Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Expts 5-7 Review
Uploaded by
Kyra Bianca R. FamacionCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Expts 5-7 Review
Uploaded by
Kyra Bianca R. FamacionCopyright:
Available Formats
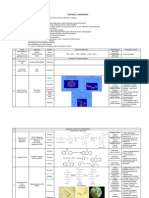
Analysis of Carbohydrates
A. General Test for Carbohydrates
Samples (1%): Glucose (mono, aldohexose), Sucrose (di), Arabinose (mono,
aldopentose), Starch (poly), cotton or filter paper suspension (poly, cellulose)
Molisch Test for Carbohydrates
- Positive Test: Purple Color at the interface of the sugar and acid (ALL)
- Dehydration of pentoses and hexoses through test reagent and form
furfural derivatives, then furfurals further react with a-naphthol to form
purple product.
- The test reagent dehydrates pentoses to form furfural and dehydrates
hexoses to form 5-hydroxymethyl furfural. The furfurals further react with
a-naphthol present in the test reagent to produce a purple product.
- Carbohydrates + H2SO4 undergo dehydration to give furfural derivatives
- Condense with alpha-naphthol or thymol to form colored products
- Pentoses yield Furfural
- Hexoses yield 5-hydroxymethylfurfurals or HMF
- Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides need to be hydrolysed to
monosaccharides and be dehydrated to give a + test
Anthrone Test for Estimation of Mono and Poly (Quali and Quanti)
- Positive Test: Deep green or blue color
- Dehydration of monosaccharides to furfural derivatives
- 50% H2SO4 used to dilute to dissolve cloudy ppt
Iodine Test for Polysaccharides (Presence of Helical Poly)
- Positive Test: Blue-black color Negative Test: Brown-blue color
- Starch (+) Dextrin (+) Glycogen ( - )
- More iodine atoms in helices=more intense color
- Starch-iodine complex and lycogen-iodine complex
B. Qualitative Tests for Sugars
Test Solutions(5%): Glucose (hexoses), Fructose (ketohexose), Arabinose (mono,
aldopentose), Maltose (di), Sucrose (di, ketohexoses), Galactose (aldohexose),
Lactose (di)
Reducing Sugar = there is a free OR group
Benedict’s Test for Reducing Carbohydrates
- Reagent contains Cu2+ ions in Alkaline sol. with Sodium Citrate added to
keep the ions in the solution, Sol. has been used for testing urine
- semi-quantitative test, Alkaline sol. of Cu are reduced by sugars having
free aldehyde or ketone group with the formation of Cu2O
- Positive Test: Deep-red Cu2O ppt Negative Test: Blue
- Glucose ( + ) Fructose ( + ) Sucrose ( - )
Barfoe
d’s Test for Reducing Monosaccharide
- Reduce monosaccharides very fast, reduce disaccharides very slow
- Use Cu(II) ions in a slightly acidic medium
- Reducing mono are oxidized by the Cu ion in sol. to form a carboxylic acid
and a red ppt of Cu (I) oxide
- Positive Test: Red Cu2O ppt within 2-3 mins, green or yellow ppt
- Maltose ( - ) Lactose ( - ) Sucrose ( - )
Seliwanoff’s Test for Ketose
- Used to differentiate ketose from aldose
- Aldoses converted to ketoses
- Reagent uses 6M HCl as the dehydrating acid and resorcinol as the
condensation reagemt
- Reagent dehydrates ketohexoses to form 5-hydroxymethylfurfural then this
further reacts with resorcinol in reagent to produce the color
- Positive Test: Cherry-red condensation product within 2 mins Negative:
no
- Ketohexoses and Di are positive
- Glucose, Galactose ( - ) Fructose ( + ) Hydrolysate from Inulin ( + )
Orcinol Test for Pentose
- Used to differentiate pentose from hexose
- Pentoses are converted to furfural by reagent and form color with orcinol
- Bial’s reagent contains orcinol (5-methylresorcinol in concentrated HCl
with a small amount of FeCl3 catalyst
- Decomposition of sugars when heated with concentrated HCl to a furfural
which then condenses with orcinol to form colored compounds
- Positive Test: Blue-green color Negative Test: Green, Red, Brown
- Arabinose ( + ) Hydrolysate from Gum Arabic ( + )
Osazone Test to Distinguish Sugars
- Sugars form osazones with phenylhydrazine
- Osazones have characteristic crystalline forms, quite definite time of
formation, and differ in their relative solubility in water
- Osazone Crystals = Yellow crystals with diff shapes under microscope
- Glucose (needle, 2 mins), Fructose (needle, 2mins), Galactose (rhombic
plate, 15-19 mins), Maltose (sunflower, ppted when cooled), Lactose
(powderpuff/Hedgehog, ppted when cooled), Arabinose (10 mins)
- Sucrose ( - ) no reaction/crystals
Mucic Acid Test for Galactose and Lactose
- Aldohexoses are converted to their corresponding dicarboxylic acids in the
presence of strong oxidizing agents like conc. HNO3
- The dicarboxylic acid produced from galactose (mucic acid) is relatively
insoluble and separates out as colorless crystals
- Positive Test: Colorless needle-like crystals (Mucic acid crystals)
- Galactose ( + ) Lactose ( + )
Lipids
A. Acrolein Test for Glycerin or Fats
- Positive Test: Colorless to yellow liquid, irritating (burnt grease or candle
wax) odor
- Glycerol ( + ) Coconut Oil ( + ) Oleic Acid ( + ) Lecithin ( - )
B. Test for Unsaturation
- Addition of Hubl’s sol. (I2 in HgCl2) across the double bond
- I2 saturation
- All double bonds are converted to single bonds when the sample solution
already has the same color as Hubl’s sol.
- Positive Test: Red-orange
-
C. Test for Phosphate
- Phosphate residues of phospholipids will react with ammonium molybdate
(NH4)2MoO4, in HNo3
- Positive Test: Yellow ppt Lecithin ( + )
D. Emulsification Test
- Suspension of liquid within another liquid
- Formation of pseudo solutions by lipids in water as micelles
- Pseudo Sol. are many bubbles oil, good emulsifying agent to put oil to the
bottom
- Positive Test: bubbles suspended in water
- 1mL coco oil + 5 drops 0.1% bile salt = small bubbles suspended in water
- 1 mL coco oil + 5 drops H2O + tiny crystal of chol. = large bubbles “
- 1 mL olive oil + 5 drops 1% aq. sol’n of lecithin = small bubbles “
E. Lieberman-Burchard or Acetic Anhydride Reaction (estimate Cholesterol)
- Chol. Will react with acetic anhydride in acidic medium (H2SO4)
- The hydroxyl groups of chol. Will react with the reagents
- Unsaturated sterols react more rapidly than the saturated ones
- Positive Test: Deep blue-green
Red or pink Purple Blue Bluish-green
F. Carr-Price Reaction for Vitamin A and related Carotenoids
- Vit A will react with antimony trichloride, SbCl3, to yield a Brilliant blue colored
product.
- Positive Test: Color change
Blue Green Gray Pink
- Cod Liver Oil ( + ) Vit A ( + ) Coco oil ( - ) Olive oil ( - )
G. Modified Furter-Meyer for Vitamin E and related Tocopherols
- Vit. E will react with n-amyl alcohol in HNO3 to yield bronze-red color
- Carotenoids and certain sterols will yield Yellow or Brown, and when present
in sufficient amounts, may mask the bronze-red color of small amount of
tocopherols
- Positive test: Bronze-red a-tocopherol ( + ) vit E ( + )
Isolation and Purification of Proteins
- Casein is soluble at pH 6.6 so it cannot be seen in milk, but solubilized as a
salt: Calcium Caseinate
- Lowering pH will lead to Isoelectric point (4.6) which makes casein become
insoluble and be seen
- Negative charges on the outer surface of the micelle are neutralized,
phosphate groups are protonated, neutral protein precipitates
- Denurturation= opens up 3D/globular form of Casein protein
- Anionic Form = pH is raised Cationic form = pH is lowered
- 1% AgNO3 = remove Cl so that casein will not have/react with HCl when
isolated
- Acetic Acid = used instead of HCl to be Cl free
Ca2+¿ caseinate +2 HCl→ Casein+CaCl ¿
2
You might also like
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
- Expt 5 CarbohydratesDocument49 pagesExpt 5 CarbohydratesColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PDFDocument56 pagesCarbohydrates PDFJustine Salvo EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesExperiment 1 CarbohydratesPrecious GaffudNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiochem Lab ReviewerDarlin Maree JamonNo ratings yet
- Molisch Test and Benedict TestDocument6 pagesMolisch Test and Benedict Testعلاوي البرشلونيNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LabDocument21 pagesCarbohydrates LabBernardMarkMateoNo ratings yet
- CHARBOHYDRATEDocument33 pagesCHARBOHYDRATENada hasan100% (1)
- Food TestsDocument1 pageFood TestsNicky360No ratings yet
- Laboratory Test For MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesLaboratory Test For MacromoleculesOdessa KwonNo ratings yet
- Test For CarbohydratesDocument15 pagesTest For CarbohydratesRandy AminolaNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 Please ContinueDocument5 pagesLab 7 Please ContinueMariano MarbellaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestDocument20 pagesQualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestFRANCEEN LEANNA KATIGBAKNo ratings yet
- A Carbohydrate Is An Organic Compound With The General Formula CMDocument6 pagesA Carbohydrate Is An Organic Compound With The General Formula CMHans Louie TabasonNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6: Qualitative Tests For Sugars and Amino AcidsDocument4 pagesExperiment 6: Qualitative Tests For Sugars and Amino AcidsAnkush RoyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Activity 1a & 1bDocument28 pagesBiochemistry Activity 1a & 1bSushmita Mia Gapuz100% (1)
- General Color Tests For Carbohydrates-2 PDFDocument48 pagesGeneral Color Tests For Carbohydrates-2 PDFTimothy John BautistaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Cell MolecDocument7 pagesCarbohydrates Cell Molecoink100% (1)
- Biochemical TestsDocument4 pagesBiochemical TestsNxxx0% (2)
- Carbohydrate AnalysisDocument63 pagesCarbohydrate AnalysisWinda EngkesaNo ratings yet
- The Molisch TestDocument12 pagesThe Molisch Testkamaksi100% (1)
- Experiment 1. Carbohydrates and Related CompoundsDocument8 pagesExperiment 1. Carbohydrates and Related CompoundsRalph Galano100% (4)
- FR Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates 1Document4 pagesFR Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates 1suzette_santos_20% (1)
- Lab 5: Qualitative Analysis Test For Carbohydrates Benedict's Test (Positive For Reducing Sugars)Document5 pagesLab 5: Qualitative Analysis Test For Carbohydrates Benedict's Test (Positive For Reducing Sugars)Sittie Fahieda AloyodanNo ratings yet
- The Molisch TestDocument9 pagesThe Molisch TestrawatanandNo ratings yet
- Act 10-13Document5 pagesAct 10-13Rane MandapatNo ratings yet
- Reactions of MonosaccharidesDocument15 pagesReactions of Monosaccharidesvishnudurga88% (8)
- Carbohydrates BiochemDocument26 pagesCarbohydrates BiochemReimond VinceNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesColor Reactions and Reducing Sugar Reactions of CarbohydratesRüveyda AkçinNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and Quantitative Tests Study GuideDocument16 pagesQualitative and Quantitative Tests Study GuideJanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3Document4 pagesLaboratory 3lili ry100% (1)
- Lab 8Document9 pagesLab 8Norjetalexis CabreraNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Carbohydrate DetectionDocument16 pagesQualitative Carbohydrate DetectionTristan Karl AbrugarNo ratings yet
- Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesCharacterization of CarbohydratesHyvieNo ratings yet
- Activity 2a Reactions of Carbohydrates Worksheet G1Document7 pagesActivity 2a Reactions of Carbohydrates Worksheet G1Reiko SakaeNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesDanluidQMalintadNo ratings yet
- Activity 2a Reactions of Carbohydrates Worksheet G1Document7 pagesActivity 2a Reactions of Carbohydrates Worksheet G1bernadil01No ratings yet
- Medina CollegeDocument20 pagesMedina CollegeOtencianoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Cell Macromolecules Centrifugation: 0.25 Molar Sucrose SolutionDocument7 pagesExperiment 1: Cell Macromolecules Centrifugation: 0.25 Molar Sucrose SolutionAngelica LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates I - Lab 4Document27 pagesQuantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates I - Lab 4Noriko Medoruma0% (3)
- Biochemistry Lectures - Lipids, Nucleic Acids, Saponification Etc,.Document6 pagesBiochemistry Lectures - Lipids, Nucleic Acids, Saponification Etc,.biochemistnurse67% (3)
- Pharmacognosy NotesDocument7 pagesPharmacognosy NotesGeniNo ratings yet
- General Properties of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesGeneral Properties of CarbohydratesShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument4 pagesTheoryDarin Rocky SumairNo ratings yet
- Chem 415 Experiment 1Document6 pagesChem 415 Experiment 1ttussenoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Test For CarbohydrateDocument24 pagesBiochemical Test For Carbohydrateanandbggu88% (8)
- Isolation From Chicken Liver and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of GlycogenDocument2 pagesIsolation From Chicken Liver and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of GlycogenAngela ResicoNo ratings yet
- Act 10Document10 pagesAct 10Lawrence Lorris CapuzNo ratings yet
- Discussion of ResultsDocument3 pagesDiscussion of ResultsMonica ClauorNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Identification of Unknown Carbohydrates by Dr. Mohammed Golam RasulDocument19 pagesCarbohydrates: Identification of Unknown Carbohydrates by Dr. Mohammed Golam RasulEka TinaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests: I. Carbohydrate FermentationDocument5 pagesBiochemical Tests: I. Carbohydrate FermentationMelody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- Test For CARBOHYDRATESDocument7 pagesTest For CARBOHYDRATESSoham N100% (2)
- Acrolein TestDocument6 pagesAcrolein TestJesserene Ramos75% (4)
- Post Lab Finals3Document21 pagesPost Lab Finals3AG SorianoNo ratings yet
- Test Media Purpose Components Reagents Expected Result Quality Control Gram StainDocument7 pagesTest Media Purpose Components Reagents Expected Result Quality Control Gram StainAngelNo ratings yet
- 3 Test For CarbohydratesDocument8 pages3 Test For CarbohydratesAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9Document3 pagesExperiment 9cherokeeNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- 4 Jurnal Ethics in Community NursingDocument10 pages4 Jurnal Ethics in Community NursingSalwa SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Health Stat Activity 104-2-1Document3 pagesHealth Stat Activity 104-2-1Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading FamacionDocument1 pageJournal Reading FamacionKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Initial Data Base: Number of Family MembersDocument10 pagesInitial Data Base: Number of Family MembersKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion IMCI AssignmentDocument2 pagesFamacion IMCI AssignmentKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion TLGDocument2 pagesFamacion TLGKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion TLGDocument2 pagesFamacion TLGKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 2Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 2Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 2Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 2Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN Survey ToolDocument14 pagesFamacion - CHN Survey ToolKyra Bianca R. Famacion100% (1)
- Famacion IMCI AssignmentDocument2 pagesFamacion IMCI AssignmentKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Final WeekDocument3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Final WeekKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Final WeekDocument3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Final WeekKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion IMCI AssignmentDocument2 pagesFamacion IMCI AssignmentKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Task 1 The Construction of The Monastery of The Transfiguration in Malaybalay City, Bukidnon. Designed by Leandro LocsinDocument2 pagesTask 1 The Construction of The Monastery of The Transfiguration in Malaybalay City, Bukidnon. Designed by Leandro LocsinKyra Bianca R. Famacion0% (2)
- Famacion - CHN Survey ToolDocument14 pagesFamacion - CHN Survey ToolKyra Bianca R. Famacion100% (1)
- Protozoa StructuresDocument2 pagesProtozoa StructuresKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Plasmodian Life CycleDocument6 pagesPlasmodian Life CycleKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- FinalsDocument1 pageFinalsKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Cestodes, Trematodes, Nematodes Life CyclesDocument10 pagesCestodes, Trematodes, Nematodes Life CyclesKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- English 7 Graded GtkyDocument1 pageEnglish 7 Graded GtkyKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Task 1 and Task 3Document2 pagesTask 1 and Task 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Talk Show With Invited ArtistDocument1 pageTask 3 Talk Show With Invited ArtistKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - Art Appropriationinal Final Output Part 1Document2 pagesFamacion - Art Appropriationinal Final Output Part 1Kyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Historical or Cultural MappingDocument1 pageHistorical or Cultural MappingKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - Task 2 Cultural Mapping For Movable HeritageDocument2 pagesFamacion - Task 2 Cultural Mapping For Movable HeritageKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Famacion - The White BirdDocument1 pageFamacion - The White BirdKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- ENG7 - Group - Historical Cultural MappingDocument27 pagesENG7 - Group - Historical Cultural MappingKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Opportunities and Barriers For Producing High Quality Fuels From The Pyrolysis of Scrap TiresDocument15 pagesOpportunities and Barriers For Producing High Quality Fuels From The Pyrolysis of Scrap TiresAbdisalamNo ratings yet
- Bilirubin Direct: ADL/V.01/110314Document1 pageBilirubin Direct: ADL/V.01/110314S MNo ratings yet
- CSR PredictionDocument10 pagesCSR PredictionROWHEITNo ratings yet
- Introduction Definitions and Sources of DrugsDocument4 pagesIntroduction Definitions and Sources of Drugssindhu mNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process of Molasses Based Disttilery 07042020Document24 pagesManufacturing Process of Molasses Based Disttilery 07042020Ankush GiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Nutrients' Flows and Cycles (Part 2)Document5 pagesChapter 5 - Nutrients' Flows and Cycles (Part 2)Joshua Neil CarigoNo ratings yet
- Norman C. Lee Blow Molding Design Guide ISBN: 978-3-446-41264-4Document8 pagesNorman C. Lee Blow Molding Design Guide ISBN: 978-3-446-41264-4PrabakaranNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy WKST KEYDocument4 pagesEnthalpy WKST KEYمحمد گراوندNo ratings yet
- Organisation FTDocument18 pagesOrganisation FTjane byersNo ratings yet
- Cikofill 2K: Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesCikofill 2K: Technical Data SheetM. KumaranNo ratings yet
- Geology of The Enterprise Hydrothermal Nickel Deposit, North-Western Province, ZambiaDocument30 pagesGeology of The Enterprise Hydrothermal Nickel Deposit, North-Western Province, ZambiaCarlos SabanNo ratings yet
- Bilgewater Flocculant 25 LTRDocument2 pagesBilgewater Flocculant 25 LTRGohNo ratings yet
- 1 Mass ConcreteDocument38 pages1 Mass ConcreteJayel GuintoNo ratings yet
- Yt-200 - 205 - 220 - 225 (Iom) PDFDocument16 pagesYt-200 - 205 - 220 - 225 (Iom) PDFVarun PatelNo ratings yet
- 1 Fire Extinguisher ClassesDocument13 pages1 Fire Extinguisher Classesm.sofiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0045206823005746 MainDocument14 pages1 s2.0 S0045206823005746 MainThaís ChouinNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of G+12 Storey Reinforced Concrete Building Using ETABSDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Design of G+12 Storey Reinforced Concrete Building Using ETABSIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Palomo, A., Fernández-Jiménez, A., Kovalchuk, G., Ordoñez, L. M., & Naranjo, M. C. (22 de Febrero de 2007)Document9 pagesPalomo, A., Fernández-Jiménez, A., Kovalchuk, G., Ordoñez, L. M., & Naranjo, M. C. (22 de Febrero de 2007)Jorge GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 2C-03-01 Rev 0Document2 pages2C-03-01 Rev 0Christian Martínez G.No ratings yet
- Recyllose - Products From Sewage: Turning Wastewater Into A Cellulose-MineDocument5 pagesRecyllose - Products From Sewage: Turning Wastewater Into A Cellulose-MineLalit Mohan Senapati100% (1)
- Molecular Characterisation of Soil-Dwelling Bacillus Thuringiensis Using Transcriptional Regulator, XRE Gene and The Crystal Protein, Cry2 GeneDocument7 pagesMolecular Characterisation of Soil-Dwelling Bacillus Thuringiensis Using Transcriptional Regulator, XRE Gene and The Crystal Protein, Cry2 GeneUMYU Journal of Microbiology Research (UJMR)No ratings yet
- Phase Change Materials, A Brief Comparison of Ice Packs, Salts, Paraffins, and Vegetable-Derived Phase Change MaterialsDocument10 pagesPhase Change Materials, A Brief Comparison of Ice Packs, Salts, Paraffins, and Vegetable-Derived Phase Change MaterialsStefanNo ratings yet
- Steps of GlycolysisDocument3 pagesSteps of GlycolysisIm jungkook JUSTIN SEAGULL A.K.A jungshookNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Osmotic PressureDocument2 pagesOsmosis and Osmotic PressureUr momNo ratings yet
- ZP11 MCE3 DTC Support Manual-20180118Document891 pagesZP11 MCE3 DTC Support Manual-20180118Adolfo FuentealbaNo ratings yet
- Geotextiles and Geomembranes: Properties, Production and Engineering ApplicationsDocument16 pagesGeotextiles and Geomembranes: Properties, Production and Engineering Applicationssai srinivasNo ratings yet
- Nano AdsorbantsDocument6 pagesNano AdsorbantsDl Al-aziz0% (1)
- Inorganic Chemistry Reactions Inorganic Chemistry Reactions (Type: Hydrolysis Reactions)Document15 pagesInorganic Chemistry Reactions Inorganic Chemistry Reactions (Type: Hydrolysis Reactions)mpNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Lecture Biochemical Process Engineering: Indicates Exercises As HomeworkDocument37 pagesExercises For Lecture Biochemical Process Engineering: Indicates Exercises As HomeworkAllalannNo ratings yet
- MercerizationDocument18 pagesMercerizationFarabbi AdittoNo ratings yet