Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy 2
Uploaded by
Jenna LynnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy 2
Uploaded by
Jenna LynnCopyright:
Available Formats
•
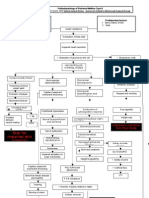
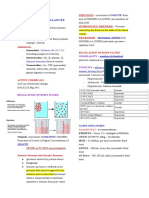
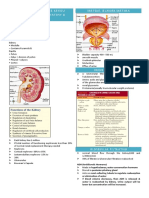
forces at Glomerular capillary that favor filtration
renal 1
2
-
Glomerular Blood Hydrostatic Pressure IGBHP) .
.
•
promotes Filtration
-
Capsular Hydrostatic Pressure ( CHD) nprhisi -
ology
•
Opposes Filtration
•
Exerted against filtration by fluid already In the capsular space ( back pressure)
-
Blood colloid osmotic Pressure CBCOP )
•
opposes Filtration
•
Resulting from proteins like albumin , Globulin , ! fibrinogens
0
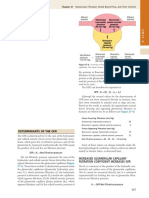
Net Filtration Pressure INFP)
NFP = ( BHP + I FOP ) -
( BCOP + IF Hp )
& N
Blood Hydrostatic lthterstitlal Blood Interstitial Fluid Hydrostatic Pressure
Pressure Fluid osmotic colloid ( Pushes back to blood )
( promote filtration) pressure osmotic
( Promote Filtration) Pressure
( promote reabsorption)
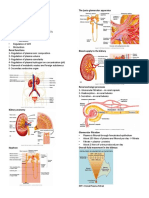
0 Glomerular filtration Rate (GFR )
Amount of filtrate in all renal corpuscles
-
usually constant ( High =
paid out low not enough Pee 'd out
-
-_
,
Directly related to pressures that determine filtration
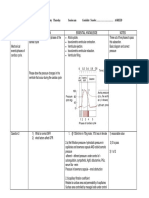
0 Auto regulatory control of GFR operates by adjusting ooo
to Flow In ÷ out of Glomerulus
Increase flow → Increase GFR
-
Constrict Afferent Arterial → Decrease blood flow ! vice versa (same for efferent)
2. Change surface Area of Glomerular capillary
-
mesang eat cells contract & decrease surface area ( decreasing AFR)
Myogenic Mechanism Of Auto regulation
•
Elevates BP
-
stretching triggers contraction of smooth muscles
-
Narrow lumen
-
510W blood flow
Decrease GFR
-
•
TUDUIO glomerular mechanism of autoregulation
macula Densa provides feedback to the Glomerulus
-
pet :[OH have less time
-
Detect increased delivery of salt 's
.
Chloride ( Happens when GFR Is 9) ( to absorbe- more lost to
-
urine
-
Inhibit NO release from juxta lomeruiar cells ( causes vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole )
↳ decreases flow in glomerular us } tr GFR
You might also like
- DM Type 2 PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesDM Type 2 PathophysiologyuzumakiruleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document1 pageAnatomy 1Jenna LynnNo ratings yet
- L2 GFRDocument14 pagesL2 GFRjanemanraaj32No ratings yet
- Determinants of The GFRDocument4 pagesDeterminants of The GFRgmsanto7No ratings yet
- L2 Renal Blood Flow and Glomerular Filtration 2023 1.2Document6 pagesL2 Renal Blood Flow and Glomerular Filtration 2023 1.2bgj9cddvxhNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3Document1 pageAnatomy 3Jenna LynnNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi 1 - Introducton Renal PhysiolgyDocument5 pagesFisiologi 1 - Introducton Renal PhysiolgyHachi Nini Shop IINo ratings yet
- 27 GuytonDocument6 pages27 GuytonBianca Louise Chan LimNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument84 pagesRenal PhysiologyFauzan HafizNo ratings yet
- Renal Electrolyte RegulationDocument10 pagesRenal Electrolyte Regulationfatidaloul2000No ratings yet
- 3 GFR 2020Document32 pages3 GFR 2020vrajNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument16 pagesExcretionamydamien705No ratings yet
- Renal System Bat NotesDocument41 pagesRenal System Bat NotesAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- 1 - Glomerular Filtration Rate GFRDocument9 pages1 - Glomerular Filtration Rate GFRHamzehNo ratings yet
- Renal System 2022Document78 pagesRenal System 2022Rahil PatelNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology: Functions of The KidneyDocument16 pagesRenal Physiology: Functions of The KidneyUsman Ali Akbar0% (1)
- Week 7 Fluid Volume Imbalances: SoluteDocument8 pagesWeek 7 Fluid Volume Imbalances: SoluteMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument89 pagesRenal PhysiologySelamu YosefNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument19 pagesRenal SystemAml Sayed Elbadwie KotbNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Urinary System (2020)Document55 pagesFundamental of Urinary System (2020)Nadya PutriNo ratings yet
- Kidney Physiology (Q & A)Document28 pagesKidney Physiology (Q & A)ramadan100% (1)
- Topic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Aubf Renal Function PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Student Version The Urinary System 2020.ppt (1402)Document20 pagesChapter 15 Student Version The Urinary System 2020.ppt (1402)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- GFR and RENAL BLOOD FLOWDocument20 pagesGFR and RENAL BLOOD FLOWEniola abdullahi AduagbaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Module NotesDocument22 pagesUrinary Module NotesAthira SureshNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology For The BoardsDocument37 pagesRenal Physiology For The BoardsRainy Day100% (1)
- NCMB 312Document7 pagesNCMB 312ENJELAH RAIKA NEYRANo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 2Document39 pagesRenal Physiology 2Hema KamatNo ratings yet
- CRRT (RVS) One Day TrainingDocument46 pagesCRRT (RVS) One Day TrainingwantoNo ratings yet
- T09-Physiology 3Document26 pagesT09-Physiology 3Mohammad AlomariNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Quick Review Review of Urinary Anatomy & Physiology Ureters, Bladder, UrethraDocument6 pagesUrinary System: Quick Review Review of Urinary Anatomy & Physiology Ureters, Bladder, UrethraLongyapon Sheena StephanieNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys & Body Fluids: 1. NephronsDocument34 pagesThe Kidneys & Body Fluids: 1. NephronsKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- 2010 2physDocument12 pages2010 2physlahiruwan123No ratings yet
- Renal PhsyiologyDocument9 pagesRenal PhsyiologyRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Glomerular UltrafiltrationDocument31 pagesGlomerular UltrafiltrationHakimah K. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument3 pagesHeart FailurehawrazfarisNo ratings yet
- Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen ExcretionDocument27 pagesSalt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretionnguyen thi van dongNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology and Fluid BalanceDocument71 pagesRenal Physiology and Fluid BalanceparthNo ratings yet
- 1 Renal FunctionDocument5 pages1 Renal FunctionChristopher BucuNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Aubf Review NotesDocument8 pagesMtap - Aubf Review NotesMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- LS607 Module 7 Renal PhysiologyDocument24 pagesLS607 Module 7 Renal PhysiologyasmaaalmesaifriNo ratings yet
- Urine FormationDocument49 pagesUrine FormationMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Glomerular Filtration RateDocument52 pagesDeterminants of Glomerular Filtration RateAbraham Dawson machachaNo ratings yet
- 11 UrinarySystemDocument63 pages11 UrinarySystemssandoval209No ratings yet
- HTC2-Physiology: Structure and Function of KidneyDocument47 pagesHTC2-Physiology: Structure and Function of KidneyVienne Yuen Wing YanNo ratings yet
- CM Lecture NotesDocument30 pagesCM Lecture NotesJefferson SorianoNo ratings yet
- Physiology, Lecture 6, Urinary SystemDocument74 pagesPhysiology, Lecture 6, Urinary SystemAli Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- MHN 15Document14 pagesMHN 15Vaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- Holes Cha 20 Urinary PT 2Document6 pagesHoles Cha 20 Urinary PT 2mlinaballerinaNo ratings yet
- 2-Renal Physiology 2 (Renal Haemodynamic and GFR)Document28 pages2-Renal Physiology 2 (Renal Haemodynamic and GFR)Iph anyiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids: Renal Function Topic OutlineDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids: Renal Function Topic OutlineBEVERLY JANE LLUVERASNo ratings yet
- Damage - Control - Resus - Quick - Reference - Guide - Medics - Corpsmen - 2023-Quick Reference Guide For Combat Medics and CorpsmenDocument1 pageDamage - Control - Resus - Quick - Reference - Guide - Medics - Corpsmen - 2023-Quick Reference Guide For Combat Medics and Corpsmenchou youNo ratings yet
- Renal Blood Flow Until Regulation of RBF and GFRDocument5 pagesRenal Blood Flow Until Regulation of RBF and GFRDoogie ReynaldoNo ratings yet
- Renal PathophysiologyDocument42 pagesRenal PathophysiologynoneyaNo ratings yet
- D - Water and Electrolyte Balance of KidneyDocument6 pagesD - Water and Electrolyte Balance of KidneyNav ThiranNo ratings yet
- The Heart and Circulatory System and The Kidney 2Document28 pagesThe Heart and Circulatory System and The Kidney 2Izzuddin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Urine ProductionDocument17 pagesUrine ProductionLeonardo Balondo DulaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument39 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseMohmmadRjab SederNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #22 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document9 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #22 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Management of Chronic KidneyDocument12 pagesNutritional Management of Chronic KidneyMARIA CASTELLANOSNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2 Mod14 Regulation of Body Fluids FinalDocument35 pagesGenbio 2 Mod14 Regulation of Body Fluids FinalacebealsabasNo ratings yet
- BiologyNotesForClass11hChapter PDFDocument7 pagesBiologyNotesForClass11hChapter PDFNaresh BorkarNo ratings yet
- Aubf Prelim 1Document59 pagesAubf Prelim 1Kat JornadalNo ratings yet
- One Year Joint Package With AIATS For NEET 2024 - Class XII PDFDocument38 pagesOne Year Joint Package With AIATS For NEET 2024 - Class XII PDFRishabh kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 Glomerular DiseasesDocument127 pages1 Glomerular DiseasesCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument32 pagesUrinary SystemYulia Dewi AsmariatiNo ratings yet
- REVALIDADocument12 pagesREVALIDAKim AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Bio 2022 Ans KeyDocument4 pagesBio 2022 Ans Keyreply2bhuvanaNo ratings yet
- Stereological Study of Kidney in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice Treated With Ethanolic Extract of Stevia Rebaudiana (Bitter Fraction)Document10 pagesStereological Study of Kidney in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice Treated With Ethanolic Extract of Stevia Rebaudiana (Bitter Fraction)Fenny Noor AidaNo ratings yet
- Unlock SGCh16Document7 pagesUnlock SGCh16SilaxNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Ial Biology Unit 5: The KidneyDocument24 pagesEdexcel Ial Biology Unit 5: The KidneyMithun ParanitharanNo ratings yet
- Methods of Paragraph DevelopmentDocument11 pagesMethods of Paragraph DevelopmentVanityHughNo ratings yet
- Aubf 2020Document447 pagesAubf 2020kurt Allen MacarilayNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument24 pagesBiology ProjectMujib Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Patho OB 2.1 - Hypertensive Disorders of PregnancyDocument7 pagesPatho OB 2.1 - Hypertensive Disorders of PregnancyPao CallejoNo ratings yet
- Nihms 843291Document91 pagesNihms 843291Mae PNo ratings yet
- Renal System PPT PresentationDocument29 pagesRenal System PPT PresentationIris AbogadoNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus AssignmentDocument6 pagesSystemic Lupus Erythematosus AssignmentnehaNo ratings yet
- Soal Kidney CompiledDocument28 pagesSoal Kidney Compiledstella pangestika100% (1)
- LECTURE 2 Urinary System - Histology HB II 2023Document79 pagesLECTURE 2 Urinary System - Histology HB II 2023Emmanuel AssopiahNo ratings yet
- AIJPMS - Volume 3 - Issue 2 - Pages 11-19Document9 pagesAIJPMS - Volume 3 - Issue 2 - Pages 11-19Elena StepanNo ratings yet
- Modul Pintas Tingkatan 5 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2018 Skema Jawapan Biologi Kertas 1 4551/1Document39 pagesModul Pintas Tingkatan 5 Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2018 Skema Jawapan Biologi Kertas 1 4551/1VentusNo ratings yet
- 8th Science NotesDocument21 pages8th Science NotesAbdul Razaque SharNo ratings yet
- Bio560 OsmoregulationDocument110 pagesBio560 OsmoregulationNuratika OthmanNo ratings yet
- 'Block E With Keys and Hints ' With YouDocument36 pages'Block E With Keys and Hints ' With YouAbdullah TanoliNo ratings yet
- Amharic ConversationDocument94 pagesAmharic Conversationtsehay asratNo ratings yet