Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 30
Uploaded by
Kevin Huang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageOriginal Title
PCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material_30
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pagePCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 30
Uploaded by
Kevin HuangCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
following basic parameters:
www.itseasyforu.com
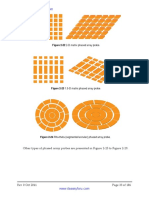
Type. Most phased array probes are of the angle beam type, designed for
use with either a plastic wedge or a straight plastic shoe (zero- degree
wedge), or delay line. Direct contact and immersion probes are also
available.
Frequency. Most ultrasonic flaw detection is done between 2 MHz and 10
MHz, so most phased array probes fall within that range. Lower and
higher frequency probes are also available. As with conventional
transducers, penetration increases with lower frequency, while
resolution and focal sharpness increase with higher frequency.
Number of elements. Phased array probes most commonly have 16 to 128
elements, with some having as many as 256. A larger number of elements
increases focusing and steering capability, which also increases area
coverage, but both probe and instrumentation costs increase as well. Each
of these elements is individually pulsed to create the wavefront of interest.
Hence the dimension across these
elements is often referred to as the active or steering direction.
Size of elements. As the element width gets smaller, beam steering capability
increases, but large area coverage requires more elements at a higher cost.
The dimensional parameters of a phased array probe are customarily
defined as follows:
(
L
W N
Figure 2-18 Dimensional parameters of a phased array probe
A = total aperture in steering of active direction
H = element height or elevation. Since this dimension is fixed,
it is often referred to as the passive plane.
p = pitch, or center-to-center distance between two successive
elements
e = width of an individual element
g = spacing between active elements
This information is used by instrument software to generate the desired
beam shape. If it is not entered automatically by probe recognition
software, then it must be entered by the user during setup.
www.itseasyforu.com
Rev 0 Oct 2011 Page 27of 186
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- PCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 36Document1 pagePCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 36Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- PCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 15Document1 pagePCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 15Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- PCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 10Document1 pagePCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 10Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- PCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 20Document1 pagePCN Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing Material - 20Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Aramco Radiographic Film Interpretation - 46-50Document5 pagesAramco Radiographic Film Interpretation - 46-50Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Measurement and Calibration Techniques: Normal Beam InspectionDocument4 pagesMeasurement and Calibration Techniques: Normal Beam InspectionKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Calibration Methods: Seen in The Figure) - This Can Be Attributed To The DivergenceDocument4 pagesCalibration Methods: Seen in The Figure) - This Can Be Attributed To The DivergenceKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Ultrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 17-20Document4 pagesUltrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 17-20Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Ultrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 9-12Document4 pagesUltrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 9-12Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducers (Emats)Document4 pagesElectromagnetic Acoustic Transducers (Emats)Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- 3.4.17 Near-Surface Resolution: Near-Surface Resolution (Dead Zone) Is The Minimum Distance From The ScanningDocument5 pages3.4.17 Near-Surface Resolution: Near-Surface Resolution (Dead Zone) Is The Minimum Distance From The ScanningKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Ultrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 21-24Document4 pagesUltrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 21-24Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 5-8Document4 pagesUltrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 5-8Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 3.5.1 DDF Beam Divergence: Figure 3-33 Dynamic Depth Focusing (DDF) : (A) Principle-Resulting Beam by ProductDocument5 pages3.5.1 DDF Beam Divergence: Figure 3-33 Dynamic Depth Focusing (DDF) : (A) Principle-Resulting Beam by ProductKevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Ultrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 1-4Document4 pagesUltrasonic Testing General Basics Fundam 1-4Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Introduction To Phased Array Ultrasonic Technology Applications 131-135Document5 pagesIntroduction To Phased Array Ultrasonic Technology Applications 131-135Kevin HuangNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)