Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GUADIZ - Concept Map Med Coro
GUADIZ - Concept Map Med Coro
Uploaded by
YESSAMIN GUADIZOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GUADIZ - Concept Map Med Coro
GUADIZ - Concept Map Med Coro
Uploaded by
YESSAMIN GUADIZCopyright:
Available Formats
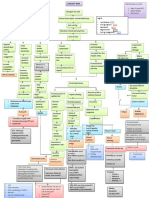
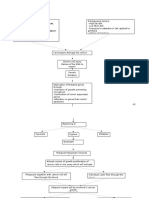
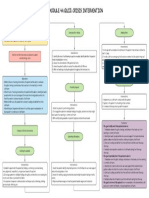
GUADIZ, Yessamin T.
Concept Map on
BSN 3 F 1 Polycystic hepatic and renal disease, bilateral
Non-modifiable risk factors:
1) Genetics Modifiable risk factors:
2) Gender (Female) 1) Stressful work environment
3) Advancing age (Above 50 y/o) (Ex- OFW)
4) Multiple pregnancies
Polycystic hepatic and renal
disease, bilateral
can occur concomitantly
Hepatic Renal
Polycystin-1 and polycystin-2 protein
Genetic ductal plate malformation and
mutations, escalated by age, exposure to
abnormal primary cilia
estrogen, and modifiable risks
Mutations and mechanical barriers
result in dysfunctional Ca2+ channels on
epithelial cells
Abnormal Ca2+ entry disrupts
intracellular Ca2+ signalling
Abnormally expandable
Expansive cell proliferation Increased fluid secretion
basement membranes
Cyst formation in the organ lining
(sacs of flattened epitheliumfilled with fluid,
replacing normal parenchyma with
dysfunctional tissue)
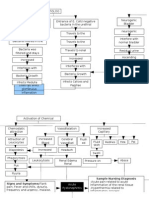
SUSPECTED
In the GIT: In the liver: CT Thorax + Whole abdomen In the kidneys:
Upper and lower tract Lobes Findings: Hypodense non-enhancing cysts All segments of the nephron
develop cysts develop cysts on both liver and kidneys bilateral develop cysts
Poor renal perfusion causing Damaged tubules leak protein and
1) UGIS (Upper Enlargement of liver causing Compression of renal
Liver damage accumulation of urine within Over stretching of renal capsule minerals into filtrate and precipitation of
gastrointestinal series): To Compression of other organs vasculature
cysts CoOxalate stones within cysts
follow
2) Chest X-Ray
1) High SGOT
and SGPT, 4.61 Bacteria accumulation in the Decreased glomerular Urinalysis:
Activation of nociceptors
and 42.5 units/L, static urine perfusion High HPF
respectively 1) Abdominal distention
(crystals)
2) High Bilirubin- 2) Early satiety
0.21 umol/ L 3) Gastro-esophageal dysfunction
(Frequent sensations of nausea
4) Poor appetite Activation of RAAS to increase
Infection
perfusion
Flank and scapular pain
12 lead ECG
1) Lactulose
Hypertension
2) D5LRS infusion
Fever and pain
Risk for imbalanced nutrition: 1) Ceftriaxone
Less than body requirements 2) Paracetamol
related to gastrointestinal
compression Chronic pain related to 1) Clonidine
renal tissue trauma 2) Amlodipine
1) High blood pressure
highest recorded: 170/100
2) Limb edema
1) Maintain weight within normal 3) Dizziness
1) Exhibits proper management of
BMI
pain using pharmacologic and non-
2) Exhibit healthy eating habits
pharmacologic measures
2) Participates in ADL's and
recreational activities
Decreased cardiac output 1) Monitor blood pressure and other
related to increased vascular vital signs. More importantly,
1) Monitor daily nutritional status before and after administration of
2) Assess ability to take take in food orally 1) Assess and document PQRST of pain. Advise resistance
patient to keep a journal on this antihypertensive drugs
3) If patient lacks strength, schedule rest 2) Position the patient comfortably,
periods before meals and open packages 2) Maintain the patient’s use of non-pharmacological
methods to control pain, such as distraction, imagery, either supine, sitting, or side
and cut up food for patient lying as per preference
4) Include patient in meal planning relaxation, massage, and heat and cold application
3) Educate the patient regarding long-term use of 1) Patient will be able to maintain 3) Educate patient on relaxation
5) Educate and encourage the family to cook adequate cardiac output techniques such as deep breathing
healthy and satiating foods for the patient medications and its possible implications
2) Manage periods of high blood exercises and diversional activities
pressure readings
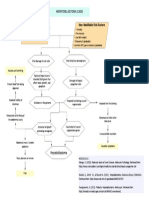
Unroofing of hepatic and renal cyst bilateral
1) Tramadol
2) Oxycodone
Pain on the incision
site rated as 5/10, sharp, 1) Decreased lower GI motility
non-radiating 2) Nausea and vomiting
Acute pain related to
surgical incision
1) Suppository dulcolax
2) Omeprazaole
1) Reports of relieved pain 3) Metronidazole
2) Appears relaxed and is 4) Insertion of NGT for
able to sleep/ rest gastric aspiration
appropriately
1) Assess PQRST of pain
2) Maintain on comfortable position and assist
with ADL's
3) Administer pain medications as per doctor's
order
4) Educate patient regarding splinting
5) Educate on relaxation techniques such as
DBE and positioning
You might also like
- Concept Map Liver CirrhosisssDocument2 pagesConcept Map Liver CirrhosisssAsniah Hadjiadatu Abdullah92% (12)
- Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology PDFJenievieve MerzaNo ratings yet
- Clin Path Lab 6 UrinalysisDocument5 pagesClin Path Lab 6 Urinalysisapi-3743217100% (6)
- Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer: Unkno Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancer: Unkno Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsKevin Ercia100% (1)
- Pathology PDFDocument28 pagesPathology PDFRoman PanditNo ratings yet
- Pathophy of Appendicitis (Or) by Mizzy BaylonDocument2 pagesPathophy of Appendicitis (Or) by Mizzy BaylonmizzybaylonNo ratings yet
- Treatment Guidelines PDFDocument293 pagesTreatment Guidelines PDFgautambobNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of AppendicitisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of AppendicitisArvin Ian Penaflor100% (3)
- R.A. 6675Document91 pagesR.A. 6675Donzzkie Don50% (2)
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- grp52 UTI PathoDocument3 pagesgrp52 UTI Pathokcdgrvn100% (3)
- PathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerDocument2 pagesPathoPhysiology of Cervical CancerJie BandelariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43: Antiulcer Drugs Mccuistion: Pharmacology: A Patient-Centered Nursing Process Approach, 10Th EditionDocument95 pagesChapter 43: Antiulcer Drugs Mccuistion: Pharmacology: A Patient-Centered Nursing Process Approach, 10Th Editionmichael patterson100% (1)
- Small Volume Parenterals by MVRR2Document37 pagesSmall Volume Parenterals by MVRR2mvrr9100% (3)
- Prostate Cancer Patho (Patient Based) by Francis OliverosDocument2 pagesProstate Cancer Patho (Patient Based) by Francis Oliverosfrancis00090100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of SepsisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Sepsisfranzent77100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Gastric Cancer Precipitating Factors: - Predisposing FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gastric Cancer Precipitating Factors: - Predisposing FactorsJu Lie AnnNo ratings yet
- Ob - Pathophysiology of Aub Endometrial Polypsversion2Document4 pagesOb - Pathophysiology of Aub Endometrial Polypsversion2TRIXY MAE HORTILLANONo ratings yet
- Marjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsDocument8 pagesMarjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsMarjorie CarganillaNo ratings yet
- Borang Diabetes Clinical AuditDocument2 pagesBorang Diabetes Clinical AuditHafizzah Mohd FirdausNo ratings yet
- GerdDocument9 pagesGerdPriyaNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMaDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF OSTEOSARCOMakyawNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cancer, The NEw PathophyDocument3 pagesOvarian Cancer, The NEw PathophylieselannjacobNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CholelithiasisLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- Nursing DX: Acute Pain Related To Surgical Manipulation (Laminectomy) As Manifested by Reports of Pain On The Lumbar Area Rated As 7/10Document1 pageNursing DX: Acute Pain Related To Surgical Manipulation (Laminectomy) As Manifested by Reports of Pain On The Lumbar Area Rated As 7/10YESSAMIN GUADIZ100% (2)
- Kidney Development, Disease, Repair and RegenerationFrom EverandKidney Development, Disease, Repair and RegenerationMelissa Helen LittleRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Pathophysiology of Colon CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Colon CancerJaymica Laggui DacquilNo ratings yet
- Urogenital Imaging: A Problem-Oriented ApproachFrom EverandUrogenital Imaging: A Problem-Oriented ApproachS. MorcosRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Dna Rep Error TMCDocument3 pagesDna Rep Error TMCKatrina Jhane MercadoNo ratings yet
- V. B.1. Pathopysiology DiagramDocument4 pagesV. B.1. Pathopysiology DiagrambezaleeljonelNo ratings yet
- Pathoo Auq NaDocument5 pagesPathoo Auq NaKatrina Jhane MercadoNo ratings yet
- Dna Rep Error Thyroid AdrenalDocument5 pagesDna Rep Error Thyroid AdrenalKatrina Jhane MercadoNo ratings yet
- Malignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)Document4 pagesMalignant Neoplasm (Ovarian Cancer)nursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Patofosiologi Gangguan GinjalDocument43 pagesPatofosiologi Gangguan GinjalKazami KurootsukiNo ratings yet
- EA Cocept Map2Document2 pagesEA Cocept Map2Katie LopezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology, Bone CancerDocument7 pagesPathophysiology, Bone CancerMaria Grace Raquel Ormeneta100% (1)
- Signs and Symptoms:Flank Sample Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PyelonephritisDocument3 pagesSigns and Symptoms:Flank Sample Nursing Diagnosis: Acute PyelonephritisjohndelfinmNo ratings yet
- Finals Colon CancerDocument38 pagesFinals Colon CancerKenji ToleroNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidney Disease PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPolycystic Kidney Disease Pathophysiologyacey torreNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Obstruction Chronic Renal Failure PDF Kidney Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageHypertension Obstruction Chronic Renal Failure PDF Kidney Endocrine Systemdancing with melancholyNo ratings yet
- How To Avoid Fluid Overload?: Konika Xvii Jogyakarta, 11 Agustus 2017Document46 pagesHow To Avoid Fluid Overload?: Konika Xvii Jogyakarta, 11 Agustus 2017LeksmanaHidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Diet Stress Hereditary AgeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: Diet Stress Hereditary AgeChucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chronic Nephropathy Diabetic Glomerulonephritis Chronic PyelonephritisDocument1 pageChronic Nephropathy Diabetic Glomerulonephritis Chronic Pyelonephritisssiton886No ratings yet
- CKD PathoDocument1 pageCKD PathoMarcieNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Hepatoblastoma CaseDocument1 pageNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Hepatoblastoma CaseALYSSA AGATHA FELIZARDONo ratings yet
- Fibrosis of The Liver - Liver and Gallbladder Disorders - MSD Manual Consumer VersionDocument2 pagesFibrosis of The Liver - Liver and Gallbladder Disorders - MSD Manual Consumer VersionAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- Schisto Patho SLHDocument5 pagesSchisto Patho SLHJosh IbalioNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Hepatic Liver CirrhosisDocument11 pagesGroup 2 - Hepatic Liver Cirrhosismelba040510No ratings yet
- Non - Glomerular Disease - Dr. LuDocument3 pagesNon - Glomerular Disease - Dr. LuMACATANGAY, GAELLE LISETTENo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection & PyelonephritisDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection & PyelonephritisUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of cholangiocarcinomaJAYCERDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of cholangiocarcinomaJAYCERirish_estrellaNo ratings yet
- Not Activity No. 7Document12 pagesNot Activity No. 7Patricia Marie Laman YadaoNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYof Biliary CirrhosisDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYof Biliary CirrhosisChristine AllonarNo ratings yet
- Specific EditedDocument12 pagesSpecific EditedLarabelle Avila CoralesNo ratings yet
- Modifiable Risk Factors: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:: IV. Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument5 pagesModifiable Risk Factors: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:: IV. Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4Sweetie PieNo ratings yet
- Cholestatic Liver DiseaseDocument35 pagesCholestatic Liver DiseasealnyhilwanyNo ratings yet
- Patho For Lung CancerDocument3 pagesPatho For Lung Cancermycah_myrabellNo ratings yet
- Bilateral: Etiology Manifestations Diagnosis Management, Prognosis, Prevention ComplicationsDocument8 pagesBilateral: Etiology Manifestations Diagnosis Management, Prognosis, Prevention ComplicationsJayesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument3 pagesDrug Study Name of Drug Dosage, Route and Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityGilianne JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis CurrentDocument18 pagesNoninvasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis CurrentValentina IorgaNo ratings yet
- 05 Micro Cell Structures Virulence Factors and ToxinsDocument12 pages05 Micro Cell Structures Virulence Factors and ToxinsNicole IrineoooNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDisorders of The Digestive SystemɪQ ʟᴇᴠᴇʟ 148ˊˎ-No ratings yet
- Lectura 10Document14 pagesLectura 10Alexandra EliasNo ratings yet
- Chronic - Pancreatitis LectureDocument6 pagesChronic - Pancreatitis LectureKiran ChavanNo ratings yet
- Congenital and Development Anomalies of The KidneyDocument4 pagesCongenital and Development Anomalies of The KidneyEMILY N CRUZ-VARGASNo ratings yet
- Guadiz Mod4a EvaluateDocument1 pageGuadiz Mod4a EvaluateYESSAMIN GUADIZNo ratings yet
- GUADIZ INFOGRAPHNeuroDocument1 pageGUADIZ INFOGRAPHNeuroYESSAMIN GUADIZNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube ThoracostomyDocument1 pageChest Tube ThoracostomyYESSAMIN GUADIZNo ratings yet
- Yguadiz TeachingDocument1 pageYguadiz TeachingYESSAMIN GUADIZNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube ThoracostomyDocument1 pageChest Tube ThoracostomyYESSAMIN GUADIZNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPYESSAMIN GUADIZNo ratings yet
- FdarDocument2 pagesFdarYESSAMIN GUADIZNo ratings yet
- Pharma FinalsDocument10 pagesPharma FinalslumpiaNo ratings yet
- Module # 5 Pharmacology NursingDocument45 pagesModule # 5 Pharmacology Nursingannyeong_123No ratings yet
- HIV Infection - Opportunistic InfectionsDocument21 pagesHIV Infection - Opportunistic InfectionszawadiNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Phytochemical Screening For Antioxidant Activity of Catharanthus Roseus L. (Whole Plant)Document7 pagesPersuasive Phytochemical Screening For Antioxidant Activity of Catharanthus Roseus L. (Whole Plant)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug ReactionDocument7 pagesAdverse Drug ReactionufahadNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Diabetes MelitusDocument7 pagesJurnal Diabetes MelitusNova RosalinaNo ratings yet
- Profile of Tirzepatide in The Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Design, Development, and Place in TherapyDocument13 pagesProfile of Tirzepatide in The Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Design, Development, and Place in TherapyDiego Andres Garcia RochaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of The Specialty of Gerontologic Nursing - : 1961 Formation of A Specialty Group For Geriatric NursesDocument5 pagesFoundations of The Specialty of Gerontologic Nursing - : 1961 Formation of A Specialty Group For Geriatric NursesDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pearls in NephrologyDocument5 pagesClinical Pearls in NephrologyEdmilson R. LimaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial AgentDocument46 pagesAntimicrobial Agentسامر الرفاعيNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticDocument3 pagesDrugs Mechanism Side Effect DiureticRebecca MarshallNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Safety Profile of Homoeopathic MotheDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Safety Profile of Homoeopathic MotheRaveendra MungaraNo ratings yet
- Elattar 2020Document6 pagesElattar 2020Thaís SagratzhiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument16 pagesCardiovascular DisordersTanwir HoussaynNo ratings yet
- Clarification of Anticholinergic Effects of Quetiapine.Document5 pagesClarification of Anticholinergic Effects of Quetiapine.Nath miaounNo ratings yet
- Pain JuniDocument36 pagesPain JuniNi Putu Ari FebriantariNo ratings yet
- Abstractbook Linz 2018 EUSAAT 2018 e VersionDocument294 pagesAbstractbook Linz 2018 EUSAAT 2018 e VersiondrfurtadoNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytics - Screening MethodsssDocument37 pagesAnxiolytics - Screening MethodsssKarthiNo ratings yet
- AntiagreganteDocument19 pagesAntiagregantecNo ratings yet
- A Glance On GSK HistoryDocument13 pagesA Glance On GSK HistoryShohaib Khan TanoliNo ratings yet
- Seizure and Anticonvulsant Medications GridDocument1 pageSeizure and Anticonvulsant Medications Gridpiyush RautNo ratings yet
- Opportunistic Infections PreventionDocument34 pagesOpportunistic Infections PreventionEvelyn LimNo ratings yet
- Terapi Definitif Keracunan ObatDocument74 pagesTerapi Definitif Keracunan ObatonyNo ratings yet
- Other Lab FontsDocument2 pagesOther Lab FontsFITROH WIDIANTONo ratings yet