Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neuroanatomy
Uploaded by
Ridz F0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views7 pagesOriginal Title
naq
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views7 pagesNeuroanatomy
Uploaded by
Ridz FCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
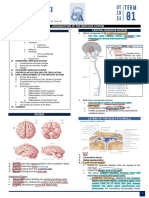
NEUROANATOMY 10.
Which of the following group of neurons is
specifically located outside the Central
1. The olfactory bulb is derived from which Nervous System?
secondary vesicle? a. Anterior gray horn
a. Telencephalon b. Posterior gray horn
b. Mesencephalon c. Posterior white horn
c. Diencephalon d. Posterior root ganglion
d. Myelencephalon 11. Which is true of the following?
2. The thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus a. The cerebrum and the cerebellum
are parts of the: have an inner white and outer gray
a. Cerebrum matter
b. Basal ganglia b. The spinal cord has an inner gray and
c. Diencephalon outer white matter
d. Tegmentum c. Both statements are true
3. Which connects the cerebellum to the pons? d. Both statements are false
a. Superior cerebellar peduncle 12. The basal ganglia are several large masses of
b. Middle cerebellar peduncle white matter located in the subcortical region
c. Inferior cerebellar peduncle of the brain
d. Vernis a. True
4. The conus medullaris is a prolongation of the b. False
pia mater that descends to attach to the back 13. The central nervous system is composed of
of the coccyx. the following structures except:
a. True a. Diencephalon
b. False b. Medulla
5. A young child was admitted to the hospital c. Sensory ganglia
because of episodes of vomiting, headache, d. Sacral segment of the spinal cord
and drowsiness. Due to the suspicion of 14. This bundle of white matter connects the 2
increased blockage of CSF flow and cerebral hemispheres.
absorption. Where is the main site of a. Internal capsule
absorption of the CSF? b. Corpus callosum
a. Arachnoid villi c. Arcuate fasciculus
b. Choroid process d. Corona radiata
c. Subarachnoid space 15. In the spinal cord, the anterior horn is derived
d. 4th ventricle from the alar plate while the posterior horn is
6. A 30-year old female had 1 week history of derived from the basal plate.
fever, headache and vomiting and was a. True
diagnosed with leptomeningitis. Which b. False
meningeal layer/s is/are inflamed? 16. The deep cerebellar nuclei arranged from
a. Arachnoid and pia lateral to medial arc:
b. Dura a. Fastigial, globose, emboliform, dentate
c. Dura and arachnoid b. Fastigial emboliform, globose, dentate
d. Pia and dura c. Dentate, emboliform, fastigial, globose
7. Where are the preganglionic neurons located? d. Dentate, emboliform, globose, fastigial
a. Cervical region 17. The sylvian aqueduct is a ventricular cavity
b. Thoracolumbar region formed by the:
c. Cervicothoracic region a. Mesencephalon
d. Cranial nerves and sacral region b. Diencephalon
8. What fissures/sulcus separates the frontal and c. Telencephalon
parietal lobes superiorly from the temporal d. Rhombencephalon
lobe inferiorly? 18. Where are the cell bodies of the nerve fibers
a. Lateral fissure conveying sensation of touch, pain,
b. Parietal Occipital sulcus temperature and vibration located?
c. Central sulcus of rolando a. Anterior horn cell
d. Longitudinal fissure b. Dorsal root ganglion
9. Upon examination of a newborn, it was c. Spinal nerve
observed that the brain, meninges and sull d. White matter of spinal cord
were not formed. Which of the following 19. The cerebrum lies above this dural fold and
developmental defects caused this? separates it from the cerebellum
a. Failure of closure of the anterior a. Falx cerebri
neuropore b. Tentorum cerebelli
b. Failure of closure of the posterior c. Periosteal layer
neuropore d. Diaphragma sella
c. Defect in secondary neurulation 20. What is the structure that forms the lateral
d. Failure of vertebral arches to fuse border of the 3rd ventricle?
a. Thalamus
b. Epithalamus
c. Midbrain Which nerve roots innervate the muscle that
d. Corpus callosum flexes the elbow, when its tendon is taped?
21. Which rapidly adapting mechanoreceptor is a. C6, C7, C8
activated when you are testing for vibration b. C5, C6
sense? c. C5, C6, C7
a. Meissner’s corpuscles d. C8, T1
b. Merkel discs 31. Which of the following is true about the
c. Pacinian corpuscles conduction in peripheral nerves?
d. Ruffini corpuscles a. Thickly myelinated fibers conduct
22. Which dermatome should be tested if you more rapidly thinly myelinated fibers.
want to assess for the sensation around the b. In nonmyelinated fibers, the action
umbilicus? potential passes continuously along
a. C7 the axolemma, progressively exiting
b. T4 neighboring areas of membrane.
c. T10 c. In myelinated fibers, the presence of a
d. T12 myelin sheath as an insulator and a
23. Muscle tone is dependent on the integrity of a myelinated nerve fiber can be
simple monosynaptic reflex arc. The following stimulated only at the nodes of
are the components of a simple reflex arc: Ranvier
a. Afferent neuron from neuromuscular d. All of the above
spindles and neurotendinous spindles 32. Which of the following is the primary
b. Efferent neuron from the anterior horn postsynaptic receptor of the neuromuscular
cell junction?
c. Efferent neuron from muscle at motor a. Dopamine receptor
end plates b. GABA receptor
d. None of the above c. Glutamate receptor
24. These structures play a role in axon transport d. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
and formation of new cell processes. 33. These cells are responsible for the formation
a. Microfilaments of myelin in the CNS
b. Microtubules a. Schwann cells
c. Neurofilaments b. Ependymal cells
d. Both A & B c. Astrocytes
25. By having the patient repetitively touch the tip d. Oligodendrocytes
of his nose and the examiner’s finger, tests 34. Myasthenia gravis is a postsynaptic
which of the following? neuromuscular junction disease wherein the
a. Muscle power synaptic transmission is impaired because of
b. Muscle coordination the destruction of acetylcholine receptors,
c. Muscle tone leading to muscle fatigue and weakness.
d. Joint position Which of the following drugs inhibits
26. Most synapses are electrical in which bridging acetylcholine and temporarily relieves the
channels permit ionic current flow to take symptoms of myasthenia?
place from one cell to the other with a a. Botulinum toxin
minimum of delay. b. Succinylcholine
a. True c. Neostigmine
b. False d. Guanidine hydrochloride
27. Which neurotransmitter is lacking in patients 35. Which of the following steps stimulates the
with Parkinson’s disease? fusion of the synaptic vesicles with the
a. Acetylcholine presynaptic membrane and causes the
b. Dopamine release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cell?
c. Glutamate a. Arrival of action potential
d. Norepinephrine b. Opening of calcium channels
28. The effect produced by a neurotransmitter is c. Influx of sodium
limited by its destruction or reabsorption. The d. Efflux of potassium
effect of acetylcholine is terminated by: 36. The resting state is characterized by which of
a. Acetylcholine reuptake the following?
b. Breakdown by choline acetylcholine a. Passive efflux of sodium
c. Hydrolysis by acetylcholine b. Potassium ions diffuse from the cell
d. None of the above cytoplasm to the tissue fluid
29. Which of the following nerve fiber types are c. Resting potential: 40 mV
the primary carriers of pain? d. None of the above
a. A alpha 37. The neuromuscular spindles receive
b. A beta information about muscle length and the rate
c. A delta and C of change in the muscle length while the
d. A gamma neurotendinous spindles sense changes in
30. A patient suspected to have GBS has absent muscle tension.
tendon reflexes in both upper extremities. a. True
b. False d. Lateral cord
38. What type of neurons are in the motor cells of 48. What event could possibly cause Hangman’s
the spinal cord? fracture?
a. Multipolar a. Fracture of pars interarticularis
b. Bipolar b. High velocity hyperextension of the
c. Unipolar head
d. Pseudounipolar c. Fracture of anterior and posterior
39. There is repolarization of the membrane after arches
the occurrence of an action potential. What d. Both A & B
should explain this event? 49. These vertebrae differ from the other
a. Opening of potassium channels segments because of costal facets.
b. Opening of sodium channels a. Cervical
c. Influx of calcium b. Thoracic
d. Impermeability of the membrane to all c. Lumbar
ions d. Sacral
40. The perineurium covers the nerve trunk 50. A 70-year old woman was found unconscious
a. True in her apartment. After regaining
b. False consciousness, she could not move her right
41. This tract is thought to include the descending arm. On examination, she also has
autonomic fibers and provides a pathway by hyperreflexia and hypertonia in the affected
which the hypothalamus can control the limb. Which of the following structures is
sympathetic outflow and the sacral affected
parasympathetic outflow a. Lateral corticospinal tract
a. Vestibulospinal tract b. Anterior spinothalamic tract
b. Lateral corticospinal tract c. Vestibulospinal tract
c. Rubrospinal tract d. Anterior gray horn
d. Reticulospinal tract 51. Following hemisection of the spinal cord,
42. All the axons from the nucleus cuneatus cross approximately at the level of T10, a patient
the median plane, join the medial lemniscus experiences loss of light touch and pressure
and terminate in the ventral posterolateral sensation on the left side of the leg. Damage
nucleus of the thalamus. to which of the following tracts could account
a. True for this deficit?
b. False a. Right fasciculus gracilis
43. Ths presents as low back pain, symmetric b. Right anterior spinothalamic tract
saddle anesthesia and muscle weakness and c. Left anterior spinothalamic tract
early bowel and bladder dysfunction. d. Left lateral spinothalamic tract
a. Caudal equina syndrome 52. This tract provides an afferent pathway for the
b. Poliomyelitis reticular formation, which plays an important
c. Conus medullaris syndrome role in influencing levels of consciousness
d. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis a. Reticulospinal tract
44. The gating theory of pain proposes that b. Spinoreticular tract
excessive non-painful touch and pressure c. Spino-olivary tract
carried by large, myelinated afferent fiber close d. Olivospinal tract
the gate for pain. 53. A 35-year old man is brought to the
a. True emergency room after sustaining injury to his
b. False back. A neurological examination reveals loss
45. The spinal nerves pass through these of flexor muscle function. Damage to which
structures tract would account for this defect?
a. Transverse foramen a. Vestibulospinal tract
b. Intervertebral foramen b. Reticulospinal tract
c. Vertebral foramen c. Rubrospinal tract
d. Lamina d. Tectospinal tract
46. Which finding would you expect in the first 24 54. The following are located in the posterior gray
hours of spinal shock syndrome? column except:
a. Hyperactive spinal reflexes a. Accessory nucleus
b. Flaccid paralysis b. Nucleus proprius
c. Intact sensation c. Nucleus dorsalis of clarke
d. Hypertension d. Substantial gelatinosa
47. If the hypertension has bilateral loss of pain, 55. This is the main excitatory neurotransmitter
temperature, light touch and pressure released by the A delta fibers and the C fibers.
sensations below the level of the lesion with a. Substance P
characteristic sacral Osparing’s, the most b. Glutamate
probable location of the lesion is at the: c. Glycine
a. Posterior cord d. Serotonin
b. Anterior cord
c. Central cord
56. The medial aspect of the left primary motor b. Phrenic nucleus
cortex represents motor activity of the right c. Lumbosacral nucleus
leg. d. Nucleus proprius
a. True 67. Which of the following is associated with
b. False proprioceptive endings (neuromuscular
57. This is present throughout the length of the spindles and tendon spindles)?
spinal cord and contains the long ascending a. Nucleus proprius
fibers from the sacral, lumbar, and lower six b. Substantia gelatinosa
thoracic spinal nerves. c. Clarke’s column
a. Fasciculus gracilis d. Visceral afferent nucleus
b. Nucleus gracilis 68. Where is the first order neuron of the
c. Fasciculus cuneatus ascending tracts?
d. Nucleus cuneatus a. Medulla
58. A 60-year old man was diagnosed with b. Posterior root ganglion
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The following c. Thalamus
year, the disease progressed and he lost the d. Posterior gray horn
use of his arms and legs. He also had 69. Which is the outermost meingeal layer of the
fasciculations and hyperreflexia. Which spinal cord?
structure/s of the spinal cord is/are affected? a. Dura
a. Posterior gray horn b. Pia
b. Lateral gray horn c. Arachnoid
c. Anterior gray horn 70. What is the deep groove on the anterior
d. Anterior gray horn and lateral surface of the spinal cord?
corticospinal tract a. Posterior median sulcus
59. The posterior spinocerebellar tract joins the b. Anterior white column
inferior cerebellar peduncle and terminates in c. Gray commissure
the cerebellar cortex while the anterior d. Anterior median fissure
spinocerebellar tract enters the cerebellum 71. Axons in this tract run up and down for one or
through the superior cerebellar peduncle. two spinal cord segments before they
a. True penetrate the posterior gray horn. Lissauer’s
b. False tract
60. In cases of ruptured disc, this part protrudes 72. Glutamate is the main excitatory
posteriorly through the anulus fibrosus, and neurotransmitter released by the A delta fibers
may compress spinal nerve roots and the and the C fibers
spinal nerve. a. True
a. Nucleus propius b. False
b. Nucleus pulposus 73. Where does the corticospinal tract decussate?
c. Substantia gelatinosa a. Various spinal levels
d. Ligamentum flavum b. Ventral tegmental decussation in the
61. Which actor suffered from a high cervical cord midbrain
injury? c. Dorsal tegmental decussation in the
a. Jackie chan midbrain
b. Bruce willis d. Cervico-medullary junction
c. Christopher reeve 74. A positive response of this test represents an
d. Tom cruise upper motor neuron lesion.
62. In the cervical region, there are 8 pairs of a. Superficial abdominal
spinal nerves and 7 cervical nerves b. Babinski
a. True c. Cremasteric
b. False d. Deep tendon reflex
63. What is the other name of this structure? 75. This tract facilitates the activity of the flexor
Odontoid process muscles and inhibits the activity of the
64. This is defined as an excessive anterior extensor muscles.
curvature of the lumbar region a. Corticospinal tract
a. Kyphosis b. Vestibulospinal tract
b. Lordosis c. Rubrospinal tract
c. Scoliosis d. Reticulospinal tract
d. Gibbus 76. This tract provides a pathway by which the
65. What ligament connects the laminae of hypothalamus can control the sympathetic and
adjacent vertebrae? parasympathetic outflow.
a. Supraspinous ligament a. Corticospinal tract
b. Anterior longitudinal ligament b. Vestibulospinal tract
c. Intertransverse ligament c. Rubrospinal tract
d. Ligamentum flavum d. Reticulospinal tract
66. This innervates the sternocleidomastoid and 77. This tract facilitates the activity of the extensor
trapezius muscles muscles and inhibits the activity of the flexor
a. Accessory nucleus muscles.
a. Corticospinal tract
b. Vestibulospinal tract
c. Rubrospinal tract
d. Reticulospinal tract
78. The lateral aspect of the left primary motor
activity of the right leg.
a. True
b. False
79. This follows acute severe damage to the
spinal cord where all the functions below the
lesion become depressed or lost. Spinal shock
80. Anterior cord syndrome consists of the
following except:
a. Bilateral loss of pain, temperature, and
light touch sensations
b. Ilateral spastic paralysis
c. Bilateral lower motor neuron paralysis
d. Bilateral loss of tactile discrimantion,
viratory and position sense
81. Brown-sequard syndrome consists of the
following except:
a. Ipsilateral lower motor neuron
paralysis
b. Ipsilateral loss of tactile discrimination,
vibratory and position sense
c. Ipsilateral spastic paralysis
d. Ipsilateral loss of pain and
temperature sensations
82. This condition manifests with both UMN and
LMN signs
a. Polio
b. GBS
c. ALS
d. Stoke
83. Cauda equina syndrome consists of low back
pain, temperature, asymmetric saddle
anesthesia and late bowel/bladder dysfunction
a. True
b. False
OT CORRELATES 21. Fatigue and pain are the two symptoms most
frequently mentioned in poliomyelits.
1. Explaining the stages of recovery to a client ○ True
with CVA to the family members is an example 22. The provision of daily passive ROM is for the
of: purpose of:
○ Education and training ○ Maintaining ROM
2. I am mixing the greens while at the same time 23. The provision of active exercises in muscular
talking to you on the phone. dystropy is for the purpose of:
○ Divided attention ○ NOTA
3. The provision of icing to a client with 24. Scapular protraction is compromised with a
decreased muscle tone is an example of: lesion to the long thoracic nerve.
○ Preparatory method ○ True
4. The provision of fast tapping to a client with 25. Clients with Guillain-Barre Syndrome would
decreased muscle tone is an example of: normally have these clinical features:
○ Preparatory method ○ Hypotonicity and fatigue
5. The prescription of a swivel spoon is an example 26. Management of sensory functions in clients with
of: peripheral nerve injuries include providing tactile
○ Preparatory method and proprioceptive stimulation
6. It refers to one's state of awareness and ○ True
alertness. 27. Drooping of the eyelids:
○ Consciousness ○ Ptosis
7. What are the spheres of orientation? 28. Clients with myasthenia gravis often complain of
○ "Person, place, time, situation" dyarthria and dysphagia. It is a condition
8. In the Neurodevelopmental FOR, limb control affecting the muscle belly itself.
should be addressed first before axial control. ○ First statement is correct. Second
○ False statement is incorrect.
9. Facilitating the completion of the client's morning 29. Clients with peripheral nerve injuries have
routine is an example of: corresponding perceptual and cognitive deficits.
○ Occupations and activities ○ False
10. The usage of an orthoses is seen in both 30. Clients with Duchenne muscular dystophy are
Biomechanical and Rehabilitation FORs. typically observed with a (-) Gowers' sign.
○ True ○ False
11. Having the client perform 10 repetitions, 3 sets 31. Clients with thoracodrosal nerve injury would
of finger flexion using the yellow digiflex is an have significant difficulty performing functional
example of: mobility using crutches.
○ Preparatory task ○ True
12. Principle of rest and stress: 32. Clients with poliomyelitis would have increased
○ Biomechanical FOR muscle tone. They have a characteristic
13. An OT providing handling techniques to a child flexion-abduction contratcure of the hip.
with Cerebral Palsy to facilitate reaching may be ○ First statement is incorrect. Second
following the asusmptions of this FOR: statement is correct.
○ Neurodevelopmental 33. The dual innervation of the interossei may
14. It refers to a state of continuous partial muscle contribute to the retaining of MCP flexion in the
contraction. lateral two fingers. The lumbricals extend the
○ Muscle tone IPs.
15. Which of the following tasks are considered to ○ First statement is incorrect. Second
be in line with the premises of the Rehabilitation statement is correct.
FOR? 34. Lesion to C5-C6 may cause difficulty reaching
○ Teaching proper body mechanics to for your back pocket. A lesion to the
office workers musculocutaneous nerve may result to difficulty
16. The OT process follows a linear approach as managing door knobs.
you go from one task to the next. ○ Both statements are correct.
○ False 35. The usage of cognitive behavioral therapy in
17. Assessment of cognitive skills is also crucial in pain management is backed up with literature.
the Rehabilitation FOR ○ True
○ True 36. Shoulder shrugs may be compromised with C5
18. The Biomechanical FOR follows up a top-down lesion. External rotation may be weakened if
approach. there is a lesion in the suprascapular nerve.
○ False ○ Both statements are correct.
19. Under the Biomechanical FOR, postural tone 37. Clients with muscular dystophy has an
and coordinaton would be given utmost affectation in the nerve fiber. They normally
emphasis in the evaluation and intervention report of an abrupt recovery process.
procedures. ○ Both statements are incorrect.
○ False 38. Retrograde massage is given to address:
20. Attention falls under global mental functions. ○ Edema
○ False 39. The purpose for recommending splints is to
○ Options A, B, C = 3, MMT of the remaining muscle groups = 2-
40. Educating clients with energy conservation, work Given these data, what is the ASIA grading?
simplification, and joint protection techniques is ○ D
in line with the premises of: 60. There is some degree of motor activity in parts
○ Rehabilitation FOR below the level of lesion in ASIA B.
41. In the event that there is weakness of finger ○ False
flexors in SCI clients, what muscles groups
should be strengthened to faciliate stronger
gripping?
○ Wrist extensors
42. Progressive resistive exercises may be provided
for partially innervated muscles.
○ True
43. Recommended managament for heterotopic
ossification:
○ Provision of PROM exercises
44. SCI Level = C5, wrist extensors MMT = 2+,
elbow extensors MMT = 2, MMT of the
remaining muscle groups = 2- Given these data,
what is the ASIA grading?
○ C
45. It is important to evaluate for light touch and
pressure senstation in SCI clients.
○ True
46. Which procedure should be performed in SCI
clients experiencing orthostatic hypotension?
○ Elevating the legs
47. Strengthening of elbow flexors is warranted in
C6, ASIA A injuries because:
○ Strengthening the remaining parts will
greatly aid task completion
48. In C7, ASIA A, there is still an intact sensation
on C7 dermatome.
○ True
49. Strengthening of elbow extensors is not
warranted in C5, ASIA A because:
○ Elbow extensors are paralyzed
50. Strengthening of wrist extensors is warranted in
C6, ASIA A because:
○ Strengthening the remaining parts will
greatly aid task completion
51. Key muscle groups at L3
○ Knee extensors
52. A damage to structures past the anterior gray
horn may produce spasticity.
○ False
53. Key muscle groups at C8:
○ Finger flexors
54. What is the rationale for the prescription of
dorsal splints?
○ Maximizing sensory feedback
55. In what level of SCI injury will the usage of
universal cuff be recommended?
○ C7
56. Which procedure should be performed in SCI
clients experiencing autonomic dysreflexia?
○ Removing the noxious stimulus
57. Long-term memory and executive functions may
be compromised in C3, ASIA clients.
○ False
58. The lack of forearm supination necessary for
scooping food in SCI clients may be
compensated with the usage of:
○ Swivel spoon
59. SCI Level = C6, elbow extensors MMT = 3+,
finger flexors MMT = 3+, finger abductors MMT
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Brain ChemicalsDocument24 pagesBrain ChemicalsZaharia CristianNo ratings yet
- Cosmeceutical PeptidesDocument7 pagesCosmeceutical PeptidesharborNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Supplementation GuideDocument13 pagesSupplementation GuideLouis Trần100% (8)
- Pharmacology Board ReviewDocument599 pagesPharmacology Board ReviewMelbhon Fabro RamosNo ratings yet
- Ncmb317 Lecture: BSN 3Rd Year 2Nd Semester Prelim 2023: Bachelor of Science in Nursing 3YBDocument62 pagesNcmb317 Lecture: BSN 3Rd Year 2Nd Semester Prelim 2023: Bachelor of Science in Nursing 3YB2 - GUEVARRA, KYLE JOSHUA M.No ratings yet
- Gamsat Practice QuestionsDocument28 pagesGamsat Practice QuestionsDr Peter Griffiths100% (6)
- Manan 1000 Q - ADocument294 pagesManan 1000 Q - ADrSamia El Wakil0% (1)
- Misbah Part 1 Pharmacology v2 PDFDocument232 pagesMisbah Part 1 Pharmacology v2 PDFLeslie VicencioNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocument36 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNo ratings yet
- (Cholinergic System) Model Questions and AnswersDocument45 pages(Cholinergic System) Model Questions and AnswersAjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology Book 2018Document304 pagesClinical Pharmacology Book 2018Sumaiya Islam KhanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantDocument18 pagesSkeletal Muscle Relaxantswaroop ranjan nandaNo ratings yet
- OT1024 PrelimsDocument63 pagesOT1024 PrelimsRidz FNo ratings yet
- OT1024 - 1S1L - Organization of The Nervous System-CompressedDocument14 pagesOT1024 - 1S1L - Organization of The Nervous System-CompressedRidz FNo ratings yet
- OT 1025 - Home ModificationDocument24 pagesOT 1025 - Home ModificationRidz FNo ratings yet
- RCY CalendarDocument13 pagesRCY CalendarRidz FNo ratings yet
- Rcy StructureDocument1 pageRcy StructureRidz FNo ratings yet
- OT 1025 - IADL Universal DesignDocument46 pagesOT 1025 - IADL Universal DesignRidz FNo ratings yet
- OT 1025 - Frame of ReferenceDocument28 pagesOT 1025 - Frame of ReferenceRidz FNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System OverviewDocument39 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System OverviewAhaisibwe GordonNo ratings yet
- Autonomic DrugsDocument4 pagesAutonomic DrugsSabrinaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key in Pharmacology Pink PacopDocument139 pagesAnswer Key in Pharmacology Pink PacopJoslin Roz GalileaNo ratings yet
- CNS Drugs TextDocument27 pagesCNS Drugs TextTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument44 pagesCholinergic Drugskhuzaima9100% (1)
- AcetylcholineDocument50 pagesAcetylcholineEliza GhinitaNo ratings yet
- Psychology A Concise Introduction 5th Edition Griggs Test BankDocument52 pagesPsychology A Concise Introduction 5th Edition Griggs Test BankPat Ochs100% (40)
- PHARMA 06. Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument6 pagesPHARMA 06. Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyCindy Mae MacamayNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step I Comprehensive ReviewDocument222 pagesUSMLE Step I Comprehensive ReviewJay KJNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology-Part 1.Document90 pagesPharmacology-Part 1.Hain YoloNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Drugs Acting On The ANSDocument18 pagesUnit 7 Drugs Acting On The ANSTherese Margarette SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic BlockersDocument39 pagesCholinergic BlockersAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Physiology ExperimentDocument18 pagesNeuromuscular Physiology ExperimentmenschNo ratings yet
- If These Are Stimulated It Produces An Array of Effects in The BodyDocument4 pagesIf These Are Stimulated It Produces An Array of Effects in The BodyAnne Giselle PatocNo ratings yet
- Bio 336 Physio Exam 1 EssaysDocument3 pagesBio 336 Physio Exam 1 EssayssheilaNo ratings yet
- Term-Project-Ii-Bch3125 ADocument8 pagesTerm-Project-Ii-Bch3125 APure PureNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument7 pagesBiological Bases of BehaviorSANTHOSH KUMAR T MNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Bachynsky - The Use of Anticholinergic Drugs For Smoking Cessation: A Pilot StudyDocument9 pagesNicholas Bachynsky - The Use of Anticholinergic Drugs For Smoking Cessation: A Pilot StudyHumiopNo ratings yet