Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stepped - Impedance Low Pass Filter: The Insertion Loss Filter
Uploaded by
Liu LiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stepped - Impedance Low Pass Filter: The Insertion Loss Filter
Uploaded by
Liu LiCopyright:
Available Formats
THE INSERTION LOSS FILTER
Filters are two-port n/w used to control the frequency response in an RF or microwave system by
allowing transmission at frequencies within the pass band of the filter and attenuation within the stop
band of the filter.
Common types are low pass, high pass band pass and band stop.
Filters are indispensable components for rejecting signals outside the operating band, attenuating
undesired mixer products, and for setting the IF bandwidth of the receiver.
Many techniques have been proposed for the design and analysis of filter circuits, but the insertion loss
method is generally preferred for the flexibility and accuracy that it provides
This method is based on network synthesis techniques, and can be used to design filters having a specific
type of frequency response.
The design low pass filter prototype that is normalized in terms of impedance and cut off frequency.
Impedance frequency scaling and transformations are then used to convert the normalized design to the
one having the desired frequency response.
For minimum insertion loss can be achieved by binomial frequency response and Chebyshev response
would satisfy a requirement for the sharpest cutoff.
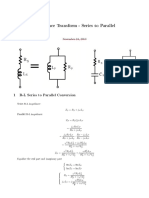
Stepped - impedance low pass filter
A relatively easy way to implement LPF in microstrip or strip line is to use alternating sections of very
high and very low characteristic impedance lines. Such filters are usually referred to as stepped-
impedance, or hi-Z low-Z filters.
The electrical performance is good as compared to stub filters.
The ratio Zh/Zl should be as large as possible, so the actual values of Zh and Zl are usually se to the
highest and lowest characteristic impedance that can be practically.
The electrical lengths of the inductor and capacitor sections are calculated as follows
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AgencyDocument40 pagesAgencyLiu LiNo ratings yet
- Nose GitDocument2 pagesNose GitLiu LiNo ratings yet
- Slot AntennaDocument6 pagesSlot AntennaLiu LiNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument37 pagesQuestion BankLiu Li100% (1)
- ResonatorsDocument4 pagesResonatorsLiu LiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 2 3 - MCQ StudentsDocument17 pagesUnit 1 2 3 - MCQ StudentsLiu Li100% (1)
- Impedance Transform - Series To ParallelDocument2 pagesImpedance Transform - Series To ParallelLiu LiNo ratings yet