Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Five Questions For Selecting A Statistical Method
Five Questions For Selecting A Statistical Method
Uploaded by
ragumohanas7602Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Five Questions For Selecting A Statistical Method
Five Questions For Selecting A Statistical Method
Uploaded by
ragumohanas7602Copyright:
Available Formats
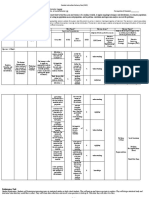
FIVE QUESTIONS FOR SELECTING A STATISTICAL METHOD
1. How many variables do you have --- just one, more than one, or
way too may?
How many JUST ONCE 2. What is your statistical objective – describe, identify/classify,
variables do compare/test, predict, or explain?
you have? 3. What scales of measurement do the variables use?
4. Are there dependent and independent variables?
DESCRIBE
WAY TOO MANY
5. Are the samples autocorrelated by location (1D, 2D, or 3D) or time/
MORE THAN ONE
sequence (1D)?
Descriptive Statistics
Discrete Scales
Counts, proportions
Conduct a cluster analysis to select Continuous Scales
representative variables Means, standard
Are some CLASSIFY COMPARE PREDICT EXPLAIN
or variable dependent deviations, medians,
Conduct a principal components analysis, and others ranges, quartiles
factor analysis, correspondence analysis, independent? Distribution Fitting
or multidimensional scaling to reduce the No Filtering One-Population [none] [none]
Statistics:
number of variables needed to represent Sorting Test
Yes Skewness, kurtosis
most of the variability Cluster analysis Discrete Scale
coefficient of variation
Graphics: Nonparametric
Histograms, box plots, statistics
Are the Continuous
dependent variables probability plots
Tests: Scales
autocorrelated?
Kolmogorov-Smirnov, t-tests, control
Anderson-Darling, charts
No Shapiro-Wilk Lillifors
DESCRIBE CLASSIFY COMPARE PREDICT EXPLAIN DESCRIBE CLASSIFY COMPARE PREDICT EXPLAIN
Yes
Same as for Cluster analysis, Same as for Discrete scale Discrete scale Same as for [none] Cluster analysis,
Same as for Same as for
single variables discriminant single variables dependent dependent single variables multi
Single variables Single variables
Cross- analysis Multi- variable Logistic variable Logistic Correlations dimensional
tabulations Population Tests regression, regression Discrete Scales scaling, principal
Correlations ANOVA, classification classification Spearman R. components
Discrete Scales ANCOVA, trees, trees, Kendall analysis,
Spearman R. nonparametric discriminant discriminant Tau, gamma correspondence
Kendall tests analysis analysis Continuous analysis
Tau, gamma Continuous Continuous Scales
Continuous scale dependent scale dependent Pearson Product
Scales variables variables Moment
Pearson Product Regression Regression, Correlation
Moment canonical
Correlation correlation
LOCATION DEPENDENT TIME DEPENDENT
Time or
location dependent?
DESCRIBE CLASSIFY COMPARE PREDICT EXPLAIN DESCRIBE CLASSIFY COMPARE PREDICT EXPLAIN
Same as for non- Same as for non- Same as for non- Smoothing
Smoothing Same as for non- Same as for non- Same as for non-
autocorrelated autocorrelated autocorrelated interpolation,
interpolation, Trend-surfaces autocorrelated autocorrelated autocorrelated Time-series
variables with a variables with a variables with a time-series
trend-surfaces, geostatistics variables with a variables with a variables with a regression,
location- location- location- regression,
geostatistics (variogramming time-dependent time-dependent time-dependent ARIMA, spectral
dependent dependent dependent ARIMA, spectral
(variogramming and kriging) variable as a variable as a variable as a analysis
variable as a variable as a variable as a analysis, neural
and kring) grouping factor grouping factor grouping factor
grouping factor grouping factor grouping factor networks
You might also like
- Facility Procedures and MaintenanceDocument34 pagesFacility Procedures and Maintenancebaba100% (1)
- Data Management: Bryan S. AmbreDocument104 pagesData Management: Bryan S. AmbreAlexander SiccuanNo ratings yet
- Module 37. Multiple RegressionDocument59 pagesModule 37. Multiple Regressiontaghavi1347No ratings yet
- JSA-017 Lifting With ForkliftDocument3 pagesJSA-017 Lifting With ForkliftMoaatazz Nouisri67% (6)
- Project Management Plan - Security Management PlanDocument10 pagesProject Management Plan - Security Management Planario widjaksonoNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instruction Delivery Plan: Private Education Assistance CommitteeDocument3 pagesFlexible Instruction Delivery Plan: Private Education Assistance CommitteeLANY T. CATAMINNo ratings yet
- Module 36. Simple Linear RegressionDocument48 pagesModule 36. Simple Linear Regressiontaghavi1347No ratings yet
- Module 34. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) PDFDocument89 pagesModule 34. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) PDFtaghavi1347No ratings yet
- Erection Testing and Commissioning of Transmission Lines & Sub-StationDocument19 pagesErection Testing and Commissioning of Transmission Lines & Sub-Stationarun kumarNo ratings yet
- 01 - Multivariate - Introduction To Multivariate AnalysisDocument38 pages01 - Multivariate - Introduction To Multivariate Analysis322OO22 - Jovanka Angella Mesinay100% (1)
- Accu Floc BrochureDocument4 pagesAccu Floc BrochureTanto WiNo ratings yet
- Research Designe and Basics of Stistics Manish JainDocument67 pagesResearch Designe and Basics of Stistics Manish JainDhrubajyoti Datta100% (1)
- CRW-2 Passanger Ship Crisis... Rev. 08Document69 pagesCRW-2 Passanger Ship Crisis... Rev. 08belen bastistaNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure Testing Procedure: Petronas Rapid Project Package 14 - Utilities, Interconnecting, Offsite UnitsDocument23 pagesHydrostatic Pressure Testing Procedure: Petronas Rapid Project Package 14 - Utilities, Interconnecting, Offsite UnitsYo Wee LiamNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument39 pagesAnswerALMACHIUS RWERENGELA86% (7)
- Cpa A1.3 - Advanced Financial Reporting - Study ManualDocument452 pagesCpa A1.3 - Advanced Financial Reporting - Study ManualDamascene100% (1)
- Mva - 2008 India School Rick LoydDocument86 pagesMva - 2008 India School Rick Loydamar_saxena60857No ratings yet
- Course Content: St. Paul University PhilippinesDocument33 pagesCourse Content: St. Paul University PhilippineslucasNo ratings yet
- 1-FIDP TemplateDocument4 pages1-FIDP TemplateMeljoy TenorioNo ratings yet
- Minggu 1 - Pengantar Analisis Multivariate PDFDocument51 pagesMinggu 1 - Pengantar Analisis Multivariate PDFHAFIDZ NUR SHAFWANNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods: (Including Modeling & Simulation)Document29 pagesQuantitative Methods: (Including Modeling & Simulation)Lea UnderscoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten & ElevenDocument19 pagesChapter Ten & ElevenaliNo ratings yet
- Statistics LectureDocument35 pagesStatistics LectureEPOY JERSNo ratings yet
- ESSB3134 Lesson 4Document6 pagesESSB3134 Lesson 4kimjjaeni527No ratings yet
- Estadístic A Descriptiv A: Dr. Lázaro Bustio Martínez Otoño 2023Document42 pagesEstadístic A Descriptiv A: Dr. Lázaro Bustio Martínez Otoño 2023guillermobur2310No ratings yet
- 02 BiostatDocument4 pages02 BiostatDavid MangawilNo ratings yet
- T-Test: T-TEST GROUPS Kelas (1 2) /missing Analysis /VARIABLES Hasil /CRITERIA CI (.95)Document2 pagesT-Test: T-TEST GROUPS Kelas (1 2) /missing Analysis /VARIABLES Hasil /CRITERIA CI (.95)Sandra Puspita NingrumNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics - Session Data VisualizationDocument37 pagesBusiness Statistics - Session Data Visualizationmukul3087_305865623No ratings yet
- Análise de RegressãoDocument77 pagesAnálise de RegressãoPedroMotaVeigaNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH Methodology: Associate Professor in Management Pondicherry University Karaikal Campus Karaikal - 609 605Document46 pagesRESEARCH Methodology: Associate Professor in Management Pondicherry University Karaikal Campus Karaikal - 609 605Archana RNo ratings yet
- Visual Guide To Machine LearningDocument349 pagesVisual Guide To Machine LearningMichelle SaverNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument3 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Summar Quant Designs ChartDocument1 pageSummar Quant Designs ChartYoni MacNo ratings yet
- Metodologi Penelitian: Prof. Dr. H. UJIANTO, MSDocument11 pagesMetodologi Penelitian: Prof. Dr. H. UJIANTO, MSRiski Arek DeathMetal SbyNo ratings yet
- StatssDocument4 pagesStatssPooja RajurkarNo ratings yet
- VPT2 Analysis Technique Presentation 10-26-16Document22 pagesVPT2 Analysis Technique Presentation 10-26-16bmack2150% (2)
- Experimental ResearchDocument8 pagesExperimental ResearchArchi VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Mind Map #5Document1 pageMind Map #5ktpc1994No ratings yet
- Figure 13.1-A Classification of Multivariate MethodsDocument4 pagesFigure 13.1-A Classification of Multivariate MethodsAN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Overview of Multivariate Techniques: Meena NotesDocument9 pagesLecture 1: Overview of Multivariate Techniques: Meena Notesmgmt6008No ratings yet
- 4 Chapter 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument20 pages4 Chapter 1 - Introduction To StatisticsCharlie RNo ratings yet
- Qunatitative AnalysisDocument30 pagesQunatitative Analysiszeren lucky cabanayanNo ratings yet
- Ace Reviewer LbolytcDocument16 pagesAce Reviewer LbolytcCarlos Joseph OngNo ratings yet
- 4 Data Analysis1Document32 pages4 Data Analysis1Mohamad AdibNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics Day 1Document61 pagesAdvanced Statistics Day 1촏교새벼No ratings yet
- Discriminant AnalysisDocument45 pagesDiscriminant AnalysisRachmat HidayatNo ratings yet
- Local Media7448206506575993530Document4 pagesLocal Media7448206506575993530Sai GuyoNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 1. Introduction and FrameworkDocument22 pagesPertemuan 1. Introduction and FrameworkJONATHAN SOELISTYONo ratings yet
- Advanced ANOVA - MANOVA - WikiversityDocument7 pagesAdvanced ANOVA - MANOVA - WikiversityDivya pathakNo ratings yet
- Operational Foundation of StatisticsDocument59 pagesOperational Foundation of StatisticsA Y I E SNo ratings yet
- Discriminant Analysis Chapter-SevenDocument7 pagesDiscriminant Analysis Chapter-SevenSoloymanNo ratings yet
- Q1. W2. The Nature of VariablesDocument18 pagesQ1. W2. The Nature of VariablesDazzle MuliNo ratings yet
- 2 Multivariate Statistics AssumptionsDocument20 pages2 Multivariate Statistics AssumptionsKristoffer N Valerie LoquiasNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variation (Ungrouped Data)Document13 pagesMeasures of Variation (Ungrouped Data)Porquez cantoNo ratings yet
- SMA 2437 L1-2 IntroductionDocument12 pagesSMA 2437 L1-2 IntroductionMarlion MokuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TermsDocument6 pagesChapter 6 TermsMuhammad Hamzi MamsorNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 6 Bab V Variabel Dan Desain Riset AkuntansiDocument15 pagesPertemuan 6 Bab V Variabel Dan Desain Riset AkuntansiSusanto ChNo ratings yet
- Hubungan SN Dan Manajemen NyeriDocument2 pagesHubungan SN Dan Manajemen NyeriVanny AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Independent Sampel T Test FixDocument3 pagesIndependent Sampel T Test FixNur FauzanNo ratings yet
- Data Processing and Analysis: The Purpose of Analyzing Data IsDocument13 pagesData Processing and Analysis: The Purpose of Analyzing Data IsJavaria EhsanNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics: MBBA 501 First Semester, 2021-2022Document39 pagesBusiness Statistics: MBBA 501 First Semester, 2021-2022Maricon DimaunahanNo ratings yet
- STATISTICSDocument1 pageSTATISTICSKEANNA RUBIANo ratings yet
- Materi Discrminant AnalysisDocument83 pagesMateri Discrminant AnalysisNur Rahmah Syah RamdaniNo ratings yet
- Bayesian ReportDocument1 pageBayesian Reportsabiqotul HusnaNo ratings yet
- IndependentDocument2 pagesIndependentRisa FairusNo ratings yet
- STAT 1 Course OutlineDocument1 pageSTAT 1 Course Outlinejive_gumelaNo ratings yet
- Research Design QUANTITATIVE RESEARCHDocument21 pagesResearch Design QUANTITATIVE RESEARCHJet JetNo ratings yet
- Mapa ConceptualDocument1 pageMapa ConceptualPaula PabonNo ratings yet
- Basic Biostatistics for Geneticists and Epidemiologists: A Practical ApproachFrom EverandBasic Biostatistics for Geneticists and Epidemiologists: A Practical ApproachNo ratings yet
- At Product Sheet MK 90dDocument2 pagesAt Product Sheet MK 90dmetalurg87No ratings yet
- Indemnity Bond (For Title Transfer) : (To Be Executed On Rs 100/-Non - Judicial Stamp Paper)Document1 pageIndemnity Bond (For Title Transfer) : (To Be Executed On Rs 100/-Non - Judicial Stamp Paper)Chaitanya Chaitu CANo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Ib1604 - Ibc201Document37 pagesGroup 3 - Ib1604 - Ibc201Bao Thanh Truc (FUG CT)No ratings yet
- TG SeriesDocument36 pagesTG SeriesLuis RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner Resume ExamplesDocument5 pagesNurse Practitioner Resume Examplesf1vijokeheg3100% (2)
- L15 (S) Analysing An Essay - 5ae14752d77d88857ec4c7f - 221110 - 095635Document6 pagesL15 (S) Analysing An Essay - 5ae14752d77d88857ec4c7f - 221110 - 095635Lam ChanNo ratings yet
- Assigning Controlling Areas and Company CodesDocument4 pagesAssigning Controlling Areas and Company Codesatsc68No ratings yet
- Apic2015 Zhao NaDocument24 pagesApic2015 Zhao NaSandip LadvaNo ratings yet
- TSA - 01 Project Cost Management PDFDocument96 pagesTSA - 01 Project Cost Management PDFAndiatma Nur Irfan WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- A Study of Urbanization in Pune DistrictDocument11 pagesA Study of Urbanization in Pune DistrictDIVYA DAHADNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet Chryso Cwa10 6039 1322Document3 pagesTechnical Data Sheet Chryso Cwa10 6039 1322velmurug_balaNo ratings yet
- 08 VESDA Pipe Network Design Guide A4 IE LoresDocument56 pages08 VESDA Pipe Network Design Guide A4 IE Loresvlaya1984No ratings yet
- IM Chapter 12 PDFDocument31 pagesIM Chapter 12 PDFMarwa Ali EissaNo ratings yet
- General Specifications Ventilation and Monitoring ParametersDocument2 pagesGeneral Specifications Ventilation and Monitoring ParametersThiết bị Điện Tử Y Sinh0% (1)
- FTP 2021 March 6000044634 IN 6000044634Document1 pageFTP 2021 March 6000044634 IN 6000044634vivek jayswalNo ratings yet
- Frameless GlassDocument29 pagesFrameless Glassmichelle geejoNo ratings yet
- 7-24 Rigging and Lifting Equipment Inspection Procedure (RV)Document8 pages7-24 Rigging and Lifting Equipment Inspection Procedure (RV)Lee JungNo ratings yet
- Sony X700Document24 pagesSony X700sreekumarNo ratings yet
- 24 34 00Document62 pages24 34 00Fazley Rabbi Akond67% (3)
- Question Bank XiiDocument47 pagesQuestion Bank XiiVIKAS AGNIHOTRINo ratings yet
- Nemo Dat RuleDocument5 pagesNemo Dat RuleTHEVINTHINI A P RAMAKRISHNAN UnknownNo ratings yet