feedback, /
where a variation from the normal (blood sugar level) triggers the correction mechanisms. /
The process is controlled by the endocrine system. /
When blood glucose level is above normal, it stimulates insulin release. /
Insulin is produced by the pancreas. /
Insulin lowers blood glucose level /
by stimulating liver cells to convert glucose to glycogen. /
Insulin also stimulates body cells to take in more glucose for respiration. /
When blood glucose level is below normal, it stimulates glucagon release. /
Glucagon is produced by the pancreas. /
Glucagon stimulates liver cells to convert glycogen to glucose. /
The glucose is released to the blood, causing an increased level of glucose in the blood.
(any 9) 1×9
Communication 2
Reading to learn (p. 18-17)
1 Insulin caused a decrease in the blood glucose level. 1
Body cells and brain cells could not get enough glucose for respiration. This led to weakness and
dizziness.1
2 As the blood glucose level dropped below normal, more glucagon and less insulin were produced by
the pancreas. Liver cells converted stored glycogen to glucose. 1
The glucose was released to the blood. As a result, the blood glucose level returned to normal. 1
3 Answers vary with Ss.
Against:
Experiments on dogs cause their suffering and death. 2
OR
For:
We need to balance the harm done on a few animals against the benefits of millions of diabetics all over
the world.
You might also like
- Psychology Now Vol2 2022 RevisedDocument132 pagesPsychology Now Vol2 2022 RevisedANJANA GUPTANo ratings yet
- NCLEX PNChartsDocument9 pagesNCLEX PNChartsTara Buantello60% (5)
- Coordination and Response PPT NotesDocument137 pagesCoordination and Response PPT NotesANWESHA BAL100% (1)
- Aristo Biology Mock Exam 2020Document58 pagesAristo Biology Mock Exam 2020yanaaNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument39 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary GlandGish KioiNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Coordination And ResponseNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLab ReportarchprestonNo ratings yet
- Atropine - Symptomatic BradycardiaDocument1 pageAtropine - Symptomatic BradycardiaSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Imaging Brain DiseasesDocument2,282 pagesImaging Brain DiseasesCarlos Hernan Castañeda Ruiz100% (2)
- Vital Point Strikes - The Art and Science o - Sang H. KimDocument1,037 pagesVital Point Strikes - The Art and Science o - Sang H. KimantoniofernandessapalochimucoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Coordination in HumansDocument5 pagesChapter 16 - Coordination in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Coordination NervousDocument17 pagesCoordination NervousNeetenin NeeteninNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesNervous SystemKin Long Chris WongNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam Practice: Chapter 16 Stimuli, Receptors and ResponsesDocument13 pagesAnswers To Exam Practice: Chapter 16 Stimuli, Receptors and ResponsesTSZ MIU YIPNo ratings yet
- Bio Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesBio Control and CoordinationR.Pearlsis SophiNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Tissue Recognition /30: Part A: Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesAssignment: Tissue Recognition /30: Part A: Epithelial Tissueapi-388753692No ratings yet
- Bio 07 K2 (Kedah) AnsDocument13 pagesBio 07 K2 (Kedah) AnsFerguson TehNo ratings yet
- SC1-021 MSDocument6 pagesSC1-021 MSPrashant SiagNo ratings yet
- The Punjab School Teaching Material of Class VIII Chapter 1 Human Organ Systems Q.no.1Document12 pagesThe Punjab School Teaching Material of Class VIII Chapter 1 Human Organ Systems Q.no.1Qulb e AbbasNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Human Nervous System 2 MSDocument9 pages5.2 Human Nervous System 2 MSTosyn AriyoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Movement in HumansDocument7 pagesChapter 17 - Movement in HumansGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 20: Locomotion and Movement Class 11Document7 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 20: Locomotion and Movement Class 11AlfaazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Paper 2 Answer SchemeDocument2 pagesChapter 2 Paper 2 Answer SchemeNor AzizahNo ratings yet
- Ncert Feb2021 Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 20Document7 pagesNcert Feb2021 Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 20Gufran AhmadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - I: Biology XDocument5 pagesWorksheet - I: Biology XDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- 2.3print Nervous System GuiaDocument7 pages2.3print Nervous System GuiaSOFI ULLISKYNo ratings yet
- PHY 6.16 Lab Plenary Testing Reflexes in Man and Motor System Examination Dr. Bartolome GuyDocument5 pagesPHY 6.16 Lab Plenary Testing Reflexes in Man and Motor System Examination Dr. Bartolome GuyKate Lynne CamonayanNo ratings yet
- Continuous Evaluation 3: 16 Coordination in HumansDocument12 pagesContinuous Evaluation 3: 16 Coordination in HumansLungNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Nervous and Senses EndocrineDocument19 pagesANAPHY Nervous and Senses EndocrineshannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- A) Vision B) Hearing C) Equilibrium D) Smell E) Taste 2. General SensesDocument6 pagesA) Vision B) Hearing C) Equilibrium D) Smell E) Taste 2. General SensesWilliam TongNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination DPPDocument4 pagesControl and Coordination DPPkalanidhkaurNo ratings yet
- 2022 4exp BB WA1 ANSDocument3 pages2022 4exp BB WA1 ANSJoshua NingNo ratings yet
- Muscle LilikhDocument36 pagesMuscle LilikhMaidyNo ratings yet
- Drew Doiron Tissues AssignmentDocument5 pagesDrew Doiron Tissues Assignmentapi-389057247No ratings yet
- Nervous Sytem-1Document7 pagesNervous Sytem-1subhroNo ratings yet
- Neurology Base AlmostdocxDocument76 pagesNeurology Base AlmostdocxAyad IdresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Detecting The EnvironmentDocument5 pagesChapter 15 - Detecting The EnvironmentGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- Did You Get ItDocument13 pagesDid You Get ItMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Deleted - Biology Practical File PDFDocument8 pagesDeleted - Biology Practical File PDFgaurav vermaNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMDocument4 pagesMIDTERMArchon BanzonNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: End-Of-Unit TestDocument2 pagesName: Class: End-Of-Unit TestJose Manuel AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- The Neurological Examination Adapted From The American Academy of Neurology Core Curriculum 2002Document4 pagesThe Neurological Examination Adapted From The American Academy of Neurology Core Curriculum 2002SmritiNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Reflexes Bell-Magendie LawDocument9 pagesAssessing The Reflexes Bell-Magendie LawRoger ViloNo ratings yet
- Muscular Tissue WorksheetDocument4 pagesMuscular Tissue WorksheetCedrick MedinaNo ratings yet
- KMS-CSECHsbiog-01253020-MayJune2022 Question 6Document3 pagesKMS-CSECHsbiog-01253020-MayJune2022 Question 6Jovanni PeterNo ratings yet
- 14 Coordination and Response: 14.1 Nervous Control in HumansDocument35 pages14 Coordination and Response: 14.1 Nervous Control in HumansPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Senses Primer - A+p - StudentDocument14 pagesLab Manual - Senses Primer - A+p - StudentsylNo ratings yet
- Biology CHP 1 Test Paper-20220127145424959329Document1 pageBiology CHP 1 Test Paper-20220127145424959329Asna NajeebNo ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document14 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12UNATHI SIZWE MAKHOKHOBANo ratings yet
- Axon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyDocument6 pagesAxon - Long Slender Projection That Conducts Electrical Impulses Away From The Cell BodyshashwatthegamerytNo ratings yet
- Ans 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsDocument2 pagesAns 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet - First Term - Bio Jan 2024 ANSWER KEY Yr 10Document9 pagesRevision Sheet - First Term - Bio Jan 2024 ANSWER KEY Yr 10lenora.fernandes-smchsNo ratings yet
- TP24 - Human Body SIGMOD Part 2Document14 pagesTP24 - Human Body SIGMOD Part 2Bethany CookNo ratings yet
- Created by Terri Street For Oktechmasters © 2000Document50 pagesCreated by Terri Street For Oktechmasters © 2000yasinalifNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Response Plants and AnimalsDocument6 pagesCoordination and Response Plants and AnimalsBarminga KamurenNo ratings yet
- Ans Paper 2 SelangorDocument12 pagesAns Paper 2 SelangorRozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 May-June 2021 EngDocument17 pagesLife Sciences P1 May-June 2021 EngDariusNo ratings yet
- Physiology: Block 1Document5 pagesPhysiology: Block 1Mavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Control-and-Coordination Chapter 7Document9 pagesControl-and-Coordination Chapter 7Sobana JoyNo ratings yet
- Ans 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsDocument2 pagesAns 1.4&1.5 Muscles & JointsAida Fithriyatur RohmahNo ratings yet
- bk2 - ch16 - Sug Ans - eDocument2 pagesbk2 - ch16 - Sug Ans - enonameNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Neuronal Signaling BIO161 Wolf S22Document27 pagesLecture 5 Neuronal Signaling BIO161 Wolf S22ahmvdNo ratings yet
- 5 Postnatal Growth of The Craniofacial Region ReviewerDocument3 pages5 Postnatal Growth of The Craniofacial Region ReviewerANNA PATRICIA SAMONTENo ratings yet
- HA L2 Assessing Head, Neck, Breasts, and Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesHA L2 Assessing Head, Neck, Breasts, and Lymphatic SystemljtorreslriejyNo ratings yet
- Human Brain Biochemistry: American Journal of BioscienceDocument13 pagesHuman Brain Biochemistry: American Journal of BioscienceEugen MNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology 1Document66 pagesKinesiology 1Aina AdesolaNo ratings yet
- WS C2 U6 Eng AnsDocument7 pagesWS C2 U6 Eng AnsyanaaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Exam Practice: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyDocument8 pagesAnswers To Exam Practice: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyyanaaNo ratings yet
- COMP2501 - Assignment - 1 - Questions - RMD 2Document7 pagesCOMP2501 - Assignment - 1 - Questions - RMD 2yanaaNo ratings yet
- Answers: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesAnswers: Techniques in Modern BiotechnologyyanaaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 9 Money Creation by Topic Past Paper Marking SchemeDocument3 pagesCh. 9 Money Creation by Topic Past Paper Marking SchemeyanaaNo ratings yet
- Math Factorization of Polynomials Ex. Suggested AnswerDocument22 pagesMath Factorization of Polynomials Ex. Suggested AnsweryanaaNo ratings yet
- Biology CH.41Document56 pagesBiology CH.41yanaaNo ratings yet
- Aristo Ch.32 Textbook AnswersDocument9 pagesAristo Ch.32 Textbook AnswersyanaaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet AnswerkeyDocument1 pageWorksheet AnswerkeyGregNo ratings yet
- 1bsn2 - Module 6Document16 pages1bsn2 - Module 6Kiana Ramosa100% (1)
- Mechanism of AcupunctureDocument15 pagesMechanism of Acupuncturewidad syairoziNo ratings yet
- Jemie Rose Pauline P Jalea ResumeDocument3 pagesJemie Rose Pauline P Jalea ResumeJemie JaleaNo ratings yet
- Fisa Evaluare DurereDocument2 pagesFisa Evaluare DurerecristianNo ratings yet
- DIALOG Praktikum BingDocument4 pagesDIALOG Praktikum BingMuthiaaNo ratings yet
- 05 - 06 - 07.curs Farmacologie Speciala (SNV)Document108 pages05 - 06 - 07.curs Farmacologie Speciala (SNV)madalinaNo ratings yet
- Asia Scale (Spine) - From Campbell BookDocument2 pagesAsia Scale (Spine) - From Campbell BookFirda Aurelia100% (1)
- Booklet CNE 8 Final AnnouncementDocument21 pagesBooklet CNE 8 Final AnnouncementYulia DamayantiNo ratings yet
- (ACV-S08) Week 08 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz (PA) - INGLES IV (3992)Document5 pages(ACV-S08) Week 08 - Pre-Task - Quiz - Weekly Quiz (PA) - INGLES IV (3992)eliseNo ratings yet
- 8.2 - The Nervous System - 1Document7 pages8.2 - The Nervous System - 1jamilNo ratings yet
- PDF Unit Plan For Sem 1 DLDocument17 pagesPDF Unit Plan For Sem 1 DLDiksha chaudharyNo ratings yet
- MKB Duffy Çeviri Ödevi-1.grupDocument62 pagesMKB Duffy Çeviri Ödevi-1.grupzhrksc1124No ratings yet
- Rhoton - Cochlear NucleiDocument12 pagesRhoton - Cochlear NucleicristianescNo ratings yet
- Mella CtsDocument34 pagesMella CtsAldo FathurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Wim Hof HandoutDocument2 pagesWim Hof HandoutAryan AhlawatNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune Autonomic GanglionopathyDocument14 pagesAutoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathyveerraju tvNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Ragina AguilaDocument55 pagesRabies: Ragina AguilaCharles Lester AdalimNo ratings yet
- Cognitive-Behavioural Components of Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy: The Role of ControlDocument11 pagesCognitive-Behavioural Components of Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy: The Role of ControlLuis UretaNo ratings yet
- NE ExampleDocument16 pagesNE ExampleCheeseNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Perception and CoordinationDocument86 pagesUnit 4 Perception and CoordinationMaríaNo ratings yet
- Slides 22 OrbitalMusclesInnervation HeadNeckAnatomyDocument25 pagesSlides 22 OrbitalMusclesInnervation HeadNeckAnatomyAli AdelNo ratings yet
- Bauman 2005 Neuroanatomic Observations of The Brain in AutismDocument5 pagesBauman 2005 Neuroanatomic Observations of The Brain in AutismJortegloriaNo ratings yet