Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dinámica Problemario (I)
Dinámica Problemario (I)
Uploaded by
David Astral0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Dinámica Problemario(I)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views4 pagesDinámica Problemario (I)
Dinámica Problemario (I)
Uploaded by
David AstralCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
INSTITUTO POLITÉCNICO NACIONAL
ESCUELA SUPERIOR DE INGENIERÍA MECÁNICA Y ELÉCTRICA
UNIDAD CULHUACAN
PROBLEMARIO 1 ECUACIONES FUNDAMENTALES
DINÁMICA DE LA PARTÍCULA
PROBLEM 11.3 BEER 7th EDITION
The motion of the slider A is defined by the
relation x = 20 sin kt, where x and t are
expressed in inches and seconds, respectively and k
is a constant. Knowing that k = 10 rad/s,
determine the position, the velocity and the
acceleration of slider A when t = 0.05 s.
PROBLEM 11.3 BEER 10th EDITION
The vertical motion of mass A is defined by the relation
x = 10 sin 2t + 15 cos 2t + 100, where x and t are expressed in
millimeters and seconds, respectively. Determine a) the position,
velocity and acceleration of A when t = 1 s, b) the maximum
velocity of A.
PROBLEM 11.8 BEER 10th EDITION
The motion of a particle is defined by the relation x = t 3- 6t2 – 36t – 40, where x
and t are expressed in feet and seconds, respectively. Determine a) when the velocity
is zero, b) the velocity, the acceleration, and the total distance traveled when x = 0.
PROBLEM 11.13 BEER 10th EDITION
The acceleration of point A is defined by the relation
a = -1.8 sin kt, where a and t are expressed in and
seconds, respectively and k = 3 . Knowing that x = 0
and v = 0.6 when t = 0, determine the velocity
and position of A when t = 0.5 s.
ELABORÓ: PROF. GILBERTO ANDRÉS SÁNCHEZ RODRÍGUEZ MARZO 2015
PROBLEM 13.2 BEDFORD 4th EDITION
The milling machine is programmed so that the
position of its head is given as a function of time
by s = 0.3 – 0.2 cos (5t) m. (When t is in
seconds, the argument of the cosine is in radians.)
a) Determine the velocity of the head as a
function of time.
b) What is the acceleration of the head at
t = 4 s.
PROBLEM 13.8 BEDFORD 4th EDITION
The rotating crank causes the position of point P as function of time to be
s = 0.4 sin (2t) m.
a) Determine the velocity and acceleration of P at t = 0.375 s.
b) What is the maximum magnitude of the velocity of P?.
c) When the magnitude of the velocity of P is a maximum, what is the acceleration
of P?
PROBLEMA 13.4 WILLIAM F. RILEY
Se da, en función del tiempo, el desplazamiento de un punto que se mueve a lo
largo del eje X.
s ( t ) = 4 sen t ( m )
a. Calcular la velocidad del punto en función del tiempo.
b. Calcular la aceleración del punto en función del tiempo.
c. Evaluar la posición, velocidad y aceleración del punto en t = 5 s.
d. Determinar la distancia total recorrida por el punto entre t = 0 y t = 5 s.
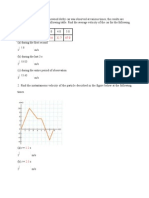
e . Representar gráficamente s – t, v – t y a – t; para 0 ≤ t ≤ 10 s
ELABORÓ: PROF. GILBERTO ANDRÉS SÁNCHEZ RODRÍGUEZ MARZO 2015
PROBLEMA 13.8 WILLIAM F. RILEY
v (t) = 8t2 - 20 ( m/s )
s (20) = 60 m
Se da, en función del tiempo, la velocidad de un punto que se mueve a lo largo del eje
X; se da su desplazamiento en cierto instante.
a. Calcular la posición del punto en función del tiempo.
b. Calcular la aceleración del punto en función del tiempo.
c. Evaluar el desplazamiento, velocidad y aceleración del punto en t = 8 s.
d. Determinar la distancia total recorrida por el punto entre t = 5 s y t = 8 s.
e. Representar gráficamente s - t, v - t y a – t ; para 0 ≤ t ≤ 10 s.
PROBLEMA 13.13 WILLIAM F. RILEY
Se da, en función del tiempo, la aceleración de un punto que se mueve a lo largo del
eje X; se dan el desplazamiento y velocidad de dicho punto en cierto instante.
a (t) = 5-3t ( m/s2 )
s (0) = 5 m
v (0) = 0 m/s
a. Calcular la posición del punto en función del tiempo
b. Calcular la velocidad del punto en función del tiempo
c. Evaluar el desplazamiento, la velocidad y aceleración del punto en t = 3 s.
d. Determinar la distancia total recorrida por el punto entre t = 3 s y t = 8 s.
e. Representar gráficamente x –t, v –t y a –t para 0 ≤ t ≤ 10 s.
ELABORÓ: PROF. GILBERTO ANDRÉS SÁNCHEZ RODRÍGUEZ MARZO 2015
PROBLEMA 13.16 WILLIAM F. RILEY
Se da, en función del tiempo, la aceleración de un punto que se mueve a lo largo del
eje X; se dan el desplazamiento y velocidad de dicho punto en cierto instante.
a ( t) = 20 sen 2t ( m/s2 )
s (10) = 0 m
v (10) = 5 m/s
a. Calcular la posición del punto en función del tiempo
b. Calcular la velocidad del punto en función del tiempo
c. Evaluar el desplazamiento, la velocidad y aceleración del punto en t = 3 s.
d. Determinar la distancia total recorrida por el punto entre t = 3 s y t = 8 s.
e. Representar gráficamente x –t, v –t y a –t para 0 ≤ t ≤ 10 s.
ELABORÓ: PROF. GILBERTO ANDRÉS SÁNCHEZ RODRÍGUEZ MARZO 2015
You might also like
- Engineering Mechanics Dynamic Bedford ch13Document197 pagesEngineering Mechanics Dynamic Bedford ch13Ozkhar AF100% (4)
- Problems 1Document11 pagesProblems 1LogoNo ratings yet
- Dls 212 - Selected Topics in General Physics: University of Northern PhilippinesDocument56 pagesDls 212 - Selected Topics in General Physics: University of Northern PhilippinesKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (5)
- H70-120 XM K005 PDFDocument766 pagesH70-120 XM K005 PDFAnthony Collucci100% (3)
- Motoare Hidraulice Cbm-HagglundsDocument4 pagesMotoare Hidraulice Cbm-HagglundsANTON NEAGUNo ratings yet
- 12 Low-Speed Crash Test Standard RCAR ProcessDocument12 pages12 Low-Speed Crash Test Standard RCAR ProcessMoHaN RaMaNa100% (1)
- Astm D7405Document4 pagesAstm D7405jegancivil100% (3)
- KinematicsDocument65 pagesKinematicsGarlapati Srinivasa Rao100% (1)
- Tut (1) Mechanics II - 2014 - 521Document9 pagesTut (1) Mechanics II - 2014 - 521JoseOrestesHinostrozaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Word Problems IDocument20 pagesCalculus Word Problems IPatricia SioNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear MotionDocument22 pagesCurvilinear MotionRjay FloresNo ratings yet
- Foundation in Science: SCP 232-Physic 2 Chapter 1 (Part 1) OscillationsDocument84 pagesFoundation in Science: SCP 232-Physic 2 Chapter 1 (Part 1) OscillationsaNo ratings yet
- Physics 211: 1D MotionDocument33 pagesPhysics 211: 1D MotionZachary Minh NhậtNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Paper (Mid Term, Summer 2015, 3rd Semester)Document1 pageDynamics Paper (Mid Term, Summer 2015, 3rd Semester)Momina AliNo ratings yet
- CH - 3 Motion in A Straight LineDocument41 pagesCH - 3 Motion in A Straight LineishayanarahtNo ratings yet
- المستندDocument13 pagesالمستندHussein Mahmood0% (1)
- Kinema TicsDocument17 pagesKinema TicsMuhammad IrvanNo ratings yet
- Area Under The GraphDocument15 pagesArea Under The Graphbjkhaw75No ratings yet
- Module 1 Wk3-4Document36 pagesModule 1 Wk3-4Dyas FerNo ratings yet
- Dynamics GLA-1c PDFDocument9 pagesDynamics GLA-1c PDFAhmad IrfanNo ratings yet
- Problems On SpeedDocument3 pagesProblems On Speedpavan kumarNo ratings yet
- Higher Eng Maths 9th Ed 2021 Solutions ChapterDocument46 pagesHigher Eng Maths 9th Ed 2021 Solutions ChapterAubrey JosephNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion (6 Hours)Document87 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion (6 Hours)aNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Rectilinear Translation MotionDocument39 pagesLesson 1: Rectilinear Translation MotionAaron EserNo ratings yet
- PhyI Assign&Answers 2011Document16 pagesPhyI Assign&Answers 2011Austin Phua Yun Hock100% (1)
- CBSE Test Paper 02 Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight LineDocument8 pagesCBSE Test Paper 02 Chapter 3 Motion in A Straight LineskNo ratings yet
- Ref Phy 10 1Document1,659 pagesRef Phy 10 1mkumarNo ratings yet
- PHY10T2KINEMATICSCALULUSDocument51 pagesPHY10T2KINEMATICSCALULUSChristiana Mae Padilla100% (2)
- 20090916Document7 pages20090916Elvio JungesNo ratings yet
- Dyna ProjectDocument58 pagesDyna ProjectCarlo Domanais0% (3)
- Fundamentals of Physics SoloutionDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Physics Soloution8310032914No ratings yet
- Ch12 Kinematics - of - A - ParticleDocument46 pagesCh12 Kinematics - of - A - ParticletarntodNo ratings yet
- Uniformlyacceleratedmotion 130924010203 Phpapp02Document35 pagesUniformlyacceleratedmotion 130924010203 Phpapp02Shierry Amor G. LangoteNo ratings yet
- Rate of ChangeDocument22 pagesRate of ChangeTrisha MariehNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Graphical Analysis of MotionDocument29 pagesLecture 2 - Graphical Analysis of Motionjcxdsr956mNo ratings yet
- Taller I-Repaso CinemáticaDocument3 pagesTaller I-Repaso CinemáticaEmmanuel Gómez LosadaNo ratings yet
- PHY10T2KINEMATICSDocument57 pagesPHY10T2KINEMATICSLuke CruzNo ratings yet
- Position: + 3.00, Where X Is in Meters and T Is in Seconds. DetermineDocument5 pagesPosition: + 3.00, Where X Is in Meters and T Is in Seconds. Determineanggian anggraeniNo ratings yet
- Phyf4 Chap2Document179 pagesPhyf4 Chap2Mohd AzlanNo ratings yet
- 143 First Assignment QuestionsDocument10 pages143 First Assignment QuestionsanyigbamarkmilbertNo ratings yet
- W) U1WorksheetsDocument15 pagesW) U1WorksheetsChairul Aspan SiregarNo ratings yet
- Equations of Motion NotesDocument12 pagesEquations of Motion NotesSurya Phani Krishna NukalaNo ratings yet
- Ie IRODOV SOLUTION PART 1Document95 pagesIe IRODOV SOLUTION PART 1alienx60582% (22)
- Engineering Mechanics Unit 5Document68 pagesEngineering Mechanics Unit 5SundraNo ratings yet
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDocument11 pagesPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierZoul HasleyNo ratings yet
- Motion. Equations, GraphsDocument12 pagesMotion. Equations, GraphsManash SinghaNo ratings yet
- PHY 151 Homework Practice Test Solutions 01Document8 pagesPHY 151 Homework Practice Test Solutions 01Dnhdj JdhsjdNo ratings yet
- Web Assign 2Document7 pagesWeb Assign 2sakshi83No ratings yet
- Kinematics Questions PDFDocument18 pagesKinematics Questions PDFZsadist20No ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- فيزياء 1Document67 pagesفيزياء 1Yousof AzzamNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies Topic 1Document2 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies Topic 1Ronaldo Latagan JrNo ratings yet
- Assinment 1Document4 pagesAssinment 1Abhijit AroopNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Problem Sheet - 4 Module - 4 Kinematics of ParticlesDocument12 pagesEngineering Mechanics Problem Sheet - 4 Module - 4 Kinematics of ParticlesCams SenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter II (Compatibility Mode)Document160 pagesChapter II (Compatibility Mode)Biruk TemesgenNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringFrom EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Ion Beams for Materials AnalysisFrom EverandIon Beams for Materials AnalysisR. Curtis BirdNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Yahari Ore No Seishun Rabu Kome (114) - Wataru Watari PDFDocument71 pagesYahari Ore No Seishun Rabu Kome (114) - Wataru Watari PDFOscar Alam GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Yahari Ore No Seishun Rabu Kome - Wataru Watari PDFDocument48 pagesYahari Ore No Seishun Rabu Kome - Wataru Watari PDFOscar Alam GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Project F1: Operational Amplifiers: Sound-To-Light Project: Prof. Tetsuo Kishimoto Prof. Varun Vohra Prof. Shigeo HayashiDocument4 pagesProject F1: Operational Amplifiers: Sound-To-Light Project: Prof. Tetsuo Kishimoto Prof. Varun Vohra Prof. Shigeo HayashiOscar Alam GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Project A1 - Resistance of Reference ResistorDocument6 pagesProject A1 - Resistance of Reference ResistorOscar Alam GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Complete Range of Sintech Make PumpsDocument8 pagesComplete Range of Sintech Make PumpssahildhingraNo ratings yet
- Koyo - Lezajevi I SpecifikacijeDocument288 pagesKoyo - Lezajevi I Specifikacijemiki-likiNo ratings yet
- Concrete Design Excel SheetDocument16 pagesConcrete Design Excel SheetCleth Hiren Santos25% (4)
- Mechanical BMC1.125 MC Us1 2BSP PN6 Q200Document8 pagesMechanical BMC1.125 MC Us1 2BSP PN6 Q200Obinna Okomgbor100% (1)
- Studying The Airflow Over A Car Using An Ahmed Body - COMSOL BlogDocument11 pagesStudying The Airflow Over A Car Using An Ahmed Body - COMSOL BlogSOURAVNo ratings yet
- Web Tension Control Systems PDFDocument12 pagesWeb Tension Control Systems PDFIsabelLimaMazahuaNo ratings yet
- 11 Holiday HomeworkDocument199 pages11 Holiday Homeworksupriyarama413No ratings yet
- Pumping of LiquidsDocument20 pagesPumping of Liquidsahmedyashar67% (3)
- Deciphering Complexity The Art of Reverse Engineering in Mechanical Engineering 20240401120140hmy8Document14 pagesDeciphering Complexity The Art of Reverse Engineering in Mechanical Engineering 20240401120140hmy8pavansvgp2003No ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument28 pages1 IntroductionZabid UllahNo ratings yet
- Structural Tank Instructions 11967-ADocument22 pagesStructural Tank Instructions 11967-Aiftikhar_khalid_1No ratings yet
- Safety Valve PDFDocument4 pagesSafety Valve PDFTARIQ IQBALNo ratings yet
- Dilution in Single Pass Arc Welds: As+As,, Asm EtaDocument9 pagesDilution in Single Pass Arc Welds: As+As,, Asm EtadayalramNo ratings yet
- L279-11 Proforma de Venta de Libros Formato Digital - GYM SADocument2 pagesL279-11 Proforma de Venta de Libros Formato Digital - GYM SAMarco RiveraNo ratings yet
- Fuchs Lubritech Group: DIN EN ISO 9001:2000Document54 pagesFuchs Lubritech Group: DIN EN ISO 9001:2000Hassan HamiNo ratings yet
- 2022-2023 Fall CE371 HW4 PDFDocument3 pages2022-2023 Fall CE371 HW4 PDFMurat EnginNo ratings yet
- Hryw 45 t5 GB PDFDocument6 pagesHryw 45 t5 GB PDFJonathan CastilloNo ratings yet
- DMA Based NRW Management - O&M Awareness ProgramDocument34 pagesDMA Based NRW Management - O&M Awareness ProgramThava ThavaNo ratings yet
- R1116010 00000 CI SPC 0007 0A Foundations and Structures Supporting MachineryDocument16 pagesR1116010 00000 CI SPC 0007 0A Foundations and Structures Supporting MachineryLNo ratings yet
- W-2-Day-2-I - Applying Fault in PSSEDocument9 pagesW-2-Day-2-I - Applying Fault in PSSEKASHIF0% (1)
- Single Dead End, Terminal Pole, Dead End Riser Pole: Saudi Arabian Oil CompanyDocument1 pageSingle Dead End, Terminal Pole, Dead End Riser Pole: Saudi Arabian Oil CompanyAbu Anas M.SalaheldinNo ratings yet
- Thickness Distribution and Mechanical Property of Sheet Metal Incremental Forming Based On Numerical SimulationDocument7 pagesThickness Distribution and Mechanical Property of Sheet Metal Incremental Forming Based On Numerical SimulationNigus TeklehaymanotNo ratings yet
- Diesel Hammer - Frank's InternationalDocument2 pagesDiesel Hammer - Frank's InternationalMiguelito BernanetNo ratings yet
- Cranes Used in Construction IndustryDocument12 pagesCranes Used in Construction IndustryNishant GauravNo ratings yet
- Acceleration & DecelerationDocument23 pagesAcceleration & Decelerationmrs azizi100% (1)
- Connecting Rod Bearings - InstallDocument3 pagesConnecting Rod Bearings - InstallPutra JawaNo ratings yet