Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acronym Meaning Source
Uploaded by
Eugenia BocaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acronym Meaning Source
Uploaded by
Eugenia BocaCopyright:
Available Formats
Acronym Meaning Source
ACS Acute Coronary Syndrome 4.3.1 Coronary CT in the Emergency Room
AI Artificial Intelligence 4.7.1 Future Developments in Cardiac CT
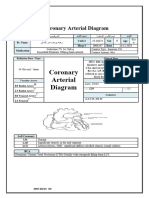
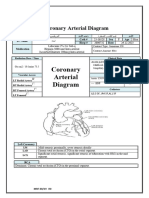
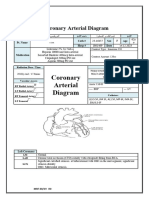
ALCAPA Anomalous Left Coronary Arising from the Pulmonary Artery 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
ARVD Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia 4.8.7 Case 42
ASD Atrial Septal Defect 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
AV Atrioventricular (valve) 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
BMI Body Mass Index 3.3.1 Learning to Adapt Cardiac CT Protocols
CABG Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting 3.3.1 Learning to Adapt Cardiac CT Protocols
CAC Coronary Artery Calcium 2.1.1 Role and Interpretation of Calcium Score CT
CAD-RADS Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System 1.4.4 Case 4
CPD Computation Flow Dynamics 2.2.2 Analysis of CT Coronary Angiography
CS Coronary Sinus 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
CT Computed Tomography
CTCA CT Coronary Angiography 2.2.1 Role of CT Coronary Angiography
CTDI CT Dose Index 3.2.1 Radiation Generation & Exposure
CTDIvol volume CT Dose Index 3.2.1 Radiation Generation & Exposure
CTDIw weighted CT Dose Index 3.2.1 Radiation Generation & Exposure
CTP CT Perfusion 4.5.1 CT Myocardial Perfusion
D1/D2 First/Second Diagonal Branch (from LAD) 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants; 1.4.1 Case 1
DICOM Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine 1.4.1 Case 1
DLP Dose Length Product 3.2.1 Radiation Generation & Exposure
ECD Endocardial Cushion Defect 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
ED Emergency Department 4.3.1 Coronary CT in the Emergency Room
ER Emergency Room 4.3.1 Coronary CT in the Emergency Room
Acronym Meaning Source
FFR Fractional Flow Reserve 2.2.2 Analysis of CT Coronary Angiography
FOV Field Of View 3.2.1 Radiation Generation & Exposure
HCM Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy 1.3.2 Contrast Agents and Drugs in Cardiac CT
HOCM Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy 1.3.2 Contrast Agents and Drugs in Cardiac CT
HU Hounsfield Units 2.1.1 Role and Interpretation of Calcium Score CT
ICA Invasive Coronary Angiography 2.2.2 Analysis of CT Coronary Angiography
ICD Implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator 4.8.7 Case 42
IV IntraVenous (Injection) 1.3.2 Contrast Agents and Drugs in Cardiac CT
IVC Inferior Vein Cava 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
LA Left Atrium 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
LAA Left Atrial Appendage 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
LAD Left Anterior Descending Artery 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants; 1.4.1 Case 1
LCA Left Coronary Artery 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
LCx Left Circumflex Artery 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants; 1.4.1 Case 1
LIMA Left Internal Mammary Artery 3.3.1 Learning to Adapt Cardiac CT Protocols
LIPV Left Inferior Pulmonary Vein 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
LM Left Main (Coronary Artery) 2.2.3 CAD-RADS for CTCA Interpretation
LMH Left Main (Coronary Artery) Height 2.4.2 Analysing CT TAVI
LOS Length Of Stay 4.3.1 Coronary CT in the Emergency Room
LPA Left Pulmonary Artery 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
LSPV Left Superior Pulmonary Vein 2.2.3 CAD-RADS for CTCA Interpretation
LV Left Ventricle 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants; 1.4.1 Case 1
LVEF Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction 4.1.1 CT Ventricular Functional Analysis
LVF Left Ventricular Function 4.1.1 CT Ventricular Functional Analysis
LVOT Left Ventricular Outflow Tract 2.4.1 Role of CT TAVI (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation)
Acronym Meaning Source
MACE Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events 4.3.1 Coronary CT in the Emergency Room
MBF Myocardial Blood Flow 2.2.2 Analysis of CT Coronary Angiography
MDT Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy 4.7.1 Future Developments in Cardiac CT
MGA Malposition of the Great Arteries 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
MGV Malposition of the Great Vessels 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
MI Myocardial Infarction 2.2.1 Role of CT Coronary Angiography
MIP Maximum Intensity Projection 3.3.1 Learning to Adapt Cardiac CT Protocols
MLA Minimum Lumen Area 2.2.1 Role of CT Coronary Angiography
MLD Minimum Luminal Diameter 2.2.1 Role of CT Coronary Angiography
MPA Main Pulmonary Artery 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
MPI Myocardial Perfusion Imaging 4.3.1 Coronary CT in the Emergency Room
MPR MultiPlanar Reformat 1.4.1 Case 1; 4.8.15 Case 40
MS Membranous Septum 2.4.2 Analysing CT TAVI
NC Non Coronary (Cusp) 2.4.2 Analysing CT TAVI
NTG Nitroglycerin 1.3.2 Contrast Agents and Drugs in Cardiac CT
OM1/OM2 First/Second Obtuse Marginal Branch (from LCx) 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants; 1.4.1 Case 1
OMT Optimal Medical Therapy 4.4.1 CT FFR
PA Pulmonary Artery 4.8.4 Case 39
PAPVR Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
PCI Percutaneous Coronary Intervention 4.4.1 CT FFR
1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy; 1.4.1
PDA Posterior Descending Artery Case 1
PET Positron Emission Tomography 4.4.1 CT FFR
PFO Patent Foramen Ovale 2.6.9 Case 14
PL Posterolateral Branch (from RCA) 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants; 1.4.1 Case 1
PV Pulmonary Vein 2.3.2 Analysis of CT for Atrial Fibrillation Therapy
Acronym Meaning Source
RA Right Atrium 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
RAA Right Atrial Appendage 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
RCA Right Coronary Artery 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants; 1.4.1 Case 1
RPA Right Pulmonary Artery 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
cvi42 labelling for posterior descending artery coming off the right
R-PDA coronary artery 1.4.1 Case 1
RSPV Right Superior Pulmonary Vein 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
RV Right Ventricle 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
RVOT Right Ventricular Outflow Tract 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
RWMA Echocardiographic Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities 2.2.2 Analysis of CT Coronary Angiography
SOV Sinus of Valsalva 2.4.2 Analysing CT TAVI
SPECT Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography 4.1.1 CT Ventricular Functional Analysis
STJ Sinotubular Junction 3.4.1 Case 21
SVC Superior Vein Cava 1.2.1 Coronary Artery Anatomy and Variants
SVG Saphenous Vein Graft 3.4.2 Case 22
TAPVR Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
TAVI Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
TAVR Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement 1.2.2 Atrial, Ventricular Anatomy, Valvular and Aortic Root Anatomy
TGA Transposition of the Great Arteries 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
TGV Transposition of the Great Vessels 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
TIMI Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 4.3.1 Coronary CT in the Emergency Room
VFA Ventricular Functional Analysis 4.1.1 CT Ventricular Functional Analysis
VSD Ventricular Septal Defect 4.2.1 CT for Congenital Heart Disease
%DS Percentage Diameter Stenosis 2.2.1 Role of CT Coronary Angiography
%AS Percentage Aortic Stenosis 2.2.1 Role of CT Coronary Angiography
You might also like
- Edward K. Chung M.D., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. (Auth.) - Ambulatory Electrocardiography - Holter Monitor Electrocardiography-Springer-Verlag New York (1979)Document236 pagesEdward K. Chung M.D., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. (Auth.) - Ambulatory Electrocardiography - Holter Monitor Electrocardiography-Springer-Verlag New York (1979)Henrique MaiaNo ratings yet
- F2-14 Budget PreparationDocument18 pagesF2-14 Budget PreparationJaved Imran100% (1)
- Toronto Notes - Cardiac SurgeryDocument32 pagesToronto Notes - Cardiac Surgerymicielij100% (1)
- CardiologyDocument52 pagesCardiologyDexzal100% (2)
- Problem Set ODocument19 pagesProblem Set OnimboNo ratings yet
- EACVI CCT Core SyllabusDocument13 pagesEACVI CCT Core SyllabushgadNo ratings yet
- C E MO NG: Linical CG RniDocument13 pagesC E MO NG: Linical CG RniSalman AlfarisyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Imaging and BiomarkersDocument23 pagesCardiac Imaging and BiomarkersShreyas NayakNo ratings yet
- 1 B-ModeDocument30 pages1 B-ModefaisalNo ratings yet
- DCLT?Document5 pagesDCLT?My selfNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument54 pagesProject Reportsanson123No ratings yet
- HCM Guidelines Made Simple Tool GL HCMDocument19 pagesHCM Guidelines Made Simple Tool GL HCMIrina Cabac-PogoreviciNo ratings yet
- Electro-Anatomical Mapping of The HeartDocument256 pagesElectro-Anatomical Mapping of The HeartHenrique MaiaNo ratings yet
- Essential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachFrom EverandEssential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Made Simple Chest PainDocument18 pagesGuidelines Made Simple Chest PainPaul JohnNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MappingFrom EverandCardiac MappingMohammad ShenasaNo ratings yet
- Evolving Diagnostic Criteria For Arrhythmogenic CardiomyopathyDocument17 pagesEvolving Diagnostic Criteria For Arrhythmogenic CardiomyopathyAlizaPinkyNo ratings yet
- Eajm 42 2 100Document3 pagesEajm 42 2 100Diana BanceuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ImagingDocument32 pagesCardiac ImagingRafid DragneelNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Basics of Echocardiography and Cardiac DopplerDocument29 pagesUnit 1 Basics of Echocardiography and Cardiac DopplerJack TomarNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cath FinalDocument3 pagesCardiac Cath Finalshamaamo19No ratings yet
- Surgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery: Clinical Questions and AnswersFrom EverandSurgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery: Clinical Questions and AnswersForrest "Dell" MooreNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CathDocument3 pagesCardiac Cathshamaamo19No ratings yet
- Rheumatology 2006 Maksimovi Iv26 31Document6 pagesRheumatology 2006 Maksimovi Iv26 31Thio GifarnoNo ratings yet
- Hamda Mohammad Sa'adeh - PCI Final ReportDocument4 pagesHamda Mohammad Sa'adeh - PCI Final Reportshamaamo19No ratings yet
- 5.RCA or LCX in Inferior MIDocument7 pages5.RCA or LCX in Inferior MIAshraf ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Circep 119 008210Document12 pagesCircep 119 008210Paul CalbureanNo ratings yet
- CARDIO 4. Med Surg Success A Q A Review Applying Critical Thinking To Test Taking by Colgrove Kathryn Cadenhead ZDocument40 pagesCARDIO 4. Med Surg Success A Q A Review Applying Critical Thinking To Test Taking by Colgrove Kathryn Cadenhead ZKarl Adrianne De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Single Coronary Artery Anomaly Case ReportDocument5 pagesSingle Coronary Artery Anomaly Case ReportJhonike NawipaNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmias From Automatici+Document24 pagesMechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmias From Automatici+Malar MannanNo ratings yet
- Restrictive CardiomyopathyDocument15 pagesRestrictive CardiomyopathyJing CruzNo ratings yet
- Isolated Right Ventricle Myocardial Infarction - Is The Right Ventricle Still The Forgotten Ventricle?Document4 pagesIsolated Right Ventricle Myocardial Infarction - Is The Right Ventricle Still The Forgotten Ventricle?Nadyaindriati96No ratings yet
- Interpreting The Athlete's ECGDocument10 pagesInterpreting The Athlete's ECGVaniaAlmiraNo ratings yet
- Primary Angioplasty in Anomalous Right Coronary Artery OriginatingDocument3 pagesPrimary Angioplasty in Anomalous Right Coronary Artery Originatingapi-560931483No ratings yet
- Neural Networks in ECG ClassificationDocument36 pagesNeural Networks in ECG ClassificationMustafa AlkhzragyNo ratings yet
- Teza de Abilitare COZMA Dragos LA 2019 Varianta FinalaDocument189 pagesTeza de Abilitare COZMA Dragos LA 2019 Varianta FinalaDragos CozmaNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument73 pagesManagement of Acute Coronary SyndromeSantosh NaliathNo ratings yet
- CathDocument2 pagesCathshamaamo19No ratings yet
- Samol2012 PDFDocument8 pagesSamol2012 PDFnaniro orinanNo ratings yet
- Basics of ECG (Dr. MD Kalimuddin)Document53 pagesBasics of ECG (Dr. MD Kalimuddin)CloudySkyNo ratings yet
- Kapur 2015Document4 pagesKapur 2015SuhartiniNo ratings yet
- Craniocervical Arterial VariationsDocument171 pagesCraniocervical Arterial VariationsMircea JunbeiNo ratings yet
- Medicine Flash Cards Shared by Ali ZeeshanDocument13 pagesMedicine Flash Cards Shared by Ali ZeeshanSarrah KingNo ratings yet
- Basic CathlabDocument26 pagesBasic CathlabwiwingNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument61 pagesIlovepdf MergedChidrup MannaNo ratings yet
- WS Emergency Echo SYMCARD 2022Document33 pagesWS Emergency Echo SYMCARD 2022IndRa KaBhuomNo ratings yet
- Pacing Clinical Electrophis - 2022 - MartiniDocument10 pagesPacing Clinical Electrophis - 2022 - MartiniRobertoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Imaging - Rotations in Radiology 2014Document543 pagesCardiac Imaging - Rotations in Radiology 2014Ni Zar100% (1)
- 58-63 DallAra JIC 2020 Feb WMDocument6 pages58-63 DallAra JIC 2020 Feb WMJose Manuel Ornelas-AguirreNo ratings yet
- Heart Sound Analysis: Theory, Techniques and Applications: Guy Amit Advanced Research Seminar May 2004Document41 pagesHeart Sound Analysis: Theory, Techniques and Applications: Guy Amit Advanced Research Seminar May 2004Juwansyah SasmitaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cases: Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesClinical Cases: Ischaemic Heart DiseaseLADY JOWAHER ALLASNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Amjcard 2018 03 369Document21 pages10 1016@j Amjcard 2018 03 369Martin De Santiago ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Index of Medical Imaging - 2011 - McConnell - Appendix 1 Common Radiological and Medical AbbreviationsDocument14 pagesIndex of Medical Imaging - 2011 - McConnell - Appendix 1 Common Radiological and Medical AbbreviationsDante Harumichi SaizouNo ratings yet
- CazuriDocument4 pagesCazuriIbănescu Iulia AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Modern Mapping and Ablation of Idiopathic Outflow Tract Ventricular ArrhythmiasDocument8 pagesModern Mapping and Ablation of Idiopathic Outflow Tract Ventricular ArrhythmiasCut Keumala PutriNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Cardiac Arrhythmias: A. Thompson and J. R. BalserDocument9 pagesPerioperative Cardiac Arrhythmias: A. Thompson and J. R. BalsererzaraptorNo ratings yet
- Chest CT Angiography For Acute Aortic Pathologic Conditions: Pearls and PitfallsDocument26 pagesChest CT Angiography For Acute Aortic Pathologic Conditions: Pearls and PitfallsJelvis BofNo ratings yet
- Catheter Ablation of Cardiac Arrhythmias: Basic Concepts and Clinical ApplicationsFrom EverandCatheter Ablation of Cardiac Arrhythmias: Basic Concepts and Clinical ApplicationsDavid J. Wilber, M.D.No ratings yet
- (Journal of Neurosurgery - Spine) Risk Factors For Deep Surgical Site Infection Following Thoracolumbar Spinal SurgeryDocument10 pages(Journal of Neurosurgery - Spine) Risk Factors For Deep Surgical Site Infection Following Thoracolumbar Spinal SurgeryEugenia BocaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Malnutrition: Putting The New Definition and Standards Into PracticeDocument16 pagesPediatric Malnutrition: Putting The New Definition and Standards Into PracticeEugenia BocaNo ratings yet
- Bouma 2016Document16 pagesBouma 2016Eugenia BocaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases PDFDocument281 pagesInfectious Diseases PDFEugenia Boca100% (1)
- Analysis of Gilad Hekselman's Feauture On Smile Like That by Esperanza SpaldingDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Gilad Hekselman's Feauture On Smile Like That by Esperanza SpaldingJordan Kerr100% (1)
- General Specification (Building) 30-01-21 198-380Document183 pagesGeneral Specification (Building) 30-01-21 198-380shujaNo ratings yet
- B.tech 3 Cse SyllabusDocument65 pagesB.tech 3 Cse SyllabusVijayendra GoudNo ratings yet
- Deadlocks: Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts - 9 EditionDocument43 pagesDeadlocks: Silberschatz, Galvin and Gagne ©2013 Operating System Concepts - 9 EditionmigadNo ratings yet
- IA EconomicsDocument3 pagesIA EconomicsElisa ElisaNo ratings yet
- Solutions and Solubility Practice Hon-18Document3 pagesSolutions and Solubility Practice Hon-18api-368121935No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 IR ModelsDocument34 pagesChapter 4 IR ModelsYohannes KefaleNo ratings yet
- Genuity Systems Limited: Membership, Certification and LicenseDocument4 pagesGenuity Systems Limited: Membership, Certification and LicenseshafatNo ratings yet
- Basic Survival Skills Training For Survival GroupsDocument5 pagesBasic Survival Skills Training For Survival GroupsevrazianNo ratings yet
- Series: Eddy-Current DynamometersDocument11 pagesSeries: Eddy-Current DynamometersDimas AndiNo ratings yet
- Cantor Set FunctionDocument15 pagesCantor Set FunctionRenato GaloisNo ratings yet
- CS687 - Access Control 1 - Spring 2020Document41 pagesCS687 - Access Control 1 - Spring 2020Dawit GetchoNo ratings yet
- NevirapineDocument2 pagesNevirapineمحمد عريف حكيمNo ratings yet
- As Me Certificate Holder ReportDocument5 pagesAs Me Certificate Holder ReportpandiangvNo ratings yet
- AkbarDocument13 pagesAkbarNihar HarinkhedeNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On Reading InterventionDocument5 pagesNarrative Report On Reading InterventionDyelain 199x100% (1)
- Tele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Document23 pagesTele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Abhishek BarwalNo ratings yet
- Javascript: Case Study To Be Used For Hands-On SessionsDocument14 pagesJavascript: Case Study To Be Used For Hands-On SessionsSettiNagarajuNo ratings yet
- Using Snap Test Kits Poster enDocument1 pageUsing Snap Test Kits Poster enMoisés RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Algorithms (Complete Course) :-Btech CSE: TopicsDocument4 pagesAlgorithms (Complete Course) :-Btech CSE: TopicsRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- University of Hargeisa GIT Pharmacology Review Questions: Name:aniisa Muse Ahmed Faculty:midwifery ID:1716642 Class:3ADocument4 pagesUniversity of Hargeisa GIT Pharmacology Review Questions: Name:aniisa Muse Ahmed Faculty:midwifery ID:1716642 Class:3AAniza Mouse100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension Read The Article Below and Then Answer The Questions That FollowDocument4 pagesReading Comprehension Read The Article Below and Then Answer The Questions That Followjuan m isazaNo ratings yet
- Newsflash MagazineDocument64 pagesNewsflash MagazineIan LuoNo ratings yet
- Effects of New Normal Education To Senior High Students of San Roque National High School RESEARCH GROUP 2 2Document11 pagesEffects of New Normal Education To Senior High Students of San Roque National High School RESEARCH GROUP 2 2Elle MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Bioshock Audio DiariesDocument6 pagesBioshock Audio DiariesGeorge CuriosoNo ratings yet
- SPM Practice June 29Document7 pagesSPM Practice June 29Isabel GohNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office 365 Customer Decision FrameworkDocument14 pagesMicrosoft Office 365 Customer Decision FrameworkthinkofdevilNo ratings yet
- Journal NeuroDocument15 pagesJournal Neurorwong1231No ratings yet