Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LACERATION - Large Laceration Can Be VAGINAL Laceration - Easier To Locate and
Uploaded by
رجمه ديوان0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesgedfd
Original Title
LACERATION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentgedfd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesLACERATION - Large Laceration Can Be VAGINAL Laceration - Easier To Locate and
Uploaded by
رجمه ديوانgedfd
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
LACERATION – large laceration can be VAGINAL Laceration – easier to locate and *CLASSIFICATION OF PERINEAL
source of infection/hemorrhage assess than cervical because its easier to LACERATION*
view
Occurs often: -First degree – vaginal mucous membrane
MANAGEMNT – A balloon tapenade may and skin of the perineum to fourchette
1. Difficulty or precipitate birth be effective if surturing doesn’t achieve
-Second degree – vagina, perineal skin,
2. Primigravidas hemostasis
fascia, levator ani muscle and perineal
3. Birth of large infants (>9LB) -An indwelling urinary catheter may be body
placed following the repair because the
4. Use of litothomy position and packing cases such pressure on the -Third degree – entire perineum,
instruments (forceps, vacuum) extending to reach the external sphincter
urethra than can interfere with voiding
of rectum
5Laceration occurs in CERVIX, VAGINA or -Document womans electronic record
PERINEUM -Fourth degree – entire perineum, rectal
when and where packing was place to be
certain to remove after 24-48hrs or before sphincter and some of the mucous
ASSESSSMENT – Anytime a uterus feels membrane of the rectum.
firm but bleeding persist suspect a discharge
laceration. PERINEAL Laceration – More likely to have RETAINED placental Fragments –
Fragments of placenta separate and left
CERVICAL Laceration – found usually on in litothomy position rather than supine
because it increases tension in perineum. stull attached to the uretus
sides of cervix near branches of uterine
artyert. Arterial bleeding is bright red than -Most likely to happen with succenturate
MANAGEMENT:
venous blood placenta ( a placenta with accessory lobe)
-Sutured and treated same as episiotomy
-Occurs immediately after detachment of -Placenta accrete (placenta that fuses with
repair
the placenta myometrium because of abnormal
-A diet in high fluid and stool softener is decidua basali layer) may also be retained
MANGAMENT – Surture prescribed for first weeks to prevent
constipation and hard tools -Can be identified with ultrasound exam
-Try to maintain an air of calm and stand
beside the woman at the head -Removing deeply embedded placenta can
-Fourth – degree laceration can lead to
long term dyspareunia, rectal lead to severe postpartal hemorrhage
-Assure her of the babys condition and
inform her longer stay in birthing room incontinence, sexual dissatisfaction they -A bloods serum containing human
usually heal without further complication chorionic gonadotropin (Hcg) hormone
-If cervical laceration appears extensive, its also reveals that part of the placenta is still
necessary to give regional anesthesia to present
relax uterine muscle and prevent pain
ASSESSMENT- If undetected, bleeding may SUBINVOLUTION – Incomplete return of -May feel flunctuant but seepage into area
not be immediate postpartal period the uterus to its pregnant size & shape, at continues and tissue is drawin taut,
4-6 weeks uterus is still enlarged and soft palpates as firm globe and feels tender.
-If fragment is small, bleeding may not be
detected until postpartum day 6-10 -Resulted from small retained placental MANAGEMENT – Report presence of
fragments, mild endometritis or hematoma, its estimated size, degree of
-Notice of abrupt discharge and large accompanying problems like uterine woman discomforts
amount of vaginal bleeding myoma interfering with complete
-Administer mild analgesics for pain relief
-On examination, uterus is found to not contraction
fully contracted MANAGEMENT – Oral administration of -Apply ice pack covered with towel to
prevent thermal injury to the skin
MANAGEMENT- Dilation and curettage methylergonovine, 0.2 mg 4x daily to
(D&C) improve uterine tone and complete -Hematoma is absorbed over next 3-4 days
involution
-Methotrexate to be prescribe to destroy -The woman may have to return birthing
retained fragments -If the uterus feels tender to palpation room to have the site incised and bleeding
suggesting endometritis is present, oral vessels ligated under local anesthesia.
-Observe change from lochia serosa or antibiotic may be prescribed.
alba black to ruba -Assure woman that it will reabsorb over
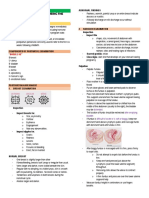
PERINEAL HEMATOMA – collection of next 6 weeks
- Hysterectomy must be performed to blood in the subcutaneous layer of the
others tissue of the perineum -If episiotomy line was open to drain
hematoma, it may be left open and packed
Most likely to occur after rapid with gauze rather than surtured.
UTERINE INVERSION – Prolapse of the spontaneous birth who have perineal
varicosities. -Record this packing was placed to remove
fundus of the uterus through to cervix so in 24-48hrs
that the uterus turns inside out May seen on the site of
laceration/Episiotomy repair if vein has -Surture line open this way heals by
DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR
punctured during surturing tertiary intention on from bottom to top
COAGULATION (DIC) – deficiency in rather than side to side so healing will
clotting caused by vascular injury ASSESSMENT- If woman reports severe occur slowly than usual primary intention
-Associated with premature separation of pain in perineal area or feeling of pressure sutureline.
placenta, missed early miscarriage or fetal between her legs.
-Instruct patient to keep clean and dry and
death in utero -It appears purplish discoloration with use sitz bath once or 2x a day
obvious swelling, it can be small as 2cm or
large as 8cm in diameter.
You might also like
- Minor Gynecological ProceduresDocument2 pagesMinor Gynecological Proceduresmkct111No ratings yet
- Erpoc CmeDocument20 pagesErpoc CmeSharon J StephenNo ratings yet
- Top 55 Most Common Sex Fantasies RevealedDocument3 pagesTop 55 Most Common Sex Fantasies Revealedvirad25No ratings yet
- Postpartal ComplicationDocument4 pagesPostpartal ComplicationHanna AligatoNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Module 3mDocument25 pagesNCM 109 Module 3mKyle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Pregnancy 2Document4 pagesComplications of Pregnancy 2MENDIETA, JACQUELINE V.No ratings yet
- Complication in Labor and DeliveryDocument6 pagesComplication in Labor and Deliveryyenyen erejerNo ratings yet
- Ncma219 Week 4Document9 pagesNcma219 Week 4Aruxi YoshiNo ratings yet
- Placental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Document3 pagesPlacental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Mary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument7 pagesCongenital Gastrointestinal DisorderDONA, Randel John T.No ratings yet
- 3 March 6, 2022 Postpartum Complications: Module No. Date: TopicDocument10 pages3 March 6, 2022 Postpartum Complications: Module No. Date: Topicanon ymousNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System and DiseasesDocument10 pagesMale Reproductive System and DiseasesMadan Kumar100% (2)
- Imperforate Anus: Preoperative CareDocument2 pagesImperforate Anus: Preoperative CareLalisaM ActivityNo ratings yet
- Immediate Management of Postpartum HemorrhageDocument5 pagesImmediate Management of Postpartum HemorrhageArtika MalaNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 13Document8 pagesOb2 Sas 13Ralph Louie ManagoNo ratings yet
- Perineal Trauma Following Vaginal BirthDocument16 pagesPerineal Trauma Following Vaginal BirthbagnilNo ratings yet
- Postpartal Complications 2023Document5 pagesPostpartal Complications 2023Brianna ValerioNo ratings yet
- M102 Remedial ModuleDocument14 pagesM102 Remedial ModuleMA. JYRELL BONITONo ratings yet
- NCM 109 Midterms - Postpartal Complications L1Document7 pagesNCM 109 Midterms - Postpartal Complications L1Leigh Angelika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Postpartum HaemorrhageDocument26 pagesPostpartum HaemorrhagePriyanka ViswanathNo ratings yet
- 109 ReviewerDocument4 pages109 ReviewerAsniya DiamelNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa: DefinitionDocument4 pagesPlacenta Previa: DefinitionCT Johara MusorNo ratings yet
- Bhabani OBG SeminarDocument28 pagesBhabani OBG SeminarSonali SamalNo ratings yet
- First 24 HoursDocument5 pagesFirst 24 HoursMjNo ratings yet
- Stage of DilatationDocument9 pagesStage of DilatationanonymousNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The High Risk Postpartal ClientDocument11 pagesNursing Care of The High Risk Postpartal ClientMarielle J GarciaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal OB - Uphi LectureDocument16 pagesAbnormal OB - Uphi LectureQuerubin DandoyNo ratings yet
- Postpartum ComplicationsDocument6 pagesPostpartum ComplicationsALCANTARA ALYANNANo ratings yet
- Common Causes of Dysfunctional Labor:: DystociaDocument8 pagesCommon Causes of Dysfunctional Labor:: DystociaAngelo ArabejoNo ratings yet
- Amplify The Learning (Ob) Week #4 - 2: Vidon, Aubrey Rose A. April 18, 2020 BSN 2Y2-2Document1 pageAmplify The Learning (Ob) Week #4 - 2: Vidon, Aubrey Rose A. April 18, 2020 BSN 2Y2-2AriaNo ratings yet
- Ob Finals Postpartum ComplicationsDocument2 pagesOb Finals Postpartum ComplicationsKurt Lemuel SisonNo ratings yet
- Maternal Physiology Changes During PregnancyDocument9 pagesMaternal Physiology Changes During PregnancyRandom CommenterNo ratings yet
- Subinvolution of The UterusDocument5 pagesSubinvolution of The UterusJanica Rose Maloloy-onNo ratings yet
- (OBa) 1.6 Matrnal Adaptations To Pregnncy (Marinas) - PacisDocument10 pages(OBa) 1.6 Matrnal Adaptations To Pregnncy (Marinas) - PacisClyde Yuchengco Cu-unjiengNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument6 pagesLabor and Deliveryjenryl91% (11)
- Birth Canal Injuries Final LectureDocument63 pagesBirth Canal Injuries Final Lecturepeter njoguNo ratings yet
- Birth Canal Injuries: Causes, Types, Prevention and ManagementDocument67 pagesBirth Canal Injuries: Causes, Types, Prevention and ManagementnamitaNo ratings yet
- LACERATIONSDocument4 pagesLACERATIONSDrake AquinoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sex and FertDocument17 pagesWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- Placental Abnormalities ExplainedDocument5 pagesPlacental Abnormalities ExplainedNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Precipitate Labor, Uterine Inversion, Uterine RuptureDocument3 pagesPrecipitate Labor, Uterine Inversion, Uterine RuptureAbbeygale Galan100% (2)
- Complications of Labor and Birth 11Document12 pagesComplications of Labor and Birth 11Gian AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Face PresentationDocument4 pagesFace PresentationRose Ann HajironNo ratings yet
- Operative Vaginal DeliveryDocument8 pagesOperative Vaginal DeliveryGerben VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nursing NotesDocument16 pagesNursing NotesChelzie LasernaNo ratings yet
- Post-partum hge - @Medicine_Way2Document6 pagesPost-partum hge - @Medicine_Way2saeed hasan saeedNo ratings yet
- OBDocument17 pagesOBMyrna Cecile NonesNo ratings yet
- Postpatum Obstetric EmergenciesDocument46 pagesPostpatum Obstetric EmergenciesSooryaNo ratings yet
- If We Certain That There Is No Second Baby, Administer The A Uterotonic DrugDocument3 pagesIf We Certain That There Is No Second Baby, Administer The A Uterotonic DrugValerie Gonzaga-CarandangNo ratings yet
- NRG 204 MidtermDocument80 pagesNRG 204 MidtermKYLA MERCADONo ratings yet
- Uterine Atony 1Document16 pagesUterine Atony 1Dèyanira Jazsmin SilosNo ratings yet
- Lp1 ReviewerDocument19 pagesLp1 ReviewerNiña Ricci MtflcoNo ratings yet
- Benign Gyne LesionDocument15 pagesBenign Gyne LesionPM Basiloy - AloNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Module 4FDocument25 pagesNCM 107 Module 4F1B - Zafra, RamoneNo ratings yet
- Managing Uterine Prolapse and RuptureDocument16 pagesManaging Uterine Prolapse and RuptureA sisonNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Module 4FDocument25 pagesNCM 107 Module 4FNotur BarbielatNo ratings yet
- Birth Canal Trauma GuideDocument31 pagesBirth Canal Trauma GuideTuhin DeyNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Regaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryFrom EverandRegaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itNo ratings yet
- Hernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mental Status Exam Template 03Document1 pageMental Status Exam Template 03رجمه ديوان100% (1)
- Mental Status Exam Template 02Document2 pagesMental Status Exam Template 02رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Neuro Anatomy & Assessment PDFDocument5 pagesNeuro Anatomy & Assessment PDFرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: Signs, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument3 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure: Signs, Symptoms and Treatmentرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Mental State Examination Template: (Please Mark Those Involved and Expand Upon If Present)Document2 pagesMental State Examination Template: (Please Mark Those Involved and Expand Upon If Present)رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: Signs, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument3 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure: Signs, Symptoms and Treatmentرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIA - Distorted and Uncontrolled Acute Myeloid LeukemiaDocument1 pageLEUKEMIA - Distorted and Uncontrolled Acute Myeloid Leukemiaرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- High Risk NewbornsDocument5 pagesHigh Risk Newbornsرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: Signs, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument3 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure: Signs, Symptoms and Treatmentرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Schistosomiasis Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument2 pagesCerebral Schistosomiasis Diagnosis & Treatmentرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Osteogenic SarcomaDocument1 pageOsteogenic Sarcomaرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Neuro Anatomy & Assessment PDFDocument5 pagesNeuro Anatomy & Assessment PDFرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Temperaure.: Treatment, Include FollowingDocument2 pagesTemperaure.: Treatment, Include Followingرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- NEPHROBLASTOMA - Wilms Tumor ASTHMA - Chronic Inflammatory Disorder RHEUMATIC FEVER - Autoimmne DiseaseDocument1 pageNEPHROBLASTOMA - Wilms Tumor ASTHMA - Chronic Inflammatory Disorder RHEUMATIC FEVER - Autoimmne Diseaseرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Micro Lab#24Document2 pagesMicro Lab#24رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Eyes,: Check For Understanding (30 Minutes)Document2 pagesEyes,: Check For Understanding (30 Minutes)رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Pressure in Relation Surrounding Minimum: ChangesDocument2 pagesPressure in Relation Surrounding Minimum: Changesرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Adenopathy: Gingivitis, ResultsDocument2 pagesAdenopathy: Gingivitis, Resultsرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Gonococcal Conjunctivitis TreatmentTITLE Diagnosing and Managing Gonorrhea in NursingTITLE Rubella in Pregnancy Risks and Prophylaxis TITLE Identifying Rashes in Pediatric PatientsDocument2 pagesGonococcal Conjunctivitis TreatmentTITLE Diagnosing and Managing Gonorrhea in NursingTITLE Rubella in Pregnancy Risks and Prophylaxis TITLE Identifying Rashes in Pediatric Patientsرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Nursing care for malaria patientDocument2 pagesNursing care for malaria patientرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Environment.: Episodes RunningDocument2 pagesEnvironment.: Episodes Runningرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- DewanDocument1 pageDewanرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Empiric Therapy: An SEO-Optimized Title for Antimicrobial TherapyDocument3 pagesEmpiric Therapy: An SEO-Optimized Title for Antimicrobial Therapyرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- UtsDocument1 pageUtsرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Brugia Malayi: Answer:E Ratio: Wuchereria LeasaymnuluaDocument1 pageBrugia Malayi: Answer:E Ratio: Wuchereria Leasaymnuluaرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Answer H: RATIO Ee Awe Og Eyeine IDocument1 pageAnswer H: RATIO Ee Awe Og Eyeine Iرجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lymphatic SystemDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lymphatic SystemJohn Lendel Maramo LunarNo ratings yet
- Lipids 2Document11 pagesLipids 2رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- Trans Chapter 16Document5 pagesTrans Chapter 16رجمه ديوانNo ratings yet
- National Family Health SurveyDocument21 pagesNational Family Health SurveyNamita Goyal100% (1)
- Ucsp 107Document3 pagesUcsp 107Darry BlanciaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper On RH BillDocument1 pageReaction Paper On RH BillAgui S. AugusthineNo ratings yet
- Mabuti Jerald C - (Template) Module 1 - Activity SheetDocument2 pagesMabuti Jerald C - (Template) Module 1 - Activity SheetMabuti Jerald CNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document15 pagesChapter 8Mati GouskosNo ratings yet
- BioethicsDocument3 pagesBioethicsJerejee Roga100% (1)
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Document23 pagesPelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Diana Rashid100% (1)
- Partograph Exercise: Case 1Document2 pagesPartograph Exercise: Case 1Madhusmita Nayak100% (1)
- Perception of Grade 11 Senior High Schoo PDFDocument30 pagesPerception of Grade 11 Senior High Schoo PDFGlamorius Enigma0% (1)
- CuprinsDocument3 pagesCuprinsdanielaNo ratings yet
- Doulas of South Australia - Qualified and Trainee DoulasDocument2 pagesDoulas of South Australia - Qualified and Trainee DoulasHelenRomeoNo ratings yet
- Teen PregnancyDocument1 pageTeen PregnancyblruddNo ratings yet
- Midwife Cover LetterDocument7 pagesMidwife Cover Letterqrhxvwljg100% (1)
- The National Birth Center Study IIDocument12 pagesThe National Birth Center Study IIapi-38108107No ratings yet
- Fetal risks of macrosomia in diabetic pregnanciesDocument27 pagesFetal risks of macrosomia in diabetic pregnanciesIful SaifullahNo ratings yet
- Kupit 2 PDFDocument26 pagesKupit 2 PDFwayan sudarsanaNo ratings yet
- NOBEL Group 1 Handout TDocument5 pagesNOBEL Group 1 Handout TAdrian GabrielNo ratings yet
- Level of Awareness and Attitude of Grade 12 GAS Students On Selected Sexually Transmitted Diseases Quantitative Research ProposalDocument37 pagesLevel of Awareness and Attitude of Grade 12 GAS Students On Selected Sexually Transmitted Diseases Quantitative Research ProposalCharlz HizonNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Its Relationship WTH Maternal Fetal Attachment in Prgenant Women in Southeast of IranDocument13 pagesAnxiety and Its Relationship WTH Maternal Fetal Attachment in Prgenant Women in Southeast of IranNida Tsaura SNo ratings yet
- Mauritius MNCH HandbookDocument66 pagesMauritius MNCH Handbooknevin KhedooNo ratings yet
- Sex EducationDocument42 pagesSex EducationBraiden ZachNo ratings yet
- Abortion PP TDocument42 pagesAbortion PP TDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Stages of Lactation ExplainedDocument35 pagesStages of Lactation ExplainedIgnacio FelicityNo ratings yet
- Totalizare GynecoDocument10 pagesTotalizare GynecoCristinaCapros0% (1)
- Improve Your Sex Life with PC Muscle ExercisesDocument8 pagesImprove Your Sex Life with PC Muscle ExercisesAnkit PalNo ratings yet
- UNAIDS Core Epidemiology Slides enDocument11 pagesUNAIDS Core Epidemiology Slides enTabarcea VitaliNo ratings yet
- APGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolDocument2 pagesAPGAR Scoring and Ballard's Assessment ToolJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- RedHotSexTips Com - Becoming A Master of Oral SexDocument12 pagesRedHotSexTips Com - Becoming A Master of Oral Sexanon-71392797% (71)
- Kinship, marriage and household typesDocument3 pagesKinship, marriage and household typesDan Gabriel LacernaNo ratings yet