Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 1.1 Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes
Uploaded by
Risciella 18Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 1.1 Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes
Uploaded by
Risciella 18Copyright:
Available Formats
WORKSHEET 1.
1
Intermolecular Forces: Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes
CAILAN,RISCIELLA BIEN E.
Name: _______________________________ February 5, 2021
Date: ___________________
12- Arnould
Grade & Section: _______________________ Score: ___________________
Objectives
• Identify the intermolecular forces and the type of crystal present in a molecule
• Determine the effect of the intermolecular forces on the properties of liquids
• Illustrate the heating curve of a substance
• Analyze the phase diagram of a substance
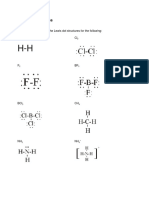
I. Put a check mark on the strongest intermolecular force present in the
following crystals (1 point each).
Metallic Ionic Network
Molecular Crystal
Crystal Crystal Crystal
Substance London Dipole-
Hydrogen Metallic Ionic Covalent
Dispersion Dipole
Bonding bonds bonds bonds
Forces Forces
1. HCl
2. Graphite
3. NaCl
4. H2O
5. Mg
6. Br2
7. BaO
8. NH3
9. C6H12O6
10. Au
II. Encircle the molecule that satisfies the given characteristic (1 point each).
1. Higher boiling point C8H18 H 2O
2. Lower vapor pressure CH4 C 2H 6
3. Lower surface tension H 2O H 2S
4. Higher viscosity H 2O CH4
5. Higher melting point CH4 NH3
6. Lower heat of vaporization CO2 HBr
7. Higher surface tension CH3OH Pb
8. Lower boiling point C5H12 C10H22
9. Lower viscosity C 2H 6 CH3OH
10. Higher vapor pressure CCl4 CBr4
III. Answer the following (5 points each):
1. Draw a heating curve when octane, a component of gasoline is warmed
from -70 °C to 130 °C. It has a melting point of -57 °C and a boiling point of
126 °C (5 points).
2. Refer to the phase diagram below:
a. Label the solid phase, liquid phase, gas phase, triple point, and critical point.
b. What is the normal boiling point of the substance? 350°C
c. What is the normal melting point of the substance? 100°C
d. What is the normal freezing point of the substance? 100°C
e. At what temperature do the gas and liquid phases become indistinguishable
from each other?
825°C
You might also like
- 95 Suzuki Sidekick Wiring DiagramDocument46 pages95 Suzuki Sidekick Wiring DiagramDominic Bufton88% (8)
- Understanding Phase Changes and the Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument90 pagesUnderstanding Phase Changes and the Kinetic Molecular TheoryVirgilio AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Observe Osmosis in Eggs with Salt SolutionsDocument2 pagesObserve Osmosis in Eggs with Salt SolutionsKenardNo ratings yet
- MS ExcelDocument37 pagesMS Excelravi100% (2)
- Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesDocument5 pagesProperties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesJohnnard BelenNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Syllabus - Core OnlyDocument89 pagesIB Chemistry Syllabus - Core OnlyHavila SaafiNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces HandoutDocument1 pageIntermolecular Forces Handoutanurag yadavNo ratings yet
- LeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1Document4 pagesLeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1John michael EstradaNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Some Properties of LiquidsDocument14 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Some Properties of LiquidsJohnRenzoMolinarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Liquids and SolidsDocument35 pagesChapter 12 - Liquids and SolidsGörkem DamdereNo ratings yet
- INTERMOLECULAR FORCES AND LIQUID PROPERTIESDocument7 pagesINTERMOLECULAR FORCES AND LIQUID PROPERTIESBleep BloopNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFDocument4 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFStefanie CorcoranNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 ChemicChemical Kinetics and Equilibriumal Kinetics and Equilibrium Notes (Answers)Document22 pagesUnit 5 ChemicChemical Kinetics and Equilibriumal Kinetics and Equilibrium Notes (Answers)Muhammad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Science Homework Book Worksheet 1: Separating Mixtures Find-a-word PuzzleDocument9 pagesYear 7 Science Homework Book Worksheet 1: Separating Mixtures Find-a-word PuzzleAngela KocevskaNo ratings yet
- Inter Molecular ForcesDocument59 pagesInter Molecular ForcesKc McCulloughNo ratings yet
- Middle School ChemistryDocument691 pagesMiddle School ChemistryChristian Homeschool-HubNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids & Intermolecular ForcesDocument9 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids & Intermolecular ForcesJeromeNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2016-2017 Term 3Document9 pagesYearly Lesson Plan 2016-2017 Term 3Fazliawati Mahayuddin50% (2)
- Electronegativity WorksheetDocument3 pagesElectronegativity WorksheetShermer100% (1)
- Models of Molecular Compounds Lab (Ms. Possible)Document5 pagesModels of Molecular Compounds Lab (Ms. Possible)Steven GomescoelloNo ratings yet
- Bond Polarity and Molecular Polarity WorksheetDocument2 pagesBond Polarity and Molecular Polarity WorksheetLaurence Domingo100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Exo and EndoDocument7 pagesLesson 3 Exo and Endoapi-385539760No ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular Forces ActivityDocument2 pagesProperties of Liquids and Intermolecular Forces ActivityEy GuanlaoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: BiologyDocument49 pagesCellular Respiration: BiologyKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulas and Properties of Common Consumer ProductsDocument35 pagesChemical Formulas and Properties of Common Consumer ProductsRhodel CabalNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 2019Document5 pagesPhysical Science 2019L Lawliet100% (1)
- Gen Chem Chapt.1Document45 pagesGen Chem Chapt.1Dave Cercado BugadorNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Liquids, Solids and Intermolecular Forces StudentDocument113 pagesCH 11 Liquids, Solids and Intermolecular Forces StudentAneeqa YounasNo ratings yet
- Raoult's Law PDFDocument12 pagesRaoult's Law PDFKeshav JoshiNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 CHM130LL Identification of Cations and AnionsDocument6 pagesLab 8 CHM130LL Identification of Cations and AnionsFatimah AzzahrahNo ratings yet
- Classification Tests For Hydrocarbons Formal Report PDF FreeDocument5 pagesClassification Tests For Hydrocarbons Formal Report PDF FreeWavingOceansNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Entropy and SpontaneityDocument14 pagesChapter 11 Entropy and Spontaneityसचिन राधेश्याम साहूNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesChemistry 2 Answer KeyMarielle BuesingNo ratings yet
- Inter Molecular ForcesDocument47 pagesInter Molecular ForcesSladjana TeslićNo ratings yet
- Classifying Matter and Energy StatesDocument7 pagesClassifying Matter and Energy StatesJam Uly GastyNo ratings yet
- Distillation of Binary LiquidsDocument29 pagesDistillation of Binary LiquidsJan Lloyd ProbitsoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Liquids ExplainedDocument41 pagesProperties of Liquids ExplainedMarielle LabradoresNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Document6 pagesChemistry Worksheet: Matter #1Anisah MahmudahNo ratings yet
- Empirical and Molecular Formula Notes PDFDocument2 pagesEmpirical and Molecular Formula Notes PDFAndre Juaquin Toledo100% (1)
- Specialized Cells: How Animal and Plant Cells Adapt for Different FunctionsDocument9 pagesSpecialized Cells: How Animal and Plant Cells Adapt for Different FunctionsJanah Pauline AbunganNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Unique Properties of Water: Lesson 1.4Document44 pagesThe Structure and Unique Properties of Water: Lesson 1.4Silhouette DreamNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Powerpoint PresentationDocument6 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Powerpoint Presentationapi-1991761550% (6)
- Laboratory Activity No. 01 - Properties of LiquidDocument2 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 01 - Properties of LiquidCzarina Relleve0% (1)
- S.4 Chemistry Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of chemistryDocument5 pagesS.4 Chemistry Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of chemistry羅絲雷朵No ratings yet
- Notes Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesNotes Intermolecular Forceslaliberte68100% (3)
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument34 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsdiahemaNo ratings yet
- New Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesNew Organic Chemistrywama ojha0% (1)
- Social Relationships and Leadership in AdolescenceDocument50 pagesSocial Relationships and Leadership in AdolescenceJoel ObtenarioNo ratings yet
- 9halogens Group PresentationDocument31 pages9halogens Group PresentationQueen GeminiNo ratings yet
- Lewis DotDocument9 pagesLewis DotLing Wang100% (1)
- Ismail Yusuf: Arts, Science and Commerce College, MumbaiDocument43 pagesIsmail Yusuf: Arts, Science and Commerce College, MumbaiBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- DP Chem Unit 7 EquilibriumDocument5 pagesDP Chem Unit 7 EquilibriumPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and States of MatterDocument26 pagesIntermolecular Forces and States of MatterKJ AlinsasaguinNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument19 pagesTopic 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- Edible Cell Biology Project RubricDocument1 pageEdible Cell Biology Project Rubricalathena alathenaNo ratings yet
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionDocument5 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic ReactionMuhammad Umar SalmanNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Paper2 - Grade 10-11 IGCSE - 2020 - MoodleDocument13 pagesTest 1 Paper2 - Grade 10-11 IGCSE - 2020 - MoodleJadNo ratings yet
- c1 - Intermolecular ForcesDocument69 pagesc1 - Intermolecular ForcesNabilah MustafaNo ratings yet
- 1st and 2nd year Chemistry test chapter questionsDocument2 pages1st and 2nd year Chemistry test chapter questionsZia Muhammad HaiderNo ratings yet
- 1A Exam 2008 Spring 1Document6 pages1A Exam 2008 Spring 1s17m0582No ratings yet
- JUST GIVE ME A REASONDocument1 pageJUST GIVE ME A REASONS fu fuNo ratings yet
- Basic CommandsDocument13 pagesBasic Commandsramana6nNo ratings yet
- Jackson 4 10 Homework Solution PDFDocument5 pagesJackson 4 10 Homework Solution PDFarmhein64No ratings yet
- 1 X SeriesDocument321 pages1 X SeriesJair Merino Aguirre100% (1)
- Effect of Upstream Dam Geometry On Peak Discharge During Overtopping Breach in Noncohesive Homogeneous Embankment Dams Implications For Tailings DamsDocument22 pagesEffect of Upstream Dam Geometry On Peak Discharge During Overtopping Breach in Noncohesive Homogeneous Embankment Dams Implications For Tailings DamsHelvecioNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing Materials Selection GuideDocument11 pages3D Printing Materials Selection GuideCarlos HernandezNo ratings yet
- Shs Genmath Module 8 Core Revised DuenasDocument42 pagesShs Genmath Module 8 Core Revised DuenasAPRIL JOY ARREOLANo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of 6T, 8T and 9T SRAM CellDocument4 pagesA Comparative Study of 6T, 8T and 9T SRAM CellijaertNo ratings yet
- Hard Gelatin CapsulesDocument58 pagesHard Gelatin Capsulesas.jessy0608No ratings yet
- Comparison of methods for determining the plateau modulus and entanglement molecular weightDocument19 pagesComparison of methods for determining the plateau modulus and entanglement molecular weightfaezehNo ratings yet
- Temperature Calibrator Specifications and FunctionsDocument1 pageTemperature Calibrator Specifications and FunctionsvihaanNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Fence Construction General NotesDocument1 pageSaudi Aramco Fence Construction General Notesabou bakar100% (1)
- CDB 4323 Assignment 1Document2 pagesCDB 4323 Assignment 1Muhammad AnwarNo ratings yet
- Data For Tightening Torque: LubricantDocument5 pagesData For Tightening Torque: LubricantAtanasio PerezNo ratings yet
- A Computer Code For Fully-Coupled Rocket Nozzle Flows - PergamentDocument131 pagesA Computer Code For Fully-Coupled Rocket Nozzle Flows - PergamentSantiago PatitucciNo ratings yet
- Sifat Bahan Pangan dan Hasil PertanianDocument39 pagesSifat Bahan Pangan dan Hasil PertanianStefanus Bayu Sindhu WijayaNo ratings yet
- Whats Map ProjectionDocument19 pagesWhats Map Projectionmahmoud abdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- Universal Uberoid WM8650 v10.1Document4 pagesUniversal Uberoid WM8650 v10.1noniggin nignogNo ratings yet
- Protein DenaturationDocument12 pagesProtein DenaturationAhmed Elhakim100% (2)
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 1Document47 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 1Yuzamrah Awang Noh50% (2)
- High Grade Water Soluble SOP For FertigationDocument2 pagesHigh Grade Water Soluble SOP For FertigationRómulo Del ValleNo ratings yet
- Folkspraak PDFDocument24 pagesFolkspraak PDFTheBluestoneGuyNo ratings yet
- Peugeot All Models Wiring Diagrams - GeneralDocument32 pagesPeugeot All Models Wiring Diagrams - GeneralFitra AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1993 Engines Eurovan - 2.5L 5-CylinderDocument20 pages1993 Engines Eurovan - 2.5L 5-Cylinderfrancesco pavanNo ratings yet
- What Is A 25V 70V or 100V Speaker SystemDocument10 pagesWhat Is A 25V 70V or 100V Speaker Systemwkchow1962No ratings yet
- NanomagnetismDocument32 pagesNanomagnetismMohammad RameezNo ratings yet
- ApeosPort C3060 C2560 C2060 BrochureDocument8 pagesApeosPort C3060 C2560 C2060 BrochureNischit Kunwar ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Simatic WinCC Professional Brochure 29052018 PDFDocument48 pagesSimatic WinCC Professional Brochure 29052018 PDFSriram SriNo ratings yet