Professional Documents
Culture Documents
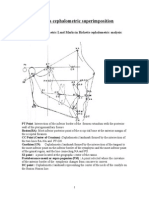
Maxillary: Figure 8-9
Maxillary: Figure 8-9
Uploaded by
AstriAl-hutami0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pages1. The maxillary occlusion rim is contoured with the plane of occlusion parallel to the base of the cast at approximately 22 mm in height anteriorly and tapering posteriorly.
2. The rim inclines labially at 15 degrees to provide lip support and the posterior rim slopes occlusally at 45 degrees from the record base.
3. The mandibular rim also has the plane of occlusion parallel to the base of the cast at approximately 18 mm anteriorly and two-thirds the height of the retromolar pad posteriorly.
Original Description:
Original Title
Occlusal Rim
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The maxillary occlusion rim is contoured with the plane of occlusion parallel to the base of the cast at approximately 22 mm in height anteriorly and tapering posteriorly.
2. The rim inclines labially at 15 degrees to provide lip support and the posterior rim slopes occlusally at 45 degrees from the record base.
3. The mandibular rim also has the plane of occlusion parallel to the base of the cast at approximately 18 mm anteriorly and two-thirds the height of the retromolar pad posteriorly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesMaxillary: Figure 8-9
Maxillary: Figure 8-9
Uploaded by
AstriAl-hutami1. The maxillary occlusion rim is contoured with the plane of occlusion parallel to the base of the cast at approximately 22 mm in height anteriorly and tapering posteriorly.
2. The rim inclines labially at 15 degrees to provide lip support and the posterior rim slopes occlusally at 45 degrees from the record base.
3. The mandibular rim also has the plane of occlusion parallel to the base of the cast at approximately 18 mm anteriorly and two-thirds the height of the retromolar pad posteriorly.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Maxillary
Figure 8–9 A properly contoured maxillary record base
and occlusion rim along with the desired dimensions. Note
that the plane of occlusion is parallel with the base of the
cast, and the labial inclination of the anterior portion of the
occlusion rim is at approximately a 150 angle to offer lip
support. The numbers provided (22 mm and 12 mm) are
averages that will generally provide slightly more wax than
necessary. This rim will be contoured intraorally to establish
the final plane of occlusion and lip support. The posterior
of the maxillary occlusion rim should slope occlusally
at approximately a 45 degree angle from the record base,
beginning approximately 8 mm from the posterior extent
of the record base. This will generally provide space for
the mandibular record base once placed intraorally.
1. Labial surface of the natural central incisors
averages 6-8 mm anterior to the middle of the
incisal papilla.
2. The rims incline at approximately a 15" angle
labially to provide adequate support for the lip
3. The plane of occlusion on the maxillary arch
should be approximately 22 mm in height, as measured from the bottom of the
notch created by the labial frenulum.
4. The posterior maxillary wax rim height is 16 mm
from the deepest point of the buccal flange. (The
maxillary occlusion rim should be approximately 12
mm in height from the record base at the crest of the
ridge in the tuberosity areas).
5. It should gradually taper toward the occlusal plane
and be approximately 8-10 mm in width in the
posterior, and 6-8 mm in width in the anterior region.
6. The upper rim terminates at the anterior aspect of the maxillary tuberosity. The
posterior of the maxillary occlusion rim should slope occlusally at approximately
a 45 degree angle from the record base, beginning approximately 8 mm from the
posterior extent of the record base. This will generally provide space for the
mandibular record base once placed intraorally
Mandibula
Figure 8–10 A properly contoured mandibular record
base and occlusion rim along with desired dimensions.
Note that the plane of occlusion runs parallel with the
base of the cast, which was trimmed to be parallel with
the residual ridges. Also the plane of occlusion is approximately
at the level of the middle-to upper-third of the
retromolar pad
1. plane of occlusion runs parallel with base of cast, which
was trimmed to be parallel with residual ridges
2. the plane of occlusion anteriorly on the mandibular arch
should be approximately 18 mm in height, as measured
from the bottom of the notch created by the labial frenulum,
3. in the posterior mandibular region the height is equal to a point representing two
thirds the height of the retromolar pad.
4. It should be approximately 8-10 mm in width in the posterior, and 6-8 mm in
width in the anterior region.
5. rims incline at a 15" angle labially to provide adequate support for the lip.
6. The lower rim terminates anterior to the retromolar pad. The rims are beveled
posteriorly towards the base to not interfere during recording of jaw relationships
You might also like
- Finishing and DetailingDocument47 pagesFinishing and DetailingSparsh Bhaskar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Endo Crown: An Approach For Restoring Endodontically Treated Right Mandibular First Molars With Large Coronal Destruction - A Case ReportDocument7 pagesEndo Crown: An Approach For Restoring Endodontically Treated Right Mandibular First Molars With Large Coronal Destruction - A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- FACEBOWDocument30 pagesFACEBOWHarini PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Face BowDocument85 pagesFace BowDeepalakshmi VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Facebow Calliper ReviewDocument5 pagesFacebow Calliper ReviewFaheemuddin Muhammad100% (3)
- Group Function Occlusion I JosDocument6 pagesGroup Function Occlusion I JosAnonymous gVCIYF6dFNo ratings yet
- Welcome Homeopathy - Dr. S. C. MadanDocument195 pagesWelcome Homeopathy - Dr. S. C. Madanreza100% (4)
- The Roth Prescription / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument85 pagesThe Roth Prescription / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academy100% (2)
- Straumann Surgical ProceduresDocument68 pagesStraumann Surgical ProceduresWuppuluri Jayanth Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Utility ArchesDocument2 pagesUtility ArchesDevanand Gupta67% (3)
- ImpactionDocument48 pagesImpactionDiaa KamalNo ratings yet
- Face Bow FINALDocument53 pagesFace Bow FINALAnna PooraniNo ratings yet
- Cephalometric Analysis PGDocument114 pagesCephalometric Analysis PGaung NaingmyoNo ratings yet
- Mouth Breathing Habit in Children PedoDocument21 pagesMouth Breathing Habit in Children PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Guide To Occlusion An IntroductionDocument75 pagesA Clinical Guide To Occlusion An IntroductionAndrei Oana100% (1)
- Otoplasty Surgical TechniqueDocument12 pagesOtoplasty Surgical TechniqueLacramioaraBalanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Molar Uprighting Using The Biocreative Reverse-Curve TechniqueDocument9 pagesStrategic Molar Uprighting Using The Biocreative Reverse-Curve TechniqueAly Osman100% (1)
- Face BowDocument107 pagesFace BowSeena SamNo ratings yet
- A Cess Cavity PreparationDocument54 pagesA Cess Cavity Preparationmandy0077No ratings yet
- Biological Considerations of Orientation, Vertical and Horizontal Jaw Relations in Complete Denture-First PartDocument43 pagesBiological Considerations of Orientation, Vertical and Horizontal Jaw Relations in Complete Denture-First PartArunNo ratings yet
- Ortho Xray MeasurmentsDocument110 pagesOrtho Xray MeasurmentsPriza RazunipNo ratings yet
- Prosthetic 6Document5 pagesProsthetic 6زهراء فاضل اجبير فعيلNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide How To Template The Hip: Lustig Sébastien MD, PHD, Prof Albert Trillat Center - Lyon - FranceDocument25 pagesStep by Step Guide How To Template The Hip: Lustig Sébastien MD, PHD, Prof Albert Trillat Center - Lyon - FranceAlaa ElbulukNo ratings yet
- Anita Kapri: Keyword: Smile Makeover, Digital Smile Design, EstheticsDocument8 pagesAnita Kapri: Keyword: Smile Makeover, Digital Smile Design, Estheticsalaesa2007No ratings yet
- Record Base and Occlusal RimDocument18 pagesRecord Base and Occlusal RimswatiNo ratings yet
- OcclusalDocument1 pageOcclusalsreenivas1990No ratings yet
- Ricketts Cephalometric SuperimpositionDocument10 pagesRicketts Cephalometric Superimpositionishtiii100% (2)
- Prosthodontics VivaDocument42 pagesProsthodontics VivaambiliNo ratings yet
- Rims & Occlusal Record PDFDocument63 pagesRims & Occlusal Record PDFAmanda AmaroNo ratings yet
- Biomatric Approach For Complete Denture DesignDocument18 pagesBiomatric Approach For Complete Denture Designفواز نميرNo ratings yet
- AnthropometricDocument11 pagesAnthropometricdrrebaNo ratings yet
- Tufts Unuversity Open Source LearningDocument2 pagesTufts Unuversity Open Source Learningizeldien5870No ratings yet
- Case HistoryDocument32 pagesCase HistorySwati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vita Complete Denture PDFDocument32 pagesVita Complete Denture PDFdr_masuodtavakolianradNo ratings yet
- Teeth AlignmentDocument11 pagesTeeth AlignmentPatrick MwauraNo ratings yet
- The Female Pelvis and Fetal SkullDocument5 pagesThe Female Pelvis and Fetal Skullrevathidadam55555No ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2021 12261680Document7 pagesMUCLecture 2021 12261680Chestnut ShopNo ratings yet
- Arrangement of Artificial Teeth: Dr. Enas Abdul-SattarDocument50 pagesArrangement of Artificial Teeth: Dr. Enas Abdul-SattarShashank AadarshNo ratings yet
- Maternalpelvis 160311112407Document22 pagesMaternalpelvis 160311112407Sunil YadavNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Occlusal RimDocument19 pagesMaxillary Occlusal Rimvarsha ammuNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Occlusal RimDocument19 pagesMaxillary Occlusal Rimvarsha ammu0% (1)
- Paranasal Sinuses NoteDocument6 pagesParanasal Sinuses NotechidiogoNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 Arrangment of TeethDocument24 pagesLec 11 Arrangment of Teethحسين العراقيNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Information For Esthetic and Functional Predictability in Severe Wear Cases.Document11 pagesTransfer of Information For Esthetic and Functional Predictability in Severe Wear Cases.jorefe12No ratings yet
- Face Bow and Jaw RelationsDocument58 pagesFace Bow and Jaw Relationsdiwakar2No ratings yet
- Face BowDocument41 pagesFace Bowasha docNo ratings yet
- PDF Segunda Parte de RoothDocument11 pagesPDF Segunda Parte de RoothMARIA LAURA RUIZ RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Pros Lec.11Document5 pagesPros Lec.11Rajh QasimNo ratings yet
- Flat Plane OcclusionDocument22 pagesFlat Plane OcclusionDavid TaylorNo ratings yet
- Short Textbook of Endodontics: AbcdeDocument7 pagesShort Textbook of Endodontics: AbcdeCristinaNo ratings yet
- New Doc 04-06-2020 12.16.36Document6 pagesNew Doc 04-06-2020 12.16.36Amir IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lec 15Document9 pagesLec 15محمد امينNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Pelvis and Fetal SkullDocument41 pagesAnatomy of Pelvis and Fetal SkullHakimah K. Suhaimi100% (1)
- Ansari 1997Document4 pagesAnsari 1997SkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The Female PelvisDocument4 pagesThe Anatomy of The Female PelvisClarissa Altamirano ArmendarizNo ratings yet
- KimDocument12 pagesKimIvanna H. A.No ratings yet
- Female Pelvis and Fetal SkullDocument37 pagesFemale Pelvis and Fetal Skullliathmahmood15No ratings yet
- VITA en Viktor Fuergut Broschuere Screen enDocument8 pagesVITA en Viktor Fuergut Broschuere Screen enHamidNo ratings yet
- Catatan Skills Lab Blok 20Document3 pagesCatatan Skills Lab Blok 20colombusligirNo ratings yet
- Model Analysis 1 / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument36 pagesModel Analysis 1 / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Articulators and Articulation.Document21 pagesArticulators and Articulation.colltfrankNo ratings yet
- MK006 105Document20 pagesMK006 105C Martin TraumatoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Ortho 2Document4 pagesQuiz Ortho 2alwasity167No ratings yet
- Mounting:: The Laboratory Procedure of Attaching Cast To AnDocument11 pagesMounting:: The Laboratory Procedure of Attaching Cast To AnDr.Maher MohammedNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2022 4162747Document8 pagesMUCLecture 2022 4162747JamesNo ratings yet
- LDEK OrthodonticsDocument10 pagesLDEK Orthodonticsmikechur-aNo ratings yet
- Access To Dental CareDocument29 pagesAccess To Dental CareNilusha93No ratings yet
- Eve TricDocument6 pagesEve TricCalimarea Adrian AndreiNo ratings yet
- Scenario 1 Blok 22 KG 2016Document5 pagesScenario 1 Blok 22 KG 2016Rohma DwiNo ratings yet
- Basic Requirements For Hospital Planning: Indian StandardDocument22 pagesBasic Requirements For Hospital Planning: Indian StandardAmol LangerNo ratings yet
- The New Flexibility: Titanium Base Asc FlexDocument28 pagesThe New Flexibility: Titanium Base Asc FlexOleg KushnirNo ratings yet
- Do Glass Ionomer Cements Prevent Caries On The Margins of Restaurations in Primary TeethDocument9 pagesDo Glass Ionomer Cements Prevent Caries On The Margins of Restaurations in Primary TeethDoruNo ratings yet
- MANUSCRIPTREALrealrealDocument49 pagesMANUSCRIPTREALrealrealJose Antonio Peralta Achaval Jr.No ratings yet
- Acute Streptococcal GingivitisDocument6 pagesAcute Streptococcal GingivitisSatish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mentored by Nature: Bradley L. JonesDocument5 pagesMentored by Nature: Bradley L. JonesAlfredo RamzNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Bone Width Preservation After Decoronation of Ankylosed Anterior IncisorsDocument4 pagesAlveolar Bone Width Preservation After Decoronation of Ankylosed Anterior IncisorsVincent LamadongNo ratings yet
- 5) Moebius SyndromeDocument4 pages5) Moebius SyndromeRoxana AndreeaNo ratings yet
- 2001 LindauerDocument14 pages2001 Lindauerosama-alaliNo ratings yet
- Create Biomimetic Class II Direct Composite Restorations Using A Sectional Matrix SystemDocument8 pagesCreate Biomimetic Class II Direct Composite Restorations Using A Sectional Matrix Systemsulis trianingsihNo ratings yet
- BookletDocument115 pagesBookletRoyal CureNo ratings yet
- Guided Tissue RegenerationDocument4 pagesGuided Tissue RegenerationNicoleta MarcuNo ratings yet
- Community Dimitry Averin Maxim Belograd ViaDocument14 pagesCommunity Dimitry Averin Maxim Belograd ViaCarlos Nieto MallquiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Dentition Space Analysis: A Review: December 2012Document7 pagesMixed Dentition Space Analysis: A Review: December 2012srinandanNo ratings yet
- Tooth Mould ChartDocument12 pagesTooth Mould ChartJoohi SharmaNo ratings yet
- One-Step Mounting of Diagnostic CastsDocument10 pagesOne-Step Mounting of Diagnostic CastsJittin JamesNo ratings yet
- Ao2019 0060Document19 pagesAo2019 0060Charlemagne Sabio GalamgamNo ratings yet
- JCO On CD-ROM (Copyright © 1998 JCO, Inc.), Volume 1984 Jan (35 - 37) - A Therapeutic Method For Selected TMJ PatientsDocument6 pagesJCO On CD-ROM (Copyright © 1998 JCO, Inc.), Volume 1984 Jan (35 - 37) - A Therapeutic Method For Selected TMJ PatientssaberNo ratings yet