Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rikken Keiki, HW Sensor, Gas Detector
Uploaded by
Rangga TaufiqurahmanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rikken Keiki, HW Sensor, Gas Detector
Uploaded by
Rangga TaufiqurahmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Catalytic
Catalytic Combustion
Combustion Method
Combustion Method Stationary
Stationary
Stationarysensor
sensor
sensor
Catalytic
Sensor:
Sensor: HW
Catalytic Combustion
HW
Combustion Method
Method
Example:
Example:
Example:HW-6239
HW-6239
HW-6239
Catalytic
Sensor: Combustion
HW Method Stationary sensor
StationaryHW-6239
Example: sensor
Sensor:
1.
1.Brief HW
Briefdescription
Sensor:
Brief description
HW
description
Stationary
Example: sensor
HW-6239
Example: HW-6239
Category
Category
Category Detectable
Detectable
Detectablegas
gas
gas
This
This
1.
This sensor
sensor
Brief
sensor detects
detectsgas
description
detects gasbased
gas basedon
based onheat
on heatgenerated
heat generatedby
generated bycombustible
by combustiblegas
combustible gasburning
gas burningon
burning onan
on an
an
1. Briefcatalyst.
oxidation
oxidation
oxidation description
catalyst.
catalyst. ItItItis
isisthe
themost
the mostwidely
most widelyused
widely usedgas
used gassensor
gas sensordesigned
sensor designedspecifically
designed specificallyfor
specifically for
for Solid
Solid
Solid
Category
Combustible
Combustible
Combustible
Detectable gas
1.
ThisBrief
sensordescription
combustible
combustible detects
gases. gas based on heat generated by combustible gas burning on an
gases. Category Detectable gas
combustible
This sensor gases.
detects
oxidation
This catalyst.
sensor detectsIt gasis
gas thebased
moston heat used
widely generated by combustible
gas sensor designed gas burning on an
specifically
gas burningfor
Category
Solid Detectable gas
Combustible
oxidation
combustiblecatalyst.
gases. It is thebased
most on heatused
widely generated by combustible
gas sensor designed specifically on an
for Solid Combustible
2.
2.Structure
2. Structure
oxidation
Structure
combustible and
catalyst. andprinciples
and
gases. It is principles
the most widely
principles used gas sensor designed specifically for Solid Combustible
combustible gases.
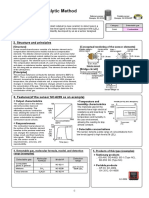
[Structure]
[Structure]
2. Structure and principles
[Structure] [Conceptual
[Conceptualrendering
[Conceptual renderingof
rendering of
ofthe
the
thesensor
sensor
sensorelements]
elements]
elements]
2.
This
ThisStructure
sensor
sensorconsists and
consistsof
of aa principles
detector
detector element
element and
and a acompensation
compensation element.
element. Oxidation
Oxidation Precious-metal Glass
Precious-metal Glass++ Precious-metal
Precious-metal
2.
This
The
The
Structure
sensor consistsand
[Structure]
detector
detectorelement
element
principles
of a detector
consists
consists of
ofaa
element and a compensation element. catalyst
coil
coilof
ofaa precious-metal
precious-metal (e.g.,
(e.g.,
Oxidation
[Conceptual
catalyst++
catalyst +
Precious-metal
rendering
wire
wirecoil
wire coil
coil of
Glass
the
+
sensor
alumina
alumina
aluminasupport
support
support
Precious-metal
elements]
wire
wire
wirecoil
coil
coil
The detector element consists of a coil of a precious-metal (e.g., [Conceptual rendering of the sensor elements]
[Structure]
platinum)
platinum) wire
wire and
andan
an oxidant
oxidant catalyst—a
catalyst—a substance
substance active
activeagainst
against
alumina
alumina
alumina
[Conceptual rendering of the Precious-metal
Glasssensor elements]
Glass +
[Structure]
This sensor
platinum)
This
combustible
combustible
consists of
gas—sintered
a
gas—sintered
detector
on
onthe
element
thecoil
coilalong
along
and
and
with
a
aan
with
compensation
wire and an oxidant catalyst—a substance active against
sensor consists of a detector element compensation
analumina
element.
aluminasupport.
support.
Oxidation
support
support
element. Oxidation
support
catalyst +
Precious-metal
Precious-metal
wire0.5-1.4
coil +
mm alumina support
0.5-1.4mm
Precious-metal
wire coil mm
0.5-1.4
0.5-1.4 mm
The
This detector
combustible element of
sensor gas—sintered
consists consists
on the
a detectorof acoil coilalong
elementof a andprecious-metal
withaan alumina(e.g.,
compensation support. Oxidation
element. alumina
catalyst + wire 0.5-1.4 mm alumina
Precious-metal
coil Glass + support 0.5-1.4 mm
Precious-metal
wire coil
The
The detector
Theelement
element
platinum) wire element
burns
burns
and an in consists
inreaction
reaction
oxidant of
to aany
toany
catalyst—acoil of asubstance
detectable
detectable precious-metal
gas.
gas. The (e.g.,
Thecompensation
active compensation
against
The
The element
detector burns
element in reaction
consists toofany
a detectable
coil of a gas.
precious-metalThe compensation
(e.g., catalyst +
alumina
support wire coil alumina support wire coil
platinum)
element
combustible wire
elementconsists
consists andofofan
gas—sintered oxidant
aaacoil
coilof
ofon catalyst—a
aaaprecious-metal
precious-metal
the coil along substance
wire
wire
with and
anandactive
glass—a
glass—a
alumina against
support. alumina 0.5-1.4 mm
element
platinum) consists
wire andof an coil of
oxidant precious-metal
catalyst—a wire
substance and glass—a
active support 0.5-1.4 mm
combustible
substance
substance
The element
substance
gas—sintered
inactive
inactive
burns
inactive against
against
in on
reaction
against
the
combustible
combustible
to any
combustible
coildetectable
along with gas.
gas—sintered
gas—sintered
gas—sintered
an alumina
on
Theonthe
on theagainst
support.
coil
coilalong
compensation
the coil along
along support 0.8-1.4
0.8-1.4 mm
mm
0.5-1.4 mm 0.8-1.4
0.8-1.4 mm
mm
0.5-1.4 mm
combustible gas—sintered onelement
theany coildetectable
along with an alumina support. 0.8-1.4 mm 0.5-1.4 mm 0.8-1.4 mm 0.5-1.4 mm
The
with
with element
an
element
with an
an alumina
alumina
consists
alumina burns of in
support.
support.
a
support. reaction
coilThis
This
of a to
element
precious-metal
This element corrects
corrects
corrects the the
wiregas.
the and The
effect
effect
effect of
glass—a compensation
of the
the
ofcompensation
the Detector
Detector element
element Compensation
Compensation element
element
The
elementelement
consists burnsof incoil
a reaction
of a to any detectable
precious-metal wire gas.
and The
glass—a Detector element Compensation element
atmosphere.
atmosphere.
substance inactiveofagainst combustible gas—sintered
atmosphere.
element consists
substance inactive a coil of
against a precious-metal
combustible wire andon
gas—sintered on
the coil along
glass—a
thethe coil along [Bridge
[Bridge0.8-1.4
[Bridge circuit]
circuit]
circuit]mm 0.8-1.4 mm
[Principles]
[Principles]
with
with
an alumina
[Principles]
substance inactivesupport.
against This element corrects
combustible
an alumina support. This element corrects the effect of the
the effect
gas—sintered on ofthe coil along Decreased
0.8-1.4
Detector
Decreased element
element
0.8-1.4
mm
element
temperature
mm temperature
0.8-1.4 mm element
Compensation
Increased
Increased
0.8-1.4 mmelement
elementtemperature
temperature
atmosphere.
The
The precious-metal
precious-metal wire
wire coil
coil heats
heats the
the detector
detector element
element to to 300℃
300℃ to
to Detector
Decreased element element
temperature Compensation
=>
Increased
=>Increased
element
element
Increasedresistance
temperature
resistance
with an alumina support. This element corrects
The precious-metal wire coil heats the detector element to 300℃ to
atmosphere. the effect of the [Bridge
=>
=>
circuit]
Decreased
Decreased
=> Decreased
resistance
Detectorresistance
element
resistance Compensation
=> Increasedelement
resistance
[Principles]
450℃.
450℃. Then,
Then,
atmosphere.
450℃. a a combustible
combustible gas
gas burns
burns onon the
the
Then, a combustible gas burns on the surface of the detector surface
surface ofof the
the detector
detector [Bridge circuit]
[Principles]
element,
element, increasing
increasingthe thetemperature
temperature of
ofdetector
the
theelement.
element. With
With tochanges
changes inin
in [Bridge Compensation
Compensation
Decreased circuit]
element temperature
Compensation Increased
Detector
Detector elementelement temperature
element
[Principles]
The
The
precious-metal
element,
temperature,
temperature,
increasing
precious-metal
thethe
wire
the
wire
coil heats the
temperature
coil
precious-metal
precious-metal heatswire
wirethe
of the
detector
coil,
coil, a a
element
element.
element
component
component
With
of to
of the
300℃ to
changes
300℃
the to
element,
element,
Decreased
=> Decreased
Decreased
=> Decreased
element
element
element
element
temperature
resistance
element temperature
resistance
++
+
VV
Detector
Increased
=> element
Increased
Increased
=> Increased
element
element
temperature
resistance
temperature
resistance
450℃.
The Then,
temperature,
precious-metala
the combustible
precious-metal
wire coil gas
heatsburns
wire on
coil,
thechangesthe
a
detector surface
component
elementof the
ofto the detector
300℃ element,
tototo V Sensor
Sensor output
output
450℃.
changes
changes Then,
inin a combustible
resistance.
resistance. The
The gas burns
resistance
resistance on the
changes surface
almost
almost ofin inthe detector
proportion
proportion => DecreasedCompensation
resistance --
-
=> Increased
Sensor
Detector output
element
resistance
element,
changes
450℃. increasing
in resistance.
Then, the
a combustible temperature
The resistance
gas burns of the
changes
on element. With
almostof
the surface in thechanges
proportion
detector in to Compensation
element +
element, increasing temperature of the Detector element
the
theconcentration
concentration ofofthethegas.
gas.TheThewire
bridge
bridge aelement.
circuit
circuit shown
shown With
inin
inofthechanges
the right
right in
figure
figure Compensation Side Side+
temperature,
the concentration
element, the precious-metal
increasing of the
the gas. The
temperature coil,
bridge
of the component
circuit shown
element. With the the element,
right
changes figure
in
element Side V
resistance
resistance Detector element
temperature,
allows
allows the
the the
sensor
sensor precious-metal
toto recognize
recognize thewire
the coil,
change
change ain component
inresistance
resistance of
as as the
thethe element,
voltage
voltage element -V RR
+
resistance R Sensor output
changes
allows theinsensor
temperature, resistance.
the The resistance
to recognize
precious-metal thewirechangechanges
coil, almost inas
incomponent
a resistance of proportion
the element,
the voltage to -V Sensor output
changes
to
todetermine
the in resistance.
determine
concentration the of theThe
theconcentration gas.resistance
concentration of
The ofthethegas.
bridge changes
gas. almostininthe
circuit shown proportion
right figure to
to determine
changes the concentration
in resistance. The of the gas. Sidevoltage
Sensor
Sensor VsSensor output
-voltageVs
the concentration
allows the sensor of
to the gas.resistance
recognize Thethe bridge
change
changes
circuit
in
almostininthe
shown
resistance as
proportion
theright figure
voltage
to Sensor
Side voltage
resistance R Vs
the concentration
allows the sensor of recognize
to the gas. The the bridge
change circuit shown inas the right figure Side
resistance R
to determine the concentration of
thethe gas. in resistance the voltage
3.
3. Features
Features
allows the sensor
3. determine
Features (of
(of
to the
the
recognize
(of the sensor sensor
sensor change HW-6239
HW-6239
in resistance as as
as thean
an example)
example)
voltage resistance R
Sensor voltage Vs
of the gas.HW-6239 as an example)
to determine the concentration of the gas. Sensor voltage Vs
○to
○Output the concentration
Outputcharacteristics
characteristics
○ Output characteristics ○○Temperature
Temperatureand
and Sensor voltage Vs
3.TheFeatures ○ Temperature and
precious-metal(of wirethe sensor HW-6239 as an example)
The precious-metal
precious-metalwire wirecoil, coil,the
the heat
heat Humidity
Humidity(%(%RH)
RH)(40℃atmosphere)
(40℃atmosphere)
Humidity (% RH) (40℃atmosphere)
3.
The Features
source,
○ source, linearly
linearly (of
changes
changes the
inin sensor
coil, the heat HW-6239
100
100
100 as an example)
humidity
humiditycharacteristics
humidity characteristics
characteristics 00 9090
○ 3.
source,Features
Output
Output
temperature
temperature
linearly (ofcoefficient.
characteristics
changes
characteristics
resistance
resistance
the
in sensor
coefficient. In In
HW-6239 as an example) ○
The
The
The
materials
materialsused
Temperature
materials
usedand
used
ininthe
in
the
the
CH
CH
CH44 0 90
The
○ precious-metal
temperature resistance wire coil, the
coefficient. heat In ○ Temperature and 1004 (% RH) (40℃atmosphere)
100
Humidity
theOutput characteristics 100 elements
elements
humidity have
have high
high electrical
characteristicselectrical 100
the
The
the
lower-explosion-limit
source,lower-explosion-limit
precious-metal
linearly changes
lower-explosion-limit wire (LEL) (LEL)
coil,
in
(LEL) the heat Output Output
Output100 ○ Temperature
elements
humidity
resistances
resistances
have highand
characteristics
and
and are
electrical
areless
less likely
likely
Humidity (% RH) (40℃atmosphere)
CH4 0 (% RH) (40℃atmosphere)
Humidity 90
The precious-metal
concentration
concentration
source, linearly region,
region,
changes wire
the
the coil,
burning
in the heat ratio
burning ratio
100 The materials
resistances and used
are in the
less likely CH4 0 90
temperature
concentration resistance
region, thecoefficient.
burning In (%) ratio
(%) humidity
toThe
tobebe affectedcharacteristics
affected
materials byby the
usedthe in the
Reading
Reading
100
Reading Temp
Tempchar
char 90
source,
reaction
reaction
temperature linearly
isis changes
proportional
proportional
resistance toto in
the
the gas
coefficient.gas In (%)
Output elements
to be have
affected high
by the electrical (%
(%LEL) CH4
LEL)
100 0 Temp char
the lower-explosion-limit
reaction is proportional (LEL)
tocoefficient.
the gas In Output The materials
temperature
temperature
elements and
have andused in theinin
humidity
humidity
high electrical (% LEL) Hum
Humchar
char
Hum char
temperature
concentration.
concentration.
the resistance
InInthis
lower-explosion-limit thisregion,
region,
(LEL)the
the ratio resistances
temperature and are
andhigh less
humidity likely
in 100
concentration
concentration. region, the
In this region, burning
the Output theelements
the use
use have
environment,
resistancesenvironment,
and are electrical
allowing
allowing
less likely Reading
the
output lower-explosion-limit
outputfromfrom
concentration the
thesensor
sensorslowly (LEL)
slowly ratio
(%)00 to
thebeuseaffected by are
environment, the less
allowing Temp char
theregion,
sensorthe burning resistances and 00
reaction
output from
concentrationis proportional
region, theto
slowlythe gas
burning ratio0 00
(%) 100 the
100 the
to reading
bereading toto
affected
temperature stay
andstay
by thealmostlikely
almost
humidity in
Reading
(% LEL) 0 Temp
Hum char
changes
changesis
reaction according
according
proportional totothethe
to change
change
the gas inin Gas
Gas concentration
concentration
(%) 0 Gas concentration 100 constant. the reading
to be affected to stay almost
byhumidity
the Reading
(% LEL) Temp char
Hum char
concentration.
changes
reaction according In this
is proportional toregion,
the thethe
tochange gasin constant.
temperature and in (% LEL) -20
-20 6060
gas
gasconcentration.
concentration.
concentration. the use environment,
constant. allowing -20 Temperature
Temperature(℃)char60
(℃)
from theIn this region,
slowlythe (%(%LEL)
LEL) Hum
output
gas concentration. sensor temperature and humidity in Temperature (℃)
○ concentration.
○Responsiveness
output from
Responsiveness In
the sensorthis region,
slowly the 0 (% LEL)
0 0 Gas concentration 100
○ ○
the
the use
Catalystenvironment,
Catalyst
reading
○theCatalyst development
development
to development
stay almost
use environment,
allowing
allowing
0
0
changes according to the change in
○output
Responsiveness
changes from the sensor
according slowly
toproduced
the change 100
100 0 0 Gas concentration
Gas Out100
GasOut the
TheThe reading
detector
detector
constant. to element
stay almost
element uses
usesaacatalyst
catalyst0that
thatpromotes
-20 promotes 60
The
Theconcentration.
gas combustion
combustion heat
heat produced ononin
the
the 100 0 (% LEL) Gas Out 100 the
The reading
detector
constant. to stay
elementalmost uses a catalyst that promotes
-20 Temperature (℃) 60
changes
The according
combustion heattoproduced
the change on inthe
gas
surface
○
concentration.
surface ofofthe
Responsiveness thedetector
detectorelement element Gas
(% concentration
LEL) ○
burning
burning
constant.
burning
reaction.
Catalystreaction.
reaction.
Having
Having
development been
been developed
developed -20
Having been developed in-house
in-house
in-house for
for
Temperature (℃)
for(℃) 60
○
gas
surfaceconcentration.
of the detector element
Responsiveness wire Output Output (% LEL) ○
gasgas
The
Catalyst
sensors,
sensors,
detector
development
this
this catalyst
elementcatalyst
uses makes
makes
a use
use
catalyst of
ofour
thatour
Temperature
proprietary
proprietary
promotes
transfers
transfers
The
○
totothe
combustion
transfers
theprecious-metal
precious-metalwire
heat produced wire
to the precious-metal
Responsiveness on the ratioOutput100
ratio
100
Gas Out
Gas Out ○ Catalyst
gas
The sensors,
detector development
this catalyst
element uses makes use of
a catalyst thatour proprietary
promotes
coil,
coil,changes
changesthe theheat
resistance
resistance ofofthe
the know-how,
know-how,
burning providing
providing
reaction. long-term
Havinglong-term
been stability.
stability.
developed
The
surface
coil,
The
combustion
of the the
changes
combustion detector produced
resistance
heat element
produced of theon the (%)
on the
ratio
(%)100 Gas Out The detector
know-how,
burning reaction. element
providing Having uses
long-term a catalyst
been developed thatin-house
stability. promotesfor
in-house for
bridge
bridgecircuit,
surface circuit,
oftothe and
andthen
detectorthentransforms
transformsinto
element into (%) gas sensors, this catalyst makes use of ourin-house
proprietary
transfers
bridge
surface circuit,
of theand
the precious-metal
then transforms
detector element wireinto Output burning reaction. Having been developed for
signals.
signals.With
transfers With
to theaahigh
highreaction
reaction
precious-metal rate,
rate, this Output
this
wire ratio Gas
GasInIn gas sensors,
know-how, this
providing catalyst makes
long-term use of
stability. our proprietary
coil, changes
signals.
transfers Withto athe
the highresistance
reaction of
precious-metal the
rate, this Output
wire ratio
(%) 0 0 Gas In gas sensors, this catalyst makes use of our proprietary
sensor
sensor
coil, excels
excelsthe
changes ininresponsiveness,
responsiveness,
resistance of the into (%) 100 know-how, providing long-term stability.
bridge
sensor circuit,
excels and then transforms
in responsiveness, ratio0 00 100
coil,
accuracy,
bridge changes
accuracy, and
circuit,andand the resistance
reproducibility.
reproducibility.
then transformsof theinto (%) 0 Time
Time(sec.)
(sec.) 100 know-how, providing long-term stability.
signals.
accuracy, With
bridge circuit, and a high reaction
reproducibility.
and then rate,
transforms this
into Gas InTime (sec.)
signals.
sensor With ain
excels high reaction
responsiveness, rate, this 0 Gas In
signals.
4.sensor
4. Detectable
Detectable With ainhigh gas,
gas, reaction
molecular rate, thisformula,
molecular formula, 0 0 100
0 0 model,
model, Timeand
and
(sec.)detection
detection
accuracy, excels responsiveness,
and reproducibility.
Gas In
5.5.Products
Productsof ofthis
thistypetype(examples)
(examples)
4. Detectable
sensor
accuracy, excels
and in gas, molecular formula,
responsiveness,
reproducibility. model, Time and
(sec.) detection
100
5. Products of this type (examples)
range
range (examples)
(examples) 0 100
accuracy,
range (examples) and reproducibility. Time (sec.) ○○Stationary
Stationaryproducts products
4. Detectable gas, molecular formula, model, and detection ○ Products
5. Stationaryofproducts
this type (examples)
4. Detectable
Detectable
Detectable
range gas
gas
(examples)
Molecular
Molecular formula,
gas, molecular
Molecular
model,
Model
Model ## and Detection
Detection
detection
Detection 5....Products
...GD-A80,
...
GD-A80,GD-A80D,
GD-A80D,
GD-A80, of
SD-1
this type
GD-A80D,
SD-1 (Type
(TypeGP),
(examples)
SD-1
GP),
(Type GP),
4. Detectable
Detectable
range gas, molecular
gas
(examples) formula formula,
formula model,
Model # and detection
range
range 5. Products
SD-D58・DCof
SD-D58・DC
○ Stationary this
(Typetype
(Type
products GP),
GP),(examples)
SD-2500
SD-2500
formula range SD-D58・DC
○ Stationary (Type GP), SD-2500
products
range (examples) Molecular
Combustible
Combustible
Combustible
Detectable
gases gas
gasesiningeneral
general -- HW-6211
HW-6211
Molecular
Detection Model # Detection
○ ...
...
GD-A80, GD-A80D,
Stationary
GD-A80, productsSD-1
GD-A80D,
(Type GP),
SD-1SD-2500
(Type GP),
Detectable
gases gas
in general -
formula HW-6211
Model # range ○○Portable
Portable products
products
... SD-D58・DC (Type GP),
Detectable
Methane
Methane gas Molecular
formula
CH
CH4 4 Model #
HW-6239
HW-6239 Detection
range ○ ... GD-A80,
Portable
...GP-1000
GP-1000
GD-A80D,
products
SD-D58・DC (Type SD-1
GP), (Type GP),
SD-2500
Combustible
Methane formula
CH HW-6239 0-100%
0-100% LEL
LEL
range SD-D58・DC (Type GP), SD-2500
Combustible
gases in general -4 HW-6211 0-100% LEL ... GP-1000
Vinyl
Vinylchloride
chloride
Combustible
gases in general
CC2H
2H
-3Cl
3Cl HW-6214
HW-6214
HW-6211 ○ Portable products
Vinyl
gases
chloride
Methane in general
High-boiler
High-boilergases
gases
C2H-3Cl
CH--4
HW-6214
HW-6211
HW-6239
HW-6228
HW-6228 ○ Portable products
... GP-1000products
Methane gases
High-boiler CH-4 HW-6239
HW-6228
0-100% LEL
0-100% LEL
○ Portable
... GP-1000 SD-1
SD-1(Type
(TypeGP)
GP)
Vinyl chloride
Methane C2CH
H3Cl HW-6214
HW-6239 ... GP-1000 SD-1 (Type GP)
Vinyl chloride C2H3Cl
4
HW-6214 0-100% LEL
High-boiler gases
Vinyl chloride C2H- 3Cl HW-6228
HW-6214
High-boiler gases - HW-6228 SD-1 (Type GP)
High-boiler gases - HW-6228 SD-1 (Type GP)
SD-1 (Type GP)
You might also like
- New Ceramic Catalytic Method Sensor Detects Wide Range of GasesDocument1 pageNew Ceramic Catalytic Method Sensor Detects Wide Range of GasesfullmarineNo ratings yet
- Middle Side Revisi 2bsjsDocument1 pageMiddle Side Revisi 2bsjsJOTA BLUEESSNo ratings yet
- Ads-S: Door Side SensorDocument6 pagesAds-S: Door Side SensorMin ZayarNo ratings yet
- Ifm Position Sensor CatalogoDocument537 pagesIfm Position Sensor CatalogoOscar VazquezNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Ut Blanco 12 Pulg ViaDocument1 page2.1 Ut Blanco 12 Pulg ViaCarolina PBNo ratings yet
- Genuine DS 5 Spare Parts SearchDocument1 pageGenuine DS 5 Spare Parts Searchvali_nedeleaNo ratings yet
- CANNON Asphalt BrochureDocument12 pagesCANNON Asphalt BrochureMohammed AliNo ratings yet
- Daily Check List Electrical PT WarlborDocument7 pagesDaily Check List Electrical PT WarlborAndriawan SuryaRama PutraNo ratings yet
- KX 15 DtamDocument2 pagesKX 15 DtamAbdelhamid SammoudiNo ratings yet
- Aquasearcher AB23 Datasheet ESDocument29 pagesAquasearcher AB23 Datasheet ESzoimar iseaNo ratings yet
- Online StoreDocument1 pageOnline Storealaaezz157No ratings yet
- SITE PLAN-2Document1 pageSITE PLAN-2SHYAM RAJNo ratings yet
- Hira-044 Amct-Ims-Hse-6003b Permanent Mechanical Installation HiraDocument4 pagesHira-044 Amct-Ims-Hse-6003b Permanent Mechanical Installation HiraZuberYousufNo ratings yet
- Sonic Catcher (English)Document2 pagesSonic Catcher (English)subwoofer123No ratings yet
- Fotoforo WelchAllynDocument10 pagesFotoforo WelchAllynDuban GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Albumin RTU BXC0222 A25 A15Document2 pagesAlbumin RTU BXC0222 A25 A15jef1234321No ratings yet
- Label QW Vzb974qbzzDocument1 pageLabel QW Vzb974qbzzNiko GultomNo ratings yet
- Applications of Sensors On CNC Machine Tools - UtmelDocument10 pagesApplications of Sensors On CNC Machine Tools - Utmeljayakrishnan psNo ratings yet
- Deluge ValveDocument1 pageDeluge ValveJosé Daniel ArenasNo ratings yet
- Obstacle Detection Sensor: Instruction ManualDocument1 pageObstacle Detection Sensor: Instruction ManualrloopelectricalsolutionsNo ratings yet
- SynaptiQ User Manual - Annex A Definition of IndicatorsDocument14 pagesSynaptiQ User Manual - Annex A Definition of IndicatorsFilipe MonteiroNo ratings yet
- B PDFDocument68 pagesB PDFCarona FeisNo ratings yet
- Industrial Scanners Catalog EN 201407Document32 pagesIndustrial Scanners Catalog EN 201407Dennis ChaiNo ratings yet
- ALN Level SwitchDocument5 pagesALN Level SwitchKandang DownloadNo ratings yet
- SchematicDocument2 pagesSchematicjcallistusNo ratings yet
- Counter Mat - Occupancy SensorsDocument1 pageCounter Mat - Occupancy SensorsZeeshan SamiNo ratings yet
- 1.wash Pipe 8-1-8 SN NNDocument1 page1.wash Pipe 8-1-8 SN NNMuhammad Rijal sembiringNo ratings yet
- Label QW-VZB974QBZZDocument2 pagesLabel QW-VZB974QBZZNiko GultomNo ratings yet
- Somke Detector + PIR GADDocument1 pageSomke Detector + PIR GADnaveen204No ratings yet
- (Manual) : Rans InstrumentsDocument2 pages(Manual) : Rans InstrumentsBerton HottuaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Scanners Catalog EN LTR 201506BDocument32 pagesIndustrial Scanners Catalog EN LTR 201506BDennis ChaiNo ratings yet
- Sizes: 4-Inch and Larger: Typical SetupDocument4 pagesSizes: 4-Inch and Larger: Typical SetupMartin Andrade100% (2)
- Elektryka 150aetDocument190 pagesElektryka 150aetSandra Krzysiek KaduczkaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Scanners Catalog en LTR 201602Document32 pagesIndustrial Scanners Catalog en LTR 201602Satwant SinghNo ratings yet
- RF Capacitance Level Sensor 2Document12 pagesRF Capacitance Level Sensor 2Adunwit TiampaeNo ratings yet
- Education Solutions CatalogDocument28 pagesEducation Solutions CatalogNenad MilosevicNo ratings yet
- R3JK Photo Sensor PDFDocument6 pagesR3JK Photo Sensor PDFzulheriyantoNo ratings yet
- KudosamDocument2 pagesKudosamAbdelhamid SammoudiNo ratings yet
- A6V10906634 enDocument2 pagesA6V10906634 enfazil yoosufNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document168 pagesUnit 319ME040 KaruthapandiNo ratings yet
- Ruggedized High Temp PMT - Jul 2020Document32 pagesRuggedized High Temp PMT - Jul 2020Pierre-olivier FournandNo ratings yet
- Instrument List and Details for River Water Pumping and Storage ProjectDocument4 pagesInstrument List and Details for River Water Pumping and Storage ProjectBack to SumateraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Certificate of Test Business Trading Name: - ABNDocument1 pageElectrical Certificate of Test Business Trading Name: - ABNCarmina AlmiñeNo ratings yet
- Roughness Inspection ReportDocument1 pageRoughness Inspection ReportwahyuNo ratings yet
- This Document Is Printed From SPI . Not For RESALE: 1600 Series Industrial Engine Electrical SystemDocument2 pagesThis Document Is Printed From SPI . Not For RESALE: 1600 Series Industrial Engine Electrical SystemJacques Van Niekerk100% (1)
- Sheet 1_Electrical Facility & Fence for RMP-2 Sat.WarehouseDocument1 pageSheet 1_Electrical Facility & Fence for RMP-2 Sat.WarehouseaxiefinityforeverNo ratings yet
- SATR-W-2008 Rev 8 FD-1Document6 pagesSATR-W-2008 Rev 8 FD-1asiqna100% (1)
- Long Distance Type Proximity SensorDocument2 pagesLong Distance Type Proximity SensorMin ZayarNo ratings yet
- Senr8579senr8579-01 Sis PDFDocument2 pagesSenr8579senr8579-01 Sis PDFdannyNo ratings yet
- 3.1.07 Schedule of Components: L D SD S PIR DN L/P P Rtls Code Description TotalDocument1 page3.1.07 Schedule of Components: L D SD S PIR DN L/P P Rtls Code Description TotalVinay PallivalppilNo ratings yet
- Nissan CVT Wiring DiagramDocument3 pagesNissan CVT Wiring Diagrambruceauto88% (16)
- 712B - Reference GuideDocument2 pages712B - Reference Guidemanpreet singhNo ratings yet
- SDX 751emDocument4 pagesSDX 751emnabil lakrafiNo ratings yet
- GSM F024 Special Pass Through Characteristics FormDocument1 pageGSM F024 Special Pass Through Characteristics FormQMSNo ratings yet
- Graystone Latest Lab Report RB1Document1 pageGraystone Latest Lab Report RB1redooonionNo ratings yet
- FSV Controllers: A Wide Variety of Control Options To Meet The Requirements of Different ApplicationsDocument8 pagesFSV Controllers: A Wide Variety of Control Options To Meet The Requirements of Different ApplicationsNazriNo ratings yet
- Applied Voltage Test System For TransformersDocument3 pagesApplied Voltage Test System For Transformerschaima haddoudiNo ratings yet
- Daily Weld Production Report: Date ApprovedDocument1 pageDaily Weld Production Report: Date ApprovedYohannan ThomasNo ratings yet
- Cosecha Del DiaDocument41 pagesCosecha Del DiaAnita TulcanNo ratings yet
- Fisherr Posi-Sealt A31A High-Performance Butterfly ValveDocument12 pagesFisherr Posi-Sealt A31A High-Performance Butterfly ValveThanapaet RittirutNo ratings yet
- Ex Protection PDFDocument41 pagesEx Protection PDFSiddharth Sahu100% (1)
- Azbil, Smart Valve PositionerDocument180 pagesAzbil, Smart Valve PositionerRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Digital ORP sensor withstands harsh conditionsDocument3 pagesDigital ORP sensor withstands harsh conditionsRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Konan Electric Co., Ltd. Air FiltersDocument150 pagesKonan Electric Co., Ltd. Air FiltersRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- PH8HF Holder PH Meter, YokogawaDocument39 pagesPH8HF Holder PH Meter, YokogawaRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- E+H, CPS42 ORP ElectrodeDocument12 pagesE+H, CPS42 ORP ElectrodeRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Level GaugeDocument10 pagesMagnetic Level GaugedharmendrabholeNo ratings yet
- Mechanical pressure switches standardDocument3 pagesMechanical pressure switches standardRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- 85000-071 - TECH - F300 - IPS PipeDocument2 pages85000-071 - TECH - F300 - IPS PipelordsethdarknessNo ratings yet
- ROTORK, Air Filter Regulator YT-200 - 205 - 220 - 225Document18 pagesROTORK, Air Filter Regulator YT-200 - 205 - 220 - 225Rangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Fischer and Porter ABB, Vairable Area Flowmeter 10A6100Document18 pagesFischer and Porter ABB, Vairable Area Flowmeter 10A6100Rangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Azbil, MagneW3000 FLEX Electromagnetic Flowmeter ConverterDocument16 pagesAzbil, MagneW3000 FLEX Electromagnetic Flowmeter ConverterRangga Taufiqurahman100% (1)
- Kobold, Pressure Sensor With Ceramic Sensor ElementDocument4 pagesKobold, Pressure Sensor With Ceramic Sensor ElementRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- KROHNE, Magnetic Level BM26A 3000, Plastic LevelDocument32 pagesKROHNE, Magnetic Level BM26A 3000, Plastic LevelRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Top-Guided Single-Seated Control Valves Selection GuideDocument28 pagesTop-Guided Single-Seated Control Valves Selection GuideRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- KROHNE, VA40 Variable Area FlowmeterDocument24 pagesKROHNE, VA40 Variable Area FlowmeterRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Azbil, Single Seated Control Valve (GLOBE)Document2 pagesAzbil, Single Seated Control Valve (GLOBE)Rangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Azbil, Single Seated Control Valve (GLOBE) 2Document20 pagesAzbil, Single Seated Control Valve (GLOBE) 2Rangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Proservo NMS83: Tank GaugingDocument56 pagesTechnical Information Proservo NMS83: Tank GaugingRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Dungs, Pressure SwitchesDocument6 pagesDungs, Pressure SwitchesRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Azbil, MagneW3000 FLEX Electromagnetic Flowmeter Converter 7th EdDocument16 pagesAzbil, MagneW3000 FLEX Electromagnetic Flowmeter Converter 7th EdRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Ti01249gen 0116Document60 pagesTi01249gen 0116Rubén VélezNo ratings yet
- XDT ManualDocument70 pagesXDT Manualmohd shafiniNo ratings yet
- Brooks Kynar, Low FlowmeterDocument8 pagesBrooks Kynar, Low FlowmeterRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- 3/2-, 5/2-And 5/3-Way Solenoid Valves For Process PneumaticsDocument18 pages3/2-, 5/2-And 5/3-Way Solenoid Valves For Process PneumaticsishmaNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa, SE202NJ Integral Electromagnetic FlowmeterDocument17 pagesYokogawa, SE202NJ Integral Electromagnetic FlowmeterRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Electronica PH PDFDocument287 pagesElectronica PH PDFLuis AlbertNo ratings yet
- Yokogawa, SC42Document12 pagesYokogawa, SC42Rangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Shs Grade 11 - TVL SmawDocument34 pagesShs Grade 11 - TVL SmawLara Jeane Losbañes100% (3)
- X-Tite EpoxyGrout 150Document2 pagesX-Tite EpoxyGrout 150jasonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics in Under 40Document18 pagesChemical Kinetics in Under 40JeromeNo ratings yet
- Api 650 Radiographic Requirement Instruction Scope: Th. 10mmDocument3 pagesApi 650 Radiographic Requirement Instruction Scope: Th. 10mmdjafourNo ratings yet
- Ballastguard Cip Cleaner 25 LTRDocument2 pagesBallastguard Cip Cleaner 25 LTRsijinjoyNo ratings yet
- 2210306WW SG1.5 00 - 0Document1 page2210306WW SG1.5 00 - 0Victor PodlozovikNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet Pipeinoc: Pipe DressingDocument1 pageProduct Data Sheet Pipeinoc: Pipe DressingSunil.GNo ratings yet
- Agglomeration HandbookDocument43 pagesAgglomeration HandbookKannanGKNo ratings yet
- SLV General Introduction To Welding TechnologyDocument35 pagesSLV General Introduction To Welding TechnologyMohammad Sobhan RajabiNo ratings yet
- Évfolyam Dolgozat - Peterke ReginaDocument6 pagesÉvfolyam Dolgozat - Peterke ReginaRegina PeterkeNo ratings yet
- Makstil Catalogue Web 2022Document6 pagesMakstil Catalogue Web 2022Matej SutaloNo ratings yet
- SAE, AISI, High Strength Steels Welding TipsDocument13 pagesSAE, AISI, High Strength Steels Welding TipsMARIO HUAMANNo ratings yet
- Me2026 Ucmp Unit 1Document32 pagesMe2026 Ucmp Unit 1velavansuNo ratings yet
- Increasing wear resistance in high-chromium tool steelsDocument19 pagesIncreasing wear resistance in high-chromium tool steelsDaniel NavarroNo ratings yet
- Crucible and High-Frequency MethodsDocument6 pagesCrucible and High-Frequency Methodsmaanka tuduNo ratings yet
- Tds Uniqflow 488u enDocument1 pageTds Uniqflow 488u enm daneshpourNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Mechanical and Metallurgical Properties of TIG Welded AlDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Mechanical and Metallurgical Properties of TIG Welded AlRiyadh MohammedNo ratings yet
- CNCtrai NDocument51 pagesCNCtrai NDavid LucioNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal DesignDocument13 pagesSheet Metal Designsivakumar subramanianNo ratings yet
- AXSON'S GLOBAL OFFERING OF HIGH-PERFORMANCE POLYMER FORMULATION EXPERTISEDocument12 pagesAXSON'S GLOBAL OFFERING OF HIGH-PERFORMANCE POLYMER FORMULATION EXPERTISEAnonymous XzqXVMjNo ratings yet
- Well Intervention WikiDocument2 pagesWell Intervention WikiMarco VelascoNo ratings yet
- Omni Libris 7 in 1 PressDocument20 pagesOmni Libris 7 in 1 PressolgaNo ratings yet
- Successful PlasteringDocument13 pagesSuccessful PlasteringCoulis UtaumireNo ratings yet
- Carbothane®134: Selection & Specification DataDocument2 pagesCarbothane®134: Selection & Specification DataEdy AeNo ratings yet
- Use of Pyroxenite in Place of DolomiteDocument4 pagesUse of Pyroxenite in Place of DolomiteDhirender KapoorNo ratings yet
- 1.emerging Grades Breakthrough Products Coatings - ArcelorMittal - 201707Document52 pages1.emerging Grades Breakthrough Products Coatings - ArcelorMittal - 201707Jerry WangNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Iron and Steelwork in Historic Structures and MachineryDocument35 pagesConservation of Iron and Steelwork in Historic Structures and MachineryJoe CorlettNo ratings yet
- Form XII Welder Qualification RecordDocument3 pagesForm XII Welder Qualification RecordpradeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Tutorvista Com Inorganic Chemistry Metallurgy HTMLDocument18 pagesChemistry Tutorvista Com Inorganic Chemistry Metallurgy HTMLSaid MajiNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Tube and Fittings: Photography Courtesy of Outokumpu, Arcelor and New Zealand Tube MillsDocument13 pagesStainless Steel Tube and Fittings: Photography Courtesy of Outokumpu, Arcelor and New Zealand Tube MillsAwang PannyNo ratings yet