Professional Documents
Culture Documents
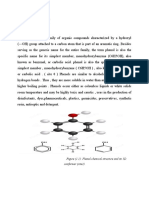
Heterofunctional Compounds
Heterofunctional Compounds
Uploaded by
NEET ncert readingOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heterofunctional Compounds
Heterofunctional Compounds
Uploaded by
NEET ncert readingCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Heterofunctional compounds are organic substances containing two or
more different functional groups that combine both the properties of the corresponding
monofunctional derivatives and their specific chemical characteristics that are most
important for ensuring the biological functions performed by these substance
2. 1.CH3CH2COOH --Propionic acid
2.C4H6O6--Tartaric acid
3. Benzoic acid is a constituent of Whitfield's ointment which is used for the treatment of
fungal skin diseases such as tinea, ringworm, and athlete's foot.
3. 1.Iron (III) ion reacts with phenols to form a purple complex. Salicylic acid
contains a phenol group, but acetylsalicylic acid does not. Therefore, if you add FeCl3
to an aspirin sample and you see a purple color, it means that there is still some
salicylic acid present and the sample is impure.
2. Ferric chloride test: Phenol reacts with neutral FeCl3 to form ferric phenoxide
complex giving violet coloration. But benzoic acid reacts with neutral FeCl3 to give a
buff-coloured precipitate of ferric benzoate.
4. Fehling's solution is a chemical reagent used to differentiate between water-
soluble carbohydrate and ketone functional groups, and as a test for reducing sugars
and non-reducing sugars, supplementary to the Tollens' reagent test. The test was
developed by German chemist Hermann von Fehling in 1849.
artaric acid in Fehling's solution binds to copper(II) ions, preventing the formation of
insoluble hydroxide salts. DL-tartaric acid (racemic acid) (when in 1:1 ratio) …
5. carboxyl group, followed by protonation of the aromatic ring of the anion so formed, ...
You might also like
- Experiment 6 - Comparative Investigation of Organic CompoundsDocument6 pagesExperiment 6 - Comparative Investigation of Organic CompoundsIson Dy100% (2)
- Report Writing On LoopsDocument11 pagesReport Writing On LoopsNEET ncert reading100% (1)
- Post-Lab Report For PhenolsDocument5 pagesPost-Lab Report For PhenolsJoan Romero67% (3)
- Ferric Chloride TestDocument13 pagesFerric Chloride TestRashid RaniaiNo ratings yet
- Tests For FlavonoidsDocument9 pagesTests For FlavonoidsPirya100% (1)
- Organic Derivatives of WaterDocument9 pagesOrganic Derivatives of Waterpagaduanjoshuaj8227100% (2)
- Alcohols and Phenols FinalDocument45 pagesAlcohols and Phenols Finalmalikchandkhokhar2211No ratings yet
- Tests For Phenolic Group SimulationDocument2 pagesTests For Phenolic Group SimulationJoao Fernando Almeida Cunha de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Phenol SDocument9 pagesPhenol SAnonymous 8rsxG4No ratings yet
- Qualitative Test For PhenolDocument5 pagesQualitative Test For PhenolTanya 60No ratings yet
- Comparative Investigation of Organic CompundsDocument6 pagesComparative Investigation of Organic CompundsKizer Dela Cruz100% (1)
- GROUP 3 - LABORATORY REPORT 4 - Compounds With Hydroxyl GroupDocument18 pagesGROUP 3 - LABORATORY REPORT 4 - Compounds With Hydroxyl GroupJESSIE FREDRICK DALANIELNo ratings yet
- Proceeding Bromometric Phenol Assay Without Starch IndicatorDocument6 pagesProceeding Bromometric Phenol Assay Without Starch IndicatorAsiyahNo ratings yet
- Phenol SDocument13 pagesPhenol SJyoti Gaba -ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Ferric Chloride TestDocument13 pagesFerric Chloride TestCarlou AbarsoloNo ratings yet
- G6 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument64 pagesG6 Alcohols Phenols and EthersHarijaNo ratings yet
- Share My Portfolio in Chem 102Document61 pagesShare My Portfolio in Chem 102Remar PabalayNo ratings yet
- Chem Activity 1Document16 pagesChem Activity 1Jarvis StarkNo ratings yet
- Handy Dan Hoyt (1926)Document8 pagesHandy Dan Hoyt (1926)Kama AlayandraNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument4 pagesPhenolAbeer AbdelganeNo ratings yet
- PhenanthrolineDocument3 pagesPhenanthrolineRega PermanaNo ratings yet
- Auxin Phenol ComplexesDocument4 pagesAuxin Phenol ComplexesCosmin-Gabriel PricopeNo ratings yet
- Our ObjectiveDocument8 pagesOur ObjectiveGOURAV GOLANo ratings yet
- Formal Report Exp 9Document13 pagesFormal Report Exp 9Rianne SolivenNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument16 pagesPhenolAmanNo ratings yet
- TEsts For UnsaturationDocument16 pagesTEsts For UnsaturationMahrishiShuklaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Phenols, Alcohols, and EthersDocument2 pagesProperties of Phenols, Alcohols, and EthersChristine TesoroNo ratings yet
- PhenolphthaleinDocument5 pagesPhenolphthaleinspace slNo ratings yet
- Lab Report # 3Document5 pagesLab Report # 3Quratul-Ain AsgharNo ratings yet
- Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesClassification Test For HydrocarbonsTinuviele EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsDocument16 pagesExperiment 9 Formal Report On Classification Test of Hydroxyl-Containing and Carbonyl-Containing Organic CompoundsLuisGabito100% (1)
- Experiment No.3 CHM143Document9 pagesExperiment No.3 CHM143MaiSakurajima100% (1)
- Identification of Alcohols and PhenolsDocument15 pagesIdentification of Alcohols and PhenolsSALIFU91% (23)
- Nomenclature of PhenolsDocument3 pagesNomenclature of PhenolsRockyNo ratings yet
- B. Physical Properties of AlcoholsDocument4 pagesB. Physical Properties of AlcoholsAnjo Pasiolco CanicosaNo ratings yet
- Index: Sr. No. Topics Page NoDocument69 pagesIndex: Sr. No. Topics Page NoRoshan Rohit100% (3)
- About Phenol:: 2. Hydrolysis ofDocument3 pagesAbout Phenol:: 2. Hydrolysis ofNazmul NayeemNo ratings yet
- Laporan Resmi ProteinDocument74 pagesLaporan Resmi ProteinAhlan RiwahyuNo ratings yet
- I. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument10 pagesI. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidLaily SafitriNo ratings yet
- Alkohol (Repaired)Document38 pagesAlkohol (Repaired)LiviaAsriNo ratings yet
- PH Eno LS: Group No #5Document16 pagesPH Eno LS: Group No #5السید طیب علی البخاری القادری السہروردیNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenols, ThiolsDocument21 pagesAlcohol, Phenols, ThiolsKatrina AllondraNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledsam cuadraNo ratings yet
- PhenolDocument16 pagesPhenolMary Chloe JaucianNo ratings yet
- Antioxidan 1Document43 pagesAntioxidan 1pardeepbthNo ratings yet
- Identification 2Document10 pagesIdentification 2Noor FarhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Class 12Document17 pagesChemistry Project Class 12ujjwalpokhrel4960No ratings yet
- Topic 2 PhenolsDocument41 pagesTopic 2 PhenolsMark K DavidNo ratings yet
- Written Report Activity 10Document6 pagesWritten Report Activity 10Trisha Valero Ferolino0% (1)
- Identification and Reaction of AlcoholsDocument6 pagesIdentification and Reaction of AlcoholsVilmer IyanaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Test For PhenolDocument6 pagesQualitative Test For PhenolRonak PandeyNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Determination of and Unknown AlcoholDocument6 pagesLab 10 Determination of and Unknown AlcoholgioNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers: Unit 11Document24 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethers: Unit 11Meenal JoshiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: CH CHDocument4 pagesAlcohols: CH CHGeraldyn CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Cita High School, Port Harcourt Subject: Chemistry Class: Ss3 Week TopicDocument107 pagesCita High School, Port Harcourt Subject: Chemistry Class: Ss3 Week TopicYushau Muhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of PhenolDocument2 pagesPhysical Properties of Phenoldanica100% (1)
- Bautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)Document4 pagesBautista, John Mhar M. (Experiment 7)2g8vdspqm5No ratings yet
- Synthetic Tannins, Their Synthesis, Industrial Production and ApplicationFrom EverandSynthetic Tannins, Their Synthesis, Industrial Production and ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2. Medulla Oblongata. Metencephalon: Pons, Cerebellum. Rhomboid Fossa - IV VentricleDocument11 pagesLesson 2. Medulla Oblongata. Metencephalon: Pons, Cerebellum. Rhomboid Fossa - IV VentricleNEET ncert readingNo ratings yet
- Sterilization: ApplicationDocument4 pagesSterilization: ApplicationNEET ncert readingNo ratings yet
- Deontological EthicsDocument4 pagesDeontological EthicsNEET ncert readingNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer ProcessorsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computer ProcessorsNEET ncert readingNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer ProcessorsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computer ProcessorsNEET ncert readingNo ratings yet