0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views10 pagesGrade 11 Math: Simple & Compound Interest
1. The document provides a self-learning home task on general mathematics for grade 11 students.
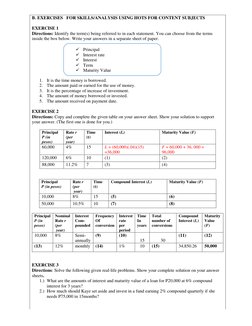
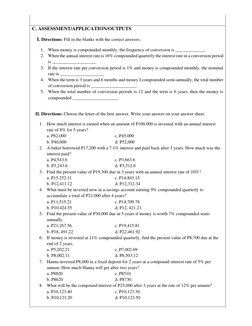
2. It covers the intended learning outcomes of computing interest, maturity value, and present value of simple and compound interest and solving related problems.
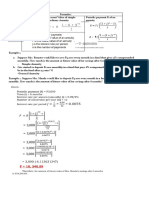
3. The task explains the concepts of simple interest, compound interest, and how to calculate interest, present value, future value, and solve sample problems involving simple and compound interest.
Uploaded by
Alex Albarando SaraososCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views10 pagesGrade 11 Math: Simple & Compound Interest
1. The document provides a self-learning home task on general mathematics for grade 11 students.
2. It covers the intended learning outcomes of computing interest, maturity value, and present value of simple and compound interest and solving related problems.
3. The task explains the concepts of simple interest, compound interest, and how to calculate interest, present value, future value, and solve sample problems involving simple and compound interest.
Uploaded by
Alex Albarando SaraososCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- General Introduction
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Compounding Frequency
- Exercises and Assessments
- Answer Key