Professional Documents
Culture Documents
First quarter ABM 2 review
Uploaded by
Psalm Ruvi TalaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
First quarter ABM 2 review
Uploaded by
Psalm Ruvi TalaCopyright:
Available Formats
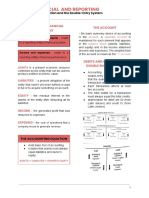
FIRST SEM, FIRST QUARTER – UNIT ASSESSMENT
REVIEWER FOR FUNDAMENTALS OF ABM 2
ADJUSTING ENTRIES - result of past events
- future economic benefits are expected to
- entries made at the end of the accounting flow to the entity
period before closing procedures to update
balances of asset, liability, revenue and CURRENT ASSETS – expects to realize the
expense accounts to make their balances asset or intends to sell or consume it on its normal
ready for their preparation of financial operating cycle
position.
- primarily for the purpose of trading
- expects to realize the asset within twelve
KINDS OF ADJUSTING ENTRIES months after reporting period
- cash or cash equivalent unless the asset is
1.) Prepaid Expenses – starts as an asset, restricted from being exchanged or used to
ends as an expense settle liability for at least twelve months after
2.) Deferred Revenue – liability – revenue reporting period
3.) Accrued Revenue – earned revenue but no
payment example:
4.) Accrued Expense – expenses were
incurred but with no payment cash prepaid expenses
5.) Asset Depreciation – systematic way of accounts receivables office supplies
allocating the value of an asset decline
NONCURRENT ASSETS – all other assets
ADJUSTING ENTRIES ADHERE TO: that is not current
- completeness example:
- freedom from error
- timeliness land land improvements
- accrual basis of accounting machineries equipments
- revenue recognition
- matching principle ♥ LIABILITIES – present obligation of the
entity from past events
- settlement is expected to result in outflow
DEPRECIATION – decline in value of an asset from the entity of resources
due to wear and tear, obsolescence and
passage of time CURRENT LIABILITIES – expects
to settle the liability on its normal operating
RESIDUAL VALUE – the value expected in the cycle
asset after its useful life - holds liability primarily for the purpose of
trading
STRAIGHT LINE DEPRECIATION - due to be settled within twelve months after
the reporting period
asset cost – residual value / life in years - does not have an unconditional right to
defer settlement for at least 12 months after
= annual depreciation
the reporting perios
example
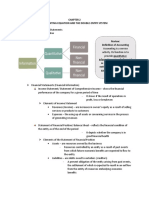
STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION trade accounts payable short term payable
salaries payable income tax
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS – structured payable
representation of the financial position and
financial performance of an entity NONCURRENT LIABILITIES – all
liabilities that is not current
- the objective of financial statements is to
provide information about the financial example
position, financial performance and cash bonds payable
flow of an entity long-term notes payable
- useful to a wide range of users in making
sound decision EQUITY – residual interest in the assets of
the entity after deducting all its liabilities
Financial statements provide info about
entity’s:
a. assets ASSETS = LIABILITIES
b. liabilities +
c. equity CAPITAL
d. income and expenses
e. contributions by and to owners in their CURRENT CURRENT LIABILITIES
company as owners ASSETS NONCURENT LIABILITIES
f. cash flows = +
NONCURRENT EQUITY
BALANCE SHEET ELEMENTS ASSETS
♥ ASSETS – resource
- result of past events
PSALM TALA
12- ABM WEDGWOOD
SCC – SHS 2021-2022
You might also like
- 8e Ch3 Mini Case Planning MemoDocument8 pages8e Ch3 Mini Case Planning Memotom0% (3)
- Basic accounting model and key concepts in 40 charactersDocument3 pagesBasic accounting model and key concepts in 40 charactersdlinds2X1No ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Financial ManagementRitesh ShreshthaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument7 pagesNotesHi NameNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument27 pagesFinancial StatementsIrish Castillo100% (1)
- Introduction To Accounting JGF - July 31 and Aug 1Document16 pagesIntroduction To Accounting JGF - July 31 and Aug 1LARINGO IanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemalonNo ratings yet
- Notes FAR 2Document9 pagesNotes FAR 2ALLYSA DENIELLE SAYATNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation TitleDocument4 pagesAccounting Equation TitleReniel MillarNo ratings yet
- FABM2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesFABM2 ReviewerMakmak NoblezaNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1ST Sem CH1234Document12 pagesFabm 1ST Sem CH1234Mary Franchesca RodaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Financial PositionDocument2 pagesStatement of Financial PositionRhianne AndradaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter DiscussionDocument10 pages1st Quarter DiscussionThea Gwyneth RodriguezNo ratings yet
- AC AcctgSplTran CompilationDocument8 pagesAC AcctgSplTran CompilationJeorjeana ManguerraNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Module 1 - 3Document5 pagesFinancial Management - Module 1 - 322-54470No ratings yet
- FINC6021 - Financial StatementsDocument126 pagesFINC6021 - Financial Statements尹米勒No ratings yet
- FARreviewerDocument5 pagesFARreviewerKimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Accounting: Basic Financial StatementsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Accounting: Basic Financial StatementsStellaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Fabm2Document7 pagesReviewer Fabm2Anne BustilloNo ratings yet
- ABO ReviewerDocument3 pagesABO ReviewerJulianne Hazel EpeNo ratings yet
- CFAS Part 5Document10 pagesCFAS Part 5AINAH SALEHA MIMBALAWAGNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting NotesDocument7 pagesFinancial Accounting NotesGan JessieNo ratings yet
- ABM 2 - Statement of Financial PositionDocument19 pagesABM 2 - Statement of Financial PositionMarlou Chester BendañoNo ratings yet
- THE Accounting Equation (Module 5, Camerino, D.)Document10 pagesTHE Accounting Equation (Module 5, Camerino, D.)Che AllejeNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter DiscussionDocument10 pages1st Quarter DiscussionCHARVIE KYLE RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument20 pagesConceptual Framework For Financial ReportingSamuel GlovaNo ratings yet
- Accounting ConceptsDocument3 pagesAccounting ConceptsVic BalmadridNo ratings yet
- ACCA101 Study Guide: Exams 1.1 Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesACCA101 Study Guide: Exams 1.1 Key ConceptsBeatrice Dominique C. PepinoNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2Document5 pagesFabm 2Robillos FaithNo ratings yet
- Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesFinancial StatementsGhillian Mae GuiangNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 3 ReviewerDocument22 pagesIntermediate Accounting 3 ReviewerRichelle Joy Bonggat100% (1)
- BSA Qualifying Exam Reviewer: Financial Accounting TheoriesDocument26 pagesBSA Qualifying Exam Reviewer: Financial Accounting TheoriesJanine AnzanoNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements: General Purpose FS: For Users Not in The Position ToDocument3 pagesFinancial Statements: General Purpose FS: For Users Not in The Position ToRoyce DenolanNo ratings yet
- LiabilitiesDocument4 pagesLiabilitiessafe.skies00No ratings yet
- Accounting Reviewer 2nd Long TestDocument45 pagesAccounting Reviewer 2nd Long TestZachary Job YuipcoNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles and Business Transactions Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageAccounting Principles and Business Transactions Cheat Sheet: by Viaheehan6No ratings yet
- Handout - Intro To Financial StatementsDocument2 pagesHandout - Intro To Financial StatementsApril SasamNo ratings yet
- (C3) The Accounting Equation & Types of AccountsDocument3 pages(C3) The Accounting Equation & Types of AccountsVenus LacambraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 2 Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemGabrielle Joshebed AbaricoNo ratings yet
- Acc124 Week 1 Ulo DDocument3 pagesAcc124 Week 1 Ulo DBaby Leonor RazonableNo ratings yet
- AccReview Part 4 of 5Document3 pagesAccReview Part 4 of 5Jenny ManalastasNo ratings yet
- FabmDocument5 pagesFabmJihane TanogNo ratings yet
- Accounting - PonesDocument4 pagesAccounting - PonesLuisa PonesNo ratings yet
- ACC111Document5 pagesACC111Trisha SacmanNo ratings yet
- SYAT Bookkeeping TutorialDocument35 pagesSYAT Bookkeeping TutorialJanelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Current Vs Non-Current AssetsDocument3 pagesCurrent Vs Non-Current AssetsTrisha GarciaNo ratings yet
- Financial Position and Cash Flow Statement OverviewDocument11 pagesFinancial Position and Cash Flow Statement OverviewHoneybunch beforeNo ratings yet
- Fabm 2 Second Quarter NotesDocument7 pagesFabm 2 Second Quarter NotesBIGTING, DANIANA MEURNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument3 pagesAccounting NotesDorothy LeeNo ratings yet
- Common practice in Philippines financial reportingDocument2 pagesCommon practice in Philippines financial reportingKaren CaelNo ratings yet
- Far 1 ReviewerDocument12 pagesFar 1 ReviewerMargarette RobiegoNo ratings yet
- PAS 1: Requirements for Financial Statement PresentationDocument1 pagePAS 1: Requirements for Financial Statement PresentationElisha ENo ratings yet
- Accounting Glossary: © OUP 2013: This Can Be Reproduced For Class Use Solely For The Purchaser's InstituteDocument13 pagesAccounting Glossary: © OUP 2013: This Can Be Reproduced For Class Use Solely For The Purchaser's InstituteAdeenaNo ratings yet
- Receivables Are Financial Assets That Represent A Contractual Right To Receive Cash or Another Financial Asset FromDocument3 pagesReceivables Are Financial Assets That Represent A Contractual Right To Receive Cash or Another Financial Asset FromMjhayeNo ratings yet
- FAR ReviewerDocument1 pageFAR ReviewerAllyson Charissa AnsayNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Acocunting and Business Management 1 2Document14 pagesFundamentals of Acocunting and Business Management 1 2kristinekaylegusimat12No ratings yet
- Balance Sheet Projected 1Document1 pageBalance Sheet Projected 1Fred CastroNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet Projected 1Document1 pageBalance Sheet Projected 1Marco Antônio Rodrigues SilvaNo ratings yet
- Proof of Cash Accounts ReceivableDocument2 pagesProof of Cash Accounts Receivablemagic costaNo ratings yet
- FAR Chapt. 7Document8 pagesFAR Chapt. 7Ryan GaniaNo ratings yet
- ACC CONCEPTS, PRINCIPLES & ASSUMPTIONSDocument4 pagesACC CONCEPTS, PRINCIPLES & ASSUMPTIONSYessameen Franco R. CastilloNo ratings yet
- For Machinery and Office EquipDocument2 pagesFor Machinery and Office EquipPsalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK AND ACCOUNTING STANDARDSDocument6 pagesCONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK AND ACCOUNTING STANDARDSPsalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- Ge 09 - The Life and Works of RizalDocument5 pagesGe 09 - The Life and Works of RizalPsalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesMidterm ReviewerPsalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Week 1Document3 pagesEntrepreneurship: Week 1Psalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- Business MathDocument2 pagesBusiness MathPsalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Week 1Document3 pagesEntrepreneurship: Week 1Psalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- First quarter ABM 2 reviewDocument1 pageFirst quarter ABM 2 reviewPsalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- Denominator Is The Number Below TheDocument2 pagesDenominator Is The Number Below ThePsalm Ruvi TalaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Audit of Investment PropertyDocument11 pagesUnit I: Audit of Investment PropertyMarj ManlagnitNo ratings yet
- ACCA SBR Course NotesDocument412 pagesACCA SBR Course NotesAhsanMughalAcca100% (11)
- Prof P. KrishnaDocument26 pagesProf P. KrishnaChetan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cost Concept and Behavior RaibornDocument40 pagesCost Concept and Behavior RaibornRJ MonsaludNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Caselet AnalysisDocument11 pagesFinancial Management Caselet AnalysisThandapani PalaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Cost ConceptDocument54 pagesChapter 2-Cost ConceptCik MinnNo ratings yet
- LBO Blank TemplateDocument15 pagesLBO Blank TemplateBrian DongNo ratings yet
- ECF1100 Individual Assignment 2 Sem 1 2022Document4 pagesECF1100 Individual Assignment 2 Sem 1 2022wesley hudsonNo ratings yet
- Cfas ReviewerDocument6 pagesCfas Reviewerkeisha santosNo ratings yet
- Acctg3&4 - QuizDocument2 pagesAcctg3&4 - QuizJobesonNo ratings yet
- Cost II AssignmentDocument4 pagesCost II AssignmentmeazadgafuNo ratings yet
- Zoca Courtyard DPRDocument24 pagesZoca Courtyard DPRbrijeshbabu1019No ratings yet
- Caplin Point LabDocument76 pagesCaplin Point Lab40 Sai VenkatNo ratings yet
- Format of Cash Flow Statement as per SEBIDocument3 pagesFormat of Cash Flow Statement as per SEBIMoses Fernandes100% (1)
- Job Orede CostingDocument13 pagesJob Orede Costingአረጋዊ ሐይለማርያምNo ratings yet
- Stock Acquisition - Subsequent To DOADocument2 pagesStock Acquisition - Subsequent To DOAShekinah Grace SantuaNo ratings yet
- Accounting FundamentalsDocument13 pagesAccounting FundamentalsMaria Nena LoretoNo ratings yet
- Premium Packaging SolutionsDocument27 pagesPremium Packaging SolutionsMiguel Couto RamosNo ratings yet
- STRAT ReviewerDocument13 pagesSTRAT ReviewerCrisel SalomeoNo ratings yet
- Enager Industries, Inc.: The Crimson Press Curriculum Center The Crimson Group, IncDocument5 pagesEnager Industries, Inc.: The Crimson Press Curriculum Center The Crimson Group, IncVakul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 10%Document3 pagesAssignment1 10%Felicia ChinNo ratings yet
- 8919 - Consolidation Subsequent To The Date of AcquisitionDocument4 pages8919 - Consolidation Subsequent To The Date of AcquisitionFayehAmantilloBingcangNo ratings yet
- IFRS 1 First-time Adoption SummaryDocument2 pagesIFRS 1 First-time Adoption SummarypiyalhassanNo ratings yet
- BCG InsideSherpa Core Strategy - Telco (Task 2 Model Answer) - FinalDocument10 pagesBCG InsideSherpa Core Strategy - Telco (Task 2 Model Answer) - FinalSiddharthNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsTULIO, Jeremy I.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Ic26 Chapter 1 Ic26: 1 MessageDocument207 pagesChapter 1 Ic26 Chapter 1 Ic26: 1 Messagekrishan kumarNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting First AssignmentDocument6 pagesFinancial Accounting First AssignmentZamzama azimiNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Internasionalisasi, Afiliasi Bisnis, Dan Research & Development Terhadap Kinerja Perusahaan Manufaktur Di IndonesiaDocument14 pagesPengaruh Internasionalisasi, Afiliasi Bisnis, Dan Research & Development Terhadap Kinerja Perusahaan Manufaktur Di IndonesiaRicky AuliaNo ratings yet