Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Losartan
Uploaded by
Kirsty Marie Supranes0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
528 views2 pages1. This document summarizes information about the drug losartan, including its classification, mechanism of action, side effects, nursing responsibilities, and patient education points.
2. Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist used to treat hypertension and reduce risk of stroke. It works by blocking vasoconstriction and aldosterone secretion.
3. Nurses should monitor blood pressure and side effects like cough, diarrhea, and dizziness. Education includes lifestyle changes, monitoring symptoms, and strict adherence to the medication regimen.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. This document summarizes information about the drug losartan, including its classification, mechanism of action, side effects, nursing responsibilities, and patient education points.
2. Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist used to treat hypertension and reduce risk of stroke. It works by blocking vasoconstriction and aldosterone secretion.
3. Nurses should monitor blood pressure and side effects like cough, diarrhea, and dizziness. Education includes lifestyle changes, monitoring symptoms, and strict adherence to the medication regimen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
528 views2 pagesDrug Study Losartan
Uploaded by
Kirsty Marie Supranes1. This document summarizes information about the drug losartan, including its classification, mechanism of action, side effects, nursing responsibilities, and patient education points.
2. Losartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist used to treat hypertension and reduce risk of stroke. It works by blocking vasoconstriction and aldosterone secretion.
3. Nurses should monitor blood pressure and side effects like cough, diarrhea, and dizziness. Education includes lifestyle changes, monitoring symptoms, and strict adherence to the medication regimen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
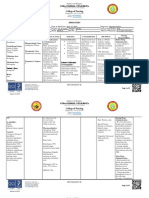
DRUG STUDY FORM
Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Nursing Responsibilities/
Adverse Effects Patient and Family Health Teachings
PHARMACOTHERAP Blocks vasoconstrictor, SE: Frequent (8%): Upper 1. Assess blood pressure periodically and compare
Generic Name EUTIC: Angiotensin II aldosterone-secreting effects respiratory tract infection. it to normal values. R: to help document
receptor antagonist of angiotensin II, inhibiting Occasional (4%–2%): Dizziness, antihypertensive effects
losartan binding of angiotensin II to AT1 diarrhea, cough. Rare (1% or less): 2. Assess for the mentioned contraindications to this
CLINICAL: receptors. Therapeutic Effect: Insomnia, dyspepsia, heartburn, drug (e.g. renal impairment, hyponatremia,
Brand Name Antihypertensive Causes back/leg pain, muscle cramps, hypovolemia, etc.). R: to prevent potential
vasodilation, decreases myalgia, nasal congestion, adverse effects
peripheral resistance, sinusitis, depression. 3. Obtain baseline status for weight, vital signs,
Cozaar
decreases B/P. overall skin condition, and laboratory tests like
AE: Overdosage may manifest as renal and hepatic function tests, serum electrolyte,
hypotension and tachycardia. and complete blood count (CBC) with differential.
Bradycardia occurs less often. R: to assess patient’s response to therapy
Institute supportive measures. 4. Administer drug on empty stomach one hour
before or two hours after meal. R: to ensure
optimum drug absorption.
5. Monitor renal and hepatic function tests R: to
alert doctor for possible development of renal
and/or hepatic failure as well as to signal need
for reduced drug dose
6. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate and rhythm.
R: to detect possible development of adverse
effects.
7. Monitor for presence of manifestations that signal
decreased in fluid volume (e.g. diarrhea, vomiting,
dehydration). R: to prevent exacerbation of
hypotensive effects of drugs.
Picture Indication Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamics
Hypertension, Well absorbed after PO PO 8. Educate patients on the importance of healthy
Nephepatically in administration. Protein Onset: N/A lifestyle choices which include regular exercise,
type 2 diabetes binding: 98%. Peak: 6hrs weight loss, smoking cessation, and low-sodium
person, to reduce Metabolized in the liver. Duration: 24hrs diet. R: to maximize the effect of
risk of CVA in Excreted in urine (35%), antihypertensive therapy.
9. Educate patients and family members about the
patients with feces (60%). Not
drug's effect on the body and manifestations that
hypertension and removed by would need reporting. R: to enhance patient
left ventricular hemodialysis. Half- life: knowledge on drug therapy and promote
hypertrophy 2 hrs; metabolite, 6–9 adherence.
hrs. 10. Emphasize to the client the importance of
strict adherence to drug therapy. R: to ensure
maximum therapeutic effects.
Reference:
- Hodgson, B. B., & Kizior, R. J. (2019). Saunders nursing drug handbook.
You might also like
- Mu CostaDocument7 pagesMu Costayvoniemaebruno0% (1)
- Generic NameDocument2 pagesGeneric NameMichael PalmaNo ratings yet
- Losartan Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Bearse Tablet InsertDocument2 pagesBearse Tablet InsertLeonard ByunNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmoxiclavDocument3 pagesDrug Study AmoxiclavIzza DeloriaNo ratings yet
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Linagliptin - DRUG STUDYDocument1 pageLinagliptin - DRUG STUDYAcads useNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MirceraDocument2 pagesDrug Study - MirceraRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolDocument3 pagesDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128No ratings yet
- Drug Study ProglinDocument2 pagesDrug Study ProglinChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- New DS3Document3 pagesNew DS3dakieNo ratings yet
- DS (Fenofibrate)Document5 pagesDS (Fenofibrate)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyKynaWeeNo ratings yet
- 13 DexamethasoneDocument2 pages13 DexamethasoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Focus Diagnosis Action ResponseDocument2 pagesFocus Diagnosis Action ResponseGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- ItoprideDocument2 pagesItoprideLesValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- NeoblocDocument2 pagesNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- IrbesartanDocument3 pagesIrbesartanapi-3797941No ratings yet
- AtorvastatinDocument2 pagesAtorvastatinKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmlodipineDocument1 pageDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJuan de Vera100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Ascorbic AcidDocument2 pagesAscorbic AcidJaymark Lambino100% (1)
- Captopril Drug StudyDocument1 pageCaptopril Drug StudyRachel Mae Dente AcedillaNo ratings yet
- Conzace Tranexamic MetoclopramideDocument5 pagesConzace Tranexamic MetoclopramideDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- FDAR - Abdominal DistensionDocument1 pageFDAR - Abdominal DistensionjaneNo ratings yet
- BiperidenDocument2 pagesBiperidenALmik HussinNo ratings yet
- Difflam Drug StudyDocument1 pageDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaNo ratings yet
- RebamipideDocument5 pagesRebamipidejunerubinNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationDocument5 pagesHydrochlorothiazide: Drug InformationKhaled ElabdNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanningDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanningSasa QuinaNo ratings yet
- Diclofenac Sodium & Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDiclofenac Sodium & Omeprazole Drug StudyMelah MunchlaxNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJonica CamposNo ratings yet
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanningDocument1 pageDischarge PlanningzbestgurlNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexDocument5 pagesDrug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- DuphalacDocument2 pagesDuphalacianecunarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Conditioning Monitoring ChartDocument2 pagesCardiovascular Conditioning Monitoring ChartDanielle Patricia Valencia OtedaNo ratings yet
- Actos Drug StudyDocument2 pagesActos Drug StudyNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- AripiprazoleDocument2 pagesAripiprazoleKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- FdarDocument1 pageFdarRoxas Cedrick100% (1)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetoprolol Drug Studykuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.2% W/V Mouth Wash: Class: IndicationsDocument3 pagesChlorhexidine Gluconate 0.2% W/V Mouth Wash: Class: IndicationsAnonymous Bt6favSF4YNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaDocument1 pageAripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaRHUBY ABENOJANo ratings yet
- Ampicillin Sulbactam 1Document2 pagesAmpicillin Sulbactam 1Queenie Gallardo Angeles100% (1)
- Regular InsulinDocument1 pageRegular InsulinKevin NelsonNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Drug Card - Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)Document2 pagesWeek 10 Drug Card - Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ)RCurry09No ratings yet
- D5WDocument1 pageD5WBreena Reubee EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- AldazideDocument2 pagesAldazideianecunarNo ratings yet
- DibencozideDocument1 pageDibencozideParsley Non100% (2)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- FenofibrateDocument4 pagesFenofibrateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EditedDocument8 pagesDrug Study EditedAcob, Jean LykaNo ratings yet
- Generic:: Drug Study #1Document1 pageGeneric:: Drug Study #1Patricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- CKD Case StudyDocument27 pagesCKD Case StudyMary Rose Vito100% (1)
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Nursing Responsibilities Action Rationale Brand NameDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Nursing Responsibilities Action Rationale Brand NameCyrill Alexandria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document2 pagesDrug Study 2Kirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug StudyDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug StudyKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- PDF ImnailingDocument16 pagesPDF ImnailingKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument4 pagesDrug Study FormKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document2 pagesDrug Study 2Kirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Initial Data BaseDocument4 pagesInitial Data BaseKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Bawang/Garlic (: RA 8423 Utilization of Medicinal Plants As An Alternative For High Cost MedicationDocument4 pagesBawang/Garlic (: RA 8423 Utilization of Medicinal Plants As An Alternative For High Cost MedicationKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Pattern Planning Intervention Evaluation IndependentDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Pattern Planning Intervention Evaluation IndependentKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument3 pagesFNCPKirsty Marie SupranesNo ratings yet
- Policy of Alergy and Adverse Drug ReactionDocument4 pagesPolicy of Alergy and Adverse Drug ReactiondmuscleNo ratings yet
- Mayo Clinic Echocardiography Course 2016Document12 pagesMayo Clinic Echocardiography Course 2016Navojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Modified Miniplates For Temporary Skeletal Anchorage in Orthodontics: Placement and Removal SurgeriesDocument16 pagesModified Miniplates For Temporary Skeletal Anchorage in Orthodontics: Placement and Removal SurgeriesAlice SpinetNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Cricothyroidotomy AdaptedDocument36 pagesTracheostomy Cricothyroidotomy AdaptedAyman Yakout100% (1)
- Q3 Health 9 Module 1Document32 pagesQ3 Health 9 Module 1Rashiel Jane Celiz100% (1)
- NCP CholeDocument8 pagesNCP CholeAndrewAlvinTemploNo ratings yet
- Shubham Book Distributors: Estimate InvoiceDocument10 pagesShubham Book Distributors: Estimate InvoiceDR. YOGESHNo ratings yet
- Fracture (Cast Care)Document6 pagesFracture (Cast Care)Vane UcatNo ratings yet
- Icu NCP 2Document2 pagesIcu NCP 2James Casauran LandagoraNo ratings yet
- Running Head: NURSING CASE STUDY/BONE FRACTURE DIP/2017/00451 1Document22 pagesRunning Head: NURSING CASE STUDY/BONE FRACTURE DIP/2017/00451 1Mur DerNo ratings yet
- Endometriosis and The Benefits of PilatesDocument10 pagesEndometriosis and The Benefits of PilatesrparucciNo ratings yet
- History TakingDocument4 pagesHistory TakingaliNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Case StudiesDocument32 pagesPediatrics Case StudiesprinceejNo ratings yet
- LeishmaniasisDocument7 pagesLeishmaniasisLuis Carlos Quinto CuzcanoNo ratings yet
- AstrazenecaDocument16 pagesAstrazenecakailas055No ratings yet
- Heat Related Illness PDFDocument1 pageHeat Related Illness PDFPisi Nopita WigatiNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of The Prevalence of Self-Medication Among Nigerian UndergraduatesDocument5 pagesA Comparative Study of The Prevalence of Self-Medication Among Nigerian UndergraduatesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 Blood Smear and Morphology AnalysisDocument8 pagesLab 7 Blood Smear and Morphology Analysisapi-309917909100% (1)
- Cupping For Patients With Inflammatory CDocument2 pagesCupping For Patients With Inflammatory CPatryk StowaszewskiNo ratings yet
- Poultry Disease Diagnosis - Picture Book-2Document2 pagesPoultry Disease Diagnosis - Picture Book-2बनकर परिवाराचा लाडका गोट्याNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Unani Formulation in Infertility Among Obese Women: A Clinical StudyDocument10 pagesEfficacy of Unani Formulation in Infertility Among Obese Women: A Clinical StudyWaseem AhmedNo ratings yet
- CASE PDL RSMP Hana (Wecompress - Com) .Id - enDocument88 pagesCASE PDL RSMP Hana (Wecompress - Com) .Id - enHana SulistiaNo ratings yet
- Mucogingival ConditionsDocument2 pagesMucogingival ConditionsMuhammad Adel100% (1)
- 00 CM-HSE-SWP-02 Incident ReportingDocument5 pages00 CM-HSE-SWP-02 Incident ReportingTigor GurningNo ratings yet
- Cops On Lookout For Fake Vaccination Cards: Ghio Ong Sheila CrisostomoDocument4 pagesCops On Lookout For Fake Vaccination Cards: Ghio Ong Sheila CrisostomoMarkAllenPascualNo ratings yet
- GBS Source 1Document4 pagesGBS Source 1PJHG50% (2)
- Proline HbA1c Net FS SP201909.00Document4 pagesProline HbA1c Net FS SP201909.00TasrifNo ratings yet
- Wellcome News 59 (July 2009)Document20 pagesWellcome News 59 (July 2009)Wellcome TrustNo ratings yet
- G-Positive Non Spore Forminmg Rods-Listeria and Coynebacterium-FinalDocument36 pagesG-Positive Non Spore Forminmg Rods-Listeria and Coynebacterium-FinalDaniel AtiehNo ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia and Claudication Unisba 2017Document65 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia and Claudication Unisba 2017nobi nobiNo ratings yet