Professional Documents
Culture Documents
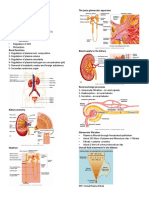
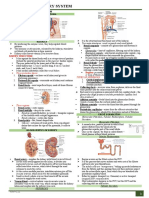
Anatomy 1
Uploaded by
Jenna LynnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy 1
Uploaded by
Jenna LynnCopyright:
Available Formats
•
Neural Regulation Of GFR at Diff Stimulation s I 2
what
.
During rest
-
.
sympathetic stimulation
•
IS low
•
Afferent ! Efferent arterioles are dilated
thymolorgy
Renal auto regulation of GFR dominates
•
During moderate stimulation
-
•
Afferent } efferent arterioles constrict
•
blood flow in & out is restricted to same degree
•
GFR decreases slightly
During large stimulation
-
•
vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole dominates
•
flow to Glomerulus drops → GFR drops
↳
Reduced urine output & greater flow to other tissues
-0 Hormonal Regulation of GFR
Angiotensin 11 : vasoconstrictor Narrows afferent ÷ efferent arterioles reduces flow
-
, ,
→
reduces GFR
Atrial Natur Hic factor increases blood volume stretches atria → release ANF
-
: ,
ANF → releases me sandlot cells → 9 surface area → TGFR
0
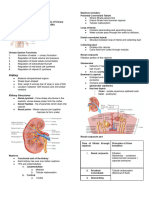
Outcomes of tubular Reabsorption & secretion
-
Reabsorption : return of most filtered water ÷ solutes to the bloodstream
↳ 99% water is reabsorbed
↳ solutes are reabsorbed ( Na ,
K, Ca , Hcoz ,
HPO 4)
↳ small proteins } peptides are absorbed via phagocytosis
-
secretion : transfer of materials from blood } tubule cells into the tubular (luminal
fluid )
↳ secretion of Ht
helps regulate blood pH
↳ secretion of the rest is waste / detoxification
0
Tubular Reabsorption ! secretion routes
-
Reabsorption : More from lumen back to blood
•
para cellular reabsorption : brethren adjacent tubule cells ( be tight junctions are not
↳ DIFFUSION
perfect )
•
Tran cellular reabsorption : through adjacent tubule cells
→
0
Tubular Reabsorption & secretion transport mechanisms
Primary Active Transport :
hydrolysis of STP used to pump
-
Seco nary Active Transport :
Energy in maintaining graint / gradient used to transport
You might also like
- Classification of DiureticDocument3 pagesClassification of DiureticJanice Malafu De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FeverDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Feverderic96% (69)
- Action Research in Araling PanlipunanDocument3 pagesAction Research in Araling PanlipunanLotisBlanca94% (17)
- KRPL Shahjahanpur Check List For Arc Welding MachineDocument1 pageKRPL Shahjahanpur Check List For Arc Welding MachineA S YadavNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual-Statistical Physics of Particles by Meheran KardarDocument165 pagesSolution Manual-Statistical Physics of Particles by Meheran KardarDanielle Nguyen7% (14)
- Anatomy 2Document1 pageAnatomy 2Jenna LynnNo ratings yet
- Water and Electrolyte Balance 1Document5 pagesWater and Electrolyte Balance 1محمد القرنيNo ratings yet
- Renal PhsyiologyDocument9 pagesRenal PhsyiologyRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi 1 - Introducton Renal PhysiolgyDocument5 pagesFisiologi 1 - Introducton Renal PhysiolgyHachi Nini Shop IINo ratings yet
- Renal System Bat NotesDocument41 pagesRenal System Bat NotesAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- ANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemDocument10 pagesANPH Wk14 - Urinary SystemSin I GangNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3Document1 pageAnatomy 3Jenna LynnNo ratings yet
- Urinary Lab OnlineDocument25 pagesUrinary Lab OnlineretterateNo ratings yet
- Happ Finals Week 16-2Document7 pagesHapp Finals Week 16-2qt potatoNo ratings yet
- 9-ch 26 - Urinary System CDocument95 pages9-ch 26 - Urinary System Clouise navorNo ratings yet
- Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen ExcretionDocument27 pagesSalt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretionnguyen thi van dongNo ratings yet
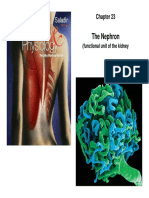
- The Nephron: (Functional Unit of The KidneyDocument14 pagesThe Nephron: (Functional Unit of The KidneyBishwambherNo ratings yet
- 11 UrinarySystemDocument63 pages11 UrinarySystemssandoval209No ratings yet
- Uia 09 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEYDocument5 pagesUia 09 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE KIDNEYIbrahim QariNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Aubf Review NotesDocument8 pagesMtap - Aubf Review NotesMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- VII - Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesVII - Urinary SystemGael QuingNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function Test (Trans)Document4 pagesKidney Function Test (Trans)Maria Leona CentenoNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes IV FluidsDocument1 pageFluids and Electrolytes IV Fluidsnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Diuretics TableDocument6 pagesDiuretics TableVie TNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerDocument30 pagesUrine Formation: Yousaf Khan Renal Dialysis LecturerSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Kidney Physiology (Q & A)Document28 pagesKidney Physiology (Q & A)ramadan100% (1)
- REN Revision LectureDocument43 pagesREN Revision Lecturegyamfi.rolandNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Urinary System (2020)Document55 pagesFundamental of Urinary System (2020)Nadya PutriNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology PDFDocument12 pagesRenal Physiology PDFLolitaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, Nephronlulu.borsikovaNo ratings yet
- Revision FileDocument14 pagesRevision FileBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Lecture 34 Kane Urinary System 4 Slides Per PageDocument8 pagesLecture 34 Kane Urinary System 4 Slides Per Pageroselyn_061001No ratings yet
- Bimbingan 7Document4 pagesBimbingan 7sean 102018039No ratings yet
- Renal Function AubfDocument11 pagesRenal Function AubfHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Excretory System, NephronDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Excretory System, NephronPaulína PalčinskáNo ratings yet
- 3 Renal PhysiologyDocument91 pages3 Renal Physiologytmqt2fbnzgNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Notes 1Document55 pagesHypertension Notes 1Chunnie JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology: Xiaohong XiaDocument128 pagesRenal Physiology: Xiaohong XiashaheenNo ratings yet
- 10 Respiratory System 2Document120 pages10 Respiratory System 2rosalyn gaboniNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument84 pagesUrinary SystemCheghe PerezNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument7 pagesRenal PhysiologyCarmela MarianoNo ratings yet
- 1 Renal FunctionDocument5 pages1 Renal FunctionChristopher BucuNo ratings yet
- From The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughDocument3 pagesFrom The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesUrinary Systemshanelhello1No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 18-Jul-2022Document5 pagesAdobe Scan 18-Jul-2022Yasticka OmerNo ratings yet
- Renal System 2022Document78 pagesRenal System 2022Rahil PatelNo ratings yet
- 25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxDocument12 pages25.6 Tubular Reabsorption - Anatomy and Physiology 2e - OpenStaxMarlene AngwaforNo ratings yet
- (Week 16) Urinary SystemDocument3 pages(Week 16) Urinary SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Reviewer - BAYLONDocument12 pagesUrinary System Reviewer - BAYLONElijah Joaquin Payumo BaylonNo ratings yet
- 15 Renal System - ATFDocument47 pages15 Renal System - ATFipek terimNo ratings yet
- Electric Signal PropagationDocument6 pagesElectric Signal Propagationpotro patoNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesRenal Physiologysachinroy07No ratings yet
- 2 - Renal PhysiologyDocument8 pages2 - Renal PhysiologyKunware TropaNo ratings yet
- NCP M7Document3 pagesNCP M7rjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- Topic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Excretion 1Document7 pagesExcretion 1swinky.dsNo ratings yet
- Test Iii Cultural Social and Political OrganizationDocument2 pagesTest Iii Cultural Social and Political OrganizationTin NatayNo ratings yet
- Tom Rockmore - Hegel's Circular EpistemologyDocument213 pagesTom Rockmore - Hegel's Circular Epistemologyluiz100% (1)
- To Word AkheebDocument31 pagesTo Word AkheebDavid Raju GollapudiNo ratings yet
- Resume LittletonDocument1 pageResume Littletonapi-309466005No ratings yet
- User Manual PocketBookDocument74 pagesUser Manual PocketBookmisu2001No ratings yet
- Membrane and TransportDocument25 pagesMembrane and TransportHafsa JalisiNo ratings yet
- Contents of HvacDocument2 pagesContents of Hvaclijo johnNo ratings yet
- BROMINE Safety Handbook - Web FinalDocument110 pagesBROMINE Safety Handbook - Web Finalmonil panchalNo ratings yet
- LAB Find Out The Bottle ContentsDocument4 pagesLAB Find Out The Bottle ContentschanNo ratings yet
- Compal Confidential: Ziwb2/Ziwb3/Ziwe1 DIS M/B Schematics DocumentDocument56 pagesCompal Confidential: Ziwb2/Ziwb3/Ziwe1 DIS M/B Schematics DocumentSuhpreetNo ratings yet
- English Lesson Plan Form 4 (Literature: "The Living Photograph")Document2 pagesEnglish Lesson Plan Form 4 (Literature: "The Living Photograph")Maisarah Mohamad100% (3)
- Valuing Construction Variation by Using PWA, FIDIC, ICWMF and CEDA Fluctuation Formula MechanismDocument5 pagesValuing Construction Variation by Using PWA, FIDIC, ICWMF and CEDA Fluctuation Formula MechanismAzman YahayaNo ratings yet
- Self-Actualization in Robert Luketic'S: Legally Blonde: A HumanisticDocument10 pagesSelf-Actualization in Robert Luketic'S: Legally Blonde: A HumanisticAyeshia FréyNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Contemporary WorldDocument4 pagesMODULE 1 - Contemporary WorldaapNo ratings yet
- David Sacks Resume February 16 2015Document1 pageDavid Sacks Resume February 16 2015api-279280948No ratings yet
- A Software Architecture For The Control of Biomaterials MaintenanceDocument4 pagesA Software Architecture For The Control of Biomaterials MaintenanceCristian ȘtefanNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Language Difference and Language Disorder - Information For Teachers Working With English Language Learners in The Schools PDFDocument23 pagesDifferentiating Language Difference and Language Disorder - Information For Teachers Working With English Language Learners in The Schools PDFIqra HassanNo ratings yet
- Coastal Blue Carbon - Methods For Assessing Carbon Stocks and Emissions Factors in Mangroves Tidal Salt Marshes and Seagrass MeadowsDocument182 pagesCoastal Blue Carbon - Methods For Assessing Carbon Stocks and Emissions Factors in Mangroves Tidal Salt Marshes and Seagrass Meadowsapi-245803001No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Career ObjectiveDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Career ObjectiveRākesh Rakhi100% (1)
- Contemplation (Murāqaba) and Spiritual Focus/attention (Tawajjuh) in The Pre-Mujaddidi Naqshibandi OrderDocument5 pagesContemplation (Murāqaba) and Spiritual Focus/attention (Tawajjuh) in The Pre-Mujaddidi Naqshibandi OrderShahmir ShahidNo ratings yet
- Digital Control Engineering 2nd Edition Fadali Solutions Manual PDFDocument3 pagesDigital Control Engineering 2nd Edition Fadali Solutions Manual PDFMohammed SalahNo ratings yet
- ASC 2020-21 Questionnaire PDFDocument11 pagesASC 2020-21 Questionnaire PDFShama PhotoNo ratings yet
- Philips fwt9200Document37 pagesPhilips fwt9200Alex BrazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 Esip For FinalDocument35 pagesChapter 34 Esip For FinalJeaniel BorlingNo ratings yet
- Two Occult Philosophers in The Elizabethan Age: by Peter ForshawDocument10 pagesTwo Occult Philosophers in The Elizabethan Age: by Peter ForshawFrancesco VinciguerraNo ratings yet
- Spies May Be Gathering Encrypted Data To Crack With Future Quantum ComputerDocument1 pageSpies May Be Gathering Encrypted Data To Crack With Future Quantum ComputerHÀ ĐỖ VIẾTNo ratings yet
- STRESS HealthDocument40 pagesSTRESS HealthHajra KhanNo ratings yet