Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Micromachined Accelerometer MMA1201P MMA2200W: Semiconductor Technical Data
Uploaded by
Minh QuốcOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Micromachined Accelerometer MMA1201P MMA2200W: Semiconductor Technical Data
Uploaded by
Minh QuốcCopyright:
Available Formats
MOTOROLA Order this document
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA by MMA1201P/D
MMA1201P
Micromachined Accelerometer MMA2200W
The MMA series of silicon capacitive, micromachined accelerometers
features signal conditioning, a 4–pole low pass filter and temperature
compensation. Zero–g offset full scale span and filter cut–off are factory set and
require no external devices. A full system self–test capability verifies system MMA1201P: Z AXIS SENSITIVITY
functionality. MMA2200W: X AXIS SENSITIVITY
Features MICROMACHINED
ACCELEROMETER
• Integral Signal Conditioning ± 40g
• Linear Output
• Ratiometric Performance
• 4th Order Bessel Filter Preserves Pulse Shape Integrity 10
9
11
• Calibrated Self–test 14
13
12
15
• Low Voltage Detect, Clock Monitor, and EPROM Parity Check Status 16
• Transducer Hermetically Sealed at Wafer Level for Superior Reliability 7
8
6
• Robust Design, High Shocks Survivability 3
4
5
2
• Two Packaging Options Available: 1
1) Plastic DIP for Z Axis Sensing (MMA1201P) DIP PACKAGE
2) Wingback for X Axis Sensing (MMA2200W) CASE 648C–04
MMA1201P
Typical Applications
• Vibration Monitoring and Recording
• Appliance Control
• Mechanical Bearing Monitoring
• Computer Hard Drive Protection
12
3
4
• Computer Mouse and Joysticks 5
6
• Virtual Reality Input Devices
WB PACKAGE
• Sports Diagnostic Devices and Systems CASE 456–06
MMA2200W
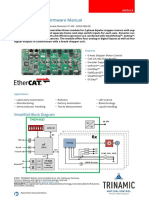
SIMPLIFIED ACCELEROMETER FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
VDD
G–CELL TEMP
INTEGRATOR GAIN FILTER VOUT
SENSOR COMP
VST CONTROL LOGIC &
SELF–TEST OSCILLATOR CLOCK GEN.
EPROM TRIM CIRCUITS
VSS
STATUS
Figure 1. Simplified Accelerometer Functional Block Diagram
REV 0
Motorola Sensor Device Data 1
Motorola, Inc. 2000
MMA1201P MMA2200W
MAXIMUM RATINGS (Maximum ratings are the limits to which the device can be exposed without causing permanent damage.)
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Powered Acceleration (all axes) Gpd 500 g
Unpowered Acceleration (all axes) Gupd 2000 g
Supply Voltage VDD –0.3 to +7.0 V
Drop Test(1) Ddrop 1.2 m
Storage Temperature Range Tstg – 40 to +105 °C
NOTES:
1. Dropped onto concrete surface from any axis.
ELECTRO STATIC DISCHARGE (ESD) 2000 volts can accumulate on the human body or associated
test equipment. A charge of this magnitude can alter the per-
WARNING: This device is sensitive to electrostatic
formance or cause failure of the chip. When handling the
discharge.
accelerometer, proper ESD precautions should be followed
Although the Motorola accelerometers contain internal
to avoid exposing the device to discharges which may be
2kV ESD protection circuitry, extra precaution must be taken
detrimental to its performance.
by the user to protect the chip from ESD. A charge of over
2 Motorola Sensor Device Data
MMA1201P MMA2200W
OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
(Unless otherwise noted: 0°C v TA v +85°C, 4.75 v VDD v 5.25, Acceleration = 0g, Loaded output(1))
Characteristic Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Operating Range(2)
Supply Voltage(3) VDD 4.75 5.00 5.25 V
Supply Current IDD 4.0 5.0 6.0 mA
Operating Temperature Range TA * 40 — +85 °C
Acceleration Range gFS — 38 — g
Output Signal
Zero g (VDD = 5.0 V)(4) VOFF 2.2 2.5 2.8 V
Zero g VOFF,V 0.44 VDD 0.50 VDD 0.56 VDD V
Sensitivity (TA = 25°C, VDD = 5.0 V)(5) S 47.5 50 52.5 mV/g
Sensitivity (VDD = 5.0 V) SV 9.3 10 10.7 mV/g/V
Bandwidth Response f –3dB 360 400 440 Hz
Nonlinearity NLOUT * 1.0 — +1.0 % FSO
Noise
RMS (.01–1 kHz) nRMS — — 3.5 mVrms
Power Spectral Density nPSD — 110 — µV/(Hz1/2)
Clock Noise (without RC load on output)(6) nCLK — 2.0 — mVpk
Self–Test
Output Response gST 20 — 30 g
Input Low VIL VSS — 0.3 x VDD V
Input High VIH 0.7 x VDD — VDD V
Input Loading(7) IIN * 30 * 110 * 300 µA
Response Time(8) tST — 2.0 10 ms
Status(12)(13)
Output Low (Iload = 100 µA) VOL — — 0.4 V
Output High (Iload = 100 µA) VOH VDD .8 * — — V
Minimum Supply Voltage (LVD Trip) VLVD 2.7 3.25 4.0 V
Clock Monitor Fail Detection Frequency fmin 50 — 260 kHz
Output Stage Performance
Electrical Saturation Recovery Time(9) tDELAY — 0.2 — ms
Full Scale Output Range (IOUT = 200 µA) VFSO 0.3 — VDD 0.3* V
Capacitive Load Drive(10) CL — — 100 pF
Output Impedance ZO — 300 — Ω
Mechanical Characteristics
Transverse Sensitivity(11) VZX,YX — — 5.0 % FSO
Package Resonance fPKG — 10 — kHz
NOTES:
1. For a loaded output the measurements are observed after an RC filter consisting of a 1 kΩ resistor and a 0.01 µF capacitor to ground.
2. These limits define the range of operation for which the part will meet specification.
3. Within the supply range of 4.75 and 5.25 volts, the device operates as a fully calibrated linear accelerometer. Beyond these supply limits
the device may operate as a linear device but is not guaranteed to be in calibration.
*
4. The device can measure both + and acceleration. With no input acceleration the output is at midsupply. For positive acceleration the output
will increase above VDD/2 and for negative acceleration the output will decrease below VDD/2.
5. The device is calibrated at 20g.
6. At clock frequency ^ 70 kHz.
7. The digital input pin has an internal pull–down current source to prevent inadvertent self test initiation due to external board level leakages.
8. Time for the output to reach 90% of its final value after a self–test is initiated.
9. Time for amplifiers to recover after an acceleration signal causing them to saturate.
10. Preserves phase margin (60°) to guarantee output amplifier stability.
11. A measure of the device’s ability to reject an acceleration applied 90° from the true axis of sensitivity.
12. The Status pin output is not valid following power–up until at least one rising edge has been applied to the self–test pin. The Status pin is
high whenever the self–test input is high.
13. The Status pin output latches high if a Low Voltage Detection or Clock Frequency failure occurs, or the EPROM parity changes to odd. The
Status pin can be reset by a rising edge on self–test, unless a fault condition continues to exist.
Motorola Sensor Device Data 3
MMA1201P MMA2200W
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION systems where system integrity must be ensured over the life
of the vehicle. A fourth “plate’’ is used in the g–cell as a self–
The Motorola accelerometer is a surface–micromachined test plate. When the user applies a logic high input to the
integrated–circuit accelerometer. self–test pin, a calibrated potential is applied across the
The device consists of a surface micromachined capaci- self–test plate and the moveable plate. The resulting elec-
tive sensing cell (g–cell) and a CMOS signal conditioning trostatic force (Fe = 1/2 AV2/d2) causes the center plate to
ASIC contained in a single integrated circuit package. The deflect. The resultant deflection is measured by the accel-
sensing element is sealed hermetically at the wafer level erometer’s control ASIC and a proportional output voltage
using a bulk micromachined “cap’’ wafer. results. This procedure assures that both the mechanical
The g–cell is a mechanical structure formed from semicon- (g–cell) and electronic sections of the accelerometer are
ductor materials (polysilicon) using semiconductor pro- functioning.
cesses (masking and etching). It can be modeled as two
stationary plates with a moveable plate in–between. The
center plate can be deflected from its rest position by sub- Ratiometricity
jecting the system to an acceleration (Figure 2). Ratiometricity simply means that the output offset voltage
When the center plate deflects, the distance from it to one and sensitivity will scale linearly with applied supply voltage.
fixed plate will increase by the same amount that the dis- That is, as you increase supply voltage the sensitivity and
tance to the other plate decreases. The change in distance is offset increase linearly; as supply voltage decreases, offset
a measure of acceleration. and sensitivity decrease linearly. This is a key feature when
The g–cell plates form two back–to–back capacitors interfacing to a microcontroller or an A/D converter because
(Figure 3). As the center plate moves with acceleration, the it provides system level cancellation of supply induced errors
distance between the plates changes and each capacitor’s in the analog to digital conversion process.
value will change, (C = Aε/D). Where A is the area of the
plate, ε is the dielectric constant, and D is the distance Status
between the plates. Motorola accelerometers include fault detection circuitry
The CMOS ASIC uses switched capacitor techniques to and a fault latch. The Status pin is an output from the fault
measure the g–cell capacitors and extract the acceleration latch, OR’d with self–test, and is set high whenever one (or
data from the difference between the two capacitors. The more) of the following events occur:
ASIC also signal conditions and filters (switched capacitor)
• Supply voltage falls below the Low Voltage Detect (LVD)
the signal, providing a high level output voltage that is ratio-
voltage threshold
metric and proportional to acceleration.
• Clock oscillator falls below the clock monitor minimum
frequency
Acceleration • Parity of the EPROM bits becomes odd in number.
The fault latch can be reset by a rising edge on the self–
test input pin, unless one (or more) of the fault conditions
continues to exist.
BASIC CONNECTIONS
Pinout Description for the Wingback Package
Figure 2. Transducer Figure 3. Equivalent
Physical Model Circuit Model
12
3
4
5
6
SPECIAL FEATURES
Filtering
The Motorola accelerometers contain an onboard 4–pole
Pin No. Pin Name Description
switched capacitor filter. A Bessel implementation is used
because it provides a maximally flat delay response (linear 1 — Leave unconnected or connect to
signal ground
phase) thus preserving pulse shape integrity. Because the fil-
ter is realized using switched capacitor techniques, there is 2 ST Logic input pin to initiate self test
no requirement for external passive components (resistors
3 VOUT Output voltage
and capacitors) to set the cut–off frequency.
4 Status Logic output pin to indicate fault
Self–Test 5 VSS Signal ground
The sensor provides a self–test feature that allows the
6 VDD Supply voltage (5 V)
verification of the mechanical and electrical integrity of the
accelerometer at any time before or after installation. This — Wings Support pins, internally connected to
feature is critical in applications such as automotive airbag lead frame. Tie to VSS.
4 Motorola Sensor Device Data
MMA1201P MMA2200W
4 MMA1201P 6
VDD MMA2200W STATUS VDD STATUS
LOGIC 2 ST R1 LOGIC 4 ST R1
INPUT 1 kΩ INPUT 1 kΩ
6 VDD VOUT 3 OUTPUT 8 VDD VOUT 5 OUTPUT
SIGNAL SIGNAL
C1 C1
C2 0.1 µF C2
0.1 µF
0.01 µF 0.01 µF
5 VSS 7 VSS
Figure 4. Wingback Accelerometer with Figure 5. DIP Accelerometer with Recommended
Recommended Connection Diagram Connection Diagram
PCB Layout
STATUS P1
ACCELEROMETER
MICROCONTROLLER
Pinout Description for the DIP Package ST P0
VSS
VOUT R A/D IN
N/C 1 16 N/C C 0.1 µF
VSS 1 kΩ C 0.01 µF
N/C 2 15 N/C VDD
C 0.1 µF
N/C 3 14 N/C VDD
VRH
ST 4 13 N/C
C 0.1 µF
VOUT 5 12 N/C
STATUS 6 11 N/C
VSS 7 10 N/C POWER SUPPLY
VDD 8 9 N/C
Figure 6. Recommend PCB Layout for Interfacing
Accelerometer to Microcontroller
NOTES:
Pin No. Pin Name Description
• Use a 0.1 µF capacitor on VDD to decouple the power
source.
1 — Leave unconnected or connect to
signal ground. • Physical coupling distance of the accelerometer to the
microcontroller should be minimal.
2 thru 3 — No internal connection. Leave
unconnected. • Place a ground plane beneath the accelerometer to reduce
noise, the ground plane should be attached to all of the
4 ST Logic input pin to initiate self open ended terminals shown in Figure 6.
test.
• Use an RC filter of 1 kΩ and 0.01 µF on the output of the
5 VOUT Output voltage accelerometer to minimize clock noise (from the switched
6 Status Logic output pin to indicate capacitor filter circuit).
fault. • PCB layout of power and ground should not couple power
7 VSS Signal ground supply noise.
• Accelerometer and microcontroller should not be a high
8 VDD Supply voltage (5 V)
current path.
9 thru 13 Trim Pins Used for factory trim. Leave • A/D sampling rate and any external power supply switching
unconnected.
frequency should be selected such that they do not inter-
14 thru 16 — No internal connection. Leave fere with the internal accelerometer sampling frequency.
unconnected. This will prevent aliasing errors.
Motorola Sensor Device Data 5
MMA1201P MMA2200W
Positive Acceleration Sensing Direction
DIP PACKAGE WINGBACK PACKAGE
12 7
16 9
1 8
1 6
*
*
* When positioned as shown, the Earth’s gravity will result in a positive 1g output
Drilling Patterns
WB PACKAGE DRILLING PATTERN
.000 .090 .190 .290 .390 .490 .590 .680
.090
∅ .049 2X ∅ .033 6X
.047 .031
Measurement in inches
ORDERING INFORMATION
Device Temperature Range Case No. Package
MMA1201P –40 to +85°C Case 648C–04 Plastic DIP
MMA2200W –40 to +85°C Case 456–06 Plastic Wingback
6 Motorola Sensor Device Data
MMA1201P MMA2200W
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
A
A B NOTES:
T B
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ASME
M
Y14.5M, 1994.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: INCH.
M
16 9
J
3. DIMENSION L TO CENTER OF LEADS WHEN
0.005 (0.13)
16X
FORMED PARALLEL.
L
B
4. DIMENSION B DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD FLASH.
1 8
INCHES MILLIMETERS
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
A 0.744 0.783 18.90 19.90
F B 0.240 0.260 6.10 6.60
N
C 0.145 0.185 3.69 4.69
D 0.015 0.021 0.38 0.53
E 0.050 BSC 1.27 BSC
F 0.040 0.70 1.02 1.78
C
G 0.100 BSC 2.54 BSC
J 0.008 0.015 0.20 0.38
K 0.115 0.135 2.92 3.43
K
L 0.300 BSC 7.62 BSC
SEATING M 0_ 10_ 0_ 10_
T PLANE N 0.015 0.040 0.39 1.01
E
G
16X D
0.005 (0.13) M T A
CASE 648C–04
ISSUE D
DIP PACKAGE
–A– NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI
C Y14.5M, 1982.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: INCH.
"
12 7 3. PLANE –X– AND PLANE –Y– SHOULD BE
ALIGNED WITHIN 0.0015”.
–Y–
–B– INCHES MILLIMETERS
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
A 0.618 0.638 15.70 16.21
1 6 B 0.240 0.260 6.10 6.60
C 0.127 0.133 3.23 3.38
–Y– –X– D 0.015 0.021 0.38 0.53
L 8 PL E 0.328 0.368 8.33 9.35
F 0.112 0.120 2.84 3.05
K 8 PL G 0.100 BSC 2.54 BSC
H 0.050 BSC 1.27 BSC
J 0.009 0.012 0.23 0.30
M H U J K 0.125 0.140 3.18 3.56
L 0.063 0.070 1.60 1.78
U D 6 PL S M 0.015 0.025 0.38 0.64
G 0.13 (0.005) M T A M B M N N 0.036 0.044 0.91 1.12
P 0.110 0.120 2.79 3.05
P S 0.025 0.035 0.64 0.89
U 0.088 0.108 2.24 2.74
E
F
–T–
CASE 456–06
ISSUE H
WB PACKAGE
Motorola Sensor Device Data 7
MMA1201P MMA2200W
Mfax is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty, representation or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application
or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages.
“Typical” parameters which may be provided in Motorola data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual
performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including “Typicals” must be validated for each customer application by customer’s
technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not designed,
intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other applications intended to support
or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury or death
may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and
hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses,
and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or
unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and
are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
How to reach us:
USA/EUROPE/Locations Not Listed: Motorola Literature Distribution; P.O. Box 5405, Denver, Colorado 80217.
1–303–675–2140 or 1–800–441–2447
JAPAN: Motorola Japan Ltd.; SPS, Technical Information Center, 3–20–1, Minami–Azabu. Minato–ku, Tokyo 106–8573 Japan.
81–3–3440–3569
ASIA/PACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; Silicon Harbour Centre, 2 Dai King Street, Tai Po Industrial Estate, Tai Po,
N.T., Hong Kong. 852–26668334
Customer Focus Center: 1–800–521–6274
Mfax: RMFAX0@email.sps.mot.com – TOUCHTONE 1–602–244–6609
Motorola Fax Back System – US & Canada ONLY 1–800–774–1848
– http://sps.motorola.com/mfax/
HOME PAGE: http://motorola.com/sps/
8 Motorola Sensor Device Data
◊ MMA1201P/D
You might also like
- j3c S Type Actuator Installation Andamp Operating ManualDocument10 pagesj3c S Type Actuator Installation Andamp Operating ManualPedro JacintoNo ratings yet
- PD42-1241 TMCL Firmware Manual Fw1.44 Rev1.01Document107 pagesPD42-1241 TMCL Firmware Manual Fw1.44 Rev1.01Deval PareekNo ratings yet
- MMA7361LDocument11 pagesMMA7361LfeliugabrielNo ratings yet
- Control de Flama Honeywell 264Document28 pagesControl de Flama Honeywell 264rubiodegoNo ratings yet
- RM7824A 24VDC Relay Module 65 0155Document20 pagesRM7824A 24VDC Relay Module 65 0155Control Cia LtdaNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument11 pagesDatasheetVictor TorresNo ratings yet
- Surface Mount Micromachined Accelerometer MMA2201D: Semiconductor Technical DataDocument9 pagesSurface Mount Micromachined Accelerometer MMA2201D: Semiconductor Technical DataRoberto MedinaNo ratings yet
- Catalogue TPSDocument64 pagesCatalogue TPSleonardovegaNo ratings yet
- 36350Document15 pages36350Testman ManNo ratings yet
- Ruiz Misely Ramos Arthur Diseño Implementacion Sistemas Monitoreo AnexosDocument664 pagesRuiz Misely Ramos Arthur Diseño Implementacion Sistemas Monitoreo Anexosvicjosh003778No ratings yet
- PD42-1270 Hardware Manual: Simplified Block DiagramDocument24 pagesPD42-1270 Hardware Manual: Simplified Block DiagramAhmad FarisNo ratings yet
- Fieldmaster User ManualDocument40 pagesFieldmaster User ManualEugenNo ratings yet
- Brainy24: External Control Panels 24 VDCDocument1 pageBrainy24: External Control Panels 24 VDCJulio Cesar Ramirez OlaveNo ratings yet
- Kap 06-4 Frequency Converter ACS 355 - 580Document28 pagesKap 06-4 Frequency Converter ACS 355 - 580MoisesNo ratings yet
- Rem615 Ansi - Manual PDFDocument58 pagesRem615 Ansi - Manual PDFAlexandre MorenoNo ratings yet
- ADT 1000 ING 2228 - B - AnDocument52 pagesADT 1000 ING 2228 - B - AnGladyz RiveraNo ratings yet
- Baker dx12 Static Motor AnalyzerDocument4 pagesBaker dx12 Static Motor AnalyzerRicardo AnastácioNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Supervisory Circuit ADM1232: Features Functional Block DiagramDocument12 pagesMicroprocessor Supervisory Circuit ADM1232: Features Functional Block Diagramjose luisNo ratings yet
- Tmcm-6213 Coe Firmware Manual: Simplified Block DiagramDocument116 pagesTmcm-6213 Coe Firmware Manual: Simplified Block DiagramMorten AndersenNo ratings yet
- EM-043 ENG - Visitor T30 M-DR - Technical Manual (216359-00-01)Document248 pagesEM-043 ENG - Visitor T30 M-DR - Technical Manual (216359-00-01)Byron Cuevas MendozaNo ratings yet
- Honeywell Burner ControllerDocument44 pagesHoneywell Burner Controllersblnt2008No ratings yet
- Seco-DC-Drives Catalog en-US Rev2005Document40 pagesSeco-DC-Drives Catalog en-US Rev2005milacronNo ratings yet
- Si720x Switch/Latch Hall Effect Magnetic Position Sensor Data SheetDocument32 pagesSi720x Switch/Latch Hall Effect Magnetic Position Sensor Data Sheetvlade naumovskiNo ratings yet
- Portable X-Ray System: AppearanceDocument2 pagesPortable X-Ray System: AppearanceTrần Thanh ViệnNo ratings yet
- Lm317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Feateeures 3 DescriptionDocument32 pagesLm317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Feateeures 3 DescriptiontheserviceNo ratings yet
- Two-Wire End-of-Line Programmable Hall-Effect Switch/Latch: Description Features and BenefitsDocument21 pagesTwo-Wire End-of-Line Programmable Hall-Effect Switch/Latch: Description Features and Benefitsmario230991No ratings yet
- TMCM-1231 Hardware Manual hw1.1 Rev1.02Document25 pagesTMCM-1231 Hardware Manual hw1.1 Rev1.02Ian MechuraNo ratings yet
- Controlink Display Module S7999Document12 pagesControlink Display Module S7999Daniel CaceresNo ratings yet
- Catalogue 8bt2 enDocument20 pagesCatalogue 8bt2 enPablo MarajNo ratings yet
- Domae Catalogue Jordan and IraqDocument32 pagesDomae Catalogue Jordan and Iraqgoyalp75No ratings yet
- Catalogue-Simoprime en PDFDocument16 pagesCatalogue-Simoprime en PDFhizbi7No ratings yet
- MAX17260Document33 pagesMAX17260123No ratings yet
- LM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument33 pagesLM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Features 3 DescriptionAlberto DanNo ratings yet
- LM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument32 pagesLM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Features 3 DescriptionCalon SuspendNo ratings yet
- LM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument32 pagesLM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Features 3 DescriptionIrham NurNo ratings yet
- LM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator (RevDocument33 pagesLM317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator (RevluisNo ratings yet
- LM 317Document31 pagesLM 317Ramiro MezaNo ratings yet
- Reliable Solid State Digital Control... : Type SSM Medium Voltage 2300 - 6900VDocument12 pagesReliable Solid State Digital Control... : Type SSM Medium Voltage 2300 - 6900VsudhakarraomNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument5 pagesDownloadVVan TanNo ratings yet
- Touchpoint Plus Wireless: Gas DetectionDocument4 pagesTouchpoint Plus Wireless: Gas DetectionNirwan Purwa LahardiNo ratings yet
- Designed For High PerformanceDocument8 pagesDesigned For High PerformanceSajeshKumarNo ratings yet
- ACS355-old 2009Document20 pagesACS355-old 2009Anmol GhagNo ratings yet
- Single Mode Family: Data Sheet 09/97Document12 pagesSingle Mode Family: Data Sheet 09/97Сергей КолосовNo ratings yet
- Manual EP200 enDocument42 pagesManual EP200 enJose AguirreNo ratings yet
- CB780/CB784 Relay Modules: FeaturesDocument36 pagesCB780/CB784 Relay Modules: Featuresszabo357No ratings yet
- Max17263 Single/Multi-Cell Fuel Gauge With Modelgauge M5 Ez and Integrated Led ControlDocument37 pagesMax17263 Single/Multi-Cell Fuel Gauge With Modelgauge M5 Ez and Integrated Led Control123No ratings yet
- Iris TgsDocument2 pagesIris Tgs김도희No ratings yet
- Premier International Series Leaflet - XPORT SALES - 2019Document2 pagesPremier International Series Leaflet - XPORT SALES - 2019Tayeb ElashhabNo ratings yet
- MODEL 1230: Ac Induction Motor ControllerDocument4 pagesMODEL 1230: Ac Induction Motor ControllerJorge MorenoNo ratings yet
- LM 2597Document50 pagesLM 2597satyendraNo ratings yet
- Guia de Producto Rev615 - AbbDocument60 pagesGuia de Producto Rev615 - Abbper47No ratings yet
- Lm317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Feateeures 3 DescriptionDocument32 pagesLm317 3-Terminal Adjustable Regulator: 1 Feateeures 3 DescriptiontheserviceNo ratings yet
- 2g/ 4g/ 8g Three Axis Low-G Digital Output Accelerometer: MMA7455LDocument27 pages2g/ 4g/ 8g Three Axis Low-G Digital Output Accelerometer: MMA7455LERIKANo ratings yet
- lm53625 q1 PDFDocument56 pageslm53625 q1 PDFPrabhansh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Model 19035 Data SheetDocument4 pagesModel 19035 Data SheetThiyagarajan RNo ratings yet
- 2.1 RCM-RDM Series - EN Ed1 03-16Document4 pages2.1 RCM-RDM Series - EN Ed1 03-16metrofireNo ratings yet
- LMP91300 Industrial Inductive Proximity Sensor AFE: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument44 pagesLMP91300 Industrial Inductive Proximity Sensor AFE: 1 Features 3 DescriptionYovi Herlin SaputraNo ratings yet
- Signet CR 5900 Data PDFDocument2 pagesSignet CR 5900 Data PDFIker BasqueAdventureNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionFrom Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Lecture 2-Introduction SenrorDocument15 pagesLecture 2-Introduction SenrorMinh QuốcNo ratings yet
- Home Work - BonusDocument3 pagesHome Work - BonusMinh QuốcNo ratings yet
- 33 Response of First Order Systems PDFDocument18 pages33 Response of First Order Systems PDFjamalNo ratings yet
- Manuscript OwnedversionDocument41 pagesManuscript OwnedversionMinh QuốcNo ratings yet
- Medin BonnetDocument5 pagesMedin BonnetMinh QuốcNo ratings yet
- TCS.B 200 RT InstructionsDocument2 pagesTCS.B 200 RT InstructionsAndres España0% (1)
- Medin Company Brochure EN Rev00Document16 pagesMedin Company Brochure EN Rev00vikas vermaNo ratings yet
- Adxl50 PDFDocument17 pagesAdxl50 PDFUni NgoNo ratings yet
- Wilaflow Legacy/G2 Ncpap AccessoriesDocument2 pagesWilaflow Legacy/G2 Ncpap AccessoriesMinh QuốcNo ratings yet
- WU-NEAT: A Clinically Validated, Open-Source MATLAB Toolbox For Limited-Channel Neonatal EEG AnalysisDocument6 pagesWU-NEAT: A Clinically Validated, Open-Source MATLAB Toolbox For Limited-Channel Neonatal EEG AnalysisMinh QuốcNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Temperature Sensor PT100 in 2-, 3-, and 4-Wire Technology Type: PT100... PT103... and PT104..Document3 pagesData Sheet Temperature Sensor PT100 in 2-, 3-, and 4-Wire Technology Type: PT100... PT103... and PT104..Minh QuốcNo ratings yet
- 002 Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring 3a - ACOG Bulletin 106 PDFDocument11 pages002 Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring 3a - ACOG Bulletin 106 PDFale_fearNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Torque Wrenches - SaltusDocument20 pagesMechanical Torque Wrenches - SaltusEnbotic AutomatykaNo ratings yet
- 4pro 6001Document1 page4pro 6001Mariano HrodNo ratings yet
- SensorDocument3 pagesSensorANo ratings yet
- Electronic Refrigeration Diagnostics: Training and Technical Support Team 07-PPT-RE-01 (Revised Jan 2009)Document40 pagesElectronic Refrigeration Diagnostics: Training and Technical Support Team 07-PPT-RE-01 (Revised Jan 2009)Khalid FarhatNo ratings yet
- Automatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmDocument47 pagesAutomatic Night Lamp With Morning Alarmbalajig47375% (8)
- ABB CT and VT Application Guide Ed3Document128 pagesABB CT and VT Application Guide Ed3Andrej Černe100% (4)
- Eppendorf 5804R Centrifuge ManualDocument42 pagesEppendorf 5804R Centrifuge ManualUma Mahesh100% (1)
- BOQ - KURIGRAM-ELECTRIC fITTINGDocument8 pagesBOQ - KURIGRAM-ELECTRIC fITTINGlse furnitureNo ratings yet
- A Practical Activity Report Submitted: For Engineering Design Project - II (UTA-014) by Akash Roll No - 101703634Document7 pagesA Practical Activity Report Submitted: For Engineering Design Project - II (UTA-014) by Akash Roll No - 101703634AKASHNo ratings yet
- 에어컨회사 회사 소개서Document22 pages에어컨회사 회사 소개서박인호No ratings yet
- Slayer ExciterDocument2 pagesSlayer ExciterSoumyajyoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Siemens Jxd6-A AjusteDocument1 pageSiemens Jxd6-A AjusteFABIAN PRUNEDANo ratings yet
- JX Instruction Manual EN 2017-06-28 PDFDocument2 pagesJX Instruction Manual EN 2017-06-28 PDFΝικόλας ΧιονάςNo ratings yet
- On Electrostatic DischargeDocument11 pagesOn Electrostatic DischargeSHIVANI PHADTARENo ratings yet
- Department of Technical EducationDocument21 pagesDepartment of Technical EducationVijaya BhaskerNo ratings yet
- TLEDocument28 pagesTLEIsrael SapnuNo ratings yet
- Platea Uno, T-740Document12 pagesPlatea Uno, T-740arsNo ratings yet
- MPPT Control of Standalone - PV System With Battery As An Energy Storage ElementDocument19 pagesMPPT Control of Standalone - PV System With Battery As An Energy Storage Elementpriyanka rawatNo ratings yet
- AMPHENOL Series 3Document36 pagesAMPHENOL Series 3PTCNo ratings yet
- Chilled Exposed Fcu TopaireDocument2 pagesChilled Exposed Fcu TopaireBuscat BatuscNo ratings yet
- EC105Document19 pagesEC105api-3853441No ratings yet
- XDDocument509 pagesXDsleepyNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric PM200 PDFDocument180 pagesSchneider Electric PM200 PDFCarlos LopezNo ratings yet
- Datasheet de P5Document5 pagesDatasheet de P5luisNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual: Group 30 ADocument70 pagesWorkshop Manual: Group 30 APer Østbø100% (1)
- Arenavision Mvf403 323012 Ffs AenDocument6 pagesArenavision Mvf403 323012 Ffs AenJorge Ricardo Aparcana MedinaNo ratings yet
- Reliability: Gerard's ColumnsDocument1 pageReliability: Gerard's ColumnsAmanda GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Katalog LBSkit & Disconnector SchneiderDocument32 pagesKatalog LBSkit & Disconnector SchneiderDicky FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Harmony Electromechanical Relays Catalog 2020Document45 pagesHarmony Electromechanical Relays Catalog 2020Gustavo PérezNo ratings yet
- Extreme Temperature, Flexible Cable Assembly: Model 3076ADocument3 pagesExtreme Temperature, Flexible Cable Assembly: Model 3076Ashibu TNo ratings yet