Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIO 204 Current Final Term Fall 2020 by Amaan Khan
Uploaded by
SharqaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BIO 204 Current Final Term Fall 2020 by Amaan Khan
Uploaded by
SharqaCopyright:
Available Formats
BIO 204 Final Term Current Fall 2020
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
Effort By Amaan Khan
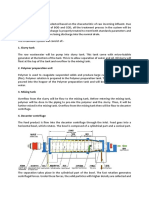
Spiral heat exchangers are also used to cool the medium after passing through the holding coil. Incoming unsterile
medium is used as the cooling agent in the first cooler so that the incoming medium is partially heated before it
reaches the sterilizer and, thus, heat is conserved.
i. The two streams of medium and cooling liquid, or medium and steam, are separated by a continuous
stainless steel barrier with gasket seals being confined to the joints with the end plates. This makes cross
contamination between the two streams unlikely.
ii. The spiral route traversed by the medium allows
sufficient clearances to be incorporated for the system to
cope with suspended solids. The exchanger tends to be self cleaning which reduces the risk of sedimentation,
fouling and 'burningon'.
Effort By Amaan Khan
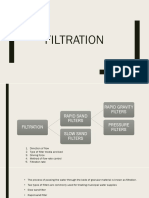
Suspended solids maybe separated from a fluid during filtration by the following
mechanisms:
i. Inertial impaction.
ii. Diffusion.
iii. Electrostatic attraction.
iv. Interception.
Inertial Impaction
Suspended particles in a fluid stream have momentum. The fluid in which the particles are suspended will flow
through the filter by the route of least resistance. However, the particles, because of their momentum, tend to travel
in straight lines and may therefore become impacted upon the fibers where they may then remain. Inertial impaction
is more significant in the filtration of gases than in the filtration of liquids.
Diffusion
Extremely small particles suspended in a fluid are subject to
Brownian motion which is random movement due to collisions with fluid molecules. Thus, such small particles tend
to deviate from the fluid flow pattern and may become impacted upon the filter fibers. Diffusion is more significant
in the filtration of gases than in the filtration of liquids.
Electrostatic attraction
Charged particles may be attracted by opposite charges on the
surface of the filtration medium.
Interception
The fibers comprising a filter are interwoven to define openings of various sizes. Particles which are larger than the
filter pores are removed by direct interception. However, a significant number of particles which are smaller than the
Effort By Amaan Khan
filter pores are also retained by interception. This may occur by several mechanisms – more than one particle may
arrive at a pore simultaneously, an irregularly shaped particle may bridge a pore, once a particle has been trapped by
a mechanism other than interception the pore may be partially occluded enabling the entrapment of smaller particles.
Interception is equally important a mechanism in the filtration of gases and liquids.
Effort By Amaan Khan
You might also like
- Sedimentation and FiltrationDocument25 pagesSedimentation and FiltrationRose BaluconNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Notes-FiltrationDocument5 pagesWater Treatment Notes-FiltrationS. FASEEH MNo ratings yet
- Washingm 1Document42 pagesWashingm 1Gauri ChavandeNo ratings yet
- Water Purification Process For A Parenteral DrugDocument3 pagesWater Purification Process For A Parenteral DrugNateNo ratings yet
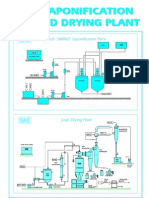
- +sapo & Drying PlantDocument4 pages+sapo & Drying Plantزياد محمدNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Basics 1670761304Document23 pagesWater Treatment Basics 1670761304AlfiNo ratings yet
- 2014 BacemanDocument7 pages2014 BacemanDilaFirizqinaNo ratings yet
- AIR QUALITY AND POLLUTION (TKA 3301) LECTURE NOTES 11 - Control Procedure PMDocument38 pagesAIR QUALITY AND POLLUTION (TKA 3301) LECTURE NOTES 11 - Control Procedure PMmamat88No ratings yet
- Mechanical OperationsDocument3 pagesMechanical Operationstrades korNo ratings yet
- SterilizationDocument15 pagesSterilizationSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Sewage & Fish Farming 1Document12 pagesSewage & Fish Farming 1Arif UllahNo ratings yet
- NabilahZieha 2016 SQ10403Document10 pagesNabilahZieha 2016 SQ10403Nabilah ZiehaNo ratings yet
- The Water Treatment ProcessDocument5 pagesThe Water Treatment Processyop_aljamalullailNo ratings yet
- LeachingDocument5 pagesLeachingizlatan910No ratings yet
- Lecture 09 Modern Particulates Mitigation TechniquesDocument20 pagesLecture 09 Modern Particulates Mitigation TechniquesGunall SNo ratings yet
- CONTENTS+ CertificateDocument15 pagesCONTENTS+ CertificateMeena SinghNo ratings yet
- Ans ApceDocument18 pagesAns ApcekalpNo ratings yet
- Midterm Project AssignmentDocument5 pagesMidterm Project AssignmentJosephine FilesNo ratings yet
- Industrial Pollution ControlDocument18 pagesIndustrial Pollution ControlAnamolNo ratings yet
- Script Toxin PDFDocument2 pagesScript Toxin PDFNickNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument212 pagesEnzymesaniya shakirNo ratings yet
- SedimentationDocument8 pagesSedimentationnoelNo ratings yet
- CETP ProcessDocument3 pagesCETP Processgsenv20r09No ratings yet
- FiltrationDocument75 pagesFiltrationSunjida Ali RiyaNo ratings yet
- Process Description For Slurry Waste Water TreatmentDocument3 pagesProcess Description For Slurry Waste Water TreatmenthasrilNo ratings yet
- Essay FiltrationDocument4 pagesEssay FiltrationAbraham Sandoya LaraNo ratings yet
- Flocculation DesignDocument10 pagesFlocculation DesignWONG TSNo ratings yet
- Floorcare BrochureDocument21 pagesFloorcare Brochuretarikpomozi1649No ratings yet
- Particulate or Dust Emission Control For IndustryDocument6 pagesParticulate or Dust Emission Control For IndustryHii Wang SingNo ratings yet
- Compile - 2 Cycles Edited 07.04.2021Document385 pagesCompile - 2 Cycles Edited 07.04.2021Vinayak U (RA1911201010039)No ratings yet
- APC Unit-5Document8 pagesAPC Unit-5puneethNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic CleaningDocument129 pagesUltrasonic Cleaningalfgraga6043No ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument34 pagesTerm PaperGourav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Filtration Definition: ContaminantsDocument6 pagesFiltration Definition: Contaminantsdeepesh chhetriNo ratings yet
- Critical ThingkingDocument5 pagesCritical ThingkingNur Nadiah KamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Finder, Which Prevents Short-Circuiting of Feed Directly Into The OverflowDocument3 pagesFinder, Which Prevents Short-Circuiting of Feed Directly Into The OverflowKudakwashe GondoNo ratings yet
- Filtr PDFDocument10 pagesFiltr PDFtiwaribcetNo ratings yet
- Sterilisation MBDocument9 pagesSterilisation MBWaliNo ratings yet
- WWW Lunchboxsessio...Document15 pagesWWW Lunchboxsessio...Mukhsi Hanafi2No ratings yet
- Module 2 EC Part CDocument18 pagesModule 2 EC Part CAastha MandaliaNo ratings yet
- Sanitary Equipment ResearchDocument27 pagesSanitary Equipment Researchjp.e.hakimNo ratings yet
- of FiltrationDocument54 pagesof FiltrationSwayam Mehta100% (1)
- S.pool Seminar 16.06.14low1Document194 pagesS.pool Seminar 16.06.14low1Miguel Angel100% (1)
- Clarifying FilterDocument7 pagesClarifying FilterPrachi GuptaNo ratings yet
- SedimentationDocument7 pagesSedimentationvivek pattaniNo ratings yet
- Drain TreatmentDocument4 pagesDrain TreatmentMauritzNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Reservoirs and FiltersDocument22 pagesHydraulic Reservoirs and FiltersMohamed ZahranNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Puu-0 4400 Operating Principles of ScrubbersDocument12 pagesLesson 2 Puu-0 4400 Operating Principles of Scrubbersssmith2007100% (1)
- Glossary of Water Treatment Terms: Term ExplanationDocument12 pagesGlossary of Water Treatment Terms: Term ExplanationprakashNo ratings yet
- Research Questions Lab 1Document7 pagesResearch Questions Lab 1Theo AlapanNo ratings yet
- Water Purification and Water Treatment of Swimming PoolDocument24 pagesWater Purification and Water Treatment of Swimming PoolNamrataNo ratings yet
- 2018 BET CHEM 01water Analysis ExperimentsDocument45 pages2018 BET CHEM 01water Analysis ExperimentsDanish AliNo ratings yet
- Water and Wastewater Engineering Prof. C. Venkobacher Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture-16Document18 pagesWater and Wastewater Engineering Prof. C. Venkobacher Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture-16kaushal patelNo ratings yet
- Aseptic and Sterilization TechniquesDocument5 pagesAseptic and Sterilization TechniquesSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Lyer-Email-Eng 1447687457 2Document4 pagesLyer-Email-Eng 1447687457 2ValiNo ratings yet
- Water Jet Machining (WJM) : Principle of The ProcessDocument30 pagesWater Jet Machining (WJM) : Principle of The ProcessMr Yasin Mech StaffNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Public Water SupplyDocument26 pagesModule 2 - Public Water SupplyTon Ton Bonda100% (1)
- Liquid Glass Transition: A Unified Theory From the Two Band ModelFrom EverandLiquid Glass Transition: A Unified Theory From the Two Band ModelNo ratings yet
- EXP 4 Injection MoldingDocument18 pagesEXP 4 Injection MoldingJasmine NguNo ratings yet
- Techno-Commercial Offer .For Krishna Hospital Cpacity of 100 KLD ETP Cum STPDocument9 pagesTechno-Commercial Offer .For Krishna Hospital Cpacity of 100 KLD ETP Cum STPAnshika RaiNo ratings yet
- University of Mosul College of Petroleum & Mining Engineering Department of Petroleum & Refining EngineeringDocument5 pagesUniversity of Mosul College of Petroleum & Mining Engineering Department of Petroleum & Refining Engineeringzabdulhadi517No ratings yet
- CFD Model AeronauticDocument36 pagesCFD Model Aeronautic陈冠江No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ConductionDocument1 pageHeat Transfer Conductionjayron de laraNo ratings yet
- Exchanger Tube Min ThicknessDocument2 pagesExchanger Tube Min ThicknessMohamed ElshehnyNo ratings yet
- Explicit Solutions For Turbulent Flow Friction Factor - A Review, Assessment and Approaches ClassificationDocument10 pagesExplicit Solutions For Turbulent Flow Friction Factor - A Review, Assessment and Approaches ClassificationChi-Hao LoNo ratings yet
- Hochdruckzubehoer Katalog eDocument192 pagesHochdruckzubehoer Katalog eFredyNo ratings yet
- 1 CoagulationDocument24 pages1 CoagulationAli RazaNo ratings yet
- q1 Module 10Document15 pagesq1 Module 10Princess Angeles Andam100% (1)
- Thermal ComfortDocument192 pagesThermal ComfortMusical Black DiaryNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture and Sequestration An OverviewDocument7 pagesCarbon Capture and Sequestration An OverviewIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Tarif RSCA Medan Apr 2022Document53 pagesTarif RSCA Medan Apr 2022ratna ninaNo ratings yet
- Pitot Solved ProblemsDocument5 pagesPitot Solved ProblemskiptooNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument6 pagesThermalLutlut PayarNo ratings yet
- Modeling Aspects in Fluidization Engineering: T. Hariharan P100061ChDocument17 pagesModeling Aspects in Fluidization Engineering: T. Hariharan P100061ChHari HaranNo ratings yet
- Doc-0083448 Rev.0Document15 pagesDoc-0083448 Rev.0Pavel HucskoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Calculation Sheet Influent DataDocument18 pagesHydraulic Calculation Sheet Influent DataMagic Master0% (1)
- Filtration2014 EN WebDocument6 pagesFiltration2014 EN WebNguyen AnNo ratings yet
- Compresores Hermticos Tecumseh Lunite Hermetique 5 17062015Document1 pageCompresores Hermticos Tecumseh Lunite Hermetique 5 17062015rafael velandi velandiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 Boundary Layer Analogies 2016IDocument59 pagesLecture 22 Boundary Layer Analogies 2016ICESAR AUGUSTO VASQUEZ RUIZNo ratings yet
- Primary Products - Gulf Tubing Company - GTCDocument3 pagesPrimary Products - Gulf Tubing Company - GTCMFNo ratings yet
- 6 Stoichiometry Cont'dDocument3 pages6 Stoichiometry Cont'dinfinitelaurels1No ratings yet
- MATERI (Heat and Mass Transfer)Document140 pagesMATERI (Heat and Mass Transfer)Miranda Amiroh SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Schematics of A Refrigeration Cycle: Air ConditionerDocument1 pageSchematics of A Refrigeration Cycle: Air ConditionerAndre EinsteinNo ratings yet
- A Review of Biomass Pyrolysis and Pyrolysis TechnologiesDocument82 pagesA Review of Biomass Pyrolysis and Pyrolysis TechnologiesNhean FierceghastNo ratings yet
- DSCVDSCVDocument15 pagesDSCVDSCVnehelet920No ratings yet
- PET Recycling Literature ReviewDocument69 pagesPET Recycling Literature ReviewPrachi ShahNo ratings yet
- Sop STPDocument5 pagesSop STPModi JayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3indumathijayakaranNo ratings yet