ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
EVAPORATION
Purwiyatno Hariyadi, Eko Hari Purnomo,
Elvira Syamsir, Nur Wulandari
Dept of Food Science and Technology
Faculty of Agricultural and Engineering Technology
Bogor Agricultural University
BOGOR
Evaporation
• An important unit operation
• Involves the application of heat to vaporize water at the
boiling point.
• Employed to remove water from dilute liquid foods to
obtain concentrated liquid products
• Microbial stability
• Reducing transportation & storage costs
• Differs from
• Dehydration (end prod: solid state)
• Distillation (end prod: fractions)
• Evaporation end prod: liquid state
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
1
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Application
• Dairy industry concentrate milk
• Fruit juice industry produce concentrates
• Jams, jellies, and preserves raise the solids
content necessary for gelling
• Sugar industry concentrate sugar solutions for
crystallization
• Raise the solids content of dilute solutions prior to
spray or freeze drying.
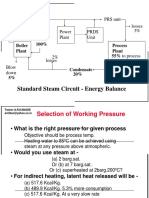
Process
• Atmospheric (open) evaporation
• Initial temperature at which the solution boils
• Some degrees above 100C, depending on the solids content
• As the solution becomes more concentrated
the evaporation temperature will rise
• Simple
• Slow
• Not very efficient (energy)
• Heat sensitive product degradation of quality (flavor,
color, etc)
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
2
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Process
• Vacuum evaporation
• Low temp
• Pressure in the evaporator 7.5 – 85.0 kPa absolute
evaporation temperatures 40 – 95°C
• Efficient energy utilization can be designed
• Heat from the vapors used to preheat the feed
• Using multiple effects
Component of vacuum evaporator
• Heat exchanger
Supply sensible & latent heat to the feed
• Device
Separate vapour from concentrated liquid phase
• Condenser
Convert the vapour back to a liquid
• Pump, steam ejector or barometric leg
Remove the condensate creating & maintaining the
partial vacuum in the system
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
3
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
A batch-type pan evaporator
Diagram of single-effect evaporator
Hasil
Evaporasi
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
4
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Diagram of multiple-effect evaporator
Boiling-Point Elevation
• The increase in boiling point over that of pure water, at a
given pressure
• Dühring’s rule:
• Simple method to estimate boiling-point elevation
• A linier relationship between the boiling-point temperature of
solution and the boiling-point temperature of water at the
same pressure
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
5
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Analysis of evaporator system
--- single-effect evaporator
• mf = mass flow rate of feed (kg/s)
• mv = mass flow rate of vapor (kg/s)
• mp = mass flow rate of product (kg/s)
• ms = mass flow rate of steam (kg/s)
• xf = solid fraction in feed (dimensionless)
• xp = solid fraction in product (dimensionless)
• T1 = boiling temperature maintained inside evaporator chamber (ºC)
• Tf = feed temperature (ºC)
• Ts = steam temperature (ºC)
• To = reference temperature (= 0oC or 32oF, for siebel’s equation)
• Hv(Ts)= enthalpy of saturated vapor at Ts (kJ/kg)
• Hc(Ts)= enthalpy of condensat at Ts (kJ/kg)
• Hv(T1)= enthalpy of saturated vapor at T1 (kJ/kg)
• Hf(Tf, xf)= enthalpy of feed (kJ/kg)
• Hp(Tp, xp)= enthalpy of product(kJ/kg)
• q = rate of heat transfer (W)
• U = overall heat transfer coefficient (W/m2.K)
• A = area of heat exchanger (m2)
• n = steam economy
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
6
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Analysis of evaporator system
--- single-effect evaporator
FEED FEED
• mf = mass flow rate of feed (kg/s)
• xf = solid fraction in feed (dimensionless)
• Tf = feed temperature (ºC)
• Hf(Tf, xf)= enthalpy of feed (kJ/kg)
Analysis of evaporator system
--- single-effect evaporator
STEAM
IN
• ms = mass flow rate of steam (kg/s)
• Ts = steam temperature (ºC)
• Hv(Ts)= enthalpy of saturated vapor at Ts (kJ/kg)
OUT
• Ts = steam temperature (ºC)
IN OUT
• ms = mass flow rate of steam (kg/s)
STEAM • Hc(Ts)= enthalpy of condensat at Ts (kJ/kg)
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
7
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Analysis of evaporator system
--- single-effect evaporator
PRODUCT PRODUCT
• mp = mass flow rate of product (kg/s)
• xp = solid fraction in product (dimensionless)
• T1 = boiling temperature maintained inside evaporator
chamber (ºC)
• Hp(Tp, xp)= enthalpy of product(kJ/kg)
Analysis of evaporator system
--- single-effect evaporator
VAPOR
VAPOR
• mv = mass flow rate of vapor (kg/s)
• T1 = boiling temperature maintained inside
evaporator chamber (ºC)
• Hv(Ts)= enthalpy of saturated vapor at Ts (kJ/kg)
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
8
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Mass balance
. .
• mf = mass flow rate of feed (kg/s)
• mv = mass flow rate of vapor (kg/s)
• mp = mass flow rate of product (kg/s)
• xf = solid fraction in feed (dimensionless)
• xp = solid fraction in product (dimensionless)
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
9
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Enthalpy balance
. , + . . . , + .
• ms = mass flow rate of steam (kg/s)
• T1 = boiling temperature maintained inside evaporator chamber (ºC)
• Tf = feed temperature (ºC)
• Ts = steam temperature (ºC)
• Hv(Ts)= enthalpy of saturated vapor at Ts (kJ/kg)
• Hc(Ts)= enthalpy of condensat at Ts (kJ/kg)
• Hv(T1)= enthalpy of saturated vapor at T1 (kJ/kg)
• Hf(Tf, xf)= enthalpy of feed (kJ/kg)
• Hp(Tp, xp)= enthalpy of product(kJ/kg)
, ,
• Enthalpy of feed or product
, 0
, 0
• cpf = specific heat content of feed (kJ/kg.°C)
• cpp = specific heat content of product (kJ/kg.°C)
Siebel’s equation:
0.8 0.2 …………………… BTU/lb.°F
3349 837.36 ……………… J/kg.°C
M = water fraction
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
10
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
,
• Enthalpy of steam (vapor, condensate) or vapor
• Obtained from the steam table
How to calculate the size of HX (to meet the
“Rate of Heat Transfer” needed?
• Rate of heat transfer:
. . . .
• q = rate of heat transfer (W)
• U = overall heat transfer coefficient (W/m2.K)
• A = area of heat exchanger (m2)
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
11
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Steam economy (n)
• Expressing the operating performance of an evaporator
system
• Ratio of rate of mass of water vapor produced from the
liquid feed per-unit rate of steam consumed
Analysis of evaporator system
--- triple-effect evaporator
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
12
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Mass balance:
Mass balance on solid fraction:
. .
Enthalpy balance:
. , + . . . , + .
. , + . . . , + .
. , + . . . , + .
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
13
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Heat transfer across HE:
. . .
. . .
. . .
Steam economy
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
14
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Example
• Apple juice is being concentrated in single-effect
evaporator. At steady-state condition, dilute juice is the
feed introduced at a rate of 0.67 kg/s. The concentration
of the dilute juice is 11% total solids. The juice is
concentrated to 75% total solids. The specific heats of
dilute apple juice and concentrate are 3.9 and 2.3
kJ/kg.°C, respectively. The steam pressure is measured
to be 273.7 kPa. The inlet feed temperature is 43.3°C.
The product inside the evaporator boils at 62.2°C. The
overall heat-transfer coefficient is assumed to be 943
W/m².°C. Assume negligible boiling-point elevation.
Calculate the mass flow rate of concentrated product,
steam requirements, steam economy, and the heat-
transfer area.
Given: System diagram:
• mf = 0.67 kg/s
• xf = 0.11
• xp = 0.75
• Ps = 273.7 kPa
• Tf = 43.3ºC
• T1 = 62.2°C
• U = 943 W/m2.K
• cpf = 3.9 kJ/kg.°C
• cpp = 2.3 kJ/kg.°C
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
15
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
Solution
1. Mass balance on solid:
. .
0.11 0.67 0.75
0.098
2. Total mass balance:
0.67 0.098
0.67 0.098 0.57
3. Enthalpy of feed and product
,
0
3.9 .° 43.3° 0° 168.9
,
0
2.3 .° 62.2° 0° 143.1
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
16
�ITP330-Prinsip Teknik Pangan – 2013/2014
4. Enthalpy of vapor and steam (saturated vapor and
condensate)
Obtained from steam table
° 2725.9
° 563.41
. ° 2613.4
5. Enthalpy balance:
. , . . . , .
0.67 168.9 2725.9
0.57 2613.4 0.098 143.1 563.41
2162.49 1390.5
0.64
6. Calculate steam economy
0.57
0.89
0.64
7. Calculate area of heat transfer
943 134 62.2
.°
0.64 2725.9 563.14 1000
20.4
ITP330- Ilmu & Teknologi Pangan/Fateta/IPB
Available at http://phariyadi.staff.ipb.ac.id/teaching/
17