Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JEE (Main) 2022 Physics Revision Bulletin
Uploaded by
FroFee F0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views4 pagesThis document provides an information bulletin on the JEE (Main) exam for 2022. It outlines 14 units that will be covered in the Physics section of the exam, including topics like kinematics, laws of motion, work, energy and power, oscillations and waves, electrostatics, magnetic effects of current and magnetism, electromagnetic induction, and alternating currents. The document provides a high-level overview of the key concepts that will be evaluated in each exam unit.
Original Description:
Original Title
Physics Syllabus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an information bulletin on the JEE (Main) exam for 2022. It outlines 14 units that will be covered in the Physics section of the exam, including topics like kinematics, laws of motion, work, energy and power, oscillations and waves, electrostatics, magnetic effects of current and magnetism, electromagnetic induction, and alternating currents. The document provides a high-level overview of the key concepts that will be evaluated in each exam unit.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
85 views4 pagesJEE (Main) 2022 Physics Revision Bulletin
Uploaded by
FroFee FThis document provides an information bulletin on the JEE (Main) exam for 2022. It outlines 14 units that will be covered in the Physics section of the exam, including topics like kinematics, laws of motion, work, energy and power, oscillations and waves, electrostatics, magnetic effects of current and magnetism, electromagnetic induction, and alternating currents. The document provides a high-level overview of the key concepts that will be evaluated in each exam unit.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
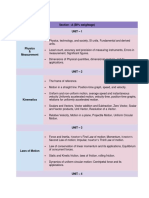
INFORMATION BULLETIN: JEE (Main) - 2022
PHYSICS Elastic and inelastic collisions in one
and two dimensions.
UNIT 1: PHYSICS AND MEASUREMENT
Physics, technology, and society, S I UNITS: ROTATIONAL MOTION
Units, fundamental and derived units, least
Centre of the mass of a two-particle
count, accuracy and prec1s1on of
system, Centre of the mass of a rigid body;
measuring instruments, Errors in
Basic concepts of rotational motion; a
measurement, Dimensions of Physics
moment of a force; torque, angular
quantities, dimensional analysis, and its
momentum, conservation of angular
applications.
momentum and its applications; the
UNIT 2: KINEMATICS moment of inertia, the radius of gyration.
Values of moments of inertia for
The frame of reference, motion in a
straight line, Position- time graph, speed simple geometrical objects, parallel and
and velocity; Uniform and non-uniform perpendicular axes theorems, and their
motion, average speed and instantaneous applications. Rigid body rotation equations
velocity, uniformly accelerated motion, of rotational motion.
velocity-time, pos1t10n-time graph,
UNIT 6: GRAVITATION
relations for uniformly accelerated motion,
Scalars and Vectors, Vector. Addition and The universal law of gravitation.
subtraction, zero vector, scalar and vector Acceleration due to gravity and its
products, Unit Vector, Resolution of a variation with altitude and depth. Kepler's
Vector. Relative Velocity, Motion in a law of planetary motion. Gravitational
plane, Projectile Motion, Uniform Circular potential energy; gravitational potential.
Motion. Escape velocity, Orbital velocity of a
satellite. Geo stationary satellites.
UNIT 3: LAWS OF MOTION
UNIT 7: PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS
Force and inertia, Newton's First law of
motion; Momentum, Newton's Second Elastic behaviour, Stress-strain relationship, Hooke's
Law. Young's modulus, bulk modulus, modulus of
Law of motion, Impulses; Newton's Third
rigidity. Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal's law
Law of motion. Law of conservation of and its applications. Viscosity. Stokes' law. terminal
linear momentum and its applications. velocity, streamline, and turbulent flow. Reynolds
Equilibrium of concurrent forces. number. Bernoulli's principle and its applications.
Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact,
Static and Kinetic friction, laws of friction, application of surface tension - drops, bubbles, and
rolling friction. capillary rise. Heat, temperature, thermal expansion;
specific heat capacity, calorimetry; change of state,
Dynamics of uniform circular motion: latent heat. Heat transfer-conduction, convection,
and radiation. Newton's law of cooling.
centripetal force and its applications.
UNIT 8: THERMODYNAMICS
UNIT 4: WORK, ENERGY, AND POWER
Thermal equilibrium, zeroth law of thermodynamics,
the concept of temperature. Heat, work, and internal
Work done by a content force and a
energy. The first law of thermodynamics. The
variable force; kinetic and potential second law of thermodynamics: reversible and
energies, work-energy theorem, power. irreversible processes. Carnot engine and its
efficiency.
The potential energy of spring
conservation of mechanical energy,
conservative and neoconservative forces;
INFORMATION BULLETIN: JEE (Main) - 2022
UNIT 9: KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
parallel combinations of resistors; Temperature
Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done on dependence of resistance.
compressing a gas, Kinetic theory of gases -
assumptions, the concept of pressure. Kinetic energy Electric Cell and its Internal resistance, potential
and temperature: RMS speed of gas molecules: difference and emf of a cell, a combination of
Degrees of freedom. Law of equipartition of energy, cells in series and parallel. Kirchhoff's laws and
applications to specific heat capacities of gases; their applications. Wheatstone bridge. Metre
Mean free path. Avogadro's number. Bridge. Potentiometer - principle and its
applications.
UNIT 10: OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
UNIT 13: MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT AND
Periodic motion - period, frequency, displacement as MAGNETISM
a function of time. Periodic functions. Simple
Biot - Savart law and its application to current
harmonic motion (S.H.M.) and its equation; phase:
carrying circular loop. Ampere's law and its
oscillations of a spring -restoring force and force
applications to infinitely long current carrying
constant: energy in S.H.M. - Kinetic and potential
straight wire and solenoid. Force on a moving charge
energies; Simple pendulum derivation of
in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Cyclotron.
expression for its time period: Free, forced and
damped oscillations, resonance. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform
magnetic field. The force between two parallel
Wave motion. Longitudinal and transverse waves,
currents carrying conductors-definition of ampere.
speed of a wave. Displacement relation for a
Torque experienced by a current loop in a uniform
progressive wave. Principle of superposition of
magnetic field: Moving coil galvanometer, its
waves, a reflection of waves. Standing waves in
current sensitivity, and conversion to ammeter and
strings and organ pipes, fundamental mode and
voltmeter.
harmonics. Beats. Doppler Effect in sound
Current loop as a magnetic dipole and its magnetic
UNIT 11: ELECTROSTATICS dipole moment. Bar magnet as an equivalent
Electric charges: Conservation of charge. Coulomb's solenoid, magnetic field lines; Earth's magnetic field
law forces between two point charges, forces and magnetic elements. Para-, dia- and
between multiple charges: superposition principle ferromagnetic substances. Magnetic susceptibility
and continuous charge distribution. and permeability. Hysteresis. Electromagnets and
permanent magnets.
Electric field: Electric field due to a point charge,
Electric field lines. Electric dipole, Electric field due
UNIT 14: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND
to a dipole. Torque on a dipole in a uniform electric
ALTERNATING CURRENTS
field.
Electromagnetic induction: Faraday's law. Induced
Electric flux. Gauss's law and its applications to find emf and current: Lenz's Law, Eddy currents. Self
field due to infinitely long uniformly charged and mutual inductance. Alternating currents, peak
straight wire, uniformly charged infinite plane sheet,
and uniformly charged thin spherical shell. Electric and RMS value of alternating current/ voltage:
potential and its calculation for a point charge, reactance and impedance: LCR series circuit,
electric dipole and system of charges; Equipotential resonance: Quality factor, power in AC circuits,
surfaces, Electrical potential energy of a system of wattless current. AC generator and transformer.
two point charges in an electrostatic field.
UNIT 15: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
Conductors and insulators. Dielectrics and electric Electromagnetic waves and their characteristics,
polarization, capacitor, the combination of capacitors Transverse nature of electromagnetic waves,
in series and parallel, capacitance of a parallel plate Electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves,
capacitor with and without dielectric medium microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet. X-rays.
between the plates. Energy stored in a capacitor. Gamma rays), Applications ofe.m. waves.
UNIT 12: CURRENT ELECTRICITY
Electric current. Drift velocity. Ohm'
resistance. Resistances of different
characteristics of Ohmic and non-ohmic conductors.
Electrical energy and power. Electrical resistivity.
Colour code for resistors; Serie
INFORMATION BULLETIN: JEE (Main) - 2022
UNIT 16: OPTICS UNIT 21: EXPERIMENTAL SKILLS
Reflection and refraction of light at plane and Familiarity with the basic approach and observations
spherical surfaces, mirror formula. Total internal ofthe experiments and activities:
reflection and its applications. Deviation and 1. Vernier calipers-its use to measure the internal
Dispersion of light by a; prism; Lens Formula. and external diameter and depth ofa vessel.
Magnification. Power ofa Lens. Combination ofthin 2. Screw gauge-its use to determine thickness/
lenses in contact. Microscope and Astronomical diameter ofthin sheet/wire.
Telescope (reflecting and refracting ) and their 3. Simple Pendulum-dissipation of energy by
magnifying powers. plotting a graph between the square of
amplitude and time.
Wave optics: wavefront and Huygens' principle.
4. Metre Scale - the mass of a given object by the
Laws of reflection and refraction using Huygens
principle ofmoments.
principle. Interference, Young's double-slit
5. Young's modulus of elasticity of the material of
experiment and expression for fringe width, coherent
a metallic wire.
sources, and sustained interference of light.
6. Surf ace tension of water by capillary rise and
Diffraction due to a single slit, width of central
effect ofdetergents,
maximum. Resolving power of microscopes and
7. Co-efficient of Viscosity of a given viscous
astronomical telescopes. Polarization, plane
liquid by measuring terminal velocity ofa given
polarized light: Brewster's law, uses of plane
spherical body,
polarized light and Polaroid.
8. Plotting a cooling curve for the relationship
UNIT 17: DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND between the temperature ofa hot body and time.
RADIATION 9. Speed of sound in air at room temperature using
Dual nature of radiation. Photoelectric effect. Hertz a resonance tube,
and Lenard's observations; Einstein's photoelectric 10. Specific heat capacity of a given (i) solid and
equation: particle nature oflight. Matter waves-wave (ii) liquid by method ofmixtures.
nature of particle, de Broglie relation. Davisson 11. The resistivity of the material of a given wire
Germer experiment. using a metre bridge.
12. The resistance ofa given wire using Ohm's law.
UNIT 18: ATOMS AND NUCLEI 13. Potentiometer-
Alpha-particle scattering experiment; Rutherford's i. Comparison ofemfoftwo primary cells.
model ofatom; Bohr model, energy levels, hydrogen ii. Determination of internal resistance of a
spectrum. Composition and size of nucleus, atomic cell.
masses, isotopes, isobars: isotones. Radioactivity
alpha. beta and gamma particles/rays and their 14. Resistance and figure ofmerit ofa galvanometer
properties; radioactive decay law. Mass-energy by halfdeflection method.
relation, mass defect; binding energy per nucleon 15. The focal length of;
and its variation with mass number, nuclear fission, (i) Convex mirror
and fusion.
(ii) Concave mirror, and
UNIT 19: ELECTRONIC DEVICES (ii) Convex lens,
using the parallax
Semiconductors; semiconductor diode: 1-V travelling microscope.
characteristics in forward and reverse bias; diode as method.
a rectifier; 1-V characteristics of LED. the 16. The plot of the angle of deviation vs angle of
photodiode, solar cell, and Zener diode; Zener diode incidence for a triangular prism.
as a voltage regulator. Junction transistor, transistor 17. Refractive index of a glass slab using a
action, characteristics of a transistor: transistor as an
18. Characteristic curves of a p-n junction diode in
amplifier (common emitter configuration) and forward and reverse bias.
oscillator. Logic gates (OR. AND. NOT. NAND and 19. Characteristic curves of a Zener diode and
NOR). Transistor as a switch. finding reverse break down voltage.
20. Characteristic curves of a transistor and finding
UNIT 20: COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS current gain and voltage gain.
Propagation of electromagnetic waves in the 21. Identification of Diode. LED, Transistor. IC.
atmosphere; Sky and space wave propagation. Need Resistor. A capacitor from a mixed collection of
for modulation. Amplitude and Frequency such items.
Modulation, Bandwidth of signals. the bandwidth of
Transmission medium, Basic Elements of a
Communication System (Block Diagram only).
INFORMATION BULLETIN: JEE (Main) - 2022
22. Using a multimeter to:
(i) Identify the base of a transistor
(ii) Distinguish between NPN and PNP type
transistor
(iii) See the unidirectional current in case of a
diode and an LED.
(iv) Check the correctness or otherwise of a
given electronic component (diode,
transistor, or IC).
You might also like
- CLASS XI (Theory) - 2021-22: Physics SyllabusDocument15 pagesCLASS XI (Theory) - 2021-22: Physics SyllabusAditya HotaNo ratings yet
- SL Arora Physics Class 11 Vol 2 Blunt LibraryDocument644 pagesSL Arora Physics Class 11 Vol 2 Blunt LibraryAyush Gupta; 11-Science; 4402100% (1)
- S.L Arora Class 11 Vol 1Document778 pagesS.L Arora Class 11 Vol 1AbijithGamer12380% (87)
- NAME DOB Mismatch DeclarationkalimDocument1 pageNAME DOB Mismatch DeclarationkalimSANDEEP RANANo ratings yet
- SL Arora Physics Class 11 Vol 2 Blunt LibraryDocument644 pagesSL Arora Physics Class 11 Vol 2 Blunt LibraryMATHEWS MATHEWS86% (14)
- SL Arora Simplified Physics Class 12 Vol 1 Blunt LibraryDocument1,179 pagesSL Arora Simplified Physics Class 12 Vol 1 Blunt LibrarykunalNo ratings yet
- SL Arora Physics Class 11 Part 1 All PDF DownloadDocument2 pagesSL Arora Physics Class 11 Part 1 All PDF DownloadNarayan Chauhan34% (123)
- SL Arora Physics Class 11 Vol 2Document644 pagesSL Arora Physics Class 11 Vol 2Anwith Goud81% (68)
- S.L. Arora Class 11 Vol-1Document778 pagesS.L. Arora Class 11 Vol-1Ayush Gupta; 11-Science; 4402100% (1)
- SL Arora Physics Class 11 PDF Book Chapters DownloadDocument1 pageSL Arora Physics Class 11 PDF Book Chapters DownloadNarayan33% (3)
- SL Arora Simplified Physics Class 12 Vol 1 Blunt LibraryDocument1,179 pagesSL Arora Simplified Physics Class 12 Vol 1 Blunt Librarychennimalaiappan andco84% (25)
- S.L Arora Physics Volume 1 2023-2024 Class 12 PDFDocument1,123 pagesS.L Arora Physics Volume 1 2023-2024 Class 12 PDFsamarthsingh080377% (39)
- Everything You Need to Know About Downloading E-books and Movies OnlineDocument301 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Downloading E-books and Movies OnlinebestNo ratings yet
- CamScanner Scanned DocumentDocument644 pagesCamScanner Scanned DocumentPraveen Tiwari50% (4)
- Cbjessco 22Document3 pagesCbjessco 22Fawaz Zaheer100% (1)
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids All DervationsDocument12 pagesMechanical Properties of Fluids All DervationsAmiya Kumar Das100% (1)
- Wave Optics Notes For Class 12Document15 pagesWave Optics Notes For Class 12roceniNo ratings yet
- S.L. Arora Class 12 Volume 2Document933 pagesS.L. Arora Class 12 Volume 2Test UserNo ratings yet
- N Avasthi ChemistryDocument554 pagesN Avasthi ChemistryPranjal BajajNo ratings yet
- SL Arora Simplified Physics Class 12 Vol 1 Blunt LibraryDocument1,179 pagesSL Arora Simplified Physics Class 12 Vol 1 Blunt Librarymuthu samyNo ratings yet
- Vedantu's Tatva's Best QuestionsDocument32 pagesVedantu's Tatva's Best QuestionsabcdNo ratings yet
- S.L. Arora Class 12 Volume 2Document933 pagesS.L. Arora Class 12 Volume 2Sarika80% (15)
- Physics XAM Idea CBSE Class 11 Term 2Document249 pagesPhysics XAM Idea CBSE Class 11 Term 2luciuszogratis561100% (1)
- Fluid Dynamics: Excess Pressure in Liquids and BubblesDocument26 pagesFluid Dynamics: Excess Pressure in Liquids and BubblesRajeenaNayim100% (9)
- Moving Coil GalvanometerDocument5 pagesMoving Coil GalvanometerGauri Sakaria100% (2)
- Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics Projectvishal toshiwal100% (3)
- Free Engineering PDFs from Learncreative HubDocument1,179 pagesFree Engineering PDFs from Learncreative HubNikitha56% (9)
- Scanned DocumentsDocument933 pagesScanned DocumentsPRAVEEN YADAW100% (3)
- English Grammar ProjectDocument16 pagesEnglish Grammar ProjectNella Paulmanal100% (1)
- Pradeep Chemistry 12 2015-2016 Volume 2Document1,006 pagesPradeep Chemistry 12 2015-2016 Volume 2MugdhaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Report Class 12 Cbse 2020-2021 On Topic GalvanometerDocument13 pagesPhysics Project Report Class 12 Cbse 2020-2021 On Topic GalvanometerNIKHIL SINGH0% (3)
- Human Eye and Colourful World NotesDocument25 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World NotesAzeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical FileDocument48 pagesPhysics Practical FileSumit Narayan0% (1)
- SL Arora XII PhysicsDocument1,255 pagesSL Arora XII PhysicsNAMAN CHADHA100% (2)
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 TPDFDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12 TPDFAjeet KUMAR MEENANo ratings yet
- SL Arora Vol 1Document1,179 pagesSL Arora Vol 1rajatc2011100% (2)
- Electric Charges and Fields: Key ConceptsDocument90 pagesElectric Charges and Fields: Key ConceptsAryan Patel100% (3)
- S.L. Arora Class 12 Volume 2 PDFDocument933 pagesS.L. Arora Class 12 Volume 2 PDFLachyClipsNo ratings yet
- 5 PostersDocument5 pages5 PostersAadiNo ratings yet
- PDF A Hand Book of Applied Mathrmatics 3 by Begashaw Moltotpdf DDDocument90 pagesPDF A Hand Book of Applied Mathrmatics 3 by Begashaw Moltotpdf DDDawit Nakachew100% (3)
- Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics Projectricha100% (1)
- Projectwork (Math)Document11 pagesProjectwork (Math)Rockstar PrinceNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEMaverick ShadeNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Worksheet Chap 8 - GravitationDocument2 pagesClass 11 Worksheet Chap 8 - GravitationdaisyNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Body EngineeringDocument2 pagesVehicle Body EngineeringMathews P Reji100% (1)
- Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument5 pagesMechanical Properties of FluidsSteveMathewKuruvillaNo ratings yet
- S.L. Arora Class 12 Volume 2Document933 pagesS.L. Arora Class 12 Volume 2LachyClips100% (3)
- How Does The Phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection Help in Optical FibresDocument29 pagesHow Does The Phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection Help in Optical FibresBleh bleh100% (1)
- Unit 4: Work, Energy and Power: JEE MAIN 2022 PHYSICS SyllabusDocument4 pagesUnit 4: Work, Energy and Power: JEE MAIN 2022 PHYSICS SyllabusAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN 2021 PHYSICS SYLLABUS: SECTION A AND BDocument4 pagesJEE MAIN 2021 PHYSICS SYLLABUS: SECTION A AND BRukmini AdithyaNo ratings yet
- Units Topics: Remark (Completion)Document4 pagesUnits Topics: Remark (Completion)siddanshNo ratings yet
- Section: A (80% Weightage) Unit - 1Document9 pagesSection: A (80% Weightage) Unit - 1maverickNo ratings yet
- Mains Syllabus ReducedDocument16 pagesMains Syllabus ReducedbaldNo ratings yet
- Reduced Syllabus of JEE Main 2024 - Physics-1698910501601Document5 pagesReduced Syllabus of JEE Main 2024 - Physics-1698910501601manavsharma17012006No ratings yet
- NEET Syllabus: Complete Physics, Chemistry & BiologyDocument23 pagesNEET Syllabus: Complete Physics, Chemistry & BiologySatyam jhaNo ratings yet
- Physics-SyllabusDocument3 pagesPhysics-Syllabusmohitabochare396No ratings yet
- PHYSICS_NMC_SYLLABUSDocument12 pagesPHYSICS_NMC_SYLLABUSexvee.gNo ratings yet
- NEET Physics SyllabusDocument8 pagesNEET Physics SyllabusNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- NEET UG 2024 - Approved - Final - RemovedDocument13 pagesNEET UG 2024 - Approved - Final - Removedyadav2007princeNo ratings yet
- Annual Exam Physics Portions G 11 2023-24Document2 pagesAnnual Exam Physics Portions G 11 2023-24luciuszogratis561No ratings yet
- My Profile SESSION 2021-22: Sub-Social ScienceDocument4 pagesMy Profile SESSION 2021-22: Sub-Social ScienceFroFee FNo ratings yet
- Maths SET - A Pre-Board 1Document5 pagesMaths SET - A Pre-Board 1FroFee FNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition: Understanding Data Types, Structures & FeaturesDocument16 pagesData Acquisition: Understanding Data Types, Structures & FeaturesFroFee FNo ratings yet
- Take Document Management Further with SmallpdfDocument1 pageTake Document Management Further with SmallpdfFroFee FNo ratings yet
- Maths SyllabusDocument3 pagesMaths SyllabusFroFee FNo ratings yet
- Data AcquisitionDocument16 pagesData AcquisitionFroFee FNo ratings yet
- Data ExplorationDocument12 pagesData ExplorationFroFee FNo ratings yet
- Skybox Manual PDFDocument32 pagesSkybox Manual PDFCato LaFalceNo ratings yet
- Physics Project - Topic - TransformerDocument21 pagesPhysics Project - Topic - TransformerSandeep TakNo ratings yet
- SIMULATION MODEL of Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorDocument9 pagesSIMULATION MODEL of Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorSri MathiNo ratings yet
- PIC16F87XA: 12.0 Comparator ModuleDocument7 pagesPIC16F87XA: 12.0 Comparator ModuleJoe FernandezNo ratings yet
- Art f5 TurboDocument17 pagesArt f5 Turbobokiooo7No ratings yet
- Bloque Carlos Gavazzi Na13d230Document2 pagesBloque Carlos Gavazzi Na13d230Billy VillaNo ratings yet
- 3WL12252CB321AA2 Datasheet enDocument7 pages3WL12252CB321AA2 Datasheet enWladimir RomeroNo ratings yet
- Panasonic Th-58pz750u CH Gp10dhu PDFDocument191 pagesPanasonic Th-58pz750u CH Gp10dhu PDFAlberto PerniaNo ratings yet
- Mems Microphone - Spm0408he5hDocument10 pagesMems Microphone - Spm0408he5hTaeung IhNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of RadarDocument4 pagesBasic Components of Radarmas3565560100% (1)
- LVC Pricelist Wef 1st July 2014Document104 pagesLVC Pricelist Wef 1st July 2014manoj031No ratings yet
- EC2251 C1 Linear and Digital Integrated CircuitsDocument1 pageEC2251 C1 Linear and Digital Integrated CircuitsRakesh Kumar DNo ratings yet
- A Review of Magnetic Repulsion EngineDocument4 pagesA Review of Magnetic Repulsion Enginejoy 11No ratings yet
- Jenis-Jenis Pre-AmpDocument6 pagesJenis-Jenis Pre-AmpFyndi Aw AwNo ratings yet
- 1 MW SPV Tech SpecificationsDocument72 pages1 MW SPV Tech SpecificationsPUSHKARKHANNA100% (1)
- v1 Diode Clipper ClamperDocument29 pagesv1 Diode Clipper ClamperRITIKNo ratings yet
- Solar TrackerDocument16 pagesSolar TrackergalaxyNo ratings yet
- LT-1007 Device Compatibility GuideDocument52 pagesLT-1007 Device Compatibility GuideadnanNo ratings yet
- Parts and Exploded Views: FLX3220FDocument19 pagesParts and Exploded Views: FLX3220Fبوند بوندNo ratings yet
- AMF9Document5 pagesAMF9Ayadi39No ratings yet
- Lab 9 The Effects of Diodes and Rectifiers in CircuitsDocument10 pagesLab 9 The Effects of Diodes and Rectifiers in Circuitsapi-709999921No ratings yet
- Service Manual Type MWTU 14 Directional Power RelayDocument28 pagesService Manual Type MWTU 14 Directional Power RelaymarkgaloNo ratings yet
- Manual Idm 8001 CCRDocument96 pagesManual Idm 8001 CCRRabie BakiraNo ratings yet
- Bul Low Voltage Series TransistorsDocument3 pagesBul Low Voltage Series TransistorsMyBriggsNo ratings yet
- Park College of Engineering and Technology Kaniyur, Coimbatore - 641 659Document2 pagesPark College of Engineering and Technology Kaniyur, Coimbatore - 641 659Jeeva RathnamNo ratings yet
- SKU-GTC-Manual-42004-659L2F (701-902)Document16 pagesSKU-GTC-Manual-42004-659L2F (701-902)Abhishek MasihNo ratings yet
- Features Description: LTC4355 Positive High Voltage Ideal Diode-OR With Input Supply and Fuse MonitorsDocument21 pagesFeatures Description: LTC4355 Positive High Voltage Ideal Diode-OR With Input Supply and Fuse Monitorsm3y54mNo ratings yet
- Service Manual - HLT-2310 - 2710 - 3010Document54 pagesService Manual - HLT-2310 - 2710 - 3010travieso112No ratings yet
- Esp Reda SLB - VSDDocument33 pagesEsp Reda SLB - VSDneoamnNo ratings yet
- 2011 - 01 - 06 - 113538 - Manual SKP Max 310 410x 710x Multi LanguageDocument13 pages2011 - 01 - 06 - 113538 - Manual SKP Max 310 410x 710x Multi LanguageJoão PauloNo ratings yet