Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Muscle Contraction: Key Points
Uploaded by
Dr Hafiz Syed Tariq Ali Syed Amir AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Muscle Contraction: Key Points
Uploaded by
Dr Hafiz Syed Tariq Ali Syed Amir AliCopyright:
Available Formats
KINESILOGY I
TYPES OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION
KEY POINTS
Isotonic contractions generate force by changing the length of the muscle and
can be concentric contractions or eccentric contractions.
A concentric contraction causes muscles to shorten, thereby generating force.
Eccentric contractions cause muscles to elongate in response to a greater
opposing force.
Isometric contractions generate force without changing the length of the
muscle.
KEY TERMS
Isometric: A muscular contraction in which the length of the muscle does not
change.
isotonic: A muscular contraction in which the length of the muscle changes.
eccentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle lengthens.
concentric: An isotonic contraction where the muscle shortens.
A muscle fiber generates tension through actin and myosin cross-bridge
cycling. While under tension, the muscle may lengthen, shorten, or remain
the same. Although the term contraction implies shortening, when referring
to the muscular system, it means the generation of tension within a muscle
fiber. Several types of muscle contractions occur and are defined by the
changes in the length of the muscle during contraction.
ISOTONIC CONTRACTIONS
Isotonic contractions maintain constant tension in the muscle as the muscle
changes length. Isotonic muscle contractions can be either concentric or
eccentric.
CONCENTRIC CONTRACTIONS
A concentric contraction is a type of muscle contraction in which the muscles
shorten while generating force, overcoming resistance. For example, when
lifting a heavy weight, a concentric contraction of the biceps would cause the
arm to bend at the elbow, lifting the weight towards the shoulder. Cross-
bridge cycling occurs, shortening the sarcomere, muscle fiber, and muscle.
ECCENTRIC CONTRACTIONS
An eccentric contraction results in the elongation of a muscle while the muscle
is still generating force; in effect, resistance is greater than force generated.
Eccentric contractions can be both voluntary and involuntary. For example, a
voluntary eccentric contraction would be the controlled lowering of the heavy
Dr. HAFIZ SYED TARIQ ALI
KINESILOGY I
weight raised during the above concentric contraction. An involuntary
eccentric contraction may occur when a weight is too great for a muscle to
bear and so it is slowly lowered while under tension. Cross-bridge cycling
occurs even though the sarcomere, muscle fiber, and muscle are lengthening,
controlling the extension of the muscle.
Dr. HAFIZ SYED TARIQ ALI
KINESILOGY I
Dr. HAFIZ SYED TARIQ ALI
KINESILOGY I
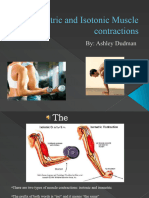
Types of Muscle Contraction: An isotonic concentric contraction results in the
muscle shortening, an isotonic eccentric contraction results in the muscle
lengthening. During an isometric contraction the muscle is under tension but
neither shortens nor lengthens.
ISOMETRIC CONTRACTIONS
In contrast to isotonic contractions, isometric contractions generate force
without changing the length of the muscle, common in the muscles of the
hand and forearm responsible for grip. Using the above example, the muscle
contraction required to grip but not move a heavy object prior to lifting would
be isometric. Isometric contractions are frequently used to maintain posture.
Dr. HAFIZ SYED TARIQ ALI
You might also like
- Types of Muscle ContractionDocument12 pagesTypes of Muscle Contractions_saikalyanNo ratings yet
- Type of Muscle ContractionDocument42 pagesType of Muscle Contractionabdul aziz100% (2)
- LECTURE 7 Types of Muscle ContractionDocument3 pagesLECTURE 7 Types of Muscle ContractionAtharva kengarNo ratings yet
- Describe The Stages of A Muscle TwitchDocument17 pagesDescribe The Stages of A Muscle TwitchshaiksardarnagulmeeraNo ratings yet
- Lec 9active & Passive InsufficiencyDocument32 pagesLec 9active & Passive InsufficiencySajida Bibi Noonari75% (4)
- WEEK 2 STRESS BREAKDocument6 pagesWEEK 2 STRESS BREAKHey itsJamNo ratings yet
- Isotonic ExerciseDocument10 pagesIsotonic ExerciseErnesto Ilagan Manlangit IIINo ratings yet
- In An Isotonic ContractionDocument2 pagesIn An Isotonic Contractionsamhi96No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Concepts of Physical ExerciseDocument33 pagesLesson 1 - Concepts of Physical ExerciseXehdrickke FernandezNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscle ContractionsDocument16 pagesTypes of Muscle ContractionsMaryam AdeelNo ratings yet
- KinesiologyDocument8 pagesKinesiologyMunirajsNo ratings yet
- Ankles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingDocument18 pagesAnkles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingJess Zausa MasulaNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatDocument14 pagesKinesiology: Chapter 2 (An Introduction To Movement) : DR: Iqra KaramatNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- physical fitness unit 4&5Document68 pagesphysical fitness unit 4&5besedegefub9131No ratings yet
- Muscle ContractionDocument2 pagesMuscle Contractionaikoii sanNo ratings yet
- Isotonic ExerciseDocument2 pagesIsotonic ExerciseInspera WooNo ratings yet
- Types of ExcerciseDocument13 pagesTypes of ExcerciseTefera LeteboNo ratings yet
- Types of Exercise: Isometric, Progressive, Isokinetic, Plyometric & Open vs Closed KineticDocument13 pagesTypes of Exercise: Isometric, Progressive, Isokinetic, Plyometric & Open vs Closed KineticTefera LeteboNo ratings yet
- Unit Four Health Related Components of Fitness and Principles of Exercise PrescriptionDocument12 pagesUnit Four Health Related Components of Fitness and Principles of Exercise PrescriptionYoseph DefaruNo ratings yet
- Myograms and Muscle ContractionDocument15 pagesMyograms and Muscle ContractionEmirDefaNo ratings yet
- What Is Isotonic StrengthDocument1 pageWhat Is Isotonic Strengthabe dereNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology Week 2 - Role of MusclesDocument3 pagesKinesiology Week 2 - Role of MusclesNur DaleelaNo ratings yet
- Isometric Exercise (Static Exercise)Document18 pagesIsometric Exercise (Static Exercise)venkata ramakrishnaiah100% (3)
- Muscular TissueDocument8 pagesMuscular TissueKaleem KhanNo ratings yet
- Mod7 - Technology, Strength Training and Muscle Power - Technology, Equipment and General Strength Training - Act1Document2 pagesMod7 - Technology, Strength Training and Muscle Power - Technology, Equipment and General Strength Training - Act1coupfrank.podcastNo ratings yet
- Isometric Exercises Are TighteningDocument1 pageIsometric Exercises Are TighteningAdrian B. OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Types of Muscle Contractions for Strength TrainingDocument1 pageTypes of Muscle Contractions for Strength TrainingJosu AzkarateNo ratings yet
- Static Stretching ExercisesDocument25 pagesStatic Stretching Exercisesearvin-ardrin-villarba-5168No ratings yet
- Muscle Contractions Isotonic and Isometric The PrefixDocument9 pagesMuscle Contractions Isotonic and Isometric The PrefixLeilanie M. GabrielNo ratings yet
- The Flexible ApproachDocument9 pagesThe Flexible ApproachBrian Le VuNo ratings yet
- 4. FlexibilityDocument6 pages4. Flexibilityroidonato12No ratings yet
- Strengthen Your Muscles and BonesDocument25 pagesStrengthen Your Muscles and BonesAshley Keith RamiloNo ratings yet
- Phatfit NotesDocument1 pagePhatfit NotesChristine Marie CayundaNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Bone Activities for a Strong BodyDocument13 pagesMuscle and Bone Activities for a Strong BodyAlex ValdecañasNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument89 pagesMusclesSelena ReyesNo ratings yet
- Muscle ContractionDocument8 pagesMuscle Contractionwx8vnnnzjhNo ratings yet
- IsometricsDocument3 pagesIsometricsgtlaau100% (1)
- Hpe Assignment 222222Document4 pagesHpe Assignment 222222abe dereNo ratings yet
- RESISTANCE EXERCISE FOR IMPAIRED MUSCLE PERFORMANCE AFTER OPERATIONDocument48 pagesRESISTANCE EXERCISE FOR IMPAIRED MUSCLE PERFORMANCE AFTER OPERATIONmilenia w. shandraNo ratings yet
- Ana203 TutorialDocument14 pagesAna203 TutorialAina AdesolaNo ratings yet
- Nelson VCE PEDocument23 pagesNelson VCE PEPNo ratings yet
- 596 - 4º Strength19-20Document7 pages596 - 4º Strength19-20AlexanderBarreraNo ratings yet
- Muscular Fitness 1Document16 pagesMuscular Fitness 1delaramajosephalexisNo ratings yet
- Stretching PDFDocument7 pagesStretching PDFBarbie TallonNo ratings yet
- Stretching For Dancers PDFDocument7 pagesStretching For Dancers PDFInés RamírezNo ratings yet
- Isometric Exercise: Overcoming Versus YieldingDocument3 pagesIsometric Exercise: Overcoming Versus YieldingKarlina DahlianingrumNo ratings yet
- Muscle Performance Exercises: Muscle Performance Is Affected by All Systems of The BodyDocument7 pagesMuscle Performance Exercises: Muscle Performance Is Affected by All Systems of The BodyBella Abbellargobel TralalaNo ratings yet
- GBS Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating PolyradiculoneuropathyDocument6 pagesGBS Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathylestari bmNo ratings yet
- Hpe AssignmentDocument4 pagesHpe Assignmentabe dereNo ratings yet
- Pe1 - Week 9.1Document12 pagesPe1 - Week 9.1Norman NarbonitaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Exercises Ii: Dr. Saeed Mohamed IbraheemDocument19 pagesTherapeutic Exercises Ii: Dr. Saeed Mohamed Ibraheemmaria magdyNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness ComponentsDocument37 pagesPhysical Fitness ComponentsYoomif TubeNo ratings yet
- PF CH 4444 NewDocument32 pagesPF CH 4444 NewFikeduNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument43 pagesMuscular SystemJonalyn ChewacheoNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Kinesiologi NeumannDocument19 pagesRangkuman Kinesiologi NeumannAnton HilmanNo ratings yet
- MUSCLESDocument6 pagesMUSCLESTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Antigravity MusclesDocument16 pagesAntigravity MusclesFemiNo ratings yet
- Document 6Document10 pagesDocument 6shivalee.abirajNo ratings yet
- Muscle Strength and Muscle ActionDocument54 pagesMuscle Strength and Muscle ActionFarrukh Shahzad100% (6)
- Smolov JRDocument1 pageSmolov JRMike GarciaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Functions and AnatomyDocument6 pagesSkeletal System Functions and AnatomyWendi KongNo ratings yet
- To Download: Click On File - Download As - Microsoft Excel (.XLSX) WWW - Drworkout.FitnessDocument4 pagesTo Download: Click On File - Download As - Microsoft Excel (.XLSX) WWW - Drworkout.FitnessGustavoAguirreValencianaNo ratings yet
- Beating Plantar Fasciitis PainDocument49 pagesBeating Plantar Fasciitis PainAllison BoswellNo ratings yet
- Build Muscle with This Isometrics WorkoutDocument40 pagesBuild Muscle with This Isometrics Workoutaeroartonline87% (31)
- Upper Body Exercises For Muscular Strength and EnduranceDocument8 pagesUpper Body Exercises For Muscular Strength and EnduranceMario Miguel De VillaNo ratings yet
- Lower Body Progressions and PregressionsDocument25 pagesLower Body Progressions and Pregressionsmaurice86No ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bengaluru, KarnatakaDocument9 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bengaluru, KarnatakaNavin ChandarNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Aditya Alfarizki 71.2017.007: Pembimbing: Dr. Rizal Daulay, SP - OT, MARSDocument25 pagesMuhammad Aditya Alfarizki 71.2017.007: Pembimbing: Dr. Rizal Daulay, SP - OT, MARSaditNo ratings yet
- What Are Some Common Challenges With BreastfeedingDocument7 pagesWhat Are Some Common Challenges With BreastfeedingAaronMaroonFiveNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Patterns ExplainedDocument3 pagesFingerprint Patterns ExplainedRyan BorcelisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MCQ - Upper LimbDocument37 pagesAnatomy MCQ - Upper LimbHome Arfaj100% (2)
- GuruMann - Exercises - Workout-Intermediate Fat LossDocument2 pagesGuruMann - Exercises - Workout-Intermediate Fat LossSuleiman AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Objective Ie. QualimedDocument10 pagesObjective Ie. QualimedPhiliaMelAbarquezNo ratings yet
- 895 1993 1 SM PDFDocument9 pages895 1993 1 SM PDFRahma TikaNo ratings yet
- Master Techniques OrthopedicsDocument378 pagesMaster Techniques OrthopedicsFabio Sales VieiraNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Hand SurgeryDocument566 pagesAtlas of Hand SurgeryCostea Hincu100% (2)
- Aaop2003 PDFDocument102 pagesAaop2003 PDFSalemNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Palpation List Term2Document37 pagesAnatomy - Palpation List Term2h_sadeghi100% (1)
- Manual Muscle Testing of Infants, Toddlers, & Preschool ChildrenDocument7 pagesManual Muscle Testing of Infants, Toddlers, & Preschool Childrendeasy100% (1)
- Acute Groin Injuries: Experiences From AspetarDocument7 pagesAcute Groin Injuries: Experiences From AspetarAbdul Wahid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The ShoulderDocument61 pagesAnatomy of The ShoulderChaman Lal KarotiaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System NotesDocument3 pagesMusculoskeletal System Notesalex blesaNo ratings yet
- Entrapment of The Posterior Interosseous Nerve - Ax ArticleDocument9 pagesEntrapment of The Posterior Interosseous Nerve - Ax ArticleNaz HossNo ratings yet
- CSS Osteoarthritis GenuDocument33 pagesCSS Osteoarthritis Genufatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Shoulder and scapular joint mobilization techniquesDocument1 pageShoulder and scapular joint mobilization techniquesmahender100% (2)
- Biomechanics of The Anterior Cruciate LigamentDocument37 pagesBiomechanics of The Anterior Cruciate LigamentRoshynta Linggar Andatu100% (1)
- Bent-Over Row WorkoutDocument3 pagesBent-Over Row Workoutserveh80No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 THE BONES AND MUSCLES A1 and A2Document15 pagesChapter 3 THE BONES AND MUSCLES A1 and A2Marinette Valencia MedranoNo ratings yet
- Care of Orthopedic Patients With Baker CystsDocument27 pagesCare of Orthopedic Patients With Baker CystsLuayon FrancisNo ratings yet