Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Components of Special and Inclusive Education
Uploaded by
Zee KimCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Components of Special and Inclusive Education
Uploaded by
Zee KimCopyright:
Available Formats
Components of Special and Inclusive Education
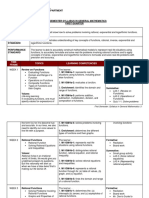
USA PHILIPPINES
CHILDFIND: CHILDFIND:
A legal requirement that schools have to Locating of CSN’s through the family
find children with disabilities and who mapping survey, advocacy campaigns and
may be entitles to special education networking with local health workers.
services. Children with special needs who are not
Covers every child from birth to age 21. in school are to be listed using Enclosure
Evaluates any child that are suspected to No. 1.
have disabilities. CSN’s shall be visited by Special
It is protected by the federal law called Education (SPED) teachers
the Individuals with Disabilities Parents should be convinced to enroll
Education Act or IDEA. their children in SPED Centers or schools
Advocates to locate CSN as early as nearest their home.
possible to enable early intervention.
It gives power to parents to seek due
process hearing to schools who turns
down evaluation to their children who are
suspected to have disabilities.
ASSESSMENT: ASSESSMENT:
Use to determine the student’s ability Continuous process of identifying the
level in various academic areas and to strengths and weaknesses of the child
guide their instruction. Use of formal and informal tools for
Multi-assessment serves as basis of proper program grade placement.
parents, teachers, specialist, and SPED Centers in the Division shall assist
counselors to identify weaknesses, regular schools in the assessment process.
strengths, and progress of a child.
Assessment is done in different method:
observation, judgement, and testing.
The purposes of assessment are screening
and identification, eligibility and
diagnosis, IEP development and
placement, instructional planning, and
evaluation.
PLACEMENT: PROGRAM OPTIONS:
Refers to the amount of time in each Regular schools with or without trained
school day that a student spends in the SPED teachers shall be provided
resource or in a general education educational services to children with
classroom, as well as the programs and special needs.
services. schools shall access educational services
The ARD committee decides the child’s from SPED Centers or SPED trained
placement and makes sure that the child teachers.
spends as much of their school day with The first program option that shall be
regular children. organized for these children is a self-
The LRE greatly depends on each child’s contained class for children with similar
unique need. disabilities which can be mono-grade or
multi-grade handled by a trained SPED
teacher.
The second option is inclusion or
placement of the child with disabilities in
general education or regular class where
he/she learns with his/her peers under a
regular teacher and/or SPED trained
teacher who addresses the child’s needs.
The third option is a resource room
program where the child with disabilities
shall be pulled out from the general
education or regular class and shall report
to a SPED teacher who provides small
group/one-on-one instruction and/or
appropriate interventions for these
children.
ACCOMMODATIONS AND CURRICULAR CURRICULUM MODIFICATIONS:
MODIFICATION:
Accommodation changes the way a Implemented in the forms of adaptations
student a student receives information. and accommodations to foster optimum
But there is no change in the learning learning based on individual’s needs and
content. potentials.
It may also refer as support services Modification in classroom instructions
provided to help CSN’s. and activities is a process that involves
Examples of accommodations are: new ways of thinking and developing
Time, setting, level of support, reduce teaching-learning practices.
response effort, sensory, fidgets and It also involves changes in any of the
visual schedules. steps in the teaching-learning process.
Modification changes what a student is Curriculum modifications shall include
taught or expected to learn. There is a service delivery options like cooperative
change in the learning content. or team teaching, consulting teacher
Examples of modifications are: quantity, program and others.
output, and alternate. The provision of support services from
professionals and specialists, parents,
volunteers, and peers or buddies to the
children with special needs is an
important feature in the inclusion
program.
PARENT INVOLVEMENT: PARENT INVOLVEMENT:
Parents involvement in deciding is vitally This plays a vital role in preparing the
important. children in academic, moral, and spiritual
Parents must be involved and here are development.
their role: Parents shall involve themselves in
- Parents can provide critical output as observing children’s performance,
they knew better the child with volunteering to work in the classroom as
disabilities teacher aide and providing support to
- Parents work closely to their children other parents.
- Provide relevant information about
the child’s strengths and weaknesses
- Parents provides comprehensive
insights for transition meetings that
discusses movement
- Parents are the best advocate of for
their children
References:
https://www.deped.gov.ph/2009/07/06/do-72-s-2009-inclusive-education-as-strategy-for-increasing-
participation-rate-of-children/
Name: Harry Bayron Lloren Age: 10 Sex: Male
Autism
Suspected Case/Difficulty/Problem: _____________________________
Yes
Was he/she submitted for evaluation: ____________________________
Doctor/Psychologist
If yes, which particular specialist/ clinician? ____________________________
Yes
Had he/she been in any SPED class/mainstream? ______________________
Where is the facility/school located? Tagbilaran City, Bohol
________________________________________
Are the parents willing to have the child schooled? ______________Yes
You might also like
- My Teacher is My Hero: Tributes to the People Who Gave Us Knowledge, Motivation, and WisdonFrom EverandMy Teacher is My Hero: Tributes to the People Who Gave Us Knowledge, Motivation, and WisdonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CTPDocument4 pagesReviewer CTPCjls KthyNo ratings yet
- Chapter III: Implementing The Curriculum/Lesson 2 Level of Knowledge Learning Styles Writing Lesson Plan Level of KnowledgeDocument8 pagesChapter III: Implementing The Curriculum/Lesson 2 Level of Knowledge Learning Styles Writing Lesson Plan Level of KnowledgeNorman C. CalaloNo ratings yet
- Fs 6 ReflectionDocument32 pagesFs 6 ReflectionshaneNo ratings yet
- Pec 204 TumboDocument3 pagesPec 204 TumboKirk Edricque HoriNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Implementation HandoutsDocument3 pagesCurriculum Implementation HandoutsChristine Joy PerionNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching 2Document5 pagesPrinciples of Teaching 2Pascual GarciaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed 6 - SpeechDocument2 pagesProf. Ed 6 - SpeechNIX TVNo ratings yet
- Traditional Point of Views On EducationDocument6 pagesTraditional Point of Views On EducationarleneNo ratings yet
- The Process of Instructional Planning Group 2 2A1Document45 pagesThe Process of Instructional Planning Group 2 2A1Jessa Mae SusonNo ratings yet
- q3 Le-W1 EnglishDocument6 pagesq3 Le-W1 EnglishSharmaine LappayNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Research in ChildDocument6 pagesModule 6 - Research in Childrushy121No ratings yet
- Physical Impairment and Self Care FOSIEDocument7 pagesPhysical Impairment and Self Care FOSIENorsaidin TungkagNo ratings yet
- Information Technology in Support of Student-Centered LearningDocument2 pagesInformation Technology in Support of Student-Centered LearningMe-Ann PoncolNo ratings yet
- Science Module - Sample PDFDocument58 pagesScience Module - Sample PDFBETHUEL P. ALQUIROZNo ratings yet
- Fs 100 Course OutlineDocument4 pagesFs 100 Course OutlinefgjxxiNo ratings yet
- Translating Competencies Into ObjectivesDocument29 pagesTranslating Competencies Into ObjectivesMaestro MertzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Module 7 Lesson 1Document4 pagesChapter 5 Module 7 Lesson 1Knowme GynnNo ratings yet
- Curiculum Week16Document6 pagesCuriculum Week16KylaMayAndradeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 TTTSCDocument19 pagesChapter 1 TTTSCJackaii Waniwan IINo ratings yet
- The Art of QuestioningDocument32 pagesThe Art of QuestioningAndrea GalangNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions For Observation and InterviewDocument1 pageGuide Questions For Observation and InterviewMaria Nativity BanarioNo ratings yet
- Educational Technology 2Document16 pagesEducational Technology 2api-312289492No ratings yet
- TOS 2nd Quarter GRADE 6Document3 pagesTOS 2nd Quarter GRADE 6Mariele Tokong Montederamos-ConteNo ratings yet
- Let Review On MotivationDocument20 pagesLet Review On MotivationAnonymous st4mP4C4No ratings yet
- Curriculum Aims, Goals and Educational Objectives: Learning CompetenciesDocument11 pagesCurriculum Aims, Goals and Educational Objectives: Learning CompetenciesMelodina AcainNo ratings yet
- Final ReflectionDocument6 pagesFinal ReflectionUGALINGAN SAADANOR A.No ratings yet
- Unit 2: Target SettingDocument3 pagesUnit 2: Target SettingJonjon BANADNo ratings yet
- 2c Mod 2 Needs Assessment Questionnaire For Beginning Teachers v1Document2 pages2c Mod 2 Needs Assessment Questionnaire For Beginning Teachers v1RaulJunioRamosNo ratings yet
- Lumangtad, Genesis C. Day 3Document9 pagesLumangtad, Genesis C. Day 3Henzy LuNo ratings yet
- Personal Communication Strategy: Aquino, Loren ADocument43 pagesPersonal Communication Strategy: Aquino, Loren AJessica Alparaz100% (1)
- City University of Pasay College of Education Assessment of Learning Module 3 Formative and Summative AssessmentDocument4 pagesCity University of Pasay College of Education Assessment of Learning Module 3 Formative and Summative AssessmentSalcedo, Angel Grace M.No ratings yet
- Reiser and BalderasDocument3 pagesReiser and BalderasRham BlaimNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Curriculum Development ModelsDocument2 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Curriculum Development ModelssetiawanNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document18 pagesModule 5Dexther JalitNo ratings yet
- EDUC9 Module 13Document5 pagesEDUC9 Module 13Jomarc Cedrick Gonzales100% (1)
- Module 5, PED 109Document25 pagesModule 5, PED 109Hepshebah De Dios Santuyo100% (1)
- Integrated ApproachDocument7 pagesIntegrated ApproachAngel King RelativesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1Harry SinghNo ratings yet
- Mental Retardation Teaching StrategiesDocument7 pagesMental Retardation Teaching Strategiesapi-25300594367% (3)
- Commission On Higher Education Region V: Module Seven in Prof - Ed 9 Components of Curriculum DesignDocument11 pagesCommission On Higher Education Region V: Module Seven in Prof - Ed 9 Components of Curriculum DesignshielaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Innovations (Crodua and Dulog)Document30 pagesCurriculum Innovations (Crodua and Dulog)Dianne CroduaNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Learning Ep 08Document13 pagesFS 1 Learning Ep 08Albie keen BarrosNo ratings yet
- FS1 CHAPTER 1 7 ActivitiesDocument43 pagesFS1 CHAPTER 1 7 ActivitiesronnqaNo ratings yet
- Implementing A Curriculum Daily in The ClassroomsDocument15 pagesImplementing A Curriculum Daily in The ClassroomsMarica PoyaoanNo ratings yet
- College of EducationDocument5 pagesCollege of EducationJessa Mae SusonNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles: John Herbert R. Gulinao, LPT, MaedDocument18 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles: John Herbert R. Gulinao, LPT, MaedAlexis Heart GloriaNo ratings yet
- FinaleDocument16 pagesFinaleapi-264508571No ratings yet
- Curdev Final ModuleDocument4 pagesCurdev Final ModuleMimi ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Fs5 Fs6 Answer For Every JournalDocument5 pagesFs5 Fs6 Answer For Every JournalRogerNo ratings yet
- REFLECTION CriticDocument1 pageREFLECTION CriticMa Princess Geromo AmuyanNo ratings yet
- Alejandro-Over All Reflections - (Chapter 1 To 4)Document9 pagesAlejandro-Over All Reflections - (Chapter 1 To 4)Angelica AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode 1Document10 pagesLearning Episode 1Mark Anthony Nieva RafalloNo ratings yet
- 3 Program Outcomes and Learning OutcomesDocument13 pages3 Program Outcomes and Learning OutcomesVanessa DacumosNo ratings yet
- Planning The Family Meals Epp4Document11 pagesPlanning The Family Meals Epp4Jesseryl Dulay CastilloNo ratings yet
- Field Study 2-Matrix of ActivitiesDocument2 pagesField Study 2-Matrix of ActivitiesJezzel ReponteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document5 pagesLesson 1Warda MamasalagatNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Computer: Tools For Analyzing of Assessment DataDocument10 pagesStatistics and Computer: Tools For Analyzing of Assessment DataLoger Kent BernabeNo ratings yet
- The Final Action For A Curriculum Material: Jessa Y. Cayabyab Bsed-Filipino MajorDocument8 pagesThe Final Action For A Curriculum Material: Jessa Y. Cayabyab Bsed-Filipino MajorAlyssa Alberto100% (1)
- 103 ExamDocument21 pages103 Examits EfrenNo ratings yet
- Sample Minutes of The MeetingDocument3 pagesSample Minutes of The MeetingZee KimNo ratings yet
- It'S More Fun in THE PhilippinDocument2 pagesIt'S More Fun in THE PhilippinZee KimNo ratings yet
- Singers and Their Creative Playlist During The 1950Document6 pagesSingers and Their Creative Playlist During The 1950Zee KimNo ratings yet
- It'S More Fun in THE PhilippinDocument2 pagesIt'S More Fun in THE PhilippinZee KimNo ratings yet
- CYCLINGDocument1 pageCYCLINGZee KimNo ratings yet
- Listening LP1Document6 pagesListening LP1Zee KimNo ratings yet
- Singers and Their Creative Playlist During The 1950Document6 pagesSingers and Their Creative Playlist During The 1950Zee KimNo ratings yet
- Speaking Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSpeaking Lesson PlanZee Kim100% (1)
- Speaking Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSpeaking Lesson PlanZee Kim100% (1)
- Speaking Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesSpeaking Lesson PlanZee Kim100% (1)
- Zyril Mae Dingal Galon Bsed-II EnglishDocument1 pageZyril Mae Dingal Galon Bsed-II EnglishZee KimNo ratings yet
- Wyoming PlatformDocument6 pagesWyoming Platformroberto_borgertNo ratings yet
- Periodic Test - II Class 2 MathematicsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Test - II Class 2 Mathematicsvishal manujaNo ratings yet
- Academic Year 2017 - 2018 (PDFDrive)Document100 pagesAcademic Year 2017 - 2018 (PDFDrive)CrystalNo ratings yet
- Build Own Robot ArmDocument10 pagesBuild Own Robot ArmabhiranyusinghNo ratings yet
- Dr. Surendra Kumar Singh: Mob No. 9810571079, 9868602770: Sociology A Blend of Theory and ApplicationDocument1 pageDr. Surendra Kumar Singh: Mob No. 9810571079, 9868602770: Sociology A Blend of Theory and Applicationsumit15509270No ratings yet
- General Mathematics Grade11 Syllabus PDFDocument11 pagesGeneral Mathematics Grade11 Syllabus PDFlip87% (15)
- Six Simple Twists The Pleat Pattern Approach To Origami Tessellation Design by Benjamin Dileonardo Parker 1482244616Document5 pagesSix Simple Twists The Pleat Pattern Approach To Origami Tessellation Design by Benjamin Dileonardo Parker 1482244616AidanNo ratings yet
- Total PointsDocument70 pagesTotal PointsakgsghssNo ratings yet
- Educative Process J. DalidaDocument12 pagesEducative Process J. DalidaChristille Joy MagsipocNo ratings yet
- Bristol's Marking Criteria For Translations Into EnglishDocument7 pagesBristol's Marking Criteria For Translations Into EnglishBlue FlameNo ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela Narrative Report: San Juan Elementary SchoolDocument1 pageBrigada Eskwela Narrative Report: San Juan Elementary Schoolmichelle c lacadNo ratings yet
- Effective Teaching EssayDocument4 pagesEffective Teaching Essayapi-4948852560% (1)
- Historical Foundation of Education: Here Starts The Lesson!Document71 pagesHistorical Foundation of Education: Here Starts The Lesson!Saludez RosiellieNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Bahasa Inggris Things in The Classroom2Document7 pagesContoh Soal Bahasa Inggris Things in The Classroom2Saleh MendidikNo ratings yet
- Literary Analysis EssayDocument2 pagesLiterary Analysis EssaySandi BerginNo ratings yet
- STI Prof AparajithDocument3 pagesSTI Prof AparajithAnish KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Sav Facilities MapDocument2 pagesSav Facilities Mapapi-281554642No ratings yet
- 2 Bac Global Test S 2 PDFDocument2 pages2 Bac Global Test S 2 PDFhamidNo ratings yet
- Young Style SurveyDocument3 pagesYoung Style SurveyJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- BLAS 100 (01415) SyllabusDocument6 pagesBLAS 100 (01415) SyllabusdspearmaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Knowledge Management in OrgaDocument12 pagesThe Role of Knowledge Management in OrgaclaudiasuarezcordovaNo ratings yet
- Typesoferrors 150106072337 Conversion Gate01Document11 pagesTypesoferrors 150106072337 Conversion Gate01Rilla ZikriaNo ratings yet
- New Grad. RequirementsDocument1 pageNew Grad. Requirementsandrewmjohnson17No ratings yet
- 18th Amendment and EducationDocument3 pages18th Amendment and EducationShakeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS: Note: Use Proper Citation.: Media and Information LiteracyDocument2 pagesQUESTIONS AND ANSWERS: Note: Use Proper Citation.: Media and Information Literacyjp marceloNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment TaskDocument3 pagesSummative Assessment Taskapi-268745806100% (1)
- Handbook Student KeukaDocument27 pagesHandbook Student KeukaLý Hoàng ThànhNo ratings yet
- Plosive and Fricative Sounds Produced by EFL Students Using Online Media: A Perspective On Learning English PhonologyDocument7 pagesPlosive and Fricative Sounds Produced by EFL Students Using Online Media: A Perspective On Learning English PhonologyBelen GarciaNo ratings yet
- Conference AgendaDocument12 pagesConference Agendapoli mekuNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 MTAP Test - 1 - OkDocument3 pagesGrade 1 MTAP Test - 1 - OkElyssa Marie Tuazon100% (5)