Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pediatric Dso
Uploaded by
Eben Ezar Dela Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views4 pagesThis document summarizes various airway and respiratory disorders as well as two acyanotic cardiovascular disorders. For each condition, it lists the cause, symptoms, diagnostics, and management. The airway/respiratory disorders discussed include streptococcal pharyngitis, tonsillitis, foreign body aspiration, epiglottitis, laryngotracheobronchitis, asthma, status asthmaticus, sudden infant death syndrome, and respiratory distress syndrome. The cardiovascular disorders discussed are atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect. Management involves medications, nursing care, and sometimes surgery depending on the specific condition.
Original Description:
Pedia
Original Title
PEDIATRIC DSO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes various airway and respiratory disorders as well as two acyanotic cardiovascular disorders. For each condition, it lists the cause, symptoms, diagnostics, and management. The airway/respiratory disorders discussed include streptococcal pharyngitis, tonsillitis, foreign body aspiration, epiglottitis, laryngotracheobronchitis, asthma, status asthmaticus, sudden infant death syndrome, and respiratory distress syndrome. The cardiovascular disorders discussed are atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect. Management involves medications, nursing care, and sometimes surgery depending on the specific condition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views4 pagesPediatric Dso
Uploaded by
Eben Ezar Dela CruzThis document summarizes various airway and respiratory disorders as well as two acyanotic cardiovascular disorders. For each condition, it lists the cause, symptoms, diagnostics, and management. The airway/respiratory disorders discussed include streptococcal pharyngitis, tonsillitis, foreign body aspiration, epiglottitis, laryngotracheobronchitis, asthma, status asthmaticus, sudden infant death syndrome, and respiratory distress syndrome. The cardiovascular disorders discussed are atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect. Management involves medications, nursing care, and sometimes surgery depending on the specific condition.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
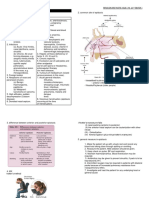
AIRWAY DISORDERS/RESPIRATORY
Disorder Cause S/Sx Diagnostics Management
1. STREPTOCOCCAL -GAHBS -Inflammation of Throat -swab and culture A. Meds:
PHARYNGITIS -Pain on swallowing throat -Antibiotics (Amox or Pen G) -> Toothbrush
(STREP THROAT) -High grade Fever should be replaced after starting antibiotics
-Headache -Antipiretics
-Swollen lymph nodes B. Diet: Fluids, Soft diet, Avoid Spicy food and
-swollen red tonsils w/ pus acid juices. Gargle with warm water
2. TONSILITIS -viral/bacterial - Inflammation of Palatine A. Meds:
TONSILS -Antibiotics (Amox or Pen G) -> Toothbrush
-Difficulty swallowing should be replaced after starting antibiotics
-Fever, lethargy -Antipiretics
-Mouth breathing B. Surgery
-Halitosis -TONSILECTOMY
-Sleep Apnea -Post Op: WOF BLEEDING (FREQUENT
SwaLLOWing or Clearing of THROAT)
3. FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION -Inhalation of -CHOCKING, Coughing, -Xray REMOVE OBJECT
foreign objects dyspnea, hoarseness, stridor -Bronchoscopy -HEIMLICH MANNEUVER (>1y.o)
-CYANOSIS, infection-> -Fluoroscopy -5 Back blows/slaps & 5 chest thrusts (<1y.o)
Death
4. EPIGLOTITIS -H.Influenzae -Dysphagia, Dysphonia -CBC (Leukocytosis) A. Meds:
type B -Drooling, Distressed respi -Elevated c reactive -Antibiotics (Chloramphenicol, co-
(Pneumococci, effort CHON amoxiclav,cefotoxime, cefuroxime)
streptococci, -High fever -Culture of epiglottis, -Steroids (DEXAmetahSONE)
staphylococci) -Sore throat -Neck Xray B. EMERGENCY Tx: INTUBATION & preparation
-Inspiratory Stridor of poss tracheostomy
-TRIPOD POSITION C. Nsg Care:
-Moist Air- O2 humidified
-Hydration
-NO VISUAL INSPECTION, INVASIVE
POCEDURE, ANXIETY-PROVOKING activity
5. LARYNGOTRACHEO- -Infectious -Inflammation & Narrowing -CBC A. Meds:
BRONCHITIS CROUP of Larynx, tranchea & -Neck Xray -Oral Steroids (DEXAmethaSONE)
-Parainfluenza bronchi -Epinephrine (via Neb)
-RSV (VIRUS) -Hacking/Barking cough- B. Nsg Care:
-0-5 y.o worse at Night -Monitor V/S, avoid anxiety-> may ET insertion
-1-2 y.o-peak -Hoarse voice, sore throat -STEAM INHALATION (cool mist humidifier or
-fever, n/v, poor appetite hot water steam
6. ASTHMA -Hypersensitivity -Dyspnea, wheezing, -Identify Allergy A. Peak Flow Rate
Response frightened Exhausted -Pulse Oximeter -Green Zone (80-100%): No asthma sx
-Genetics -Peak Flow Meter -YELLOW Zone (50-80%)- contact AP
-RED ZONE (<50%)-> MEDS-> Contact AP
B. Meds:
1. Reliever-> Bronchodilator-> Ventolin/
Albuterole, Theophylline, Comolyn Na)
2. Anti-Inflamatory-> Glucocorticoids (
*Inhalation- Budesonide, fluticasone
*Oral/IV- Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone
3. Combi Drugs
C. Nsg Care:
-ORTHOPNEIC position
7. STATUS ASTHMATICUS -Progression of -INC HR & RR A. Meds:
attack-> -DEC BREATH SOUNDS -Continue Reliver meds
Unresponsive to (SILENT CHEST) -IV steroids
therapy -Cyanosis B. Emergency Care: ET
-Allergens C. Nsg Care: Asist ET
8. SUDDEN INFANT DEATH -CRIB DEATH -Sudden Death A. Prevention
SYNDROME (SIDS) -1mos-1y.o. -M. Risk Factors-> poor -SUPINE Position
-2-4mos- peaks lifestyle -Avoid exposure to smoke
-Sleeping on -NB Risk Factors: cyanosis, -Own Sleeping environments- NO quilts,
PRONE position tachycardia, resp d/o, blankets, pillows
hypothermia, poor feeding B. Psychological assistance to parents
9. RESPIRATORY DISTRESS -PRETERM at Risk -INC RR, CHEST -ABG A. Surfactant Replacement (ET Tube)
SYNDROME (RDS) RETRACTIONS, EXPIRATORY -XRAY -O2 ventilation
GRUNT -< Lecithin/- -supportive care
-cyanosis, hypothermia Sphingomyelin ratio
(Normal- 2:1)
CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS
ACYANOTIC Disorder Cause S/Sx Management
1. ATRIAL SEPTAL -Opening between ATRIA -dyspnea, fatigue, failure to thrive A. Surgery (closure) – 1-3y.o.
DEFECT (ASD) -FO did not close -SPLIT S2 (2nd intercostal space LSB- pulmonic -Dacron Patch
-FEMALES valve) -Open Heart surgery
B. Nsg. Care
-Complications: Left untreated-> endocarditis->
leads to HEART FAILURE
-Post-OP: -Monitor ARRYTHMIA, Administer
Antibiotics
2. VENTRICULAR -Ventricular septum -dyspnea, fatigue, failure to thrive, respi infxn -SAME with ASD
SEPTAL DEFECT (VSD) opening -PANSYSTOLIC MURMUR (L; 2nd ICS)
-MOST COMMON
3. PATENT DUCTUS -Descending Aorta to -CLUBBING, dyspnea, -SAME with ASD
ARTERIOSUS (PDA) pulmo artery -LOUD “MACHINERY MURMUR” (-2nd-3rd ICS)
-Premature
-Maternal rubella
-FEMALES
CYANOTIC Disorder Cause S/Sx Management
1. TETRALOGY OF PROV -dyspnea, fatigue, failure to thrive, systolic murmur A. Surgery (closure) – 1-2y.o.
FALLOT (TOF) -Pulmonary stenosis -Polycythemia, Tet spells- CYANOTIC SPELLS-> -Blalock-Taussig Shunt- Anastomose subclavian
-Right Vent hypertrophy cyanosis during stressful or painful procedures art and pulmo while waiting for reparative
-Overriding Aorta surgery
-Ventricular Septal Defect **Post-op -Monitor Arrythmia, Avoid BP and
Venipuncture in Rt ARM
B. Nsg Care
-Complications: Left untreated-> leads to
THROMBOEMBOLISM, CVA
-O2-> KNEE-CHEST POSITION, SQUATTING
2. TRANSPOSITION OF -Transposed Aorta -Cyanosis, murmurs A. Surgery -1wk-3mos
GREAT VESSELS (TOG) -Transposed pulmo artery -Baloon catheter to create artificial ASD
-MALE or Large babies (9- -(Arterial Switch Procedure- JATENE Procedure)
10lbs)
3. TOTAL ANOMALOUS -Pulmonary v. drain -Cyanosis, Fatigue A. Surgery
PULMONARY VENOUS to SVC or R atrium PGE, surgery (re-implant pulmoveins to L
RETURN (TPV) -PDA or foramen atrium)
ovale essential
4. COARCTATION OF Constriction of -asymptomatic HPN, irritability, headache, A. Surgery- 2y.o
AORTA (COA) descending epistaxis, dyspnea, leg claudication, higher BP in -Angiography and surgery
aorta upper extremities, dec femoral and distal pulses -Post-op- Monitor ABD PAIN, INC BP
-MALE B. Nsg Care
-Complications: Left untreated-> leads to chronic
HPN, CVA
OTHER Disorder Cause S/Sx Management
1. KAWASAKI DSE/ -Rare childhood disease -Spiking fever x 5 days, A. Diagnostic- clinical only as it can’t be seen in
MUCOCUTANEOS that affects the -bilateral conjunctivitis, reddened pharynx, blood and urine
LYMPH NODE blood vessels -dry lips, strawberry tongue, B. Complications- May lead to ANEURYSM and
SYNDROME (inflammation) -cervical lymphadenopathy, peripheral edema, MI
-before puberty, peaks erythema and desquamation, truncal rash B. Meds: Salicylates(Aspirin) and IV
4y.o. Immunoglobulins
C. Nsg Care:
-Monitor for HF-> dec urine output, tachy, dob
-LIVE VACCINES (Varicella, MMR)- >should be
delayed up to 11mos after IV Immunoglobulins
administration
2. RHEUMATIC FEVER -Autoimmune-> GABHS DIAGNOSTIC S/SX: A. Meds:
(1-3wks after untreated -Salicylate
infxn) 5 MAJOR CRITERIA (JONES CRITERIA) -Corticosteroid
-6-15 y.o. peaks 8 y.o 1. J-oints- POLYARTHRITIS -Antibiotics (Benzathine, penicillin)
2. H-eart()-CARDITIS -Ibuprofen
3. N-odules- subcutaneous nodule -Digoxin
4. E- rytHema marginatum -Phenobarbital
5. S- Sydenham’s chorea (St. Vitu’s Dance) -Diazepam
B. Nsg Care
6 MINOR CRITERIA -Prevent further Infection
1. Fever
2. Polyarthralgia
3. History of RF
4. INC ESR
5. Antecedent STREP infection
6. Prolonged PR interval (1st degree Heartblock)
POSITIVE RF: 2 major/1major + 2 minor present
You might also like
- CONSENT FORM Kap Dengue LatestDocument6 pagesCONSENT FORM Kap Dengue Latestfairus_fz821575No ratings yet
- Laboratory Critical - Panic Value List - Stanford Health CareDocument4 pagesLaboratory Critical - Panic Value List - Stanford Health CareLABNo ratings yet
- 07a Ongoing MR Outbreak Surveillance SystemDocument23 pages07a Ongoing MR Outbreak Surveillance SystemDevendra Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - Acute Otits MediaDocument31 pagesCase Presentation - Acute Otits MediaJean nicole Garibay0% (1)
- PRONE Position Wheezing Chest Retractions Grunt: - Chocking - Hacking/Barking Cough-Worse at NightDocument3 pagesPRONE Position Wheezing Chest Retractions Grunt: - Chocking - Hacking/Barking Cough-Worse at NightEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- RespDisord (PART B & C)Document4 pagesRespDisord (PART B & C)GraceNo ratings yet
- Flash CardDocument2 pagesFlash CardRoy CabuenasNo ratings yet
- CA1 MidtermsDocument30 pagesCA1 MidtermsJhonny pingolNo ratings yet
- PleurisyDocument4 pagesPleurisyJohiarra Madanglog TabigneNo ratings yet
- Pertussis Whooping Cough Diphtheria: Communicable DiseasesDocument8 pagesPertussis Whooping Cough Diphtheria: Communicable DiseasesbenejohnNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseVinceNo ratings yet
- Disaster Caused BY Biological AgentsDocument25 pagesDisaster Caused BY Biological AgentsKaren Mae Dacoco MamuyacNo ratings yet
- Mindmap BedahDocument120 pagesMindmap BedahKavin Maalan SadasseevanNo ratings yet
- ENT Summery TABLEDocument19 pagesENT Summery TABLEtaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30: Nursing Care of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument4 pagesChapter 30: Nursing Care of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SsytemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SsytemJessica GlitterNo ratings yet
- MS Notes MidtermsDocument13 pagesMS Notes MidtermsWelfe DupitNo ratings yet
- High Ent YielDocument15 pagesHigh Ent YielJana AldourNo ratings yet
- Medical EmergenciesDocument71 pagesMedical EmergenciespinkgirljojiNo ratings yet
- General Anesthesia Notes - JalaDocument6 pagesGeneral Anesthesia Notes - JalaJulie Anne AciertoNo ratings yet
- PcolDocument17 pagesPcolThea JulianaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 1 NotesDocument11 pagesMed Surg 1 NotesMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Conditions Arf Ards PeDocument4 pagesPleural Conditions Arf Ards PeNoreen PadillaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal: Nclex-Rn ReviewerDocument34 pagesGastrointestinal: Nclex-Rn ReviewerJohnasse Sebastian NavalNo ratings yet
- September 13 - NCM 112 (Mam G)Document2 pagesSeptember 13 - NCM 112 (Mam G)Aaron DayloNo ratings yet
- Viral (Aseptic) Meningitis) Main Cause of Common ColdDocument4 pagesViral (Aseptic) Meningitis) Main Cause of Common ColdKatie Anne SaylerNo ratings yet
- ASTHMA & COPD (Emphysema, CB) (CHAP 20)Document10 pagesASTHMA & COPD (Emphysema, CB) (CHAP 20)Abegail QuintoNo ratings yet
- Vih MT#2Document8 pagesVih MT#2cjNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease: GBS Strep. Pneumonia Chlamydia Pneumonia H.influenza S.aureusDocument7 pagesInfectious Disease: GBS Strep. Pneumonia Chlamydia Pneumonia H.influenza S.aureusIman Sama-aliNo ratings yet
- MS ReviewerDocument10 pagesMS Reviewermarybeth abelidoNo ratings yet
- ENT TransDocument7 pagesENT TransanonymousNo ratings yet
- Fever and Cough 1Document34 pagesFever and Cough 1Alusio Navosailagi VUNIIVINo ratings yet
- Syncope (90% of All Emergencies)Document5 pagesSyncope (90% of All Emergencies)César HelenoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders & TB in Children (Part I and Ii) - Dr. MendozaDocument17 pagesRespiratory Disorders & TB in Children (Part I and Ii) - Dr. MendozaRea Dominique CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders: Parainfluenza, RSV, RhinovirusDocument5 pagesRespiratory Disorders: Parainfluenza, RSV, RhinovirusSoojung Nam100% (1)
- PEDIA Review TransesDocument12 pagesPEDIA Review TransesJennie KimNo ratings yet
- No Oral HygieneDocument14 pagesNo Oral HygieneFrances Isabella OlasimanNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease NotesDocument23 pagesInfectious Disease NotesaparnaNo ratings yet
- WITH Notes - COMMUNICABLE DISEASE - PROF. ARCHIE ALVIZ - HANDOUTSDocument8 pagesWITH Notes - COMMUNICABLE DISEASE - PROF. ARCHIE ALVIZ - HANDOUTScammel ramosNo ratings yet
- Hypernatremia Hyperkalemia: of Increased Serum K+Document3 pagesHypernatremia Hyperkalemia: of Increased Serum K+edited_chenNo ratings yet
- Airway ManagementDocument4 pagesAirway ManagementEllamae DerupeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing HandoutDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Nursing HandoutRyan Mae Tutor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric PEDocument2 pagesPaediatric PEAzizi RafieNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument3 pagesCommunicable DiseasesYuri G. FelipeNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics - Lower AirwayDocument3 pagesPediatrics - Lower AirwayJasmine KangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument20 pagesNursing Care PlanmelliaiNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaNurliyana GhazaliNo ratings yet
- S T A R T: Imple Riage ND Apid ReatmentDocument17 pagesS T A R T: Imple Riage ND Apid ReatmentNavine NavNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Alergi InhalanDocument10 pagesKuliah Alergi InhalanInggriht Senny BondangNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Patho & SignsDocument1 pagePneumonia Patho & SignsVishalNo ratings yet
- ENT Ear I Scenarios (Compiled)Document35 pagesENT Ear I Scenarios (Compiled)rumman tariqNo ratings yet
- Asthma and Atopic Eczema Asthma and Atopic Eczema Asthma and Atopic Eczema Asthma and Atopic EczemaDocument14 pagesAsthma and Atopic Eczema Asthma and Atopic Eczema Asthma and Atopic Eczema Asthma and Atopic EczemaTom Mallinson100% (1)
- Quiz 1 PULMONOLOGY (Basics Table)Document2 pagesQuiz 1 PULMONOLOGY (Basics Table)Paige HardekopfNo ratings yet
- THT 1Document26 pagesTHT 1Arina MutiNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis: A Practical GuideFrom EverandAnaphylaxis: A Practical GuideAnne K. EllisNo ratings yet
- Notes on Diseases of Swine, Sheep, Poultry and the Dog: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentsFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Swine, Sheep, Poultry and the Dog: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentsNo ratings yet
- The Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaFrom EverandThe Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaNo ratings yet
- Notes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Rolls Over Prone To Suppine Extrusion Reflex (GONE) - 4mos - 2 TBSP SEMI-SOLID Food - Good Head Control - Palmar Grasps/ReachesDocument2 pagesRolls Over Prone To Suppine Extrusion Reflex (GONE) - 4mos - 2 TBSP SEMI-SOLID Food - Good Head Control - Palmar Grasps/ReachesEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Abstinence SyndromeDocument1 pageNeonatal Abstinence SyndromeEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Opposite To K (Potassium) Seizure: Electrolytes Normal Values Function Hypo Hyper Na (Sodium) 135-145 Meq/LDocument2 pagesOpposite To K (Potassium) Seizure: Electrolytes Normal Values Function Hypo Hyper Na (Sodium) 135-145 Meq/LEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 3 Month of Pregnancy Abortion 1st Daughter Twin Babies: Changes Felt by Patient Changes Observed by ExaminerDocument5 pages3 Month of Pregnancy Abortion 1st Daughter Twin Babies: Changes Felt by Patient Changes Observed by ExaminerEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Waves and Intervals Heart Activity Normal/Abnormal (1 Small Box 0.04sec) (1 Big (5 Small) 0.2sec)Document6 pagesWaves and Intervals Heart Activity Normal/Abnormal (1 Small Box 0.04sec) (1 Big (5 Small) 0.2sec)Eben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ruddy Complexion: Hematologic Disorders Disorder Cause S/SX & DX Management 1. Polycythemia Vera (Inc RBC)Document3 pagesRuddy Complexion: Hematologic Disorders Disorder Cause S/SX & DX Management 1. Polycythemia Vera (Inc RBC)Eben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorder A: Cluster Types Description Approach A. ParanoidDocument4 pagesPersonality Disorder A: Cluster Types Description Approach A. ParanoidEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Post-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeDocument5 pagesPost-Strep Infxn Ddressler's Sydrome: Endocarditis Valvular Dse Pericarditis Cardiac TamponadeEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Endocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Document8 pagesEndocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Eben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Endometritis History: Disorder Signs and Symptom ManagementDocument8 pagesEndometritis History: Disorder Signs and Symptom ManagementLourdes Angelie G. VirayNo ratings yet
- Sore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaDocument19 pagesSore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaainaNo ratings yet
- (From The Department of Bacteriology, School of Medicine, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Syria) Plates 64 A CD 65Document18 pages(From The Department of Bacteriology, School of Medicine, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Syria) Plates 64 A CD 65diantinurwindaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Infectious Diseases and PDocument2 pagesClimate Change Infectious Diseases and PTazul IslamNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument3 pagesInfection ControlHazelina VillamorNo ratings yet
- Oxaciline PDFDocument12 pagesOxaciline PDFamatoryfictionliteraNo ratings yet
- Exam Preparation For BIOL1008: Infectious Diseases SectionDocument11 pagesExam Preparation For BIOL1008: Infectious Diseases SectionEleanor LauNo ratings yet
- MAS110 - Week 1 - Infection Control Worksheet 2Document4 pagesMAS110 - Week 1 - Infection Control Worksheet 2geonikawilliamsNo ratings yet
- Medical Law and Ethics 4th Edition Fremgen Test Bank DownloadDocument16 pagesMedical Law and Ethics 4th Edition Fremgen Test Bank Downloadrosakien8871yc100% (32)
- Demo M IDocument22 pagesDemo M IK60 TRẦN MINH QUANGNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal PAS B Ing Kelas 11Document13 pagesContoh Soal PAS B Ing Kelas 11razzany rauufadine sutomyNo ratings yet
- Dengue IGG IGM X 10 All TestDocument1 pageDengue IGG IGM X 10 All TestKaren Ramos CardenasNo ratings yet
- Public HealthDocument19 pagesPublic HealthOneofakind mnlNo ratings yet
- 05-S-2019 Dengue Ordinance of Barangay San CarlosDocument6 pages05-S-2019 Dengue Ordinance of Barangay San CarlosRonel Rosal MalunesNo ratings yet
- SeptemberDocument119 pagesSeptemberThami KNo ratings yet
- Colloidal Silver and ShinglesDocument7 pagesColloidal Silver and ShinglesduhitijeloNo ratings yet
- UC Davis Koret Shelter Medicine Program - Feline - Panleukopenia - 2012-05-01Document5 pagesUC Davis Koret Shelter Medicine Program - Feline - Panleukopenia - 2012-05-01Kitt KaosNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 QiDocument3 pagesNCP 2 QiKarlo Tuazon SedigoNo ratings yet
- Med Respi T&D QuestionsDocument14 pagesMed Respi T&D QuestionsD PatelNo ratings yet
- Vantocil IB Antimicrobial-Antiviral ActivityDocument5 pagesVantocil IB Antimicrobial-Antiviral ActivityMinh LêNo ratings yet
- CHN Quiz ZZZ EssDocument24 pagesCHN Quiz ZZZ Essnavarro.janicamaeNo ratings yet
- London Children's Academy Enrolment Forms 2023Document11 pagesLondon Children's Academy Enrolment Forms 2023Gideon AnumbaNo ratings yet
- Warts TreatmentDocument1 pageWarts TreatmentvinothksNo ratings yet
- Natural SelectionDocument2 pagesNatural SelectionMoath AbusheikhaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectDocument11 pages3 - Gastrointestinal Dis - 2020 - Hunter S Tropical Medicine and Emerging InfectThaiz P.SNo ratings yet