Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IGCSE Physics Worksheet 2 1
IGCSE Physics Worksheet 2 1
Uploaded by
Trúc Hồ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesOriginal Title
312336109-IGCSE-Physics-Worksheet-2-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 2 1
IGCSE Physics Worksheet 2 1
Uploaded by
Trúc HồCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Worksheet 2.
1
Speed–time graphs
Solve some more problems involving speed–time graphs.
Notes
For a speed–time graph:
the steeper the slope, the greater the acceleration
distance travelled area under speed–time graph.
Questions
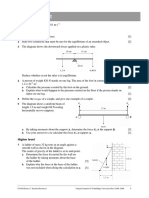
1 The graph shows how the speed of a car changed as it travelled along a
road.
a What was the car’s speed at the start?
b How fast was the car travelling after 10 s?
c How can you tell from the graph that, after 15 s, the car reached a
steady speed?
d What was the car’s speed after 15 s?
e How far did the car travel during the first 15 s?
f How far did the car travel during the first 30 s?
© Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ® Physics
Worksheet 2.1 1
2 The table shows how a train’s speed changed during part of its journey.
Speed / m/s 30 30 30 25 20 15
Time / s 0 20 40 60 80 100
a Draw a speed–time graph using the data in the table.
b Describe in words the motion of the train.
c From your graph, deduce the distance travelled by the train in 100 s.
3 Read this description of a car’s journey along a road.
At first, the car was stuck behind a slow bus. It travelled at a steady
speed of 8.0 m/s for 50 s. Then the bus turned off the road and the
driver increased the car’s speed so that, after another 10 s, it reached
a speed of 20 m/s. It travelled at this speed for 40 s.
a Draw a speed–time graph using the information in the description.
b The car’s journey was in three sections. From your graph, deduce the
distance travelled by the car in each section of its journey, and the
total distance it travelled.
© Cambridge University Press 2014 IGCSE ® Physics
Worksheet 2.1 2
You might also like
- Pressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsDocument14 pagesPressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsMohamed Jameel77% (31)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/42Summer ShuanNo ratings yet
- Waves Questions For 10 IGCSE Physics Formal ExamsDocument10 pagesWaves Questions For 10 IGCSE Physics Formal Examspixelhobo80% (5)
- Force - Grade 7 Science - Physics Test RevisionDocument2 pagesForce - Grade 7 Science - Physics Test RevisionRoygunEdwin0% (1)
- Earth in Space - Level 5 - QuestionsDocument20 pagesEarth in Space - Level 5 - QuestionsmanojNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Chapter 1 Questions and Answers - SolutionsDocument81 pagesIGCSE Physics Chapter 1 Questions and Answers - SolutionsAiyuu100% (2)
- 9-1-Forces-And-Motion (Edexcel Igcse) WorksheetDocument6 pages9-1-Forces-And-Motion (Edexcel Igcse) Worksheetertugoz100% (2)
- IGCSE Physics MCQ 1 Movement and PositionDocument7 pagesIGCSE Physics MCQ 1 Movement and PositionTaha ArshadNo ratings yet
- Moments WorksheetDocument2 pagesMoments Worksheetarieljuwo80% (5)
- 8 States of MatterDocument4 pages8 States of Matterrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 Density MCQDocument11 pagesYr 10 Density MCQsurabhiNo ratings yet
- SUVAT Practice WorksheetDocument1 pageSUVAT Practice WorksheetJorge100% (2)
- Earth in Space - Level 3 - QuestionsDocument6 pagesEarth in Space - Level 3 - Questionsmanoj50% (2)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 17.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 17.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 9.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 9.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 2.2Document3 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 2.2Alex Datsyuk100% (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.3Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.3Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- Unit Physics WorksheetsDocument10 pagesUnit Physics WorksheetsVarshLok100% (2)
- 04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..Document3 pages04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..Ashani0001100% (1)
- IGCSE - Physics - MCQ 3 - Forces and MovementDocument7 pagesIGCSE - Physics - MCQ 3 - Forces and MovementKyi Nue KhinNo ratings yet
- Light Worksheet IGCSE PhysicsDocument5 pagesLight Worksheet IGCSE PhysicspottyNo ratings yet
- 11.1f Distance Time TESDocument13 pages11.1f Distance Time TESshamsNo ratings yet
- Vector QuestionsDocument3 pagesVector QuestionsNudrat100% (4)
- Electromagnetic Effects (Multiple Choice) QP (Answer)Document37 pagesElectromagnetic Effects (Multiple Choice) QP (Answer)Catherine Dharshini LabrooyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 IG I Physics (1) Adding ForcesDocument3 pagesWorksheet 6 IG I Physics (1) Adding ForcesRaj Malkan100% (1)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.2Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.2Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- Motion Speed-Time Graphs Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE GCSE O Level Physics 0625Document11 pagesMotion Speed-Time Graphs Classified Past Paper 2 Solved IGCSE GCSE O Level Physics 0625IGCSE Physics & Chemistry100% (1)
- IGCSE Grade 6 PhysicsDocument5 pagesIGCSE Grade 6 PhysicsSathya MarieNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsDocument32 pagesIGCSE 23 Current&VoltageInCircuitsSam JordanNo ratings yet
- Static-Electricity (Edexcel Igcse) WorksheetDocument9 pagesStatic-Electricity (Edexcel Igcse) Worksheetertugoz100% (1)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 8.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 8.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- Refraction WorksheetDocument2 pagesRefraction WorksheetRicardo Johnson0% (1)
- Physics Year 9 Schemes of WorkDocument12 pagesPhysics Year 9 Schemes of WorkMaoga2013100% (1)
- CHAPTER 10 SC Measuring MotionDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 10 SC Measuring MotionEunice Xiiao Wenn100% (2)
- IGCSE Physics - Section 1 - Forces and Motion - Practice Exam Questions. Question 1Document20 pagesIGCSE Physics - Section 1 - Forces and Motion - Practice Exam Questions. Question 1Gajendra50% (2)
- Waves and Interference Worksheet 2Document14 pagesWaves and Interference Worksheet 2Freya SawNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Sound and Waves QP MSDocument5 pagesIGCSE Physics Sound and Waves QP MShasnizaaziz39No ratings yet
- Equations of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesEquations of Motion WorksheettuvvacNo ratings yet
- Pressure 2022-2023 18.2Document7 pagesPressure 2022-2023 18.2JAKE PAULNo ratings yet
- Gcse Physics: Boyle's Law QuestionsDocument3 pagesGcse Physics: Boyle's Law Questionsamvijayagopal75% (4)
- O Level Wave MCDocument6 pagesO Level Wave MCDora Aye0% (1)
- IGCSE Mock Test Paper - Static ElectricityDocument5 pagesIGCSE Mock Test Paper - Static ElectricityRizzzme100% (1)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 16.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 16.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- Igcse 33 LightwavesDocument36 pagesIgcse 33 LightwavesHany ElGezawy100% (7)
- Cambridge IGCSE Physics Coursebook Second Edition (Cambridge University Press) - Pages-DeletedDocument22 pagesCambridge IGCSE Physics Coursebook Second Edition (Cambridge University Press) - Pages-DeletedMariam ShehabNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesHooke's Law Worksheetibnurasheeda75% (4)
- Thermal Physics CIE IGCSE 0625 PPQDocument11 pagesThermal Physics CIE IGCSE 0625 PPQPeter IsigiNo ratings yet
- Name - IGCSE-Hooke's Law WorksheetDocument10 pagesName - IGCSE-Hooke's Law WorksheetHayaa KhanNo ratings yet
- 5054 Space Physics Practice QuestionsDocument14 pages5054 Space Physics Practice QuestionsSoya BeansNo ratings yet
- Turning Forces - MomentsDocument4 pagesTurning Forces - Momentsphydotsi100% (4)
- IGCSE Physics Workbook Answers: 1 Measurement and MotionDocument16 pagesIGCSE Physics Workbook Answers: 1 Measurement and MotionBasratul RafidNo ratings yet
- Physics 5054 OL P1 MCQs 2015-2019 All VsDocument309 pagesPhysics 5054 OL P1 MCQs 2015-2019 All VsHanaa Ibrahim Ali50% (2)
- Radioactive Worksheet IGCSEDocument2 pagesRadioactive Worksheet IGCSESyakti PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Sankey Diagram Efficiency + Energy TransferDocument4 pagesSankey Diagram Efficiency + Energy TransferSelwah Hj AkipNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 23.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 23.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- 1 Mass, Weight, Density and VolumeDocument7 pages1 Mass, Weight, Density and Volumeelty TanNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (1)
- IGCSE Thermal Physics WorksheetDocument1 pageIGCSE Thermal Physics Worksheetgdsuta67% (3)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 15.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 15.1Alex Datsyuk0% (1)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 20.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 20.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 11.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 11.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 18.2Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 18.2Alex Datsyuk50% (2)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 16.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 16.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 18.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 18.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 22.1Document3 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 22.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 23.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 23.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 8.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 8.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 10.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 10.1Alex Datsyuk50% (2)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 12.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 12.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 7.2Document3 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 7.2Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 7.3Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 7.3Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.2Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.2Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.1Alex Datsyuk100% (1)
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 6.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 6.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.3Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 3.3Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 5.1Document3 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 5.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 7.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 7.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 4.1Document2 pagesIGCSE Physics Worksheet 4.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet