Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supply Behaviour
Supply Behaviour
Uploaded by
Prakash SelvanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supply Behaviour
Supply Behaviour
Uploaded by
Prakash SelvanCopyright:
Available Formats
Supply
S= F(Price of Vehicle, Input cost, Technology, Expectations about future price)
Note: Although there are many more factors, we will limit out study to the above-mentioned factors.
Price of vehicle: When the price of the vehicle increase, the producers supply more as well as
new producers enter the market. This will lead to a further increase in supply, ceteris paribus.
GST tax regime was implemented in 2017, a consolidated tax (18% to 28%) replaced the
two tax system of VAT and excise duty. It reduced the manufacturing cost in 2018 and
boosted production in the industry.
Input costs: When input costs increase, the of vehicles will not increase, ceteris paribus. Some of the
input parameters involved in the manufacturing are discussed below which will affect automobile
supply.
Aluminium: LME of rolled products from FY 17-20 decreased from $ 3997MT to $
3236MT. It enabled more production in the automobile industry.
Glass: Price increased by 1% compared to the previous financial year of 2019, this
caused a reduction in production volume of vehicles.
Labour: In the context of Maruti, post-COVID, the labour wages decreased; however, the
pandemic with norms of social distancing makes it challenging and thus impacting the
vehicular supply.
Technology: Advancement in technology in the manufacturing process leads to an increase in
the supply of the vehicle. For eg.
Machine vision: It involves the use of imaging processes such as 3D imaging, X-ray
imaging and others. The manual inspection time is getting reduced.
Expectation about future price: When an automobile company predicts a rise in selling price
of their vehicle, they try to reserve their inventories for future and reduce immediate production
volume. For eg. When BS-VI norms were introduced, manufacturers expected an increase in
price of the vehicle in future. In FY-2019 Q2, sales & production of Maruti dropped for BS-IV
vehicles since customers wanted to buy BS-VI vehicles which were due to be rolled out in the
next year.
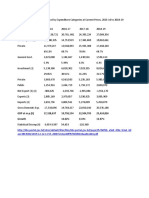
25000
19,401 19,314
20000 18,795 18,224 17,309 16,330
15,776 14,749
14,218
Sales volume in units
15000 12,677 12,444 12,934
10000
5000
Source(s): Autoportal.com; ID 869977
Fig 1: Maruti Suzuki swift sales across the month in 2019, showing the decline in Q2.
Supply Curve
Based on the parameters discussed in the previous section, the following will be the supply
equation was derived.
Q = w*P + x*IC + y*T + z*EP
Where,
P – Represents the total market price of the vehicle
IC – Represents the input costs
T – Represents the technological impact on vehicular supply
EP – Represents the expectation about the future price.
w, x, y & z - Co-efficient for the input parameters
You might also like
- Indian Tyre Industry: FY2018 Margins To Crimp On High Cost InventoryDocument5 pagesIndian Tyre Industry: FY2018 Margins To Crimp On High Cost InventoryAbhijeet Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Saftu Laments Job LossesDocument37 pagesSaftu Laments Job LossesJacaranda FM NewsNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis Automobile Profile TestDocument13 pagesFinancial Analysis Automobile Profile TestRahul ShettyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Q3 Financial - Presentation - Qiii - 2018-19Document9 pages2019 Q3 Financial - Presentation - Qiii - 2018-19Anand SNo ratings yet
- OTT Marketing PDFDocument12 pagesOTT Marketing PDFTushar YadavNo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 2Document25 pagesQ3 Lesson 2eotteokhaeeotteokhaeNo ratings yet
- 2018 Sports OutlookDocument16 pages2018 Sports OutlookFooyNo ratings yet
- Auto Industry Update 2020 - v1Document8 pagesAuto Industry Update 2020 - v1Khoi Nguyen100% (1)
- Fsez at A GlanceDocument22 pagesFsez at A GlanceQaz TopazNo ratings yet
- CelastroFinanceModel-4.1Document17 pagesCelastroFinanceModel-4.1Seemant SengarNo ratings yet
- Sewing Machine AssemblyDocument26 pagesSewing Machine AssemblyRobel KefelewNo ratings yet
- Two-Wheeler Sector: Shape Shifting in The Wake of BS-VI and ElectrificationDocument64 pagesTwo-Wheeler Sector: Shape Shifting in The Wake of BS-VI and Electrificationadityakhanna83No ratings yet
- Tire Industry AnalysisDocument14 pagesTire Industry AnalysisSoniya DhyaniNo ratings yet
- Industry InsightsDocument9 pagesIndustry Insightssumit6singhNo ratings yet
- Escorts: All-Round Optimism Bolsters Constructive ViewDocument10 pagesEscorts: All-Round Optimism Bolsters Constructive ViewasdhahdahsdjhNo ratings yet
- Estados Financieros Mercadona ... NavarroDocument19 pagesEstados Financieros Mercadona ... NavarroRichard NavarroNo ratings yet
- Applied Maths ProjectDocument10 pagesApplied Maths ProjectDarsh KansalNo ratings yet
- BUS 209 Class On June 10, 2020Document5 pagesBUS 209 Class On June 10, 2020Yasir ArafatNo ratings yet
- M&M ReportDocument12 pagesM&M Reportdevendradeshpande123No ratings yet
- Auto and Auto ComponentsDocument21 pagesAuto and Auto Componentszoheb jafriNo ratings yet
- R&D, Advertisement and Market Share: Telecommunications Industry in IndiaDocument34 pagesR&D, Advertisement and Market Share: Telecommunications Industry in IndiadebajyotimondalNo ratings yet
- Applied Cost AccountingDocument2 pagesApplied Cost AccountingamaljacobjogilinkedinNo ratings yet
- Auto Compendium Fy21 v2Document16 pagesAuto Compendium Fy21 v2Aswin KondapallyNo ratings yet
- Pdffile 1700758477537Document19 pagesPdffile 17007584775379tkpvc46rgNo ratings yet
- Mahindra & Mahindra LTD.: Key Result Highlights - Q4FY17Document6 pagesMahindra & Mahindra LTD.: Key Result Highlights - Q4FY17anjugaduNo ratings yet
- Mahindra Mahindra Research Report 1697198304Document28 pagesMahindra Mahindra Research Report 1697198304Utkarsh MaruNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Automobile IndustryDocument5 pagesPresentation On Automobile IndustryKanoj AcharyNo ratings yet
- Ev in IndiaDocument26 pagesEv in Indiakiran kumarNo ratings yet
- Juishat Financial Plan: College Park, Dipolog City Tel. No. (065) 212-8049 WebsiteDocument11 pagesJuishat Financial Plan: College Park, Dipolog City Tel. No. (065) 212-8049 WebsiteMeosjinNo ratings yet
- Sem 2 Economics AssignmentDocument12 pagesSem 2 Economics Assignmentjagrit garg100% (1)
- Global - IT Services, February 2019Document32 pagesGlobal - IT Services, February 2019ashvarybabulNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills: Presentation On: Industry Report (Automobiles)Document14 pagesCommunication Skills: Presentation On: Industry Report (Automobiles)Satyam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Study Id51495 Smart-CitiesDocument66 pagesStudy Id51495 Smart-CitiesIan TanNo ratings yet
- Fy 2021 Presentation 1504 CompressedDocument20 pagesFy 2021 Presentation 1504 CompressedGuilherme SouzaNo ratings yet
- Pitch Document - TransourceDocument30 pagesPitch Document - TransourceKraftbuy comNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Motors ReportDocument11 pagesBajaj Motors Reportsatyammishra.p2325No ratings yet
- Corporate Performance Q3 FY19Document12 pagesCorporate Performance Q3 FY19Gautam MehtaNo ratings yet
- Study - Id43034 - Digital Market Outlook Connected Car ReportDocument90 pagesStudy - Id43034 - Digital Market Outlook Connected Car ReportSubrataNo ratings yet
- India MF Industry Beyond AuM 1683607463Document8 pagesIndia MF Industry Beyond AuM 1683607463Aritra SenNo ratings yet
- Equity Research Report HMCDocument7 pagesEquity Research Report HMCyadhu krishnaNo ratings yet
- Mahindra & Mahindra: Strong Quarter New Launches To Drive GrowthDocument9 pagesMahindra & Mahindra: Strong Quarter New Launches To Drive Growthparchure123No ratings yet
- Auto - WordDocument10 pagesAuto - WordPremkantjhaNo ratings yet
- Tech Mahindra - Revenue Share by Industry 2022 - StatistaggDocument2 pagesTech Mahindra - Revenue Share by Industry 2022 - StatistaggMayank NegiNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure Analysis of Mahindra and Mahindra Limited: Submitted To Dr. Suveera GillDocument21 pagesCapital Structure Analysis of Mahindra and Mahindra Limited: Submitted To Dr. Suveera GillNeha KumarNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Submitted To: Dr. Vivek SaneDocument15 pagesStrategic Management: Submitted To: Dr. Vivek SaneMilind VatsiNo ratings yet
- Total Factor Productivity For Major Industries - 2022Document15 pagesTotal Factor Productivity For Major Industries - 2022Novica SupicNo ratings yet
- DIWALI PICK 2022-12-October-2022-904894269Document12 pagesDIWALI PICK 2022-12-October-2022-904894269RamNo ratings yet
- Syed Ali Masood 27120 IBF ReportDocument23 pagesSyed Ali Masood 27120 IBF ReportSyed Usarim Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Measuring Domestic Output and National Income-MacroeconomicDocument38 pagesMeasuring Domestic Output and National Income-Macroeconomiccuishan makNo ratings yet
- Euromonitor - Industry Capsules - Movie Theatres in India - ISIC 9212Document13 pagesEuromonitor - Industry Capsules - Movie Theatres in India - ISIC 9212shubhamwaghadhare100% (1)
- Performance Analysis Name: Akshay Thakker (C-4) : SalesDocument2 pagesPerformance Analysis Name: Akshay Thakker (C-4) : SalesJay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Study of Consumer Buying Behaviour and Preferences IN Small Car SegmentDocument37 pagesStudy of Consumer Buying Behaviour and Preferences IN Small Car SegmenthimclashNo ratings yet
- Global Car Manufacturing: April 2019Document42 pagesGlobal Car Manufacturing: April 2019Abhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Financial ReviewDocument28 pagesCorporate Financial ReviewIshan KakkarNo ratings yet
- CB Insights Mobility Report 2020Document77 pagesCB Insights Mobility Report 2020k2mahenNo ratings yet
- RIL SegmentsDocument47 pagesRIL Segmentsdeepsinghrawat06No ratings yet
- India: Performance of Electric Vehicle Industry: Quarterly Update: Q1 FY 2021 (Apr'2020 - Jun'2020)Document10 pagesIndia: Performance of Electric Vehicle Industry: Quarterly Update: Q1 FY 2021 (Apr'2020 - Jun'2020)SoundararajanNo ratings yet
- Advacned Accounting IIDocument8 pagesAdvacned Accounting IIHamda AminNo ratings yet
- Afm Report Group 1 (Tata Motors)Document40 pagesAfm Report Group 1 (Tata Motors)ASHIKA DUGARNo ratings yet
- Exporting Services: A Developing Country PerspectiveFrom EverandExporting Services: A Developing Country PerspectiveRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Mcdonalds HistoryDocument1 pageMcdonalds HistoryPrakash SelvanNo ratings yet
- STP Analysis: Segmentation & TargetingDocument1 pageSTP Analysis: Segmentation & TargetingPrakash SelvanNo ratings yet
- Pricing StrategyDocument1 pagePricing StrategyPrakash SelvanNo ratings yet
- About The Company: Competition AnalysisDocument1 pageAbout The Company: Competition AnalysisPrakash SelvanNo ratings yet
- Marketing ObjectiveDocument1 pageMarketing ObjectivePrakash SelvanNo ratings yet
- 5C AnalysisDocument1 page5C AnalysisPrakash SelvanNo ratings yet
- Đề cương KTQTDocument6 pagesĐề cương KTQTNguyễn Thị Hồng HạnhNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Fundamentals 2015 Whittenburg 33rd Edition Test Bank Full DownloadDocument31 pagesIncome Tax Fundamentals 2015 Whittenburg 33rd Edition Test Bank Full Downloadjoannarobertscxaympjdnw100% (42)
- Itr-1 Sahaj Indian Income Tax Return: Acknowledgement Number: 996215700300819 Assessment Year: 2019-20Document6 pagesItr-1 Sahaj Indian Income Tax Return: Acknowledgement Number: 996215700300819 Assessment Year: 2019-20Satyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Edward GlaserDocument10 pagesEdward Glaserh67phxy2100% (1)
- PWC TP Perspectives Challenging TimesDocument64 pagesPWC TP Perspectives Challenging TimeshossainmzNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To TaxationDocument45 pages1 Introduction To TaxationCherrie Arianne Fhaye NarajaNo ratings yet
- Cir Vs St. LukesDocument15 pagesCir Vs St. LukesLalaine FelixNo ratings yet
- P6 SMART Notes Till 03.25Document61 pagesP6 SMART Notes Till 03.25Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Invoice: Email Info@greensoul - Online Website Greensoul - OnlineDocument1 pageInvoice: Email Info@greensoul - Online Website Greensoul - OnlineANIL KUMAR REDDYNo ratings yet
- Acctg Changes, Error Correction, Prior ErrorDocument3 pagesAcctg Changes, Error Correction, Prior ErrorLayJohn LacadenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four FundDocument13 pagesChapter Four FundnaodbrtiNo ratings yet
- Apr 2015 REALityDocument6 pagesApr 2015 REALityJohn LawsNo ratings yet
- NadiyaDocument61 pagesNadiyaAnonymous 22GBLsme1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Value Added Tax On Importation Multiple Choice: Theory - Agricultural or Marine Food Products: Part 1Document20 pagesChapter 2-Value Added Tax On Importation Multiple Choice: Theory - Agricultural or Marine Food Products: Part 1Carlo Baculo0% (2)
- Del Mar vs. PagcorDocument30 pagesDel Mar vs. PagcorG Ant MgdNo ratings yet
- In The Calculation of Return On Shareholders Investments The Referred Investment Deals WithDocument20 pagesIn The Calculation of Return On Shareholders Investments The Referred Investment Deals WithAnilKumarNo ratings yet
- BIR (Philippines) FBT Guidelines: Revenue Regulation 50-18Document16 pagesBIR (Philippines) FBT Guidelines: Revenue Regulation 50-18Cuayo JuicoNo ratings yet
- Markscheme: November 2016Document17 pagesMarkscheme: November 2016Jiwoo ChoiNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement (Short Form) Division: (Attach A Completed Schedule A)Document4 pagesFinancial Statement (Short Form) Division: (Attach A Completed Schedule A)rfortier6760No ratings yet
- National Savings CertificateDocument12 pagesNational Savings CertificateSiddesh PaiNo ratings yet
- AIO ThinkCentre Edge 72z - 92zDocument10 pagesAIO ThinkCentre Edge 72z - 92zJagabandhu PradhanNo ratings yet
- Miami Gazette From Jan 3, 1973-Jan 13, 1975 - Pt1.Document202 pagesMiami Gazette From Jan 3, 1973-Jan 13, 1975 - Pt1.marylcookpubliclibraNo ratings yet
- ACCO 20133: Income Taxation (Midterm Examination)Document7 pagesACCO 20133: Income Taxation (Midterm Examination)Kim EllaNo ratings yet
- Yojana February 2012Document52 pagesYojana February 2012Anshuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- A BIG Response To Wollstonecraft's Dilemma: Laura BambrickDocument13 pagesA BIG Response To Wollstonecraft's Dilemma: Laura BambrickCaptainSparrow77No ratings yet
- GDocument101 pagesGKartickDuttaNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Analysis 2Document2 pagesHorizontal Analysis 2Mayolito WajeNo ratings yet
- Kai Garden Residences Hinoki Building Unit and Parking Slot Computation (January 2020 Reservations)Document10 pagesKai Garden Residences Hinoki Building Unit and Parking Slot Computation (January 2020 Reservations)Lem MikeeNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Financial Sustainability of Taiwan's Health System: Modelling Health Expenditure Through 2035 by SJ TsaiDocument41 pagesUnderstanding The Financial Sustainability of Taiwan's Health System: Modelling Health Expenditure Through 2035 by SJ TsaisjtsaiNo ratings yet
- Brochure-Shriram-Genius-Plan-Offline TeluguDocument12 pagesBrochure-Shriram-Genius-Plan-Offline TeluguPraveen BabuNo ratings yet