Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PARADO Pathogenesisofcovid
PARADO Pathogenesisofcovid
Uploaded by
Eanna Parado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
PARADO_pathogenesisofCovid
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pagePARADO Pathogenesisofcovid
PARADO Pathogenesisofcovid
Uploaded by
Eanna ParadoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
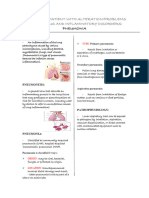
PATHOGENESIS OF
transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurs
primarily between people through direct,
indirect, or close contact with infected
people through infected secretions such as
Stage 1: Asymptomatic state (initial 1–2 saliva and respiratory secretions, or through
days of infection) their respiratory droplets, which are expelled
when an infected person coughs, sneezes,
talks or sings.
virus can be detected
by nasal swabs
Stage 2: Upper airway and conducting
airway response (next few days)
The virus propagates and migrates down
the respiratory tract along the conducting
airways, and a more robust innate
immune response is triggered. Nasal
swabs or sputum should yield the virus
(SARS-CoV-2) as well as early markers of
For about 80% of the infected patients, the
disease will be mild and mostly restricted to the innate immune response. At this time,
the upper and conducting airways. These the disease COVID-19 is clinically
individuals may be monitored at home with manifest
conservative symptomatic therapy. Stage 3: Hypoxia, ground glass infiltrates,
and progression to ARDS
The virus now reaches the gas exchange units
of the lung and infects alveolar type II cells.
Both SARS-CoV and influenza preferentially
infect type II cells compared to type I cells. The
infected alveolar units tend to be peripheral
and subpleural. SARS-CoV propagates within
type II cells, large number of viral particles are
released, and the cells undergo apoptosis and
die. The end result is likely a self-replicating
pulmonary toxin as the released viral particles
infect type II cells in adjacent units.
You might also like
- Agesta Sacred Codes ListDocument22 pagesAgesta Sacred Codes Listmimigogo93% (14)
- Research Proposal: (Company Name)Document9 pagesResearch Proposal: (Company Name)Sagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Therapeutic Exercise Foundations and Techniques 6th Edition KisnerDocument5 pagesTest Bank For Therapeutic Exercise Foundations and Techniques 6th Edition KisnerSharonScottdizmr100% (60)
- CKD Case StudyDocument27 pagesCKD Case StudyMary Rose Vito100% (1)
- NCM 112 Covid-19Document5 pagesNCM 112 Covid-19Fifa100% (1)
- Viral TransmissionDocument22 pagesViral TransmissionUmer ZohaibNo ratings yet
- Reducir La Transmision Del Sars Cov 2Document4 pagesReducir La Transmision Del Sars Cov 2Sarita CadenaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Virus Infections: Understanding COVID-19: PrimerDocument5 pagesRespiratory Virus Infections: Understanding COVID-19: PrimerNaresh world SinghNo ratings yet
- The Epidemiological Triangle On COVID 19Document2 pagesThe Epidemiological Triangle On COVID 19Pinku KhanNo ratings yet
- Insights: Reducing Transmission of Sars-Cov-2Document4 pagesInsights: Reducing Transmission of Sars-Cov-2epraetorianNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Infection: Origin, Transmission, and Characteristics of Human CoronavirusesDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 Infection: Origin, Transmission, and Characteristics of Human CoronavirusesVeronicaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Mascarillas Protegen Aun Mal PuestasDocument11 pagesCoronavirus Mascarillas Protegen Aun Mal PuestasYamile Esther Vergara CuelloNo ratings yet
- Strukur VirusDocument7 pagesStrukur Viruscika daraNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 InforgraphicsDocument1 pageCOVID-19 InforgraphicsLavigne EmphasisNo ratings yet
- Lyza Joy N. Bolos Grafe 10 Assertive English Quarter 4 LAS-2Document7 pagesLyza Joy N. Bolos Grafe 10 Assertive English Quarter 4 LAS-2Lyza Joy Naag BolosNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With Alteration/Problems in Infectious and Inflammatory DisordersDocument8 pagesCare of Patient With Alteration/Problems in Infectious and Inflammatory Disordersyn8jg9fwx6No ratings yet
- Cause: Symptomatic) or Have Very Mild Symptoms, and Can Also Spread The VirusDocument3 pagesCause: Symptomatic) or Have Very Mild Symptoms, and Can Also Spread The VirusGrayNo ratings yet
- Chain of InfectionDocument1 pageChain of Infectionugochinyere OnumbaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis: Covid-19, H1N1, Sars-Cov, and Mers-CovDocument10 pagesComparative Analysis: Covid-19, H1N1, Sars-Cov, and Mers-CovEdelrose Lapitan100% (1)
- MERAJ AACOP CoronaDocument1 pageMERAJ AACOP CoronaMeraj SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Knowledge For Healthcare Students & ProfessionalsDocument1 pageCOVID-19 Knowledge For Healthcare Students & ProfessionalsNisa septianiNo ratings yet
- Consequences of Cov-19 Infection 2Document15 pagesConsequences of Cov-19 Infection 2MustafaNo ratings yet
- Viral Infections Acquired Indoors Through Airborne, Droplet or Contact TransmissionDocument9 pagesViral Infections Acquired Indoors Through Airborne, Droplet or Contact TransmissionClaudio SollarenNo ratings yet
- COVID19 Research PaperDocument9 pagesCOVID19 Research PaperLove AmitNo ratings yet
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2Document31 pagesSevere Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2Ian VillacrusisNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Lungs - Michelle CumbaaDocument1 pagePathogens of The Lungs - Michelle CumbaaMicroposterNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Infection: Origin, Transmission, and Characteristics of Human CoronavirusesDocument6 pagesCOVID-19 Infection: Origin, Transmission, and Characteristics of Human CoronavirusesmirakeNo ratings yet
- Science of Masking FullDocument28 pagesScience of Masking FullVyanky Shedge0% (1)
- Explanation Text Essay Writing WorksheetDocument2 pagesExplanation Text Essay Writing WorksheetThoriq KNo ratings yet
- Systematic Review On Novel Corona Virus: Origin, Transmission, Role of Immunity and Ayurveda As Therapeutic Potential in Treating COVID-19Document9 pagesSystematic Review On Novel Corona Virus: Origin, Transmission, Role of Immunity and Ayurveda As Therapeutic Potential in Treating COVID-19Sabrina JonesNo ratings yet
- Severe - Acute - Respiratory - Syndrome - Coronavirus - 2 WikiDocument30 pagesSevere - Acute - Respiratory - Syndrome - Coronavirus - 2 WikiUnggul YudhaNo ratings yet
- Birao Sas 11 Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument10 pagesBirao Sas 11 Microbiology and ParasitologyFrancis Jacob Dejecacion GarcesNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument8 pagesCommunicable DiseasesjadantonioNo ratings yet
- Name: Ishak Djafar Class: Xi Science 2: General StatementDocument2 pagesName: Ishak Djafar Class: Xi Science 2: General StatementMohamad Iswanto RahmanNo ratings yet
- The Common Cold: Diane E. PappasDocument5 pagesThe Common Cold: Diane E. PappasMFerdyYahyaRamadhanNo ratings yet
- Ten Reason Airborne Covid19 92Document3 pagesTen Reason Airborne Covid19 92Miguel AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Ten Scientific Reasons in Support of Airborne Transmission of Sars-Cov-2Document3 pagesTen Scientific Reasons in Support of Airborne Transmission of Sars-Cov-2tuanda222No ratings yet
- Coronaviruses Perlman-and-McIntosh 155 PDFDocument12 pagesCoronaviruses Perlman-and-McIntosh 155 PDFVenkatesan DevendranNo ratings yet
- COVID-19: Coronavirus Replication, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic StrategiesDocument7 pagesCOVID-19: Coronavirus Replication, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic StrategiesSarahNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document37 pagesCovid 19Jackson KalwijiNo ratings yet
- LINESES MAXILLA Chain of Infection WorksheetDocument5 pagesLINESES MAXILLA Chain of Infection Worksheetlineses.pkhNo ratings yet
- 16.science and Technology 3 Target - Prelims - 2020Document46 pages16.science and Technology 3 Target - Prelims - 2020naseerNo ratings yet
- Covid SNTDocument7 pagesCovid SNTChetan MitraNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Brief Compilation of Facts: Letter To EditorDocument3 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019: A Brief Compilation of Facts: Letter To Editorporkodi sudhaNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: Department: Roll No.: Subject: Course Code: Cr. HR.: Submitted To: Date of Submission: TopicDocument2 pagesName: Class: Department: Roll No.: Subject: Course Code: Cr. HR.: Submitted To: Date of Submission: TopicAnoosha FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseLordson Gem P. IbonNo ratings yet
- Influenza Virus and SARS-CoV-2 - PathogenesisDocument17 pagesInfluenza Virus and SARS-CoV-2 - PathogenesisTatiana DiazNo ratings yet
- Ca2 CDNDocument17 pagesCa2 CDNcrix crixNo ratings yet
- Prelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderDocument3 pagesPrelims - GMJ Lecture - Module 2 III DisorderjuiceNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseaseDocument10 pagesInfectious Diseaseshawnray1222No ratings yet
- Infectious Disease (Part 1) : Viral DiseasesDocument11 pagesInfectious Disease (Part 1) : Viral Diseasesmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- IPIntJComprAdvPharmacol 5-2-49 57Document9 pagesIPIntJComprAdvPharmacol 5-2-49 57jmakbar AkbarNo ratings yet
- Working in Lap of Corona Virus Disease (Covid - 19) at HMCH Hazaribagh JharkhandDocument3 pagesWorking in Lap of Corona Virus Disease (Covid - 19) at HMCH Hazaribagh JharkhandBIOMEDSCIDIRECT PUBLICATIONSNo ratings yet
- Infection PreventionDocument38 pagesInfection PreventionAmanda ScarletNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Nursing Notes Edited by Lovely Jovellanos 1Document4 pagesBasic Concepts of Nursing Notes Edited by Lovely Jovellanos 1Love Jovellanos ÜNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jun 01, 2022Document13 pagesAdobe Scan Jun 01, 2022rameshsolanki2046No ratings yet
- 4 M O MalpaniDocument4 pages4 M O MalpaniiyerrohitNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NCM 112Document4 pagesModule 1 NCM 112Kyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- COVID-19, Chronicle of An Expected Pandemic: EditorialDocument6 pagesCOVID-19, Chronicle of An Expected Pandemic: EditorialTheYeye97No ratings yet
- TP 3 Sexto AñoDocument3 pagesTP 3 Sexto Añomiss polyNo ratings yet
- COVIDDocument7 pagesCOVIDSky AgtarapNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension How Coronavirus Hijacks Your Cells: Apart On Contact With SoapDocument2 pagesReading Comprehension How Coronavirus Hijacks Your Cells: Apart On Contact With SoapPriscila LuftNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 SlidesDocument6 pagesCOVID-19 Slideskibu.cmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Infections of The Eye and Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesChapter 16 Infections of The Eye and Nervous SystemEanna ParadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Non-Specific Host Defense MechanismDocument5 pagesChapter 10 Non-Specific Host Defense MechanismEanna ParadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Specific Host Defense MechanismDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Specific Host Defense MechanismEanna ParadoNo ratings yet
- Infections of Gastrointestinal TractDocument12 pagesInfections of Gastrointestinal TractEanna ParadoNo ratings yet
- AIF - Hortatory Exposition TextDocument5 pagesAIF - Hortatory Exposition TextMbeXecute Bayha KolerisNo ratings yet
- Paleo Health Check ReportDocument11 pagesPaleo Health Check ReportVijayasarathi DharmarajNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Behavioral HealthDocument398 pagesFoundations of Behavioral HealthNhi TrầnNo ratings yet
- Best Team Memorial Respondent Nmims National Virtual Moot 20210519 200602 1 26Document26 pagesBest Team Memorial Respondent Nmims National Virtual Moot 20210519 200602 1 26diksha chouhanNo ratings yet
- Instructor's Presentation-Tumor MarkersDocument57 pagesInstructor's Presentation-Tumor MarkersMACOB, ETHELHYN JHANENo ratings yet
- AnticoagulatsDocument52 pagesAnticoagulatsanaya khan StudentNo ratings yet
- MSDS Corn CobDocument2 pagesMSDS Corn CobMUHAMMAD YOGA BRILLIANTONo ratings yet
- Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease - With STUDENT CONSULT Online Access, 8e (PDFDrive - Com) - 89-105Document17 pagesRobbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease - With STUDENT CONSULT Online Access, 8e (PDFDrive - Com) - 89-105bgfhnfgNo ratings yet
- 4 - Subclinical HypothyroidismDocument10 pages4 - Subclinical HypothyroidismAlejandra RNo ratings yet
- J HLC 2017 11 007Document8 pagesJ HLC 2017 11 007The Curious BenzNo ratings yet
- Academic Question Paper Test 8Document23 pagesAcademic Question Paper Test 8nguyenhonghanh0% (2)
- Saq 1Document68 pagesSaq 1joe kayongoNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONAIRE Research Final PDFDocument2 pagesQUESTIONAIRE Research Final PDFAli AfaqNo ratings yet
- Mentor Booklet (Jul 2021)Document207 pagesMentor Booklet (Jul 2021)skocabzzNo ratings yet
- 欧洲呼吸学会成人及儿童慢性咳嗽诊治指南Document31 pages欧洲呼吸学会成人及儿童慢性咳嗽诊治指南GaryNo ratings yet
- Human Diseases 6th Edition 2023 - 240401 - 210418Document610 pagesHuman Diseases 6th Edition 2023 - 240401 - 210418sc749518No ratings yet
- A Review of Return To Plau Issues and Sports Related ConcussionDocument8 pagesA Review of Return To Plau Issues and Sports Related ConcussionMarco FerreiraNo ratings yet
- HydrocortisoneDocument3 pagesHydrocortisoneunkown userNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia: by DR PP GevaoDocument46 pagesThalassemia: by DR PP GevaoAbubakar JallohNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulphate 1mg/1ml Emergency MedicationDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulphate 1mg/1ml Emergency MedicationRafiq EsufzaeNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument47 pagesHypothyroidismMuhammad Naqiuddin NaqiNo ratings yet
- 1 OnlineDocument6 pages1 Onlineanalisaapil312No ratings yet
- Identification: Infosafe No.: LPSIZ Issued Date: 30/03/2015 Issued By: Sibelco Australia LimitedDocument7 pagesIdentification: Infosafe No.: LPSIZ Issued Date: 30/03/2015 Issued By: Sibelco Australia Limitedsentient.bean8226No ratings yet
- Invitation Letter With Written Pledge EnglishDocument2 pagesInvitation Letter With Written Pledge EnglishADA ADA SAJANo ratings yet
- Caee Study For Clinical RotationsDocument8 pagesCaee Study For Clinical RotationseyesontheskyNo ratings yet
- Isk - AapDocument14 pagesIsk - AapRoberto SoehartonoNo ratings yet