Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 Marine Fuel Handling & Pre-Treatment
10 Marine Fuel Handling & Pre-Treatment
Uploaded by
anOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10 Marine Fuel Handling & Pre-Treatment
10 Marine Fuel Handling & Pre-Treatment
Uploaded by
anCopyright:
Available Formats
Disc # 10
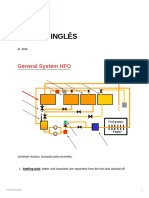
Marine Fuel Handling and Pre-treatment.
1.1 What kind of information should the Bunker Delivery Note contain?
Density at 15ºC, viscosity at 50ºC, water content in % by volume and flash point in °C.
1.2 Fuel tanks should sounded both before and after bunkering. Should this be done on:
Both vessels.
1.3 Three samples should be collected during bunkering of fuels. What is to be done with this?
One should be kept onboard, one should be handed over to supplier and one should be sent for
analysis.
2.1 Storage tanks should be kept at a certain temperature, in order to allow reliable pumping of high
viscosity fuels. The temperature is:
45ºC.
2.2 For heating of fuel oils, the temperature:
Should not exceed a temperature of 10ºC below the actual flash point.
2.3 Two possible leakages may occur in the tank heating system. How is this detected?
Both A and B.
3.1 What is the main difference between the purifier and the clarifier?
The clarifier does not remove water.
3.2 What is the difference in content between the settling tank and the service tank?
The settling tank contains untreated fuel oil, while the service tank contains purified fuel oil.
3.3 Which components can not be removed by the purifiers?
Sulfur and vanadium
4.1 Which one of these fuel parameters causes most damages to engine components?
Ash.
4.2 What is the typical viscosity at the injection pump?
10-20 cSt.
4.3 In which part of the liner do abrasive particles cause most damage?
Upper part.
4.4 At which ratio is sodium to vanadium particularly undesirable?
1: 3.
4.5 If running on fuel oil is bad ignition quality with long ignition delay. What is the best method to
reduce this delay?
Increase scavenging temperature.
You might also like
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Crude Oil WashingDocument3 pagesCrude Oil Washingbrendanrodrigues75% (8)
- Gas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsFrom EverandGas-Liquid And Liquid-Liquid SeparatorsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- CD.10 Marine Fuel Handlling and Pre-TreatmentDocument1 pageCD.10 Marine Fuel Handlling and Pre-TreatmentJarosławWierzganowskiNo ratings yet
- 0010 Marine Fuel Handling & Pre-TreatmentDocument1 page0010 Marine Fuel Handling & Pre-TreatmentChim LieuNo ratings yet
- AviationDocument13 pagesAviationraj mohanNo ratings yet
- Module 8.2 Fuel Oil TreatmentDocument5 pagesModule 8.2 Fuel Oil Treatmentdepedromarjan05No ratings yet
- Marine Operations Notes Part 2Document32 pagesMarine Operations Notes Part 2Ekiyo PiusNo ratings yet
- What Is Heavy Fuel Oil Used ForDocument10 pagesWhat Is Heavy Fuel Oil Used ForWaqar Younas NumberdarNo ratings yet
- Handout Fuel Oil & Lube Oil PDFDocument49 pagesHandout Fuel Oil & Lube Oil PDFMalik ForbesNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mainenance and Safety PDFDocument54 pagesBoiler Mainenance and Safety PDFBallu BaluNo ratings yet
- A Masters Guide To Using Fuel Oil Onboard ShipsDocument74 pagesA Masters Guide To Using Fuel Oil Onboard ShipsPatetico Pianto LupoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.3 - Energy 3.3.1 Combustion: Gas Oil and Heavy Fuel OilDocument38 pagesUnit 3.3 - Energy 3.3.1 Combustion: Gas Oil and Heavy Fuel OilSatyam PandyaNo ratings yet
- Switchboard Safety Devices: What Are ?Document8 pagesSwitchboard Safety Devices: What Are ?Chamika Dilshan WickramawardenaNo ratings yet
- Fuels and Combustion PDFDocument24 pagesFuels and Combustion PDFLalit MohanNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument24 pagesFuels and CombustionRavindra_1202No ratings yet
- Introduction To Fuels: OilDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Fuels: Oilkcp1986No ratings yet
- 07 Fuel Oil SystemsDocument54 pages07 Fuel Oil SystemsBabu Aravind100% (1)
- Trouble Shooting in Diesel EngineDocument11 pagesTrouble Shooting in Diesel EngineAnik Das 8040No ratings yet
- IchemDocument3 pagesIchemLoi GoNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument24 pagesFuels and Combustionvijayraju100% (1)
- Fuels and CombustionDocument26 pagesFuels and CombustionEjaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquid FuelDocument18 pagesProperties of Liquid FuelTin Aung Kyi100% (2)
- Module 8.1 Fuel Oil Properties and TestingDocument7 pagesModule 8.1 Fuel Oil Properties and Testingdepedromarjan05No ratings yet
- Provão InglêsDocument16 pagesProvão InglêsnetomatosferreroNo ratings yet
- 1.2.4 Classification of Petroleum:: Department of Fuel and Energy 3 Class 1 Term /lecture 4Document8 pages1.2.4 Classification of Petroleum:: Department of Fuel and Energy 3 Class 1 Term /lecture 4Zayn AhmedNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil QuestionsDocument4 pagesCrude Oil QuestionsMontazer WorkNo ratings yet
- Energy ManagementDocument195 pagesEnergy ManagementKiran Alla100% (1)
- All About BunkeringDocument55 pagesAll About Bunkeringkamaldscl100% (1)
- Black Smoke From The Funnel What To Do CDocument3 pagesBlack Smoke From The Funnel What To Do CsaraashunNo ratings yet
- Untitled 4Document1 pageUntitled 4Baraa Al SayedNo ratings yet
- 3 Fuel Properties and EffectsDocument28 pages3 Fuel Properties and EffectsZohaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Properties of Heavy Fuel OilDocument3 pagesProperties of Heavy Fuel Oilmavericksailor50% (2)
- What Are The Different Types of Coal? Mention Its Uses?: NthraciteDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Different Types of Coal? Mention Its Uses?: NthraciterestarterNo ratings yet
- Feature: Vlsfos - The Concerning Fuel Management Issues So Far...Document6 pagesFeature: Vlsfos - The Concerning Fuel Management Issues So Far...romeo del rosarioNo ratings yet
- 2020 Sulphur Cap Seminar - Istanbul - 30 Oct 2019 PDFDocument94 pages2020 Sulphur Cap Seminar - Istanbul - 30 Oct 2019 PDFHasan CiçinNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 - Me139lDocument18 pagesExpt 2 - Me139lEdward Vincent SanchezNo ratings yet
- Members Section Fuel Oil Fuel Oil TestingDocument3 pagesMembers Section Fuel Oil Fuel Oil TestingArun SNo ratings yet
- Test Case: Fuel Quality Under ScrutinyDocument3 pagesTest Case: Fuel Quality Under ScrutinyTrịnh Quang PhóngNo ratings yet
- University of Bright StarتقيمDocument10 pagesUniversity of Bright Starتقيممحمد أحمد عبداللطيفNo ratings yet
- Function of A Lubricant: Ref To Page 48 Diesel Engines 3rd Edition, A J WhartonDocument11 pagesFunction of A Lubricant: Ref To Page 48 Diesel Engines 3rd Edition, A J Whartonapi-3701567No ratings yet
- Liquid FuelsDocument21 pagesLiquid FuelsvaibhavNo ratings yet
- 4B 6kochi BlogspotDocument71 pages4B 6kochi BlogspotHisham AreekkanNo ratings yet
- Che 460 Oil and Natural Gas UpgradingDocument20 pagesChe 460 Oil and Natural Gas UpgradingLeslie SquireNo ratings yet
- Pra Ukp 1Document35 pagesPra Ukp 1Fauzan FatihNo ratings yet
- A Turbine Flow Meter Is A Widely Used Tool For Measuring The Rate of Flow of A Given FluidakamDocument10 pagesA Turbine Flow Meter Is A Widely Used Tool For Measuring The Rate of Flow of A Given FluidakamIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Freight Ship Fuel: Heavy Oil: Morten Simonsen Vestlandsforsking 21 October 2009Document10 pagesFreight Ship Fuel: Heavy Oil: Morten Simonsen Vestlandsforsking 21 October 2009moritataNo ratings yet
- Annexure K - Technical Requirements For Fuel Oil Scoring Rev 3Document4 pagesAnnexure K - Technical Requirements For Fuel Oil Scoring Rev 3joatdhsNo ratings yet
- Mixed Exams. IchemDocument9 pagesMixed Exams. Ichemchristian popeNo ratings yet
- Two Marks Advanced Ic EnginesDocument5 pagesTwo Marks Advanced Ic EnginesrajapratyNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Fuels & Combustion - Revised (Table Format)Document9 pages2.1 Fuels & Combustion - Revised (Table Format)Gajanan JagtapNo ratings yet
- Reason For Cracked Fuelpump Blocks Checklist For Investigation of Cracked Fuel Pump BlocksDocument4 pagesReason For Cracked Fuelpump Blocks Checklist For Investigation of Cracked Fuel Pump BlockscarmaNo ratings yet
- Department of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokDocument4 pagesDepartment of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokWalid AdnanNo ratings yet
- Naval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyFrom EverandNaval Diesel Engineering: The Fundamentals of Operation, Performance and EfficiencyNo ratings yet
- Oil Spill Remediation: Colloid Chemistry-Based Principles and SolutionsFrom EverandOil Spill Remediation: Colloid Chemistry-Based Principles and SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Operator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingFrom EverandOperator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Liquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionFrom EverandLiquid Fuels: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Metallurgy DivisionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- All Answered "YES": Worker's Representatives Workers EmployerDocument32 pagesAll Answered "YES": Worker's Representatives Workers EmployeranNo ratings yet
- 9 Fuel Oil SustemDocument1 page9 Fuel Oil SustemanNo ratings yet
- 41 Operation of Generators EDocument2 pages41 Operation of Generators EanNo ratings yet
- 256 Team Leader Ship #0256Document1 page256 Team Leader Ship #0256anNo ratings yet