Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Solid Stat The Solid Stat The Solid Stat The Solid Stat The Solid Stateeeee
Uploaded by
susenthil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
solidstate-pages-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThe Solid Stat The Solid Stat The Solid Stat The Solid Stat The Solid Stateeeee
Uploaded by
susenthilCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
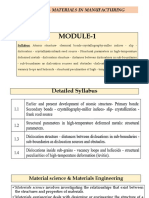
Unit
Objectives The Solid Stat
Statee
1
After studying this Unit, you will be
able to
The vast majority of solid substances like high temperature
• describe general characteristics of
superconductors, biocompatible plastics, silicon chips, etc. are destined
solid state; to play an ever expanding role in future development of science.
• distinguish between amorphous
and crystalline solids;
• classify crystalline solids on the We are mostly surrounded by solids and we use them
basis of the nature of binding more often than liquids and gases. For different
forces; applications we need solids with widely different
• define crystal lattice and unit cell; properties. These properties depend upon the nature of
• explain close packing of particles; constituent particles and the binding forces operating
• describe different types of voids between them. Therefore, study of the structure of solids
and close packed structures; is important. The correlation between structure and
• calculate the packing efficiency of properties helps in discovering new solid materials
different types of cubic unit cells; with desired properties like high temperature
• correlate the density of a superconductors, magnetic materials, biodegradable
substance with its unit cell polymers for packaging, biocompliant solids for surgical
properties;
implants, etc.
• describe the imperfections in
solids and their effect on
From our earlier studies, we know that liquids and
properties; gases are called fluids because of their ability to flow.
• correlate the electrical and The fluidity in both of these states is due to the fact that
magnetic properties of solids and the molecules are free to move about. On the contrary,
their structure. the constituent particles in solids have fixed positions
and can only oscillate about their mean positions. This
explains the rigidity in solids. In crystalline solids, the
constituent particles are arranged in regular patterns.
In this Unit, we shall discuss different possible
arrangements of particles resulting in several types of
structures. The correlation between the nature of
interactions within the constituent particles and several
properties of solids will also be explored. How these
properties get modified due to the structural
imperfections or by the presence of impurities in minute
amounts would also be discussed.
You might also like
- Solid StateDocument2 pagesSolid Statesharmabeefarms1992No ratings yet
- Modul 6 The Solid StateDocument31 pagesModul 6 The Solid StateACHMAD ZULFAN ALMAHDY 1No ratings yet
- Chem TextDocument1 pageChem TextthatisthatNo ratings yet
- Gchem2 Q3 Las WK1 Day5Document2 pagesGchem2 Q3 Las WK1 Day5mae.joan.reposposaNo ratings yet
- 12th Science HSC Chemistry I PDFDocument14 pages12th Science HSC Chemistry I PDFSayyed SohelNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-solid State Part 1Document2 pagesCHAPTER-solid State Part 1Arpandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- 1.solid StateDocument33 pages1.solid StateBHAVITH SD VNS 06No ratings yet
- Introduction Soft MatterDocument40 pagesIntroduction Soft MatterSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Crystalline and Amorphous SolidsDocument3 pagesModule 5 - Crystalline and Amorphous Solidsmm.vince21No ratings yet
- Q and A CrystalDocument3 pagesQ and A Crystalysaaa. rbNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Solid StateDocument36 pages1.1 Solid Stateilias1973100% (1)
- Ap Chem Unit 3 Review PacketDocument7 pagesAp Chem Unit 3 Review Packetapi-77411869No ratings yet
- By Prin Ces Ir: He Olid TateDocument49 pagesBy Prin Ces Ir: He Olid TateVinayNo ratings yet
- Solid State Notes Jee Main and Advanced PDFDocument36 pagesSolid State Notes Jee Main and Advanced PDFVedant BiyaniNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem2 ModuleDocument19 pagesGen Chem2 ModuleAinon SalendabNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Engineering Materials: Polycrystalline SolidDocument5 pagesChapter - 6 Engineering Materials: Polycrystalline SolidSanjiv BadheNo ratings yet
- Solid State - Study Material - Yak9Document33 pagesSolid State - Study Material - Yak9Amrit Kumar BiswasNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Regulation of Cell Function With Geometrically Modulated Elastomeric SubstratesDocument7 pagesMechanical Regulation of Cell Function With Geometrically Modulated Elastomeric Substratesa12312sdfsdrtwerNo ratings yet
- 02-01 Introduction To Structures in MetalsDocument6 pages02-01 Introduction To Structures in MetalsidanfriNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their PropertiesDocument59 pagesIntermolecular Forces of Liquids and Solids Solids and Their PropertiesAndre Jose ErminoNo ratings yet
- Genchem2 q3m2b Solids-And-imf FinalDocument50 pagesGenchem2 q3m2b Solids-And-imf Finalroxtonandrada8No ratings yet
- Research and Scientific Investigation Project By: &: Xam BuenavistaDocument21 pagesResearch and Scientific Investigation Project By: &: Xam BuenavistaJose Dary LocsinNo ratings yet
- LP - GP - Coulomb's LawDocument9 pagesLP - GP - Coulomb's LawAllyza SobosoboNo ratings yet
- LessonPPT1 KMTDocument64 pagesLessonPPT1 KMTRaiv LondresNo ratings yet
- Solids and Their PropertiesDocument31 pagesSolids and Their PropertiesTrexi Mag-asoNo ratings yet
- Unit III CrystollographyDocument56 pagesUnit III Crystollographymwita mwitaNo ratings yet
- Ebookneonclasseschemistryeng 2Document63 pagesEbookneonclasseschemistryeng 2rameshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemistry of Engineering MaterialsDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Chemistry of Engineering Materialsksm rachasNo ratings yet
- I. The Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterDocument5 pagesI. The Kinetic Molecular Theory of MatterKwon NieNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument41 pagesSolid State45 XI A Subham SharmaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE - Solids-01-02-03-04Document111 pagesLECTURE - Solids-01-02-03-04kanika thakurNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM4Document11 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - Q3 - SLM4Jonnel RoqueNo ratings yet
- LP - GC - Nature of SolidsDocument9 pagesLP - GC - Nature of SolidsAllyza SobosoboNo ratings yet
- VISCOELASTICITY Power Point PresentationDocument26 pagesVISCOELASTICITY Power Point PresentationNathaly CuasialpudNo ratings yet
- LeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1Document4 pagesLeaP - Chemistry 2 Q3 Week 1John michael EstradaNo ratings yet
- MTLE 4960 - Biology in Materials Science - Exam 1. Study GuideDocument2 pagesMTLE 4960 - Biology in Materials Science - Exam 1. Study Guidelongxuan xuNo ratings yet
- UNIT - II InorganicDocument28 pagesUNIT - II Inorganicharirajans71No ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Anelastic Deformation in Solid Polymers: Solidlike and Liquidlike ProcessesDocument13 pagesMechanisms of Anelastic Deformation in Solid Polymers: Solidlike and Liquidlike Processesنرگس باویNo ratings yet
- Class Note - Jellur - LastDocument54 pagesClass Note - Jellur - LastUltimate 7No ratings yet
- Solidstate Part 1Document35 pagesSolidstate Part 1Gopikrishna ThirunavukarasuNo ratings yet
- Crystalline and Non Crystalline SolidsDocument6 pagesCrystalline and Non Crystalline SolidsJosue TellezNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM 2 LESSON 3 Intermolecular Forces of Solids and Their Properties1.1Document27 pagesGEN CHEM 2 LESSON 3 Intermolecular Forces of Solids and Their Properties1.1Loraine Castro0% (1)
- Gases vs. Liquids and SolidsDocument67 pagesGases vs. Liquids and SolidsRenolsa EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Liquid Crystals in Cell Biology: The Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, DenmarkDocument11 pagesPhysics of Liquid Crystals in Cell Biology: The Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, DenmarkHimanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SolidsDocument99 pagesChapter 3 - SolidsnnooorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document2 pagesLecture 1Gabriel JocsonNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument11 pagesSolid StateGomathi VarshiniNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument9 pagesMatterryienlucNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument9 pagesChemistry Reviewervillasencio.shaneeNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document150 pagesModule 1Renjin J BrightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3JeromeNo ratings yet
- Rheology 2023Document10 pagesRheology 2023Alina TilekNo ratings yet
- Feature: JournalDocument12 pagesFeature: JournalmahbubeNo ratings yet
- Amorphous Pharmaceutical Solids PreparatDocument16 pagesAmorphous Pharmaceutical Solids PreparatDevi Ratna YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Class: XII-JEEDocument44 pagesChemistry: Class: XII-JEEtortenhumNo ratings yet
- Robert Darwin D. Gabriel 20160200113Document6 pagesRobert Darwin D. Gabriel 20160200113Robert Darwin GabrielNo ratings yet
- Liquid Crystalline Semiconductors: Materials, properties and applicationsFrom EverandLiquid Crystalline Semiconductors: Materials, properties and applicationsRichard J. BushbyNo ratings yet
- Self-Assembly of Nano- and Micro-structured Materials Using Colloidal EngineeringFrom EverandSelf-Assembly of Nano- and Micro-structured Materials Using Colloidal EngineeringNo ratings yet
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument6 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnersusenthilNo ratings yet
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument6 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnersusenthilNo ratings yet
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument7 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award Winnersusenthil100% (1)
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument6 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnersusenthilNo ratings yet
- O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnerDocument6 pagesO.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor & Author: Indira Award WinnersusenthilNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Matter: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument16 pagesMagnetism Matter: Multiple Choice QuestionssusenthilNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Practice Paper 01Document24 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Practice Paper 01susenthilNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom: Unit 2Document2 pagesStructure of Atom: Unit 2susenthilNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom: Unit 2Document3 pagesStructure of Atom: Unit 2susenthilNo ratings yet
- An Elementary School Classroom...Document13 pagesAn Elementary School Classroom...susenthilNo ratings yet
- Table 2.1 Properties of Fundamental Particles: 2.2.1 Thomson Model of AtomDocument6 pagesTable 2.1 Properties of Fundamental Particles: 2.2.1 Thomson Model of AtomsusenthilNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom: Unit 2Document5 pagesStructure of Atom: Unit 2susenthilNo ratings yet
- Safety Quiz Ans. SheetDocument2 pagesSafety Quiz Ans. SheetsusenthilNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Syllabus: Overview of CourseDocument3 pagesAP Chemistry Syllabus: Overview of CoursesusenthilNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom: Unit 2Document10 pagesStructure of Atom: Unit 2susenthilNo ratings yet
- PolyOne Syncure™ System S112BL Polyethylene, Crosslinked (XLPE) Datasheet RW90Document3 pagesPolyOne Syncure™ System S112BL Polyethylene, Crosslinked (XLPE) Datasheet RW90Amina Malek AyaNo ratings yet
- Présentation PowerPoint PDFDocument68 pagesPrésentation PowerPoint PDFAssis RochaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01: Unit 2 - Week 1Document3 pagesAssignment 01: Unit 2 - Week 1Parkash SinghNo ratings yet
- A. Atoms: Engineering MaterialsDocument36 pagesA. Atoms: Engineering MaterialsAmpolNo ratings yet
- Electronics Instrumentation 15EI251 PDFDocument94 pagesElectronics Instrumentation 15EI251 PDFlvrevathiNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument85 pagesFluid MechanicsClaire De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- ENERGETIC ANALYSIS OF AN ABSORPTION CHILLER USING NH3-LiNO3 ASDocument14 pagesENERGETIC ANALYSIS OF AN ABSORPTION CHILLER USING NH3-LiNO3 ASAlvaro Antonio Ochoa VillaNo ratings yet
- Errata Aci 318-08aDocument3 pagesErrata Aci 318-08agodfreye1No ratings yet
- IEC 60471 - 1980 Dimensions of Clevis and Tongue Couplings of String Insulator Units enDocument6 pagesIEC 60471 - 1980 Dimensions of Clevis and Tongue Couplings of String Insulator Units enJuanNo ratings yet
- Design of Shafts and KeysDocument106 pagesDesign of Shafts and KeysLoay MohammedNo ratings yet
- TC301D Datasheet: 1. DescriptionDocument5 pagesTC301D Datasheet: 1. DescriptionMehmet Ali SüzerNo ratings yet
- Bojowald - Canonical Gravity and Applications: Cosmology, Black Holes, and Quantum GravityDocument313 pagesBojowald - Canonical Gravity and Applications: Cosmology, Black Holes, and Quantum GravitySascha_L100% (1)
- You'Ve Got A Problem: DV DT C M V V T Time S, G, CDocument3 pagesYou'Ve Got A Problem: DV DT C M V V T Time S, G, CagusNo ratings yet
- Application of Jute Fiber in Soil StabilizationDocument8 pagesApplication of Jute Fiber in Soil StabilizationMary Joy ManayagaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Assignment OBTDocument2 pagesPrelim Assignment OBTPeter Paul DobNo ratings yet
- International Studies Final Exam-BumuloDocument22 pagesInternational Studies Final Exam-BumuloBielan Fabian GrayNo ratings yet
- Googlepreview PDFDocument89 pagesGooglepreview PDFFaris FadliNo ratings yet
- ICEMS 2013 Final Program PosterDocument30 pagesICEMS 2013 Final Program PosterAmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Find The Six Circular Functions of The Below. 1. 8Document4 pagesFind The Six Circular Functions of The Below. 1. 8Sir LogNo ratings yet
- Seesaw CandleDocument4 pagesSeesaw CandleAbhisheik TripathiNo ratings yet
- Liquid CrystalDocument44 pagesLiquid Crystalshreeji2017No ratings yet
- Refrigeration 22.1Document29 pagesRefrigeration 22.1preceiuxNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Level LST400: Open Channel Flow TransmitterDocument12 pagesUltrasonic Level LST400: Open Channel Flow TransmitterVaranasi AnilNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies FrictionDocument24 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies FrictionAcademic FreezePleaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01b Solar RadiationDocument40 pagesChapter 01b Solar RadiationOmar AljohaniNo ratings yet
- WEG Severe Duty Is Standard With W22 Motors USAW22SEVDUTY.7.2017 Brochure English WebDocument16 pagesWEG Severe Duty Is Standard With W22 Motors USAW22SEVDUTY.7.2017 Brochure English WebPAULO SOUZANo ratings yet
- Supp Ex On Past Paper Atomic World I (Up To Bonding) (QN)Document2 pagesSupp Ex On Past Paper Atomic World I (Up To Bonding) (QN)England NgNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument49 pagesDifferentiationFawziah NabihaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion AssignmentDocument5 pagesDiffusion AssignmentAshley Kyaw100% (1)
- HS 420Document1 pageHS 420sayed abotalibNo ratings yet