Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rangamati Science & Technology University Assignment on Pay Model & Compensation Strategy
Uploaded by
Ferdous AminOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rangamati Science & Technology University Assignment on Pay Model & Compensation Strategy
Uploaded by
Ferdous AminCopyright:
Available Formats
Rangamati Science & Technology
University
Assignment On
The Pay Model & Compensation Strategy
Course Name: Compensation Management
Course Code: MGT-506
SUBMITTED TO
Mohona Biswas
Assistant Professor
Department of Management
Rangamati Science & Technology University
SUBMITTED BY:
Firoz Ahammad Bhuiyan
Reg.No: 2018-21-31
Roll: 31
Department of Management
Rangamati Science & Technology University
Submission Date: 20th July, 2021
Question 1: What Is Compensation/Pay?
“Compensation refers to all forms of financial returns and tangible services and benefits employees
receive as part of an employment relationship”- G.T. Milkovich and J.M. Nemwan in 2002.
Compensation includes the basic salary as well as rewards in the form of bonuses, overtime, leave,
insurance, company car, expense account, and other benefits. Not all compensation models are
alike. Some plans put the emphasis on the basic salary, while others are more focused on using
performance incentives. Some organization also offer profit share schemes to their employees if
they help to increase production and lower costs.
Question 2: What do you mean by Pay Model?
The Pay Model of Compensation and benefits helps managers to structurally design and
understand the compensation system for their employees. The model consists of three main
components:
a) Objective of the remuneration model
b) The policy that is the foundation for the structure
c) The techniques that link the policy to the objectives.
Figure 1: The Pay Model
Question 3: What are the objectives of compensation? Discuss them briefly.
Compensation Objective
Pay systems are designed to achieve certain objective. The basic objective are-
a) Efficiency
b) Fairness
c) Ethics
d) Compliance with law and regulation.
Let describe these objective below-
Efficiency: Efficiency can be stated more specifically as-
1. Improving performance, increasing quality, delighting customers and stockholders
2. Controlling labor cost
Fairness: Fairness is a fundamental objective of pay systems. Fairness means-
1. Ensure Fair treatment by recognizing both employee contributions and employee needs
2. Procedural fairness is the process used to make pay decisions and suggests that the way a pay
decision is made may be as important to the employee as the results of the decisions.
Ethics: Ethics refers to how an organization-
1. care about how its results are achieved
2. Managing pay sometimes creates ethical dilemmas
3. Manipulating results to ensure executive bonus payouts, misusing statistics used to measure
competitors’ pay rates, and shaving the hours recorded in employees’ time cards are all too common
examples of ethical lapses
Compliance with law and regulation: Compliance as a pay objective means conforming to
federal and state compensation laws and regulations. If law changes, pay systems need to be
change, too, to ensure contained compliance. As companies go global, the must comply with the
laws of all the countries in which they operate.
Question 4: Briefly discuss the policy decisions of the pay model
Four Policy Choices
Every employee must address the policy decisions shown on the left side of the pay model-
1. Internal alignment
2. External competitiveness
3. Employee contributions
4. Management
Let discuss about these objective briefly-
Internal alignment: Internal alignment refers to comparisons among jobs or skill levels inside a single
organization.
Jobs and people s’ skills are compared in terms of their relative contributions to the organization's
business objectives
Pertains to the pay rates both for employees doing equal work and for those doing dissimilar work
External competitiveness: Internal competitiveness refers to pay comparisons with competitors.
Compensation relationships external to the organization: comparison with competitors
Effects of decisions regarding how much and what forms have a twofold effect on objectives: To
ensure that pay is sufficient to attract and retain employees, To control labor costs to ensure
competitive pricing of products/ services
Employee contributions: Employee contributions focus on Relation emphasis placed on employee
performance as it directly affects employee’s attitudes and work performance.
Performance based pay affects fairness: employees need to understand the basis for judging
performance in order to believe that their pay is fair.
Management: A policy regarding management of the pay system is the lust building block in our model.
Management means ensuring that the right people get the right pay for achieving the right objectives in the
right way. The greatest system design in the world is useless without competent management.
Question 5: What is strategic compensation Question? What do you mean by
strategic compensation?
A strategic compensation strategy guides an organization’s approach to managing total employee
compensation. In the past, compensation may have been just a paycheck, but today it’s much more.
Employees seek employers that not only pay them a competitive wage, but also provide benefits
and programs which help them address other financial costs, such as healthcare and retirement
plans.
Question 6: What is Strategic Choice? Show it with a diagram.
Strategic Choice involves a whole process through which a decision is taken to choose a particular
option from various alternatives. There can be various methods through which the final choice can
be selected upon. Managers and decision makers keep both the external and internal environment
in mind before narrowing it down to one.
Strategy refers to the fundamental directions that an organization has chosen. An organization
defines its strategy through the tradeoffs it makes in choosing what (and what not) to do. Exhibit
2.2 relates these strategic choices to the quest for competitive advantage. At the corporate level,
the fundamental strategic choice is, what business should we be in? At the business unit level, the
choice shifts to, how do we gain and sustain competitive advantage? How do we win in those
businesses? At the function level the strategic choice is, how should total compensation help gain
and sustain competitive advantage? The ultimate purpose—the “so what?”—is to gain and sustain
competitive advantage.
Figure 2: Strategic Choice
Question 7: Discuss four steps of developing compensation strategy
Developing a compensation strategy involves four simple steps-
1. Assess Total Compensation Implications
2. Fit Policy Decisions to Strategy
3. Implement Strategy
4. Reassess the Fit
While the steps are simple, executing them is complex. Trial and error, experience, and insight play major
roles.
Figure 3: Four steps of developing compensation strategy
Step 1: Assess Total Compensation Implications
Think about any organization’s past, present, and, most vitally, future. What factors in its business
environment have contributed to the company’s success? Which of these factors are likely to become more
(or less) important as the company looks ahead? It classifies the factors as competitive dynamics,
culture/values, social and political context, employee/union needs, and other HR systems.
Step 2: Map a Total Compensation Strategy
The compensation strategy is made up of the five choices outlined in the pay model: objectives, alignment,
competitiveness, contributions, and management. Mapping these decisions is step 2 in developing a
compensation strategy. The aim is to make the right compensation choices based on how the organization
competes.
Steps 3 and 4: Implement and Reassess
Step 3 is to implement the strategy through the design and execution of the compensation system. The
compensation system translates strategy into practice—and into people’s bank accounts. Step 4, reassess
and realign, closes the loop. This step recognizes that the compensation strategy must change to fit changing
conditions. Thus, periodic reassessment is needed
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Sample Questionnaire On Customer Satisfaction in BanksDocument6 pagesSample Questionnaire On Customer Satisfaction in BanksFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Jahangirnagar University 1st Year BBA Provisional Results 2020-2021Document2 pagesJahangirnagar University 1st Year BBA Provisional Results 2020-2021Ferdous AminNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Rupali Bank LTD: BUS 401, SPRING 2019Document52 pagesInternship Report On Rupali Bank LTD: BUS 401, SPRING 2019Nokib AhammedNo ratings yet
- Forming Equation (Class-1+2+3+4) : Easy Questions: Single EquationDocument24 pagesForming Equation (Class-1+2+3+4) : Easy Questions: Single EquationFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Acceptance LetterDocument1 pageAcceptance LetterFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 8Document14 pagesParts of Speech 8Chaloemporn ChantongNo ratings yet
- Working from home challenges and changes in Japan during COVID-19Document13 pagesWorking from home challenges and changes in Japan during COVID-19Ferdous AminNo ratings yet
- Abul Khair GroupDocument1 pageAbul Khair GroupFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: Rangamati Science & Technology UniversityDocument17 pagesAssignment On: Rangamati Science & Technology UniversityFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Acceptance LetterDocument1 pageAcceptance LetterFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- HRM-502 (Labor Law and Text & Cases)Document9 pagesHRM-502 (Labor Law and Text & Cases)Ferdous AminNo ratings yet
- Welcome To My Presentation: Rangamati Science & Technology UniversityDocument10 pagesWelcome To My Presentation: Rangamati Science & Technology UniversityFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Rangamati Science & Technology University: Welcome To Our PresentationDocument11 pagesRangamati Science & Technology University: Welcome To Our PresentationFerdous AminNo ratings yet
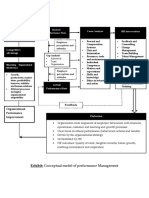
- Organizational Performance Improvement Strategy AnalysisDocument1 pageOrganizational Performance Improvement Strategy AnalysisFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Exhibit: Concept Model of Performance Management: Employee Perceptions and AttitudesDocument1 pageExhibit: Concept Model of Performance Management: Employee Perceptions and AttitudesFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: Rangamati Science & Technology UniversityDocument17 pagesAssignment On: Rangamati Science & Technology UniversityFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Mohona Mam Assignment/Arnob. Compensation PDFDocument5 pagesMohona Mam Assignment/Arnob. Compensation PDFFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- International Human Resource Management: Managing People in A Multinational ContextDocument19 pagesInternational Human Resource Management: Managing People in A Multinational ContextReazulNo ratings yet
- FULLTEXT01Document42 pagesFULLTEXT01Ferdous AminNo ratings yet
- IHRM 6th Edition Dowling Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesIHRM 6th Edition Dowling Solutions ManualFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- A Study On Trends and Challenges in Global HRM: Mrs. A. Mary FrancinaDocument7 pagesA Study On Trends and Challenges in Global HRM: Mrs. A. Mary FrancinaFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Mohona Mam Assignment/Ferdous - 2018-21-28Document9 pagesMohona Mam Assignment/Ferdous - 2018-21-28Ferdous AminNo ratings yet
- APA Style Reference Citations: Library Resource GuideDocument7 pagesAPA Style Reference Citations: Library Resource GuideAmyfarhana91No ratings yet
- Chapter One: Compensation: A Component of Human Resource SystemsDocument15 pagesChapter One: Compensation: A Component of Human Resource SystemsFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Forming Equation (Class-1+2+3+4) : Easy Questions: Single EquationDocument24 pagesForming Equation (Class-1+2+3+4) : Easy Questions: Single EquationFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- KOTTIKA - Market-Driving - Strategy - and - Personnel - Attributes - 2018Document41 pagesKOTTIKA - Market-Driving - Strategy - and - Personnel - Attributes - 2018Ferdous AminNo ratings yet
- Rtfuq - (: SFR.HDocument1 pageRtfuq - (: SFR.HFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- Department of National Defence: CanadaDocument31 pagesDepartment of National Defence: CanadaFerdous AminNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- BCG MatrixDocument4 pagesBCG MatrixAJEET893032100% (1)
- Tottenham Hotspur PLCDocument6 pagesTottenham Hotspur PLCdelf20% (2)
- DocumentDocument22 pagesDocumentsunilgudu190919No ratings yet
- Robbins Chapter 3 CultureDocument39 pagesRobbins Chapter 3 CultureMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- Konrath 14Document11 pagesKonrath 14MaskurNo ratings yet
- A Case Study in Perfect CompetitionDocument7 pagesA Case Study in Perfect CompetitionAddy Elia83% (6)
- DWERP BrochureDocument6 pagesDWERP Brochureronak shahNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1. MrketingDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 1. MrketingEricka Jean EspielNo ratings yet
- ISO 19011-2018 Terms and DefinitionsDocument4 pagesISO 19011-2018 Terms and DefinitionsredaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Bank For Strategic Marketing 9 E by CravensDocument13 pagesTest Bank Bank For Strategic Marketing 9 E by CravensRizwan100% (1)
- Master International Business and SustainabilityDocument1 pageMaster International Business and SustainabilityAsif NawazNo ratings yet
- SAP FICO New GL Accounting TrainingDocument41 pagesSAP FICO New GL Accounting TrainingDeepti Siripurapu100% (1)
- Ihrd 2Document22 pagesIhrd 2Krishna PatelNo ratings yet
- 15CV662Document2 pages15CV662UmeshNo ratings yet
- Blue Zone Systems PVT LTD IntroductionDocument9 pagesBlue Zone Systems PVT LTD IntroductionMilind DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- SDM AA Exam QuestionDocument3 pagesSDM AA Exam QuestionDonib PoonNo ratings yet
- Construction Recruitment Company Profile V07102021 EmailDocument14 pagesConstruction Recruitment Company Profile V07102021 EmailTakudzwaNo ratings yet
- Auditing AssignmentDocument4 pagesAuditing AssignmentDENEKEW LESEMINo ratings yet
- Recruitment SourcesDocument7 pagesRecruitment SourcesPuneet Jindal0% (1)
- Operations Manager in Miami FT Lauderdale FL Resume Omar IserDocument3 pagesOperations Manager in Miami FT Lauderdale FL Resume Omar IserOmarIserNo ratings yet
- Amazon Operating Model PDFDocument6 pagesAmazon Operating Model PDFJiva TuksNo ratings yet
- MAN101 PM WSU 2020 T1 FinalDocument7 pagesMAN101 PM WSU 2020 T1 FinalYen Trinh LeNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture About Environmental Management Systems: Department of Management Clemson UniversityDocument40 pagesThe Big Picture About Environmental Management Systems: Department of Management Clemson UniversitySamina PachaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER+1+Engineering+Management+by+Dr +Robert+MedinaDocument10 pagesCHAPTER+1+Engineering+Management+by+Dr +Robert+MedinaChristalee Samin100% (1)
- Earnings Management, Tax Shelters, and Managerial MotivationsDocument18 pagesEarnings Management, Tax Shelters, and Managerial MotivationspeaceendswithmeNo ratings yet
- Start Your Venture at GEB BootcampDocument35 pagesStart Your Venture at GEB BootcampAarya ShahNo ratings yet
- Ecsy Cola Question2Document8 pagesEcsy Cola Question2Dhagash SanghaviNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 POR 18530Document7 pagesAssignment2 POR 18530Hira RazaNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Plan: Your Career PathDocument12 pagesPersonal Development Plan: Your Career PathEduardo Aguirre ArenasNo ratings yet
- Core Banking Cedar ViewDocument4 pagesCore Banking Cedar ViewRohit ManchandaNo ratings yet