Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 2.2: Acceleration Problems
Uploaded by
Trúc Hồ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
329 views3 pagesOriginal Title
312336092-IGCSE-Physics-Worksheet-2-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
329 views3 pagesWorksheet 2.2: Acceleration Problems
Uploaded by
Trúc HồCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Worksheet 2.
2
Acceleration problems
Solve some more problems involving acceleration.
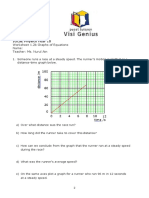
1 The diagram shows the speed–time graphs for four cars.
The table shows four descriptions, one for each car.
Car Description How you know
moving at constant
velocity
speeding up with
constant acceleration
slowing down with
constant acceleration
moving with varying
acceleration
© Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ® Physics
Worksheet 2.2 1
Copy the table and write A, B, C or D in the first column to show which
car’s motion corresponds to each description. In the last column,
indicate how you know.
2 A car is initially stationary. It sets off and reaches a speed of 20 m/s in
12.5 s. Calculate its acceleration.
3 A car is travelling at 8.0 m/s in a straight line. It accelerates with an
acceleration of 1.0 m/s2.
a By how much will its speed increase in 10 s?
b What will its speed be after 10 s?
4 The graph shows how the velocity of an aircraft changed as it followed a
straight path through the air.
a What was the aircraft’s velocity at the start?
b After how long did the aircraft reach a steady velocity?
c What was this velocity?
d Calculate the aircraft’s acceleration during the first 100 s of the section
of its journey represented by the graph.
e Calculate the distance travelled by the aircraft during the 600 s of its
journey represented by the graph.
© Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ® Physics
Worksheet 2.2 2
5 Read the following description of a car’s motion.
A car started off from the traffic lights. Its acceleration was 2.0 m/s2. It
continued to accelerate until it reached a speed of 18 m/s. Then it
travelled at this speed for 20 s.
a How long did it take the car to reach a speed of 18 m/s?
b Draw a speed–time graph to show the car’s motion.
c How far did the car travel during the journey described above?
© Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ® Physics
Worksheet 2.2 3
You might also like
- 3d Trigonometry PDFDocument16 pages3d Trigonometry PDFZoon AANo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Bearings Higher IGCSE Questions 9 1 StandardDocument2 pagesTrigonometry Bearings Higher IGCSE Questions 9 1 StandardHaddonesKimberlyNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Bounds Higher GCSE Exam Style QuestionsDocument1 pageUpper and Lower Bounds Higher GCSE Exam Style Questionsdanexxo100% (1)
- Maths WorksheetDocument4 pagesMaths Worksheetharpreet singh100% (1)
- Work For The Week of Oct 2009Document3 pagesWork For The Week of Oct 2009ftnmrd7No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Past Papers (0620)Document488 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Past Papers (0620)Marium AtifNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 3 - Forces and MovementDocument3 pagesIGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 3 - Forces and Movementeminnayal.enNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Higher IGCSE Questions 9 1Document15 pagesDifferentiation Higher IGCSE Questions 9 1Sri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- 86342059-IGCSE-Physics-Density 1Document12 pages86342059-IGCSE-Physics-Density 1Vedant NavaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 İb PhysicsDocument1 pageGrade 11 İb PhysicsKemal OzturkNo ratings yet
- Organisation of Cells (2.1.2) CIE IGCSE Biology Revision Notes 2023 Save My Exams 6Document1 pageOrganisation of Cells (2.1.2) CIE IGCSE Biology Revision Notes 2023 Save My Exams 6Ruchika Jha100% (1)
- 0417 m17 QP 31Document8 pages0417 m17 QP 31Popi MastroianniNo ratings yet
- Cuboid 3 Planes SymmetryDocument38 pagesCuboid 3 Planes SymmetrylittlegusNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Maths Unit ConversionsDocument3 pagesIGCSE Maths Unit ConversionsJenkins CK TsangNo ratings yet
- Bivariate DataDocument8 pagesBivariate DataJillur HoqueNo ratings yet
- Distance Time Graphs WorksheetDocument5 pagesDistance Time Graphs WorksheetMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet MYP 4Document10 pagesRevision Sheet MYP 4Manan SachdevaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - Physics - MCQ 3 - Forces and MovementDocument7 pagesIGCSE - Physics - MCQ 3 - Forces and MovementKyi Nue KhinNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Find Percentage of A Quantity: Fill in The BlanksDocument3 pagesGrade 6 Find Percentage of A Quantity: Fill in The BlanksAnonymous na314kKjOANo ratings yet
- 2.experimental TechniquesDocument5 pages2.experimental TechniquesSarah WongNo ratings yet
- Waves and Interference Worksheet 2Document14 pagesWaves and Interference Worksheet 2Freya SawNo ratings yet
- DFMFullCoverage BearingsDocument4 pagesDFMFullCoverage BearingsNewtonNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements & Compounds 1 MS PDFDocument8 pagesAtoms, Elements & Compounds 1 MS PDFClinton ChikengezhaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1.2bDocument5 pagesWorksheet 1.2bNurulAinMatAron100% (1)
- O Level Add Math: Coordinate Geometry - CircleDocument6 pagesO Level Add Math: Coordinate Geometry - CirclelampamoyehrNo ratings yet
- Ict Igcse Paper 3 Revision WebauthoringDocument8 pagesIct Igcse Paper 3 Revision WebauthoringPrayrit JainNo ratings yet
- CBSE MATHEMATICS TRIANGLES TOPIC SA-1Document2 pagesCBSE MATHEMATICS TRIANGLES TOPIC SA-1Balmukund KumarNo ratings yet
- Suvat Equation WorksheetDocument1 pageSuvat Equation WorksheetDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11AdeenaNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument5 pagesCircular MotionsurabhiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticeDocument27 pagesIGCSE Physics Paper 4 PracticealfaazmcsNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 5.3 Reflection of WavesDocument3 pagesTUTORIAL 5.3 Reflection of WavesnurularissaNo ratings yet
- MomentsDocument5 pagesMomentsPichakorn100% (1)
- Constructions (FH) - Edexcel GCSE MathsDocument3 pagesConstructions (FH) - Edexcel GCSE MathsRenad Mahmoud FawzyNo ratings yet
- Motion Speed-Time Graphs Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE GCSE O Level Physics 0625Document11 pagesMotion Speed-Time Graphs Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE GCSE O Level Physics 0625IGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (1)
- Mathematics B PDFDocument3 pagesMathematics B PDFSamiha IslamNo ratings yet
- Diffraction (Structured) QP 1Document7 pagesDiffraction (Structured) QP 1jean lamarNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Materials WorksheetDocument16 pagesProperties of Matter and Materials Worksheetrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Mass, Weight and Density: Class-VII Physics Question BankDocument16 pagesMeasurement of Mass, Weight and Density: Class-VII Physics Question BankLov VanthinNo ratings yet
- Pressure and gas propertiesDocument6 pagesPressure and gas propertiesSherazNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine AssignmentDocument4 pagesSimple Machine AssignmentVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- IGSCE Business Studies Question PaperDocument12 pagesIGSCE Business Studies Question PaperLamarNo ratings yet
- Physics 0625 Classified Paper 1 GuideDocument273 pagesPhysics 0625 Classified Paper 1 GuideNoobNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics: 4 Waves Exam-Style QuestionsDocument8 pagesAQA Physics: 4 Waves Exam-Style QuestionsMoses AhmedNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-chapter Questions CambDocument2 pagesAnswers To End-Of-chapter Questions CambJetaNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion Problems: Solve in 5 Secs Without FormulasDocument24 pagesRatio and Proportion Problems: Solve in 5 Secs Without FormulascnkrbtncdxobNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Nisha zehraNo ratings yet
- 5.2 RadioactivityDocument15 pages5.2 RadioactivityAnonymous v5RkWPNo ratings yet
- Wave Refraction and DiffractionDocument6 pagesWave Refraction and DiffractionDora AyeNo ratings yet
- Planes of SymmetryDocument19 pagesPlanes of SymmetryArafath BasheerNo ratings yet
- Data HandlingDocument16 pagesData HandlingShilpaNo ratings yet
- 0580 - m16 - QP - 22-Past Apers - IGSCDocument12 pages0580 - m16 - QP - 22-Past Apers - IGSCchand_basha_80% (1)
- CBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 1Document7 pagesCBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 1sanaNo ratings yet
- 0580 s20 QP 22 PDFDocument12 pages0580 s20 QP 22 PDFRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- 06 0625 32 2015 91111.inddDocument2 pages06 0625 32 2015 91111.inddRana SlimNo ratings yet
- Worksheet September 2021 CH 6: Energy Resources and Transformations Grade: 9 Subject: PhysicsDocument1 pageWorksheet September 2021 CH 6: Energy Resources and Transformations Grade: 9 Subject: PhysicsAnish KanthetiNo ratings yet
- Complete Physics For Cambridge IGCSERG Workbook (Dragged) 2Document8 pagesComplete Physics For Cambridge IGCSERG Workbook (Dragged) 2Trúc HồNo ratings yet
- Complete Physics For Cambridge IGCSERG Workbook (Dragged) 3Document2 pagesComplete Physics For Cambridge IGCSERG Workbook (Dragged) 3Trúc HồNo ratings yet
- SSAT Math (Dragged) 4Document2 pagesSSAT Math (Dragged) 4Trúc HồNo ratings yet
- Physics - Study Guide - Tim Kirk - Oxford 2014 (Dragged) 5Document13 pagesPhysics - Study Guide - Tim Kirk - Oxford 2014 (Dragged) 5Trúc HồNo ratings yet
- Practice percents questionsDocument2 pagesPractice percents questionsTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Practice percents questionsDocument2 pagesPractice percents questionsTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Interior and Exterior Angles - Regular PolygonsDocument3 pagesInterior and Exterior Angles - Regular PolygonsTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- June 2015 (v1) QPDocument16 pagesJune 2015 (v1) QPTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- RelativityDocument2 pagesRelativityTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- 6 Circular OxfordDocument4 pages6 Circular OxfordGajendraNo ratings yet
- June 2015 (v2) QPDocument16 pagesJune 2015 (v2) QPTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- SSAT Math (Dragged) 6Document2 pagesSSAT Math (Dragged) 6Trúc HồNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 14.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 14.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- Volume of 3D Shapes - AdvancedDocument5 pagesVolume of 3D Shapes - AdvancedTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Areas and Volumes of Similar ShapesDocument6 pagesAreas and Volumes of Similar ShapesTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Questions: Electricity and Magne TismDocument5 pagesQuestions: Electricity and Magne TismTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Dimensions - Length, Area and VolumeDocument3 pagesDimensions - Length, Area and VolumeTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 2.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 2.1Alex Datsyuk100% (1)
- Intertu Education: Page 1 of 20 Concordian International SchoolDocument20 pagesIntertu Education: Page 1 of 20 Concordian International SchoolTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 7 1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 7 1Trúc HồNo ratings yet
- Topic - 11 - ALL - QUESTIONS - Pagenumber (Dragged)Document19 pagesTopic - 11 - ALL - QUESTIONS - Pagenumber (Dragged)Trúc HồNo ratings yet
- Gcse Physics Answers and Mark Schemes: ChargeDocument8 pagesGcse Physics Answers and Mark Schemes: ChargeTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of CircuitsDocument26 pagesMaking Sense of CircuitsTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Unit A181 02 Modules p1 p2 p3 Higher TierDocument12 pagesQuestion Paper Unit A181 02 Modules p1 p2 p3 Higher TierTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics Charge QuestionsDocument20 pagesGCSE Physics Charge QuestionsNahid MerghaniNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.3Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.3Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- International Baccalaureate HandbookDocument62 pagesInternational Baccalaureate HandbookTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Unit A182 02 Physics Modules p4 p5 p6 Higher Tier JuneDocument18 pagesMark Scheme Unit A182 02 Physics Modules p4 p5 p6 Higher Tier JuneTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Unit A181 02 Unit 01 Modules p1 p2 p3 Higher Tier JuneDocument17 pagesMark Scheme Unit A181 02 Unit 01 Modules p1 p2 p3 Higher Tier JuneTrúc HồNo ratings yet