Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade X - Polynomials: Section-1
Uploaded by
devesh chaudharyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade X - Polynomials: Section-1
Uploaded by
devesh chaudharyCopyright:
Available Formats
QB-2 (202122)
Grade X - Polynomials
SECTION-1
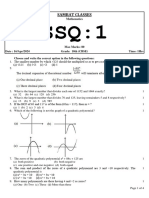
1. State the number of zeroes of the polynomials represented by the following graphs
(a)
(b)
zeroes lying between -2 and 0.
(c)
(d)
2. If the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x2 + (a + 1) x + b are 2 and –3, then a and b are
respectively equal to and .
2
3. If one zero of the quadratic polynomial x + 3x + k is 2, then the value of k is .
4. If 1 is a zero of a polynomial, then the value of a is ______________.
5. The number of polynomials having zeroes –2 and 5 is:
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) more than 3
6. Given that one zero of the polynomial ax2 + bx + c is 0, what is the second zero?
7. If one of the zeroes of the cubic polynomial ax3 + bx2 + cx + d is zero, find the product of the
other two zeroes.
8. The quadratic polynomial p(y) with sum –15 and one of the zeroes as –7 is:
(a) y2 – 15y – 56
(b) y2 – 15y + 56
(c) y2 + 15y + 56
(d) y2 + 15y – 56
9. From the following polynomials, choose the correct opptions which suits best:
3 3 1 1
(i) 3x 2 − 2 3x + 3 (ii) x − 5x2 − x − 1 (iii) x + (iv) 5 x 2 − 3 x + 2
2 2 x
(a) None of them are polynomials
(b) all are polynomials
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (iii) only
10. If the degree of the polynomial p(x) is n, then the maximum number of zeroesit can have
is:
a) n b) n2 c) n3 d) none of these
SECTION-2
11. α, β are the roots of the quadratic polynomial p(x) = x2 – (k – 6) x + (2k + 1). Find the value
of k, if α+β = αβ
12. If the product of zeroes of the polynomial ax2 – 6x – 6 is 4, find the value of a.
13. Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 3x 2 − 8 x + 4 3 and verify the relation between
the zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial.
14. What real no. should be subtracted from the polynomial (3x3+10x2-14x+9) so that (3x -2)
divides it exactly?
15. If and are zeroes of the polynomial ax2 + bx + c , then find a quadratic polynomial whose
1 1
zeroes are and
16. If α and β are zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = kx2 + 4x + 4 such that
α2 + β2 = 24, find the value of k.
17. On dividing x 3 − 3x 2 + x + 2 by a polynomial g (x) , the quotient and remainder are x − 2 and
− 2 x + 4 respectively. Find g (x) .
SECTION-3
18. If α, β are zeroes of the polynomial x2– 2x – 8, then form a quadratic polynomial whose
zeroes are 2α and 2β
19. Check whether the polynomial g(x) = x3 – 3x + 1 is the factor of polynomial p(x) = x5 –
4x3+x2+3x+1
20. Find the zeroes of the polynomial 4 3 x2 +5x -2 3 and verify the relation between the
zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial.
21. If α, β, γ are zeroes of the polynomial 6x3 + 3x2 – 5x + 1.
Find the value of α–1 + β–1 + γ–1
22. Find all the zeroes of the polynomial x3 + 3x2 – 2x – 6, if two of its zeroes are − 2 and 2
23. Divide 3x2 – x3 – 3x + 5 by x – 1 – x2 and verify the division algorithm.
24. If the polynomial x4 + 2x3 + 8x2 + 12x + 18 is divided by another polynomial x2 + 5, the
remainder comes out to be px + q. Find the values of p and q.
25. If 1 and −2 are zeroes of the polynomial x3 + 10 x 2 + px + q , then find the values of p and q.
3
26. Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product of whose zeroes are 2 and −
2
respectively. Also find its zeroes.
SECTION-4
27. What must be added to the polynomial f(x) = x4 + 2x3 – 2x2 + x – 1 so that the resulting
polynomial is exactly divisible by x2 + 2x – 3?
28. If the remainder on division of x3 + 2x2 + kx + 3 by x – 3 is 21, find the quotient and the
value of k. Hence, find the zeroes of the cubic polynomial x3 + 2x2 + kx – 18.
29. Find all the zeroes of the polynomial 2x4 – 10x3 + 5x2 + 15x – 12, if it is given that two of
3
its zeroes are
2
30. Find all other zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 – 11x – 6, if one of its zero is –3.
You might also like
- PolynomialsDocument6 pagesPolynomialsAVINASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- STD 10 - Math - Polynomials - All Types Ques.Document10 pagesSTD 10 - Math - Polynomials - All Types Ques.Guna DharshiniNo ratings yet
- Asm 2222222222Document5 pagesAsm 2222222222p5jp29697cNo ratings yet
- G-10 POLYNOMIALS WorksheetDocument4 pagesG-10 POLYNOMIALS WorksheetkondavetimurthyNo ratings yet
- G-10 PolynomialsDocument4 pagesG-10 PolynomialskondavetimurthyNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Synopsis: + BX + C Where A, B, C Are Real + BX + CX + D, Where A, B, C Are RealDocument9 pagesPolynomials Synopsis: + BX + C Where A, B, C Are Real + BX + CX + D, Where A, B, C Are RealThanveer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Polynomials: PX A Ax Ax Ax A X Ax Aaaaa ADocument9 pagesPolynomials: PX A Ax Ax Ax A X Ax Aaaaa AJay GauravNo ratings yet
- Assignment Class X (2019-20) 1 Mark Questions:: PolynomialsDocument5 pagesAssignment Class X (2019-20) 1 Mark Questions:: PolynomialsDhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument1 pagePolynomialsPreetishNo ratings yet
- Polynomials WSDocument2 pagesPolynomials WSTimothy SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths CH 2 PolynomialsDocument3 pagesClass 10 Maths CH 2 PolynomialsananramsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MinimalDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Minimalhackerboy99356No ratings yet
- MathsDocument2 pagesMathscponnusamy411No ratings yet
- 2 PolynomialsDocument10 pages2 PolynomialsDROZON GAMING YTNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - PolynomialsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 - Polynomialsbaby doodlesNo ratings yet
- Class X: Polynomial: Alfa Circle Contact No:-9621645520Document1 pageClass X: Polynomial: Alfa Circle Contact No:-9621645520Career 1stNo ratings yet
- Polynomials For Printing (ADITYA)Document9 pagesPolynomials For Printing (ADITYA)Srinivasan SakthivelNo ratings yet
- PolynomialDocument8 pagesPolynomialRadhaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Polynomials 1Document4 pagesPolynomials 1Shashswat PatelNo ratings yet
- Algebra - AssignmentDocument79 pagesAlgebra - AssignmentUNKNOWN LEGENDNo ratings yet
- MCQ CH - 2Document6 pagesMCQ CH - 2Gunn SinglaNo ratings yet
- CBSE X MathematicsDocument8 pagesCBSE X MathematicsmicrodotcdmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2jaitashri.kNo ratings yet
- 10th Maths Chapter - Polynomial Cbse Test Paper-3Document1 page10th Maths Chapter - Polynomial Cbse Test Paper-3Jegan ShanjaiNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Chapter 02 Polynomials Practice Paper 02 1Document3 pagesMaths Class X Chapter 02 Polynomials Practice Paper 02 1Anonymous SOQFPWBNo ratings yet
- Polynomials - Worksheet1Document2 pagesPolynomials - Worksheet1ckankaria749No ratings yet
- WS PolynomialsDocument4 pagesWS PolynomialsAaratrika DasNo ratings yet
- Polynomials 50marks 1Document2 pagesPolynomials 50marks 1Rehan MotiwalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2rohitbhatt0508No ratings yet
- Polynomials Assignment (23-24)Document2 pagesPolynomials Assignment (23-24)Jahnvi KambojNo ratings yet
- Right Magnitude in Right Direction: Useful Concepts - IDocument6 pagesRight Magnitude in Right Direction: Useful Concepts - IAnand Kumar JatavNo ratings yet
- Polynomials Class 9Document3 pagesPolynomials Class 9hollowgamingyt3012No ratings yet
- Polynomials Revision Tracker STDDocument14 pagesPolynomials Revision Tracker STDOfficial WorkNo ratings yet
- 10 2 PolynomialsDocument3 pages10 2 PolynomialsFakerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document1 pageChapter 1rohitbhatt0508No ratings yet
- Part - I: Pre Rmo: EquationsDocument9 pagesPart - I: Pre Rmo: EquationsKeshav RamukaNo ratings yet
- Caps 2Document3 pagesCaps 2shheNo ratings yet
- X Ntse Coordinate Test-8Document3 pagesX Ntse Coordinate Test-8raghuNo ratings yet
- G-10 Polynomials-New-1Document4 pagesG-10 Polynomials-New-1kondavetimurthyNo ratings yet
- Class: X Mathematics Assignment: 2 April 2010 Chapter: POLYNOMIALSDocument1 pageClass: X Mathematics Assignment: 2 April 2010 Chapter: POLYNOMIALSYash KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- G-10 Polynomials-New-2Document4 pagesG-10 Polynomials-New-2kondavetimurthyNo ratings yet
- 2.polynomials A4S BooksDocument26 pages2.polynomials A4S BooksSidMusixNo ratings yet
- Class X Mathematics Question Bank 2017-18Document41 pagesClass X Mathematics Question Bank 2017-18akhil.jNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Mathematics IDocument6 pagesFundamental Mathematics IAnand Kumar JatavNo ratings yet
- Worksheet PolynomialDocument1 pageWorksheet Polynomialgurdeepsarora873850% (2)
- Polynomials Question BankDocument12 pagesPolynomials Question BankSumukh Gowda.MNo ratings yet
- Assig - Polynomials (Previous Year)Document3 pagesAssig - Polynomials (Previous Year)shambhaviNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument3 pagesPolynomialsADARSH KUMAR BEHERANo ratings yet
- Polynomials Assignment 8 - 0Document3 pagesPolynomials Assignment 8 - 0Perajothi PalanirajaNo ratings yet
- Real Polynomial SSQ 2024Document4 pagesReal Polynomial SSQ 2024switchangryNo ratings yet
- Equations and Inequalitites Extra PracticeDocument14 pagesEquations and Inequalitites Extra PracticeGuo HeqiNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument5 pagesQuadratic Equationanshul.swainNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Quadratic EquationDocument11 pagesWorksheet Quadratic EquationSameer saNo ratings yet
- Holiday Home Work Maths Class XDocument3 pagesHoliday Home Work Maths Class XAprojeet BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Olynomials: Download All NCERT Books PDF From WWW - Ncert.onlineDocument18 pagesOlynomials: Download All NCERT Books PDF From WWW - Ncert.onlineImran MustaqNo ratings yet
- Important Questions: Exam Practice PolynomialsDocument4 pagesImportant Questions: Exam Practice PolynomialsSachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Attachment Summary Sheet Time Value of MoneyDocument9 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet Time Value of Moneydevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary Sheet Time Value of MoneyDocument9 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet Time Value of Moneydevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary Sheet Time Value of MoneyDocument9 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet Time Value of Moneydevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary PPPDocument9 pagesAttachment Summary PPPdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Alternate Sources of FinanceDocument7 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Alternate Sources of Financedevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary PPPDocument9 pagesAttachment Summary PPPdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Equity MarketsDocument19 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Equity Marketsdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For: Income Statement and Balance SheetDocument11 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For: Income Statement and Balance Sheetdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet Derivatives-Options: 27 Final Selections in RBI Grade B 2017 Final Results Awaited For RBI Grade B 2018Document13 pagesSummary Sheet Derivatives-Options: 27 Final Selections in RBI Grade B 2017 Final Results Awaited For RBI Grade B 2018devesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention DerivativesDocument15 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention Derivativesdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Attachment Summary Sheet Time Value of MoneyDocument9 pagesAttachment Summary Sheet Time Value of Moneydevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Bonds (Basics + Advanced)Document12 pagesSummary Sheet - Helpful For Retention For Bonds (Basics + Advanced)devesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Finance and Management: Previous Year Questions Marathon SessionDocument63 pagesFinance and Management: Previous Year Questions Marathon Sessiondevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Attachment RBI Grade B 2019 Finance Theory 5 MCQS A Day Lecture 2 PDF Lyst8723Document30 pagesAttachment RBI Grade B 2019 Finance Theory 5 MCQS A Day Lecture 2 PDF Lyst8723devesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Attachment Guidelines On Money Market InstrumentsDocument43 pagesAttachment Guidelines On Money Market Instrumentsdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Attachment RBI Grade B 2019 Finance Theory 5 MCQS A Day Lecture 18 PDF Lyst2051Document24 pagesAttachment RBI Grade B 2019 Finance Theory 5 MCQS A Day Lecture 18 PDF Lyst2051devesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Finance (Theory) : MCQ Series Lecture - 11Document24 pagesFinance (Theory) : MCQ Series Lecture - 11devesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Finance (Theory) : MCQ Series Lecture - 5Document24 pagesFinance (Theory) : MCQ Series Lecture - 5devesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument12 pagesTissueschandankrdumkaNo ratings yet
- Attachment RBI Grade B 2019 Finance Theory 5 MCQS A Day Lecture 2 PDF Lyst8723Document30 pagesAttachment RBI Grade B 2019 Finance Theory 5 MCQS A Day Lecture 2 PDF Lyst8723devesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Finance and MANAGEMENT: Rbi Faqs Priority Sector LendingDocument51 pagesFinance and MANAGEMENT: Rbi Faqs Priority Sector Lendingdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- First Review (2021 - 2022) : Section-ADocument3 pagesFirst Review (2021 - 2022) : Section-Adevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- Grammar Practice Fill in The Blank With The Present Perfect Form of The Verb in Parentheses. The First One Has Been Done For YouDocument2 pagesGrammar Practice Fill in The Blank With The Present Perfect Form of The Verb in Parentheses. The First One Has Been Done For Youdevesh chaudharyNo ratings yet
- 58 Topper 21 101 1 1 7 Tissues Up201506181308 1434613126 797Document10 pages58 Topper 21 101 1 1 7 Tissues Up201506181308 1434613126 797V AnandNo ratings yet
- Guide Rail Bracket AssemblyDocument1 pageGuide Rail Bracket AssemblyPrasanth VarrierNo ratings yet
- (Guide) Supercharger V6 For Everyone, Make Your Phone Faster - Xda-DevelopersDocument7 pages(Guide) Supercharger V6 For Everyone, Make Your Phone Faster - Xda-Developersmantubabu6374No ratings yet
- Wilson v. Baker Hughes Et. Al.Document10 pagesWilson v. Baker Hughes Et. Al.Patent LitigationNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Wellwash ACDocument99 pagesUser Manual - Wellwash ACAlexandrNo ratings yet
- Hung201 PDFDocument14 pagesHung201 PDFMua Dong Tuyet RoiNo ratings yet
- Merchant Accounts Are Bank Accounts That Allow Your Business To Accept Card Payments From CustomersDocument43 pagesMerchant Accounts Are Bank Accounts That Allow Your Business To Accept Card Payments From CustomersRohit Kumar Baghel100% (1)
- Software Requirements SpecificationDocument9 pagesSoftware Requirements SpecificationSu-kEm Tech LabNo ratings yet
- Alpha Tech India Limited - FinalDocument4 pagesAlpha Tech India Limited - FinalRahul rNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lab #2 - Microscopy & Microscopic Examination of Living MicroorganismsDocument53 pagesWeek 1 Lab #2 - Microscopy & Microscopic Examination of Living MicroorganismsNgoc PhamNo ratings yet
- Nanomedicine Lecture 2007Document59 pagesNanomedicine Lecture 200778912071No ratings yet
- Role of Quick Response To Supply ChainDocument15 pagesRole of Quick Response To Supply ChainSanuwar RashidNo ratings yet
- Mineral Claim Purchase and Sale Agreement FinalDocument5 pagesMineral Claim Purchase and Sale Agreement Finaldaks4uNo ratings yet
- Ingredients EnsaymadaDocument3 pagesIngredients Ensaymadajessie OcsNo ratings yet
- Psi Engines Product Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesPsi Engines Product Sheet PDFDaniel DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Source BookDocument128 pagesCompressed Air Source Bookgfollert100% (1)
- Where Business Happens Where Happens: SupportDocument19 pagesWhere Business Happens Where Happens: SupportRahul RamtekkarNo ratings yet
- FoodhallDocument3 pagesFoodhallswopnilrohatgiNo ratings yet
- Annual Presentation 18 19 EILDocument41 pagesAnnual Presentation 18 19 EILPartha Pratim GhoshNo ratings yet
- E-Cat35xt014 Xtro PhantomsDocument32 pagesE-Cat35xt014 Xtro PhantomsKari Wilfong100% (5)
- Copy - of - Commonlit - Meet The Fearless Cook Who Secretly Fed and Funded The Civil Rights Movement - StudentDocument6 pagesCopy - of - Commonlit - Meet The Fearless Cook Who Secretly Fed and Funded The Civil Rights Movement - Studentlilywright08No ratings yet
- Goodman Aula 1 e 2Document17 pagesGoodman Aula 1 e 2Danilo TetNo ratings yet
- VERITAS NetBackup 4 (1) .5 On UnixDocument136 pagesVERITAS NetBackup 4 (1) .5 On UnixamsreekuNo ratings yet
- General LPG Installation Guide PDFDocument60 pagesGeneral LPG Installation Guide PDFgheorghe garduNo ratings yet
- Yusuf Mahmood CVDocument3 pagesYusuf Mahmood CVapi-527941238No ratings yet
- Applied Social Research A Tool For The Human Services 9th Edition Monette Test Bank 1Document36 pagesApplied Social Research A Tool For The Human Services 9th Edition Monette Test Bank 1wesleyvasquezmeoapcjtrb100% (25)
- Plant Gardening AerationDocument4 pagesPlant Gardening Aerationut.testbox7243No ratings yet
- Comparison of Offline and Online Partial Discharge For Large Mot PDFDocument4 pagesComparison of Offline and Online Partial Discharge For Large Mot PDFcubarturNo ratings yet
- Opening The Third EyeDocument13 pagesOpening The Third EyekakamacgregorNo ratings yet
- Topics For Oral PresentationDocument6 pagesTopics For Oral PresentationMohd HyqalNo ratings yet
- SAP IAG Admin GuideDocument182 pagesSAP IAG Admin GuidegadesigerNo ratings yet