Professional Documents
Culture Documents
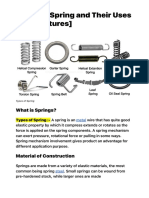
Spring: Springs Are Elastic Bodies
Uploaded by
Pranjal Dogra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views30 pagesOriginal Title
Spring
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views30 pagesSpring: Springs Are Elastic Bodies
Uploaded by
Pranjal DograCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 30
SPRING
Springs are elastic bodies
(generally metal) that can be twisted,
pulled, or stretched by some force.
They can return to their original
shape when the force is released.
In other words it is also termed as
a resilient member.
CLASSIFICATION OF SPRINGS
1) WIRE SPRINGS (Helical springs): (Constant / Variable pitch)
a) Tension helical spring (Conical, barrel)
b) Compression helical spring (Conical, barrel)
c) Torsion spring
d) Spiral spring
2) FLAT PLATE SPRING (Leaf springs)
3) AIR SPRINGS
4) AUTO COIL SPRINGS
5) GAS SPRINGS
COMPRESSION HELICAL SPRING
TENSION HELICAL SPRING
CONICAL SPIRAL SPRING
BARREL COMPRESSION SPRING
TORTION HELICAL SPRING
Flat Plate torsion spring
LEAF SPRING
AIR SPRING
AIR SPRING AUTO COIL SPRING
GAS SPRING
TENSION HELICAL SPRING (OR) EXTENSION SPRING
1. It stretches apart to create load.
2. The gap between the successive coils is small.
3. The wire is coiled in a sequence that the turn is
at right angles to the axis of the spring.
4. The spring is loaded along the axis.
5. The springs are provided with hooks at both
ends to apply load.
6. By applying load the spring elongates in action
Compression springs
• It is useful when the spring is used for energy storage purposes.
• This should not be used when springs are subjected to fatigue.
BARREL SPRING
Barrel springs are specialized of the conventional
helical compression spring.
Variable diameters act in the same way as variable
pitch to promote consecutive coiling closing
TORSION SPRING
1. It is also a form of helical spring, but it rotates
about an axis to create load.
2. It releases the load in an arc around the axis.
3. Mainly used for torque transmission
SPIRAL SPRING
1. It is made of a band of steel wrapped around itself a
number of times to create a geometric shape.
2. It has a few rotations and also contains a thicker band of
steel.
3. It releases power when it unwinds.
LEAF SPRING
•Sometimes it is also called as a semi-elliptical
spring.
•It provides dampness and springing function.
Air Spring
• Air springs are mechanical device
using confined air to absorbed the
shock of motion
• It is mostly used in automobiles
Auto coil spring
•A section of spring steel rod wound in a
spiral pattern or shape.
•Car coil springs are widely used in both
front and rare suspension systems.
•These coils cusion and absorb the shocks
and bumps as the vehical is driven.
Gas springs
•A gas spring is a type of spring that
uses compressed gas contained in a
cylinder and variably compressed by
piston, to exert a force.
•Adjustable gas springs can be found
in multiple applications.
SPRING MATERIALS
1) Hard drawn high carbon steel. 9)Chrome vanadium.
2) Oil tempered high carbon steel. 10) Chrome silicon.
3) Stainless steel
4) Copper or nickel based alloys.
5) Phosphor bronze.
6) Inconel.
7) Monel
8) Titanium.
APPLICATIONS OF SPRINGS
1) To apply forces and controlling motion, as in brakes and clutches.
2) Measuring forces, as in the case of a spring balance.
3) Storing energy, as in the case of springs used in watches and toys.
4) Reducing the effect of shocks and vibrations in vehicles and machine
foundations.
TERMINOLOGIES IN A COMPRESSION HELICAL
SPRING
1)Free length : overall length of spring in the unloaded
condition.
2)Pitch : the distance from center to center of wire in
adjacent active coils.
4)Solid length : Length of the compression spring when
under sufficient load to bring all coils into contact with
adjacent coils.
5)Pitch angle : It is the angle between the plane of coil and
plane perpendicular to axis of the spring .
TERMINOLOGIES IN A COMPRESSION HELICAL
SPRING
6) Variable diameter springs: Those springs whose coil
diameter is different along the axis of the springs.
7) Constant diameter springs: Those springs in which the
diameter of the all coils of spring is same.
8) Constant pitch springs: Those springs in which the
distance between the two same points lying on the
successive coils is same throughout the spring length.
9) Variable pitch springs: Those springs in which pitch of
spring varies along the length of the spring.
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Engineering Fluid Mechanics 11th Ed - Donald F. Elger, Barbara A. LeBret, Clayton T. Crowe, John A. RobertsonDocument30 pagesSolution Manual For Engineering Fluid Mechanics 11th Ed - Donald F. Elger, Barbara A. LeBret, Clayton T. Crowe, John A. RobertsonAfshar Arabi0% (4)
- 507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesFrom Everand507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- Basic MechanicalDocument23 pagesBasic MechanicalSundar SivamNo ratings yet
- SpringsDocument21 pagesSpringsPrajwalNo ratings yet
- Edm MicroprojectDocument18 pagesEdm MicroprojectAkshay KhangreNo ratings yet
- Closed Coil Helical SpringsDocument12 pagesClosed Coil Helical SpringsAtish Kumar100% (7)
- Springs: Shammy Kumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engg. SRM University, CHENNAIDocument25 pagesSprings: Shammy Kumar Assistant Professor Department of Mechanical Engg. SRM University, CHENNAIAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Emd Micro Project FinalDocument15 pagesEmd Micro Project Finalom pawarNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Laboratory Mini Project-Report: Guide Name: TitleDocument16 pagesStrength of Materials Laboratory Mini Project-Report: Guide Name: TitleVISHNU PRAKASH RNo ratings yet
- Springs: Definition For SpringDocument20 pagesSprings: Definition For Springmuna222No ratings yet
- Chapter - I: 1.1 SpringDocument46 pagesChapter - I: 1.1 SpringAswin KarthickNo ratings yet
- Mod 6 Book 5 Springs Bearings Control Systems GearsDocument40 pagesMod 6 Book 5 Springs Bearings Control Systems Gearsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Category One: Helical SpringsDocument4 pagesCategory One: Helical SpringsNduati JohnNo ratings yet
- Definition For SpringDocument18 pagesDefinition For SpringamanpurushothNo ratings yet
- DME ActivityDocument10 pagesDME ActivityRushikeshNo ratings yet
- Wa00Document10 pagesWa00RushikeshNo ratings yet
- W7S1Document16 pagesW7S1rajuNo ratings yet
- Class 1 and 2Document72 pagesClass 1 and 2Apurba barmanNo ratings yet
- Dme Unit V (17.11.22)Document16 pagesDme Unit V (17.11.22)sathiaNo ratings yet
- Spring (Device)Document7 pagesSpring (Device)Deepak VermaNo ratings yet
- Design of Helical and Leaf SpringsDocument92 pagesDesign of Helical and Leaf Springs208W1A1027Sec-A LINGAMANENI KOWSHIKNo ratings yet
- Type of SpringDocument6 pagesType of SpringIman SadeghiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 SpringsDocument14 pagesChapter 06 SpringsRobel Metiku0% (1)
- Spring Is AnDocument3 pagesSpring Is AnVishnu NairNo ratings yet
- DME-Cotter and Knuckle JointDocument91 pagesDME-Cotter and Knuckle JointAnjanKumarMishraNo ratings yet
- SpringsDocument7 pagesSpringssreeramNo ratings yet
- Types of Springs and Their ClassificationsDocument5 pagesTypes of Springs and Their ClassificationsHamza ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Designofspring 190916095639Document16 pagesDesignofspring 190916095639ManojKumar MNo ratings yet
- Automatic Spring Rolling MachineDocument34 pagesAutomatic Spring Rolling MachineJilly Arasu100% (3)
- Name: Deepak Bhanushali EN ROLL: 160050119504 CLASS: ME-3 (A)Document24 pagesName: Deepak Bhanushali EN ROLL: 160050119504 CLASS: ME-3 (A)ABHISHEK CHOUDHARINo ratings yet
- DME Unit 5 Springs PDFDocument51 pagesDME Unit 5 Springs PDFsachinroy8638No ratings yet
- Automatic Spring Rolling Machine111Document34 pagesAutomatic Spring Rolling Machine111srajaprojects100% (6)
- SPRINGS v2Document14 pagesSPRINGS v2ChilsonHangadZerdaNo ratings yet
- Types of SpringsDocument5 pagesTypes of SpringsSwapnil Singh SolankiNo ratings yet
- SpringsDocument16 pagesSpringsaravindangokul687No ratings yet
- Asmit M B Armiet AxleDocument12 pagesAsmit M B Armiet AxleAsifNo ratings yet
- Design of SpringsDocument30 pagesDesign of SpringsKunal Ahiwale100% (1)
- R19 Dmm-I - Unit-5Document16 pagesR19 Dmm-I - Unit-5Sufiyan MohammedNo ratings yet
- AMSM Module 4Document27 pagesAMSM Module 4Shaji EtNo ratings yet
- ME 7 - Activity 6Document9 pagesME 7 - Activity 6Rygen Faye Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Upon Completion of This Chapter, Student Should Be Able ToDocument43 pagesLearning Objectives Upon Completion of This Chapter, Student Should Be Able ToAnonymous ytZsBOVNo ratings yet
- Module-Ii: Suspension Drive LineDocument47 pagesModule-Ii: Suspension Drive LineJhomz BaldrezNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Elements of Machine Design Micro Project' With YouDocument10 pagesI Am Sharing 'Elements of Machine Design Micro Project' With YouUttareshwar Mohalkar100% (1)
- Springs Are Fundamental Mechanical Components Found in Many Mechanical SystemsDocument4 pagesSprings Are Fundamental Mechanical Components Found in Many Mechanical SystemsZandro GagoteNo ratings yet
- Project On Leaf SpringDocument8 pagesProject On Leaf SpringAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-Dwg TerminologyDocument32 pagesChap 1-Dwg TerminologyZhafri SyazwiNo ratings yet
- ME-603 SpringsDocument15 pagesME-603 Springskanaktanu54No ratings yet
- CH 23Document65 pagesCH 23gowrisankarNo ratings yet
- Suspension 001Document26 pagesSuspension 001Vincentius NikimNo ratings yet
- Suspention SystemDocument25 pagesSuspention SystemraviNo ratings yet
- List The Elements of Suspension SystemDocument11 pagesList The Elements of Suspension Systemchethan vl0% (1)
- Spring Suspension Wheeled Vehicles EllipticalDocument2 pagesSpring Suspension Wheeled Vehicles Ellipticalsubhamgupta7495No ratings yet
- Modern Bamboo SplitterDocument14 pagesModern Bamboo SplitterSenthil Kumar100% (1)
- Document 1Document2 pagesDocument 1Navindra DharmolingumNo ratings yet
- Mechanical SpringsDocument17 pagesMechanical SpringsAldrin BernardoNo ratings yet
- The Inner Workings of a Watch - A Simple Guide for Enthusiasts of Clockwork MechanismsFrom EverandThe Inner Workings of a Watch - A Simple Guide for Enthusiasts of Clockwork MechanismsNo ratings yet
- Metalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsFrom EverandMetalwork and Machining Hints and Tips for Home Machinists: 101 Plans and DrawingsNo ratings yet
- The Art of Watch Repair - Including Descriptions of the Watch Movement, Parts of the Watch, and Common Stoppages of Wrist WatchesFrom EverandThe Art of Watch Repair - Including Descriptions of the Watch Movement, Parts of the Watch, and Common Stoppages of Wrist WatchesNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Clockwork - Lever Escapements, Cylinder Escapements, Verge Escapements, Shockproof Escapements, and Their Maintenance and RepairFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Clockwork - Lever Escapements, Cylinder Escapements, Verge Escapements, Shockproof Escapements, and Their Maintenance and RepairRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Weat Herr Adar: Ref:Powel lpg-139Document3 pagesWeat Herr Adar: Ref:Powel lpg-139Pandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Control Cables PDFDocument28 pagesControl Cables PDFPandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Screw Thread PDFDocument45 pagesScrew Thread PDFPandurang Nalawade67% (3)
- Car - 145 Test Paper 01Document7 pagesCar - 145 Test Paper 01Pandurang Nalawade50% (2)
- Control Cables PDFDocument28 pagesControl Cables PDFPandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan NoDocument2 pagesLesson Plan NoPandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Servomechanism DefectsDocument2 pagesServomechanism DefectsPandurang Nalawade0% (1)
- Radio 1Document2 pagesRadio 1Pandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Car 66 Class Test 05Document5 pagesCar 66 Class Test 05Pandurang Nalawade100% (1)
- All Previous Session Questions+ (Paper 1) PDFDocument131 pagesAll Previous Session Questions+ (Paper 1) PDFDev JadhavNo ratings yet
- Aic PDFDocument7 pagesAic PDFPandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Radi Oalti Meter: Ref:Powel lpg-189Document4 pagesRadi Oalti Meter: Ref:Powel lpg-189Pandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Rules - 1937Document10 pagesAircraft Rules - 1937Pandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Dgca Paper-1 Oct 2008: D) A & C Are Correct A) QC Dept A. Operator A) MSMDocument9 pagesDgca Paper-1 Oct 2008: D) A & C Are Correct A) QC Dept A. Operator A) MSMPandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Dgca Paper 1 - June 12: a.Subpart-FDocument12 pagesDgca Paper 1 - June 12: a.Subpart-FPandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Car MDocument5 pagesCar MPandurang Nalawade100% (1)
- Carver Training and Services Pvt. Ltd. BaramatiDocument9 pagesCarver Training and Services Pvt. Ltd. BaramatiPandurang NalawadeNo ratings yet
- METGUIDEDocument75 pagesMETGUIDEWei Kang ChiaNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution: Sue GordonDocument39 pagesThe Normal Distribution: Sue GordonCorina-Ştefania TudoracheNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Under InsulationDocument14 pagesCorrosion Under InsulationSethuraman Saravanakumar100% (2)
- NOVA-65 Rev03 SmallDocument2 pagesNOVA-65 Rev03 Smallrocket-vtNo ratings yet
- CHAP 1 ElearnDocument70 pagesCHAP 1 ElearnYting TanNo ratings yet
- Rotare Vane PumpsDocument10 pagesRotare Vane PumpsZoran DjurdjevicNo ratings yet
- 60 - Experimental and Simulation Study of Induced Flow Vibration in PipelinesDocument6 pages60 - Experimental and Simulation Study of Induced Flow Vibration in PipelinesDaniel Andres VargasNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument28 pagesStoichiometryDayasagar VSNo ratings yet
- Chemical Ideas Section 11 AnswersDocument2 pagesChemical Ideas Section 11 AnswersvkrmmahalNo ratings yet
- Fmce MCQ QBDocument21 pagesFmce MCQ QBGOKULJOTHI RNo ratings yet
- Catalogo ServomotorDocument36 pagesCatalogo ServomotorLuis LopezNo ratings yet
- Process Definition File Documentation6 PDFDocument8 pagesProcess Definition File Documentation6 PDFVictor Hugo OrtizNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Enhancement by Using Hybrid Nanofluids Al O & Fe O in Heat ExchangersDocument17 pagesHeat Transfer Enhancement by Using Hybrid Nanofluids Al O & Fe O in Heat ExchangersbalajiNo ratings yet
- En 13108-20 (2016) (E)Document8 pagesEn 13108-20 (2016) (E)tavi9050% (2)
- Raw Mix DesignDocument22 pagesRaw Mix DesignRizwanKhan100% (1)
- Shear Strength of Concrete Beam Cast Using Broken Bricks AggregatesDocument19 pagesShear Strength of Concrete Beam Cast Using Broken Bricks AggregatesSaraj GillNo ratings yet
- UTOPEX2Document4 pagesUTOPEX2emregnesNo ratings yet
- Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) : Applications, Structure, and Related Photophysical BehaviorDocument24 pagesGreen Fluorescent Protein (GFP) : Applications, Structure, and Related Photophysical BehaviorNuria MelchorNo ratings yet
- Effects of Transverse Reinforcement On Seismic Performance of ColumnsDocument9 pagesEffects of Transverse Reinforcement On Seismic Performance of ColumnsAhmad YaniNo ratings yet
- Delft Mooring Numerical and Physical ModelsDocument106 pagesDelft Mooring Numerical and Physical ModelsJoão Paulo Mendes FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Existing Steel Railway Bridges Evaluation PDFDocument8 pagesExisting Steel Railway Bridges Evaluation PDFGuilherme AlencarNo ratings yet
- Test On WreDocument16 pagesTest On WreDoyle Merrill33% (3)
- ANR ParameterDocument2 pagesANR ParameterpoteNo ratings yet
- Sub ModellingDocument3 pagesSub ModellingktkambleNo ratings yet
- Upstroke Jars: Europe Learning Centre WCP Training SchlumbergerDocument32 pagesUpstroke Jars: Europe Learning Centre WCP Training Schlumbergerام فاطمة البطاطNo ratings yet
- MWM TCG 2020Document4 pagesMWM TCG 2020MohammadFaisalAmjadNo ratings yet
- Workshop 2 DaumDocument25 pagesWorkshop 2 DaumAqsha QNo ratings yet
- Static Failure Theories: Uniaxial TestDocument11 pagesStatic Failure Theories: Uniaxial TestsantoshNo ratings yet
- Energy, Catalysis and Biosynthesis Lecture NotesDocument17 pagesEnergy, Catalysis and Biosynthesis Lecture Notesmina catNo ratings yet