Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Independent
Uploaded by
SHEILA MAE SACLOT0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views3 pagesNursing Diagnosis
Original Description:
COPD
Original Title
NCP COPD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNursing Diagnosis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Independent
Uploaded by
SHEILA MAE SACLOTNursing Diagnosis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
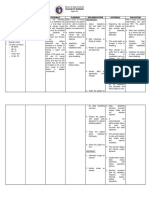
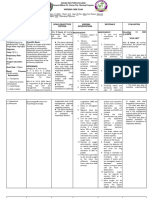
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation
Date: 08/25/2021 Impaired gas Within 30 minutes Independent After my 30 minutes
Time: 8:15 AM exchange related to span of my nursing 1. Assess respirations: quality, 1. Rapid, shallow span of my nursing
altered delivery of care rate, pattern, depth, and breathing, and care:
Objective cues: oxygen as evidenced Client will be able to breathing effort. hypoventilation affect gas Client maintained a
Abdominal by tachypnea. maintain respiration exchange by affecting C02 respiration of 18.
breathing of 25 to 20cpm levels. Flaring of the
PaO2 of 73mmHg Rationale: . nostrils, dyspnea, use of
and an A-a O2 Impaired gas accessory muscles, -GOAL MET-
gradient of 32mmHg exchange occurs tachypnea and or apnea
112 bpm due to alveolar- are all signs of severe
RR-26 CPM capillary membrane distress that require SHEILA MAE SACLOT
changes, such as immediate intervention. SN,UM
fluid shifts and fluid
collection into 2. Auscultate lung sounds. 2. Absence of lung
interstitial space and Also assess for the presence sounds, JVD and/or
alveoli. This leads to of jugular vein distention tracheal deviation could
excess or deficit of (JVD) or tracheal deviation. signify a Pneumothorax or
oxygen at the Hemothorax.
alveolar capillary
membrane with 3. Assess for signs of 3. Tachycardia,
impaired carbon hypoxemia. restlessness, diaphoresis,
dioxide elimination. headache, lethargy and
confusion are all signs of
hypoxemia.
4. Monitor vital signs. 4. To obtain baseline data
5. Monitor ABG 5. Increase PaCO2 and
decreasing PaO2 are signs
of respiratory failure.
6. Use Pulse Oximetry to 6. Pulse oximetry is used
monitor O2 Saturation ; to detect changes in
assess arterial blood gases oxygenation.
(ABGs).
7. Monitor heart rate and 7. Tachycardia is usually
rhythm and blood pressure. present as a result of
fever and/or dehydration
but may represent a
response to hypoxemia.
8. Position the patient with 8. Promotes better lung
head of bed 45 degrees (if expansion and improved
tolerated). gas exchange.
9. Pace activities and provide 9. Even simple activities,
rest periods to prevent such as bathing, can
fatigue. increase oxygen
consumption and cause
fatigue.
Dependent:
10. Administer oxygen 10. The purpose of
therapy as ordered oxygen therapy is to
maintain adequate
oxygenation.
You might also like
- Acid-Base Balance and Oxygenation: Blood GasesDocument5 pagesAcid-Base Balance and Oxygenation: Blood GasesMarcus, RN100% (6)
- RN Expert Guides Cardiovascular Care PDFDocument512 pagesRN Expert Guides Cardiovascular Care PDFSteven Berschaminski100% (1)
- Respiratory DisordersDocument15 pagesRespiratory Disordersmnlstr100% (5)
- Acid-Base and Electrolyte Handbook for Veterinary TechniciansFrom EverandAcid-Base and Electrolyte Handbook for Veterinary TechniciansAngela Randels-ThorpNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Taste PathwayDocument13 pagesTaste PathwayLavanya KalapalaNo ratings yet
- Psychia Case Study Group 2 July 4 2021Document75 pagesPsychia Case Study Group 2 July 4 2021SHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Module 11Document26 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Module 11weissNo ratings yet
- Biohackers Handbook ImmunityDocument37 pagesBiohackers Handbook ImmunityDaniel PopNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Gas ExchangeGabriel Tolentino70% (10)
- Module 11. Pre-Natal DevelopmentDocument5 pagesModule 11. Pre-Natal DevelopmentRachel Joy SaldoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern - NCPDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern - NCPHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- Nervous Systems: Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen FitzpatrickDocument100 pagesNervous Systems: Lecture Presentations by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen FitzpatrickSallyNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 N 2Document5 pagesNCP 1 N 2Cuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PediaDocument18 pagesDrug Study PediaCyx17No ratings yet
- PRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPRIORITY 2: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Excessive or Thick Secretions Tree Secondary To PneumoniaElay Pedroso100% (1)
- Practical BotanyDocument123 pagesPractical BotanyKasraSr100% (12)
- Respiratory ModalitiesDocument87 pagesRespiratory ModalitiesLj Ferolino100% (2)
- Syllabus For BiochemistryDocument8 pagesSyllabus For BiochemistryJenny Lyn Nebres100% (1)
- Clinical and Experimental Restricted Environmental StimulationDocument333 pagesClinical and Experimental Restricted Environmental Stimulationst.machadoNo ratings yet
- Hashim Clinical Log 3Document10 pagesHashim Clinical Log 3Hashim AlsammawiNo ratings yet
- NCP Difficulties in BreathingDocument4 pagesNCP Difficulties in BreathingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveIngrid Eunice ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Independentyanny03No ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentHazel MiraranNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis OUTLINEDocument3 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysis OUTLINEPaula TapilNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- 296 - Renal Pathology) Respiratory AcidosisDocument4 pages296 - Renal Pathology) Respiratory AcidosisMuhammadR1No ratings yet
- COPD NCPs For Presentation and WordDocument4 pagesCOPD NCPs For Presentation and WordMichaela JapsayNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure Concept MapDocument1 pageAcute Respiratory Failure Concept Mapjenievysenerez100% (1)
- Icu 2Document9 pagesIcu 2GemilleDaphneAndradaNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State University College of Health Sciences Marawi CityDocument17 pagesMindanao State University College of Health Sciences Marawi CityBella DonnaNo ratings yet
- Copd - Midterm NotesDocument2 pagesCopd - Midterm NotesInday BertaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: IndependentAlyssa Marie SantosNo ratings yet
- Non Respi O2 CO2 TransportDocument13 pagesNon Respi O2 CO2 TransportRicky JalecoNo ratings yet
- Diana Kyla A. Punay Bsn-Dash-6: Subjective Data: Short Term: Short TermDocument3 pagesDiana Kyla A. Punay Bsn-Dash-6: Subjective Data: Short Term: Short TermZoè AshtrönNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System V4Document25 pagesRespiratory System V4Mohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- 3.05 PHYSIOLOGY-Control of RespirationDocument2 pages3.05 PHYSIOLOGY-Control of RespirationDi CanNo ratings yet
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- Week 7 NCP CHFDocument3 pagesWeek 7 NCP CHFSeth Michael Daniel BenauroNo ratings yet
- Icu 2Document9 pagesIcu 2GemilleDaphneAndradaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 NCP Patient FDocument12 pagesGROUP 8 NCP Patient FasdasdNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument22 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureSampada GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- NCP - Or-Rotation 2Document12 pagesNCP - Or-Rotation 2Vian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Bernadas NCPDocument3 pagesBernadas NCPBernadas, Jhon Kristopher C.No ratings yet
- 297 - Renal Pathology) Respiratory AlkalosisDocument3 pages297 - Renal Pathology) Respiratory AlkalosisMuhammadR1No ratings yet
- NCP and Drug StudyDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug StudyKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Alteration in Ventilatory FunctionDocument5 pagesAlteration in Ventilatory FunctionMary Danielle SaludarioNo ratings yet
- L4 PDFDocument12 pagesL4 PDFMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- Small Animal Oxygen TherapyDocument10 pagesSmall Animal Oxygen Therapytaner_soysuren100% (1)
- NCP BauanDocument2 pagesNCP BauanJoedelynne Diane Endaya GarciaNo ratings yet
- CMM Alkalosis, AcidosisDocument1 pageCMM Alkalosis, AcidosisTriccie Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in AcidDocument11 pagesDisturbances in AcidShannen Alija M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKimmy DoraNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationPrincess CaidoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Modalities PPT - KateDocument80 pagesRespiratory Modalities PPT - KateShara SampangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AnemiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan AnemiaNat B. AntipoloNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument11 pagesCase AnalysisCZAR VINCENT WAYNE SEVANDAL BAYLONNo ratings yet
- Blok KGD Pemicu 7Document93 pagesBlok KGD Pemicu 7LuzjrNo ratings yet
- Assessment RationalesDocument3 pagesAssessment RationalesEllee HadesNo ratings yet
- 1 6 - Oxygen-TherapyDocument62 pages1 6 - Oxygen-TherapyJUSTIN ALZATENo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- CapnographyInCats Feline ABVP2015 HeidiLShaffordDocument2 pagesCapnographyInCats Feline ABVP2015 HeidiLShaffordCarolina Duque RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument5 pagesCase PresentationJARIETTA OCHOANo ratings yet
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and PalateDocument8 pagesCleft Lip and PalateSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AccidentDocument7 pagesCardiovascular AccidentSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument5 pagesRRLSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Curriculum-Vitae RicoDocument2 pagesCurriculum-Vitae RicoSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Seminar - This Is A Type of Academic Activity Happened Within An Instruction orDocument13 pagesSeminar - This Is A Type of Academic Activity Happened Within An Instruction orSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- ATORVASTATINDocument1 pageATORVASTATINSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToDocument2 pagesDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- DELIRIUMDocument7 pagesDELIRIUMSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- CATARACTDocument8 pagesCATARACTSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Drug StudySHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Letters & ResumeDocument4 pagesLetters & ResumeSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Elaborate The QuoteDocument1 pageElaborate The QuoteSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Saturn: Significant Events in The Philippines From 1521-1861Document5 pagesSaturn: Significant Events in The Philippines From 1521-1861SHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Case Study CHF Final Output Group 2Document83 pagesCase Study CHF Final Output Group 2SHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Elaborate The QuoteDocument1 pageElaborate The QuoteSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Guiding PrincipleDocument1 pageGuiding PrincipleSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Elaborate The QuoteDocument1 pageElaborate The QuoteSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NCM 118 FinalDocument15 pagesDrug Study NCM 118 FinalSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Computer Tomografia Toracelui: Anatomia Radiologica A Plamanului Si MediastinuluiDocument82 pagesComputer Tomografia Toracelui: Anatomia Radiologica A Plamanului Si MediastinuluikoxNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 9.1: Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity 9.1: Skeletal SystemCrystal Jade RetuyaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Zhatka Final - PDF BiologyDocument24 pagesNCERT Zhatka Final - PDF BiologyKunal Dattatray SapateNo ratings yet
- Functional Organization of Motoneuron Pool and Its InputsDocument85 pagesFunctional Organization of Motoneuron Pool and Its InputsPabloNo ratings yet
- PHYS30012 - Week7 - Heat AcclimationDocument20 pagesPHYS30012 - Week7 - Heat AcclimationDennis GuNo ratings yet
- Parasitology PresentationDocument28 pagesParasitology PresentationSamuel WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Ginger Rhizomes (Zingiber Officinale) A Spice With Multiple Healthbeneficial PotentialsDocument11 pagesGinger Rhizomes (Zingiber Officinale) A Spice With Multiple Healthbeneficial PotentialsRabeea NasirNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia in The Newborn and Infant: M.A. Sperling O. Escobar O. Pinhas-HamielDocument2 pagesHypoglycemia in The Newborn and Infant: M.A. Sperling O. Escobar O. Pinhas-HamielDaniela CioboataNo ratings yet
- Holes Human Anatomy and Physiology 13Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument49 pagesHoles Human Anatomy and Physiology 13Th Edition Shier Test Bank Full Chapter PDFJakeOwensbnpm100% (9)
- Electron Transport ChainDocument35 pagesElectron Transport ChainNusrat JahanNo ratings yet
- Visual PerceptionDocument12 pagesVisual Perceptionamelia99No ratings yet
- Electron Transport Channel & Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument55 pagesElectron Transport Channel & Oxidative PhosphorylationShahabNo ratings yet
- Asmolov, A. G. (1986) - Basic Principles of A Psychological Analysis in The Theory of Activity. Soviet Psychology, 25 (2), 78-102Document26 pagesAsmolov, A. G. (1986) - Basic Principles of A Psychological Analysis in The Theory of Activity. Soviet Psychology, 25 (2), 78-102glauber stevenNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument13 pagesExcretory Products and Their Eliminationaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- MLS 111B LABORATORY ENDTERM Very FinalDocument6 pagesMLS 111B LABORATORY ENDTERM Very FinalJohanna MarieNo ratings yet
- The Bone Marrow Niche For Haematopoietic Stem CellsDocument21 pagesThe Bone Marrow Niche For Haematopoietic Stem CellsHitomi-No ratings yet
- Concept Strengthening Sheet CSS 01 Based On CST 01 & 02 BotanyDocument4 pagesConcept Strengthening Sheet CSS 01 Based On CST 01 & 02 BotanyAyush KullarkarNo ratings yet
- FBS 101.forest Botany: Undag, Vens Ric V. BSF-1Document8 pagesFBS 101.forest Botany: Undag, Vens Ric V. BSF-1VENS RIC VIOS UNDAGNo ratings yet
- Natural Defense and Immunity: Biol S302FDocument68 pagesNatural Defense and Immunity: Biol S302FLo Yuen ChanNo ratings yet
- Classification of Injuries FMTDocument30 pagesClassification of Injuries FMTkhadzx100% (2)
- EFA - Module 2 r1Document57 pagesEFA - Module 2 r1Jerry CañeroNo ratings yet
- GEN. BIO. 2 Q4 Wk2A MENDELSSOHN L. AJESTA IIDocument12 pagesGEN. BIO. 2 Q4 Wk2A MENDELSSOHN L. AJESTA IIJohn Paul Luzgano AganapNo ratings yet