Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MODULE 4: Developmental Stages in Middle and Late Adolescence
Uploaded by
Ness Acelle CruzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 4: Developmental Stages in Middle and Late Adolescence
Uploaded by
Ness Acelle CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
Universidad de Sta.
Isabel | Basic Education Department
MODULE 4: Developmental Stages in Middle and
Late Adolescence
I. OVERVIEW
“Every person has a limitless room for growth.” – Abraham Maslow
As an individual, you need to see yourself as competent and autonomous. Desiring to
become everything that you are capable of becoming, it involves being in touch with your
feelings and experiencing a blast of life journeys up to the extent of self-fulfilment, hence,
self-actualization.
This module is about the developmental stages in middle and late adolescence. You will
encounter Erik Erikson’s Psychosocial Development and know that internal conflicts
within oneself is normal. As you go on with this module, you will be able to distinguish
the developmental tasks and skills of Filipinos adolescents.
II. TIME FRAME
You are given 5 days (September 20- 25, 2021) to complete this module. Every Friday is
a PRIME day. If you encounter difficulty along the way, do not hesitate to message me
through my email mpabico@usi.edu.ph or call/text me via my messenger account
Marga Garcia Pabico.
III. STANDARDS
A. CONTENT STANDARD
The learner demonstrates understanding of the skills and tasks appropriate for middle
and late adolescence, and preparatory to early adulthood.
B. PERFORMANCE STANDARD
The learner is able to make a list of ways to become responsible adolescents
prepared for adult life.
C. VALUE STANDARD
The learner is able to value his/her own responsibility for self-growth.
IV. LEARNING TARGETS
At the end of this module, you should be able to say, “I can…”
1. Classify various developmental tasks according to developmental stage.
2. Evaluate one’s development in comparison with persons of the same age group.
3. List ways to become a responsible adolescent prepared for adult life.
Module 4 | Personal Development | First Quarter Page | 1
Universidad de Sta. Isabel | Basic Education Department
V. INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN
Day 1-2
1. Accomplish Worksheet 1 found on page 5 of this module.
2. Read Chapter 4, Developmental Stages in Middle and Late Adolescence on pages
35-45 and answer the following questions provided on page 4 of this module.
Day 3
1. Read the attachment found on the 3rd and 4th page of this module entitled Erikson’s
Eight Stages of Psychosocial Development. List/highlight the important concepts
that you’ve learned from your readings.
Day 4
1. Accomplish Worksheet 4 found on page 7-8 of this module.
REFERENCES
1. Santos, R.R. (2019). Personal development (2nd ed.). Manila: Rex Book Store, Inc.
2. Ramos, M.L. (2017). Personal development: A journey to self-awakening. Quezon:
C&E Publishing, Inc.
3. Serrano, A.C (2016). Personal Development. Manila: Unlimited Books Library
Services & Publishing Inc.
4. Corpuz, B.B. et al (2010). Child and adolescent development. Quezon: Lorimar
Publishing Inc.
Module 4 | Personal Development | First Quarter Page | 2
Universidad de Sta. Isabel | Basic Education Department
Attachment
ERIKSON’S EIGHT STAGES OF PSYCHOSOCIAL DEVELOPMENT
Erik Homburger Erikson (born Erik Salomonsen; 15 June 1902 – 12 May 1994) was a German-
American developmental psychologist and psychoanalyst known for his theory on psychological
development of human beings. He may be most famous for coining the phrase
identity/psychosocial crisis.
The term psychosocial is derived from two source words namely psychological (relating to
mind, brain, personality, etc) and social (external relationships and environment). The term is
extended to bio psychosocial, in which bio means life.
The theory is a basis for broad or complex discussion and analysis of personality and
behaviour, and also for understanding and for facilitating personal development.
Each stage involves a psychosocial crisis of two opposing emotional forces referred as contrary
dispositions. Each crisis relates to corresponding life stage. Erikson used the words syntonic for
the first listed positive disposition in each crisis and dystonic for the second listed negative
disposition. To signify the opposing or conflicting relationship between each pair of forces or
dispositions, Erikson connected them with the word versus.
If a stage is managed well, we carry a certain virtue or psychosocial strength which will help us
through the rest of the stages of our lives. Successfully passing through each crisis involves
achieving a healthy ratio or balance between the two opposing dispositions that represent each
crisis.
On the other hand, if we don’t do so well, we may develop maladaptation’s and malignancies,
as well as endanger our future development. A malignancy involves too little of the positive and
too much of the negative aspect of the task. A maladaptation involves too much of the positive
and too little of the negative.
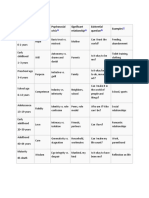
Stage Psychosocial Virtue Maladaptation Malignancy Key
Module 4 | Personal Development | First Quarter Page | 3
Universidad de Sta. Isabel | Basic Education Department
Crisis Question
Trust vs. Hope Sensory Withdrawal Is my world
Infancy
Mistrust maladjustment (depression, safe?
(Birth-18
(overly trusting, paranoia and
months)
even gullible) possibly
psychosis)
Early Autonomy vs. Will Impulsiveness Compulsiveness Can I do
Childhood Shame and things by
(18 months Doubt myself or
to 3 years) need I always
rely on
others?
Late Initiative vs. Courage Ruthlessness Inhibition Am I good or
Childhood/ Guilt bad?
Play Age
(3 to 5
years)
School Age Industry vs. Competenc Narrow Inertia (includes How can I be
(6 to 12 Inferiority y virtuosity those who suffer good?
years) inferiority
complex)
Adolescenc Identity vs. Fidelity Fanaticism Repudiation Who am I?
e Role and where
(12 to 20 Confusion am I going?
years)
Young Intimacy vs. Love Promiscuity Exclusion Am I loved
Adulthood Isolation and wanted?
(20 to 25
years)
Middle Generativity Care Overextension Rejectivity Will I provide
Adulthood vs. Stagnation something of
(25 to 65 real value?
years)
Late Integrity vs. Wisdom Presumption Disdain Have I lived a
Adulthood Despair full life?
(65 years to
death)
Module 4 | Personal Development | First Quarter Page | 4
Universidad de Sta. Isabel | Basic Education Department
Name: ___________________________________________ Section:
_____________________
Worksheet 1.
INSTRUCTION: Make a collage out of your pictures from infancy, babyhood, childhood and
adolescence. Describe how you changed overtime. What changes did you observed specifically
on:
a. Your body
b. Your feelings and emotions
c. Your socialization with other people
d. Your beliefs, thoughts and cognition
e. Your spiritual core values/beliefs
Module 4 | Personal Development | First Quarter Page | 5
Universidad de Sta. Isabel | Basic Education Department
Name: ___________________________________________ Section: _____________________
Worksheet 2.
Instruction: Refer to your Personal Development textbook. Read Chapter 4, Developmental Stages
in Middle and Late Adolescence on pages 35-45 and answer the following questions.
1. Examine your thoughts and behaviour and explain how these are affected by the changes
happening to your physical body and to your brain development.
2. Which developmental task and skill do you want to develop for yourself? How will you
develop them?
3. What other factors, aside from those that were discussed, do you think influence or
determine self-identity or self-concept?
Module 4 | Personal Development | First Quarter Page | 6
Universidad de Sta. Isabel | Basic Education Department
Name: ___________________________________________ Section: _____________________
Worksheet 3.
On Becoming a Responsible Adolescent
Being an adolescent isn’t easy. Adolescents can be put under enormous amounts of stress in
school, at home, and with friends, and the expectation to be perfect can be crippling. Luckily,
adolescents who want to be responsible can find lots of help in different places. Being a
responsible adolescent is all about finding who you are and following a couple of simple rules. On
the space provided, write a journal on how to become a responsible adolescent in preparation for
your adult life. Be guided with the rubrics provided.
Module 4 | Personal Development | First Quarter Page | 7
Universidad de Sta. Isabel | Basic Education Department
CRITERIA EXEMPLARY PROFICIENT NEEDS POOR
4 3 IMPROVEMENT 1
2
Organization Information was Information was Information was Information was
presented in a presented in a presented in a not presented in a
logical, interesting, logical, manner which logical, interesting
creative and straightforward does not or creative
engaging sequence which adequately convey sequence. Does
sequence which conveys the the information in a not convey the
conveys the meaning in a manner the reader information in a
meaning in a manner the reader can completely manner the reader
manner the reader can understand. understand. can understand.
can understand.
Content Demonstrated a Demonstrated a Not completely Lack of
knowledge depth firm grasp of the familiar or understanding of
understanding of content. Ability to comfortable with content. Unable to
the content and answer basic content. Limited answer basic
ability to provide questions. ability to answer questions.
explanations and basic questions.
elaborate on
concept/issues.
Personal Journal shows Journal shows Journal shows Journal shows
Connection detailed personal clear personal somewhat clear vague personal
experiences with experiences with personal experiences with
the topic. the topic. experiences with the topic.
the topic.
Grammar and Journal is highly Journal is polished; Journal is Inadequate
Mechanics polished; no maximum of one adequate; discussion; more
grammar or grammar or maximum of two than two spelling
spelling errors. spelling error. grammar or or grammar errors.
spelling errors.
Module 4 | Personal Development | First Quarter Page | 8
You might also like
- Peer Influence and Students' Motivation of Senior High School Students in Jose Maria CollegeDocument42 pagesPeer Influence and Students' Motivation of Senior High School Students in Jose Maria CollegeAngelline Aranas Omandam100% (1)
- Erik Erikson's Stages of Personality DevelopmentDocument22 pagesErik Erikson's Stages of Personality DevelopmentCarl Collado100% (1)
- Erik Erikson's: Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument44 pagesErik Erikson's: Stages of Psychosocial Developmentbea locsinNo ratings yet
- Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of DevelopmentDocument4 pagesErikson's Psychosocial Stages of DevelopmentJerome ReyNo ratings yet
- PD Lesson 3 Developmental Stages in Middle and Late AdolescenceDocument31 pagesPD Lesson 3 Developmental Stages in Middle and Late AdolescenceEL Fuentes100% (2)
- Infancy: Trust vs. Mistrust (0 To 1 Year)Document5 pagesInfancy: Trust vs. Mistrust (0 To 1 Year)karyl lynNo ratings yet
- Erickson's Theory PDFDocument19 pagesErickson's Theory PDFNatasha ShangeNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument68 pagesPsychosocial DevelopmentDonita BinayNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Developmental TasksDocument8 pagesAdolescent Developmental TasksCharles PabalateNo ratings yet
- Erik Erikson's Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument35 pagesErik Erikson's Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentMa. Rochelle CabralesNo ratings yet
- Chapter I FactorsDocument39 pagesChapter I FactorsElaine DaquilNo ratings yet
- English 9 2st Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesEnglish 9 2st Quarter ExamAngelique Buned SerranoNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial TheoryDocument30 pagesPsychosocial TheoryChing MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Rashika Maithani ResearchDocument50 pagesRashika Maithani Researchdeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- IELTS Speaking Vocabulary BookletDocument18 pagesIELTS Speaking Vocabulary Bookletnica100% (3)
- Masculinity UNESCODocument133 pagesMasculinity UNESCOapi-3827549No ratings yet
- Erik Erikson'S (8 SPD) 8 Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument2 pagesErik Erikson'S (8 SPD) 8 Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentCath Domingo - LacisteNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Development PrinciplesDocument5 pagesChild and Adolescent Development PrinciplesCiara Janine Meregildo100% (3)
- Personal Development Lesson 2Document54 pagesPersonal Development Lesson 2Ysay FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Approximate Age Virtues Psychosocial Crisis Significant Relationship Existential ExamplesDocument4 pagesApproximate Age Virtues Psychosocial Crisis Significant Relationship Existential ExamplesKim SanchezNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Erikson's Psycho-Social Theory of Development (Study Guide)Document4 pages3.3 Erikson's Psycho-Social Theory of Development (Study Guide)Kathleen NicoleNo ratings yet
- Growth Theories of Erikson and KohlbergDocument6 pagesGrowth Theories of Erikson and KohlbergPhie-phie elexNo ratings yet
- Developmental Tasks and Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument13 pagesDevelopmental Tasks and Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentJhade RelletaNo ratings yet
- Erik Eriksons Stages of Psychosocial Development 2795740Document11 pagesErik Eriksons Stages of Psychosocial Development 2795740Godwin EzekielNo ratings yet
- Developmental Stages of Middle and Late AdolescentsDocument7 pagesDevelopmental Stages of Middle and Late AdolescentsArianna Angelica C. GrantNo ratings yet
- 2020 Eric Erickson Psychoanalysis TheoryDocument29 pages2020 Eric Erickson Psychoanalysis TheoryHarley Justiniani Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ADT Lecture - Social and Emotional Development (Slides)Document65 pagesADT Lecture - Social and Emotional Development (Slides)sahil.7inNo ratings yet
- Stages of Development & Developmental TasksDocument2 pagesStages of Development & Developmental TasksWindy KimNo ratings yet
- Chapters-6-7-EDFLCTDocument27 pagesChapters-6-7-EDFLCTjnpolines.chmsuNo ratings yet
- DEBASHREE - SINHAERICKSON2021 02 18eriksonDocument3 pagesDEBASHREE - SINHAERICKSON2021 02 18eriksonAgung SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Physical Self: Astro Dominic Nituda Lemuel Ben Broqueza Camille Joy D. AnsusDocument10 pagesPhysical Self: Astro Dominic Nituda Lemuel Ben Broqueza Camille Joy D. AnsusJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- Psychological Perspectives on Self DevelopmentDocument9 pagesPsychological Perspectives on Self DevelopmentJohn MichaelNo ratings yet
- Psycho Social Theory EriksonDocument2 pagesPsycho Social Theory Eriksonapi-38378970% (1)
- Erickson's Psychosocial Stages of Development for AdolescentsDocument3 pagesErickson's Psychosocial Stages of Development for AdolescentsVince AlcanseNo ratings yet
- Civics AssignmentDocument14 pagesCivics Assignmentksaim7466No ratings yet
- References Notes For Module 1Document12 pagesReferences Notes For Module 1kimberly montinolaNo ratings yet
- Eriksons Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument41 pagesEriksons Stages of Psychosocial Developmentjeff kotxNo ratings yet
- CAL Midterm Lesson-2Document11 pagesCAL Midterm Lesson-2magstinoangelicaNo ratings yet
- activity 2 FL_bc55227825e6746cc6399c279820eea6Document2 pagesactivity 2 FL_bc55227825e6746cc6399c279820eea6Richelle MasingNo ratings yet
- Erik Erikson - Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument15 pagesErik Erikson - Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentGenes LesacaNo ratings yet
- Child Development Theories ExplainedDocument41 pagesChild Development Theories ExplainedAmihan GrandeNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning - Module 3Document171 pagesFacilitating Learning - Module 3Rema MandaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Erik Erikson's Psycho - Social Theory of DevelopmentDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Erik Erikson's Psycho - Social Theory of DevelopmentBianca GatapiaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 11-Lesson 7Document26 pagesEDUC 11-Lesson 7hydeerosario0118No ratings yet
- Module7 130118170434 Phpapp02 PDFDocument41 pagesModule7 130118170434 Phpapp02 PDFnepen theNo ratings yet
- CLIENTELLEDocument52 pagesCLIENTELLEangeloarevalo462No ratings yet
- Erikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development ExplainedDocument4 pagesErikson's Psychosocial Stages of Development ExplainedAhron Jay AriendaNo ratings yet
- Erik Erikson's Psychosocial Theory of DevelopmentDocument28 pagesErik Erikson's Psychosocial Theory of DevelopmentRied Nepomuceno100% (1)
- Erik Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument20 pagesErik Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial DevelopmentJanet Brigida CatiponNo ratings yet
- UNDSELF_Lesson3.pptxDocument16 pagesUNDSELF_Lesson3.pptxV-JAY BACKONGNo ratings yet
- Values DevelopmentDocument15 pagesValues DevelopmentSteve ColbertNo ratings yet
- Theory On Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument23 pagesTheory On Psychosocial DevelopmentLorena MapaNo ratings yet
- Erikson's Eight StagesDocument3 pagesErikson's Eight StagesNovelyn MitraNo ratings yet
- Theories of Learners DevelopmentDocument16 pagesTheories of Learners DevelopmentArlyn TuballasNo ratings yet
- Handout 3 Developmental Skills and TasksDocument2 pagesHandout 3 Developmental Skills and TasksLee OrtizNo ratings yet
- NSTP O1Document8 pagesNSTP O1Sheridan AcosmistNo ratings yet
- Eric Erickson Eight Stages TheoryDocument28 pagesEric Erickson Eight Stages TheoryGienova AblaoNo ratings yet
- Erikson TheoryDocument8 pagesErikson TheoryOgechi AjaaNo ratings yet
- Erikson's Psychosocial Stages Summary ChartDocument2 pagesErikson's Psychosocial Stages Summary ChartmarianelinelNo ratings yet
- Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development ExplainedDocument11 pagesErikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development ExplainedCyriel Ashana S. FlorencioNo ratings yet
- Course-Module - Educ 1 Week 5Document19 pagesCourse-Module - Educ 1 Week 5Mariel Bandada100% (1)
- Developmental Reading Course OverviewDocument25 pagesDevelopmental Reading Course OverviewAiza C. Abungan-GalzoteNo ratings yet
- Developmental Stages AdolescenceDocument12 pagesDevelopmental Stages AdolescenceJoy Rose CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Erikson's Psychosocial Developmental Theory: by HarpreetDocument21 pagesErikson's Psychosocial Developmental Theory: by Harpreetapi-480118398No ratings yet
- Jean Piaget: Cognitive Development Cognitive Stages of DevelopmentDocument21 pagesJean Piaget: Cognitive Development Cognitive Stages of DevelopmentJøshüaNo ratings yet
- Erikson Stagesaof Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument9 pagesErikson Stagesaof Psychosocial DevelopmentsakNo ratings yet
- Activity Module 5Document5 pagesActivity Module 5DAVID FUGEN LLANDINONo ratings yet
- A Study of The Aggressiveness Behavior of Senior High School Students of de La Salle Lipa As Predicted by The Perceived Parenting Styles of Their ParentsDocument32 pagesA Study of The Aggressiveness Behavior of Senior High School Students of de La Salle Lipa As Predicted by The Perceived Parenting Styles of Their ParentsVince Catapang100% (1)
- Social Media Linked to Worse Student Mental HealthDocument34 pagesSocial Media Linked to Worse Student Mental HealthMaeganNo ratings yet
- 2017 Term 2 Week 1 NewsletterDocument4 pages2017 Term 2 Week 1 Newsletterapi-325718693No ratings yet
- AN ANALYSIS OF SLANG TERMS USED IN SOCIAL MEDIADocument5 pagesAN ANALYSIS OF SLANG TERMS USED IN SOCIAL MEDIAJonel CarballoNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Case StudyDocument4 pagesAdolescent Case Studykaushik_1991No ratings yet
- EBOOK Human Sexuality Self Society and Culture Ebook PDF Version Download Full Chapter PDF KindleDocument61 pagesEBOOK Human Sexuality Self Society and Culture Ebook PDF Version Download Full Chapter PDF Kindlejames.mcneil996100% (39)
- ListeDesTests 1Document25 pagesListeDesTests 1Nadia Farhana FiraNo ratings yet
- Final FTC 1 BseDocument5 pagesFinal FTC 1 BseMichelle Mirador MinimoNo ratings yet
- Risk Behavior in Adolescnece Risk FactorsDocument11 pagesRisk Behavior in Adolescnece Risk FactorsLaica BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Childhood PsychopathologyDocument103 pagesChildhood PsychopathologySrijeeta ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Sosc1 ClippingsDocument17 pagesSosc1 ClippingsSheena Salva QuilangNo ratings yet
- Sex Education: Politicians, Parents, Teachers and Teens: Special AnalysisDocument4 pagesSex Education: Politicians, Parents, Teachers and Teens: Special AnalysisrosieNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Inggirs YohDocument8 pagesPresentasi Inggirs YohxyohNo ratings yet
- Verb TensesDocument3 pagesVerb TensesThamara LetíciaNo ratings yet
- Lifespan Development Seventh Canadian Edition 7Th Edition Full ChapterDocument41 pagesLifespan Development Seventh Canadian Edition 7Th Edition Full Chapterjamie.gardner403100% (23)
- Constantinou 2011Document9 pagesConstantinou 2011Cosmin TudoriNo ratings yet
- Montana TikTok InvestigationDocument44 pagesMontana TikTok InvestigationFox NewsNo ratings yet
- Health-7 Q3 M1Document18 pagesHealth-7 Q3 M1edel dearce IIINo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument49 pagesPersonal DevelopmentJohn Gemil JavierNo ratings yet
- Children Who Murder - ReviewDocument21 pagesChildren Who Murder - ReviewJelena DebeljakNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Physical and Sexual Self Part 1 Official - 1Document27 pagesModule 7 Physical and Sexual Self Part 1 Official - 1May RodeoNo ratings yet
- HEALTHY YOUTH PROGRAMSDocument194 pagesHEALTHY YOUTH PROGRAMSAbigail AnziaNo ratings yet