Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Xi Comparison With Revised Syllabus 2021-22
Uploaded by
Avyukta SOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Xi Comparison With Revised Syllabus 2021-22
Uploaded by
Avyukta SCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
Original syllabus 2021 - Term wise Syllabus 2022 - Deleted
22 22 Portion
s
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 1|Page
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
Chapter–1:
Syllabus assigned for first term Physical
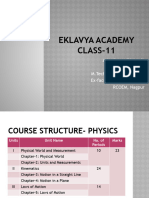
Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Unit I: Physical World and Measurement 6 World
10 Periods Periods Physics-scope
Chapter–1: Physical World Chapter–1: Physical World and
Physics-scope and excitement; nature of Physics-scope and excitement; nature of excitement;
physical laws; Physics, technology and physical laws; Physics, technology and nature of
society. society. (To be discussed as a part of physical laws;
Introduction and integrated with other topics) Physics,
technology
Chapter–2: Units and Measurements Chapter–2: Units and Measurements and society
Need for measurement: Units of Need for measurement: Units of (To be
measurement; systems of units; SI units, measurement; systems of units; SI units, discussed as a
fundamental and derived units. Length, mass fundamental and derived units. Length, mass part of
and time measurements; accuracy and and time measurements; accuracy and Introduction
precision of measuring instruments; errors in precision of measuring instruments; errors in and integrated
measurement; significant figures. measurement; significant figures. with other
Dimensions of physical quantities, Dimensions of physical quantities, topics)
dimensional analysis and its applications. dimensional analysis and its applications.
Unit II: Kinematics 24 Periods Unit II: Kinematics 16 Periods
Chapter–3: Motion in a Straight Line Chapter–3: Motion in a Straight Line Chapter-3 :
Frame of reference, Motion in a straight line: Elementary concepts of differentiation and Motion in a
Position-time graph, speed and velocity. integration for describing motion, uniform straight line
Elementary concepts of differentiation and and non- uniform motion, average speed and Frame of
integration for describing motion, uniform instantaneous velocity, uniformly accelerated reference,
and non- uniform motion, average speed and motion, velocity - time and position-time Motion in a
instantaneous velocity, uniformly accelerated graphs. Relations for uniformly accelerated straight line:
motion, velocity - time and position-time motion (graphical treatment). Position-time
graphs. Relations for uniformly accelerated graph, speed
motion (graphical treatment). and velocity
Chapter–4: Motion in a Plane Chapter–4: Motion in a Plane
Scalar and vector quantities; position and Scalar and vector quantities; position and
displacement vectors, general vectors and displacement vectors, general vectors and
their notations; equality of vectors, their notations; equality of vectors,
multiplication of vectors by a real number; multiplication of vectors by a real number;
addition and subtraction of vectors, relative addition and subtraction of vectors, relative
velocity, Unit vector; resolution of a vector in velocity, Unit vector; resolution of a vector in
a plane, rectangular components, Scalar and a plane, rectangular components, Scalar and
Vector product of vectors. Motion in a plane, Vector product of vectors. Motion in a plane,
cases of uniform velocity and uniform cases of uniform velocity and uniform
acceleration projectile motion, uniform acceleration-projectile motion, uniform
circular motion. circular motion.
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 2|Page
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
Unit III: Laws of Motion 14 Periods
Chapter–5: Laws of Motion
Intuitive concept of force, Inertia, Newton's Unit III: Laws of Motion 10 Periods Chapter-5
first law of motion; momentum and Newton's Chapter–5: Laws of Motion Laws of
second law of motion; impulse; Newton's Intuitive concept of force, Inertia, Newton's Motion
third law of motion. first law of motion; momentum and Newton's Intuitive
second law of motion; impulse; Newton's concept of
Law of conservation of linear momentum and third law of motion. (Recapitulation only) force, Inertia,
its applications. Equilibrium of concurrent Newton's first
forces, Static and kinetic friction, laws of Law of conservation of linear momentum and law of motion;
momentum and
friction, rolling friction, lubrication. its applications. Equilibrium of concurrent Newton's
Dynamics of uniform circular motion: forces, Static and kinetic friction, laws of second law of
Centripetal force, examples of circular motion friction, rolling friction, lubrication. motion;
(vehicle on a level circular road, vehicle on a Dynamics of uniform circular motion: impulse;
banked road). Centripetal force, examples of circular motion Newton's third
(vehicle on a level circular road, vehicle on a law of motion
banked road).
Unit IV: Work, Energy and Power 12 Unit IV: Work, Energy and Power 12
Periods Periods
Chapter–6: Work, Energy and Power Chapter–6: Work, Energy and Power
Work done by a constant force and a variable Work done by a constant force and a variable
force; kinetic energy, work-energy theorem, force; kinetic energy, work-energy theorem,
power. Notion of potential energy, potential power. Notion of potential energy, potential
energy of a spring, conservative forces: energy of a spring, conservative forces:
conservation of mechanical energy (kinetic conservation of mechanical energy (kinetic
and potential energies); non-conservative and potential energies); non-conservative
forces: motion in a vertical circle; elastic and forces: motion in a vertical circle; elastic and
inelastic collisions in one and two inelastic collisions in one and two
dimensions. dimensions.
Unit V: Motion of System of Particles and Unit V: Motion of System of Particles and
Rigid Body 18 Periods Rigid Body 16 Periods
Chapter–7: System of Particles and Chapter–7: System of Particles and Chapter-7
Rotational Motion Rotational Motion System of
Centre of mass of a two-particle system, Centre of mass of a two-particle system, Particles and
momentum conservation and Centre of mass momentum conservation and Centre of mass Rotational
motion. Centre of mass of a rigid body; motion. Centre of mass of a rigid body; Motion
Centre of mass of a uniform rod. Moment of a Centre of mass of a uniform rod. Moment of a
force, torque, angular momentum, law of force, torque, angular momentum, law of Statement of
conservation of angular momentum and its conservation of angular momentum and its parallel and
applications. Equilibrium of rigid bodies, applications. Equilibrium of rigid bodies, perpendicular
rigid body rotation and equations of rotational rigid body rotation and equations of rotational axes theorems
motion, comparison of linear and rotational motion, comparison of linear and rotational and their
motions. Moment of inertia, radius of motions. Moment of inertia, radius of applications.
gyration, values of moments of inertia for gyration, values of moments of inertia for
simple geometrical objects (no derivation).
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 3|Page
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
simple geometrical objects (no derivation).
Statement of parallel and perpendicular
axes theorems and their applications.
Unit VI: Gravitation 12 Periods Unit VI: Gravitation 8 Periods Chapter-8
Chapter–8: Gravitation Chapter–8: Gravitation Gravitation
Kepler's laws of planetary motion, universal Universal law of gravitation. Acceleration due Kepler's laws
law of gravitation. Acceleration due to gravity to gravity (recapitulation only) and its of planetary
and its variation with altitude and depth. variation with altitude and depth. motion,
Gravitational potential energy and Gravitational potential energy and Acceleration
gravitational potential, escape velocity, orbital gravitational potential, escape velocity, orbital due to gravity
velocity of a satellite, Geo-stationary velocity of a satellite, Geo-stationary
satellites. satellites.
Syllabus assigned for Term II
Unit VII: Properties of Bulk Matter 24 Unit VII: Properties of Bulk Matter 22 Chapter-9
Periods Periods Mechanical
Chapter–9: Mechanical Properties of Chapter–9: Mechanical Properties of Properties of
Solids Solids Solids
Elastic behaviour, Stress-strain relationship, Stress-strain relationship, Hooke's law, Elastic
Hooke's law, Young's modulus, bulk Young's modulus, bulk modulus behaviour,
shear modulus
modulus, shear modulus of rigidity, Poisson's of rigidity,
ratio; elastic energy. Poisson's ratio;
elastic energy.
Chapter–10: Mechanical Properties of Chapter–10: Mechanical Properties of
Fluids Fluids
Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal's law Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal's law
and its applications (hydraulic lift and and its applications (hydraulic lift and
hydraulic brakes), effect of gravity on fluid hydraulic brakes), effect of gravity on fluid
pressure. Viscosity, Stokes' law, terminal pressure. Viscosity, Stokes' law, terminal
velocity, streamline and turbulent flow, velocity, streamline and turbulent flow,
critical velocity, Bernoulli's theorem and its critical velocity, Bernoulli's theorem and its
applications. Surface energy and surface applications. Surface energy and surface
tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure
across a curved surface, application of surface across a curved surface, application of surface
tension ideas to drops, bubbles and capillary tension ideas to drops, bubbles and capillary
rise. rise.
Chapter–11: Thermal Properties of Matter Chapter–11:Thermal Properties of Matter Chapter-11
Heat, temperature, Heat, temperature, (recapitulation only) Thermal
thermal expansion; thermal expansion of thermal expansion; thermal expansion of properties
solids, liquids and gases, anomalous solids, liquids and gases, anomalous matter
expansion of water; specific heat capacity; expansion of water; specific heat capacity; Heat,
Cp, Cv - calorimetry; change of state - latent Cp, Cv - calorimetry; change of state - latent temperature,
Heat transfer-
heat capacity. Heat transfer-conduction, heat capacity. Heat transfer-conduction, conduction,
convection and radiation, thermal convection and radiation (recapitulation only), convection and
conductivity, qualitative ideas of Blackbody thermal conductivity, qualitative ideas of radiation
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 4|Page
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
radiation, Wein's displacement Law, Stefan's Blackbody radiation, Wein's displacement
law, and Greenhouse effect. Law, Stefan's law, and Greenhouse effect.
Unit VIII: Thermodynamics 12 Periods Unit VIII: Thermodynamics 10 Periods Chapter-12
Chapter–12: Thermodynamics Chapter–12: Thermodynamics Thermodyna
Thermal equilibrium and definition of Thermal equilibrium and definition of mics
temperature (zeroth law of thermodynamics), temperature (zeroth law of thermodynamics),
heat, work and internal energy. First law of heat, work and internal energy. First law of Heat engine
thermodynamics, isothermal and adiabatic thermodynamics, isothermal and adiabatic and
processes. Second law of thermodynamics: processes. Second law of thermodynamics: refrigerator.
reversible and irreversible processes, Heat reversible and irreversible processes
engine and refrigerator.
Unit IX: Behaviour of Perfect Gases and Unit IX: Behaviour of Perfect Gases and
Kinetic Theory of Gases 08 Periods Kinetic Theory of Gases 08 Periods
Chapter–13: Kinetic Theory Chapter–13: Kinetic Theory
Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done
in compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases in compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases
- assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic - assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic
interpretation of temperature; rms speed of interpretation of temperature; rms speed of
gas molecules; degrees of freedom, law of gas molecules; degrees of freedom, law of
equi-partition of energy (statement only) and equi-partition of energy (statement only) and
application to specific heat capacities of application to specific heat capacities of
gases; concept of mean free path, Avogadro's gases; concept of mean free path, Avogadro's
number. number.
Unit X: Oscillations and Waves 26 Periods Unit X: Oscillations and Waves 23 Periods
Chapter–14: Oscillations Chapter–14: Oscillations
Periodic motion - time period, frequency, Periodic motion - time period, frequency,
displacement as a function of time, periodic displacement as a function of time, periodic
functions. Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M) functions. Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M)
and its equation; phase; oscillations of a and its equation; phase; oscillations of a
loaded spring- restoring force and force loaded spring- restoring force and force
constant; energy in S.H.M. Kinetic and constant; energy in S.H.M. Kinetic and
potential energies; simple pendulum potential energies; simple pendulum
derivation of expression for its time period. derivation of expression for its time period.
Free, forced and damped oscillations Free, forced and damped oscillations
(qualitative ideas only), resonance. (qualitative ideas only), resonance.
Chapter–15: Waves Chapter–15: Waves Chapter-15
Wave motion: Transverse and longitudinal Wave motion: Transverse and longitudinal Waves
waves, speed of travelling wave, displacement waves, speed of travelling wave, displacement Fundamental
relation for a progressive wave, principle of relation for a progressive wave, principle of mode and
harmonics,
superposition of waves, reflection of waves, superposition of waves, reflection of waves,
Doppler effect.
standing waves in strings and organ pipes, standing waves in strings and organ pipes,
Beats
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 5|Page
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
fundamental mode and harmonics, Beats,
Doppler effect.
PRACTICALS Practicals:
PRACTICALS Total Periods: 60 Syllabus for TERM I Total Periods: 16 No
The record, to be submitted by the students, at investigatory
The record, to be submitted by the students, at the time of their First term examination, has project and
the time of their annual examination, has to include: Activity to be
to include: Record of at least 4 Experiments, to be demonstrated
• Record of at least 12 Experiments [with 6 performed by the students 8 experiments
from each section], to be performed by the Record of at least 3 Activities [with 3 each ( clubbed
students. from section A and section B], to be based on
• Record of at least 6 Activities [with 3 each demonstrated by teacher. skills ) in
from section A and section B], to be 8Marks place of 12
performed by the students.
• Report of the project to be carried out by the
students.
EVALUATION SCHEME
Time Allowed: Three hours Max. Marks: 30 Time Allowed: One
Two experiments one from each section 7+7 and half hours
Marks Max. Marks: 30
Practical record (experiment and activities) 5 Two experiments
Marks one from each
One activity from any section 3 Marks section 8 Marks.
Investigatory Project 3 Marks Practical record 2Marks
Viva on experiments, activities and project 5 (experiment and
Marks activities) 2 Marks.
Total 30 Marks Viva on 5 Marks
SECTION–A experiments, and
Experiments activities 5 Marks.
1. To measure diameter of a small spherical/ Total 15 Marks. 15 Marks
cylindrical body and to measure internal Syllabus assigned for Practical Term I
diameter and depth of a given beaker/
calorimeter using Vernier Calipers and hence
find its volume. Experiments: -
2. To measure diameter of a given wire and 1. To measure diameter of a small spherical/
thickness of a given sheet using screw gauge. cylindrical body and to measure internal
3. To determine volume of an irregular lamina diameter and depth of a given beaker/
using screw gauge. calorimeter using Vernier Calipers and hence
4. To determine radius of curvature of a given find its volume.
spherical surface by a spherometer. 2. To measure diameter of a given wire and
5. To determine the mass of two different thickness of a given sheet using screw gauge.
objects using a beam balance. OR
6. To find the weight of a given body using To determine volume of an irregular lamina
parallelogram law of vectors. using screw gauge.
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 6|Page
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
7. Using a simple pendulum, plot its L-T2 3. To determine radius of curvature of a given
graph and use it to find the effective length of spherical surface by a spherometer.
second's pendulum. 4. To determine the mass of two different
8. To study variation of time period of a objects using a beam balance.
simple pendulum of a given length by taking 5. To find the weight of a given body using
bobs of same size but different masses and parallelogram law of vectors.
interpret the result. 6. Using a simple pendulum, plot its L-T2
9. To study the relationship between force of graph and use it to find the effective length of
limiting friction and normal reaction and to second's pendulum.
find the co- efficient of friction between a OR
block and a horizontal surface. To study variation of time period of a simple
10. To find the downward force, along an pendulum of a given length by taking bobs of
inclined plane, acting on a roller due to same size but different masses and interpret
gravitational pull of the earth and study its the result.
relationship with the angle of inclination θ 7. To study the relationship between force of
by plotting graph between force and sinθ. limiting friction and normal reaction and to
find the co- efficient of friction between a
Activities block and a horizontal surface.
1. To make a paper scale of given least count, OR
e.g., 0.2cm, 0.5 cm. To find the downward force, along an
2. To determine mass of a given body using a inclined plane, acting on a roller due to
metre scale by principle of moments. gravitational pull of the earth and study its
3. To plot a graph for a given set of data, with relationship with the angle of inclination θ by
proper choice of scales and error bars. plotting graph between force and sin θ.
4. To measure the force of limiting friction for Activities
rolling of a roller on a horizontal plane. 1. To make a paper scale of given least count,
5. To study the variation in range of a e.g., 0.2cm, 0.5 cm.
projectile with angle of projection. 2. To determine mass of a given body using a
6. To study the conservation of energy of a metre scale by principle of moments.
ball rolling down on an inclined plane (using 3. To plot a graph for a given set of data, with
a double inclined plane). proper choice of scales and error bars.
7. To study dissipation of energy of a simple 4. To measure the force of limiting friction for
pendulum by plotting a graph between rolling of a roller on a horizontal plane.
square of amplitude and time. 5. To study the variation in range of a
projectile with angle of projection.
6. To study the conservation of energy of a
ball rolling down on an inclined plane (using
SECTION–B a double inclined plane).
Experiments 7. To study dissipation of energy of a simple
1. To determine Young's modulus of elasticity pendulum by plotting a graph between square
of the material of a given wire. of amplitude and time.
2. To find the force constant of a helical
spring by plotting a graph between load and Class XI Syllabus for TERM II Total
extension. Periods: 16
3. To study the variation in volume with Experiments 15 Marks
pressure for a sample of air at constant 1. To determine Young's modulus of
temperature by plotting graphs between P and elasticity of the material of a given wire.
V, and between P and 1/V. OR
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 7|Page
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
4. To determine the surface tension of water To find the force constant of a helical spring
by capillary rise method. by plotting a graph between load and
5. To determine the coefficient of viscosity of extension.
a given viscous liquid by measuring terminal 2. To study the variation in volume with
velocity of a given spherical body. pressure for a sample of air at constant
6. To study the relationship between the temperature by plotting graphs between P
temperature of a hot body and time by and V, and between P and 1/V.
plotting a cooling curve. 3. To determine the surface tension of water
7. To determine specific heat capacity of a by capillary rise method.
given solid by method of mixtures. OR
8. To study the relation between frequency To determine the coefficient of viscosity of
and length of a given wire under constant a given viscous liquid by measuring
tension using sonometer. terminal velocity of a given spherical body.
9. To study the relation between the length of 4. To study the relationship between the
a given wire and tension for constant temperature of a hot body and time by
frequency using sonometer. plotting a cooling curve.
10. To find the speed of sound in air at room 5. To determine specific heat capacity of a
temperature using a resonance tube by two given solid by method of mixtures.
resonance positions.
Activities 6. To study the relation between frequency
1. To observe change of state and plot a and length of a given wire under constant
cooling curve for molten wax. tension using sonometer.
2. To observe and explain the effect of OR
heating on a bi-metallic strip. To study the relation between the length of
3. To note the change in level of liquid in a a given wire and tension for constant
container on heating and interpret the frequency using sonometer.
observations. 7. To find the speed of sound in air at room
4. To study the effect of detergent on surface temperature using a resonance tube by two
tension of water by observing capillary rise. resonance positions.
5. To study the factors affecting the rate of
loss of heat of a liquid. Activities
6. To study the effect of load on depression of 1. To observe change of state and plot a
a suitably clamped metre scale loaded at cooling curve for molten wax.
(i) its end (ii) in the middle. 2. To observe and explain the effect of
7. To observe the decrease in pressure with heating on a bi-metallic strip.
increase in velocity of a fluid. 3. To note the change in level of liquid in a
container on heating and interpret the
observations.
4. To study the effect of detergent on
surface tension of water by observing
capillary rise.
5. To study the factors affecting the rate of
loss of heat of a liquid.
6. To study the effect of load on depression
of a suitably clamped metre scale loaded at
(i) its end (ii) in the middle.
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 8|Page
Comparison of term wise Syllabus with original
Syllabus Class: XI
Session 2021-22
7. To observe the decrease in pressure with
increase in velocity of a fluid.
P. K. Patidar, KV Khargone 9|Page
You might also like
- Revised Syllabus Comparison With Original Syllabus 2020-21-Class 11Document5 pagesRevised Syllabus Comparison With Original Syllabus 2020-21-Class 11John Kevin 12A22No ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Ncert Textbook (Rationalised 2023-24)Document7 pagesClass 12 Physics Ncert Textbook (Rationalised 2023-24)rajvanshiaditya549No ratings yet
- Comparison of Revised Physics Syllabus 2020-21Document7 pagesComparison of Revised Physics Syllabus 2020-21Krish Maheshwari100% (1)
- Cbse Classs 11 Physics Syllabus 2019 20Document13 pagesCbse Classs 11 Physics Syllabus 2019 20PANKAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- The Indian Community School, Kuwait Syllabus Plan For The Year 2017-2018Document8 pagesThe Indian Community School, Kuwait Syllabus Plan For The Year 2017-2018Zainab NaginaNo ratings yet
- NEET Syllabus 2023 PhysicsDocument5 pagesNEET Syllabus 2023 PhysicsVogolus machatteNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsAkash Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Splitup Syllabus Physics XI 2023-24Document4 pagesSplitup Syllabus Physics XI 2023-24aknk1000No ratings yet
- 11th PhysicsDocument10 pages11th PhysicsPrivacy 01No ratings yet
- Physics Syllabus Class 11Document4 pagesPhysics Syllabus Class 11Dhanay GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Syllabus For Higher Secondary First Year CourseDocument6 pagesPhysics: Syllabus For Higher Secondary First Year CoursesatishNo ratings yet
- 5 6258304504651842354Document193 pages5 6258304504651842354PevolNo ratings yet
- Sri Sathya Sai Vidya Vihar, Indore Physics-Xi Annual Examination 2021 S.NO. Unit IDocument6 pagesSri Sathya Sai Vidya Vihar, Indore Physics-Xi Annual Examination 2021 S.NO. Unit IpranjaliNo ratings yet
- CLASS XI (Theory) - 2021-22: Physics SyllabusDocument15 pagesCLASS XI (Theory) - 2021-22: Physics SyllabusAditya HotaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Syllabus 2021-22Document9 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Syllabus 2021-22Anshul BhallaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS (Code No. 042) Course Structure Class XI (Theory) (2018-19)Document9 pagesPHYSICS (Code No. 042) Course Structure Class XI (Theory) (2018-19)arpit sharmaNo ratings yet
- 129 Physics Xi, Xii 2023 24Document16 pages129 Physics Xi, Xii 2023 24Abantika DevNo ratings yet
- Physics SrSec 2022-23Document24 pagesPhysics SrSec 2022-23Lets StartNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 2022-23 SyllabusDocument24 pagesPhysics Class 12 2022-23 SyllabusAviralTNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument76 pagesUntitledSanjay RKNo ratings yet
- PCDocument117 pagesPCClint BryNo ratings yet
- Syllabus (Physics)Document4 pagesSyllabus (Physics)Ishhani TalpatraNo ratings yet
- 7 PhysicsDocument19 pages7 Physicsapi-352990570No ratings yet
- NEET Physics SyllabusDocument8 pagesNEET Physics SyllabusNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Jee Main 2024 As On 01 November 2023 Pages 4Document1 pageSyllabus For Jee Main 2024 As On 01 November 2023 Pages 4pojahag371No ratings yet
- 41 PhysicsDocument19 pages41 PhysicsSenpai KorouNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Eng 202122Document8 pages11 Physics Eng 202122pankaj sodhiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Class Ix and Xi TopicsDocument2 pagesComparison of Class Ix and Xi TopicsvarunazimNo ratings yet
- Physics: UNIT-VI: Statistics and ProbabilityDocument12 pagesPhysics: UNIT-VI: Statistics and ProbabilityM CHANDRASEKHARNo ratings yet
- Cbse Board Physics SyllabusDocument4 pagesCbse Board Physics Syllabusapi-139761950No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument17 pagesSyllabusakdn1528No ratings yet
- SM 11 Physics Eng 201617 PDFDocument325 pagesSM 11 Physics Eng 201617 PDFNiranjan kumarNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Syllabus 2022-23Document17 pagesClass 11 Physics Syllabus 2022-23akmNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Term Wise Physics Syllabus 2021-22Document8 pagesCBSE Class 11 Term Wise Physics Syllabus 2021-22VBCA 11 B4 KRITHICK BALA BNo ratings yet
- NEET Syllabus PDFDocument23 pagesNEET Syllabus PDFSatyam jhaNo ratings yet
- Jupeb 2019 Physics SyllabusDocument14 pagesJupeb 2019 Physics SyllabusjulliehenerdeszNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS (Code No. 042) Course Structure Class XI (Theory) (2018-19)Document19 pagesPHYSICS (Code No. 042) Course Structure Class XI (Theory) (2018-19)BarunMondalNo ratings yet
- 11th Physics SyllabusDocument3 pages11th Physics SyllabusFreQuency Career InsTituteNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam Physics Portions G 11 2023-24Document2 pagesAnnual Exam Physics Portions G 11 2023-24luciuszogratis561No ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus in Physics STD XI For 2020 21Document5 pagesRevised Syllabus in Physics STD XI For 2020 21Barca LuisNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Assigned For Term I (Theory) : Biology at EaseDocument19 pagesSyllabus Assigned For Term I (Theory) : Biology at EaseDILSHAD AYJNISHDNo ratings yet
- Physics Session 2018 19 Term Wise SyllabusDocument12 pagesPhysics Session 2018 19 Term Wise SyllabusEASY TECHSNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 2Document3 pagesKinematics 2C.Madan KumarNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I Basic Concepts& EquilibriumDocument1 pageUNIT - I Basic Concepts& EquilibriumMahesh J. UmaNo ratings yet
- NEET Physics Syllabus 2024 - Overview of Exam TopicsDocument14 pagesNEET Physics Syllabus 2024 - Overview of Exam TopicsMasroor ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Physics Syllabus 11thDocument9 pagesPhysics Syllabus 11thVaibhav Kumar100% (1)
- Class 11 PhysicsDocument15 pagesClass 11 Physicsanand maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Physics Class Xi 2013 14Document241 pagesPhysics Class Xi 2013 14Rajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument336 pagesPHYSICSG Srinivasa Rao100% (2)
- Physics Syllabus 2024Document5 pagesPhysics Syllabus 2024C1B-33-AdityaNo ratings yet
- Model Papers XiDocument69 pagesModel Papers XiManit100% (1)
- LIST OF TOPICS IN PHYSICS JeeDocument6 pagesLIST OF TOPICS IN PHYSICS JeeLalasaNo ratings yet
- All India PreDocument24 pagesAll India PrearsathmohamedNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For The Unit Test-2Document1 pageSyllabus For The Unit Test-2TGC NINJANo ratings yet
- Sacred Heart Neet Lesson PlanDocument25 pagesSacred Heart Neet Lesson PlanBALAYASJNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Physics GAT (UGTP) 2013: Section - B Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesSyllabus - Physics GAT (UGTP) 2013: Section - B Page 1 of 8Saikrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Physics SyllabusDocument4 pagesPhysics SyllabusFroFee FNo ratings yet
- Phys FinalDocument17 pagesPhys FinalkroybarasatNo ratings yet
- Design of Lifting Hook: Earth Fill Load (Dl2)Document21 pagesDesign of Lifting Hook: Earth Fill Load (Dl2)Asaru DeenNo ratings yet
- MOM LAB REPPORT No 4Document10 pagesMOM LAB REPPORT No 4Faizan AnjumNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-03 Velocity and Graphs PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics 01-03 Velocity and Graphs PDFwade aryanNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) With Answers On Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) With Answers On Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagraml8o8r8d8s8i8v8100% (1)
- Module 1Document146 pagesModule 1DARSAN DEVANANDNo ratings yet
- Module 2 PDFDocument18 pagesModule 2 PDFNidonama E. KabmatNo ratings yet
- CelerityDocument23 pagesCelerityswabrightNo ratings yet
- Electricity Shobhit Nirwan PDFDocument10 pagesElectricity Shobhit Nirwan PDFAbhishek97% (32)
- Topic 2 - Analysis of Flanged Section (Ec2)Document20 pagesTopic 2 - Analysis of Flanged Section (Ec2)RCdesign201267% (3)
- Retaining Wall CalculationDocument6 pagesRetaining Wall Calculationabubakar aliNo ratings yet
- 6143 PDFDocument24 pages6143 PDFgoogley71No ratings yet
- Wind TurbineDocument10 pagesWind TurbineJohn Marcelino Y. NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Frame AnalysisDocument11 pagesBicycle Frame Analysisraghunath670743No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document44 pagesChapter 1NadiaNo ratings yet
- Constitutive Equation For AISI4140 Steel Applicable To A Wide Range of Strain Rates at Elevated TemperaturesDocument6 pagesConstitutive Equation For AISI4140 Steel Applicable To A Wide Range of Strain Rates at Elevated TemperaturesWinston SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Two Way Slab (First Slab Level Slabs)Document15 pagesTwo Way Slab (First Slab Level Slabs)Anjali DudhyalNo ratings yet
- WS Physics 312 E L4Document2 pagesWS Physics 312 E L4Eira SethiNo ratings yet
- MODULAR QUIZ - 48 - Theory 3Document9 pagesMODULAR QUIZ - 48 - Theory 3Cornelio J. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Problem SetsDocument23 pagesMachine Design Problem SetsMAX LAPINGCAO100% (1)
- Statics Problems & SolutionsDocument39 pagesStatics Problems & SolutionsYanli Baltero Cruz100% (1)
- Response of Full-Scale Three-Story Flat-Plate Test Structure To Cycles of Increasing Lateral LoadDocument12 pagesResponse of Full-Scale Three-Story Flat-Plate Test Structure To Cycles of Increasing Lateral LoadThai DamNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations and Electromagnetic WavesDocument20 pagesMaxwell's Equations and Electromagnetic WavesDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Compound Pendulum 2016Document5 pagesCompound Pendulum 2016Mubashar Fareed100% (1)
- PHET Forces 1D WorksheetDocument2 pagesPHET Forces 1D WorksheetNabil HamidehNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The Philippines: The Students As A Graduate of The BSME Program Will Be Able ToDocument4 pagesTechnological University of The Philippines: The Students As A Graduate of The BSME Program Will Be Able ToMarvin Sarmiento TalimonganNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument3 pagesEngineering MechanicszacpopecornNo ratings yet
- Pitot Tube Fluids EssayDocument12 pagesPitot Tube Fluids EssaysceroxNo ratings yet
- Problem Set-02Document2 pagesProblem Set-02linn.pa.pa.khaing.2020.2021.fbNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory Question BankDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic Theory Question BankDakshayaniDurgaNo ratings yet
- Day 6 SolutionsDocument4 pagesDay 6 SolutionsLiz KiNo ratings yet