Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Front Office Accounting
Uploaded by
Jeevesh ViswambharanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Front Office Accounting
Uploaded by
Jeevesh ViswambharanCopyright:
Available Formats
Front Office Accounting
Table of Contents
Front office accounting system
There are two types of accounts maintained by front office department with front
office accounting system:
FOLIOS
VOUCHERS
POINTS OF SALE (POS)
LEDGERS
ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS
CREDIT MONITORING
FRONT OFFICE ACCOUNTING SYSTEM FORMULA
INTERNAL CONTROL IN THE FRONT OFFICE
SETTLEMENT OF ACCOUNTS
Front office accounting system
Creates and maintains an accurate accounting record for each guest or non guest
account.
Front office accounting system tracks financial transactions through the guest cycle.
Front office accounting system ensures internal control over cash and non cash
transactions.
Front office accounting system records settlement for all goods and services provided.
Find latest hospitality resources at hmhub
|1
Front Office Accounting
There are two types of accounts maintained by front office department with front office
accounting system:
1. Guest Account
A guest account in front office accounting system is to record of financial transaction
between a guest and the hotel. It is created when the guests guarantee their reservations or
during registration. The front office usually seeks payment for charges during the departure
and settlement stage of the guest cycle.
2. Non-Guest Account
A hotel may extend in-house charge privileges to local businesses or agencies as a means of
promotion or to groups sponsoring meetings at the hotels. The front office creates non-guest
accounts to track these transactions which may also be called house accounts or city
accounts.
FOLIOS
Front office transactions are charted on account statements called folios. A folio is a
statement of all transactions (debits and credits) affecting the balance of a single account.
There are basically five types of folios used in front office accounting and maintained with
front office accounting system:
1. Guest Folios – Accounts assigned to individual guests or guestrooms.
2. Master Folios – Accounts assigned to more than one guest or guestroom, usually
applicable for group accounts.
3. Non-Guest or Semi-Permanent Folios – Accounts assigned to non-guest business or
agencies with hotel charge purchase privileges.
4. Employee Folios – Accounts assigned to employees with charge purchase privileges.
5. Split Folios – Accounts assigned to a guest on his/her request to split his/her charges and
payments between two personal folios – one to record expenses to be paid by the
sponsoring business company and the other to record personal expenses to be paid by
the guest. In this case two folios are created for the same guest.
VOUCHERS
A voucher details a transaction to be posted to a front office account. There are several
Find latest hospitality resources at hmhub
|2
Front Office Accounting
types of vouchers used in front office accounting system:
1. Cash Voucher – A voucher used to support a cash payment transaction at the front desk.
2. Charge Voucher – A voucher used to support a charge purchase transaction that takes
place somewhere other than the front office.
3. Allowance Voucher – A voucher used to support an account allowance.
Find latest hospitality resources at hmhub
|3
Front Office Accounting
4. Cash Advance Voucher – A voucher used to support cash flow out of the hotel, either
directly to or on behalf of the guest.
5. Correction Voucher – A voucher used to support the correction of a posting error which is
rectified before the close of business on the day the error was made.
6. Credit Card Voucher – A form designated by the credit card company to be used for
imprinting the credit card and recording the amount charged.
7. Paid-Out Voucher – A voucher used to support the cash disbursed by the hotel on behalf
Find latest hospitality resources at hmhub
|4
Front Office Accounting
of a guest.
8. Transfer Voucher – A voucher used to support a reduction in balance on one folio and an
equal increase in balance on another. Transfer vouchers are used for transfers between
guest accounts and for transfers from guest accounts to non-guest accounts when they
are settled by credit cards.
9. Travel Agency Voucher – In travel agent guaranteed reservation, the travel agent
forwards a voucher to the hotel as proof of payment and guarantees that the prepaid
amount will be sent to the hotel when the voucher is returned to the travel agency for
payment.
POINTS OF SALE (POS)
The term ‘point of sale’ denotes the location at which goods or services are purchased. Any
hotel department that collects revenue for its goods and services is considered a point of
sale. The front office accounting system must ensure that all charge purchases at these
points of sale are posted to the proper guest or non-guest account. A computerized POS
system allows terminals at the points of sale to communicate directly with a front office
computer system, and helps front office staff to create a well documented folio statement
with a minimum number of errors. Some basic information to be provided by the POS
includes the amount of the charge, name of the POS outlet, room number, name of the guest
and a brief description of the charge.
Find latest hospitality resources at hmhub
|5
Front Office Accounting
LEDGERS
A ledger is a summary grouping of accounts. A front office ledger is a collection of front
office account folios. There are two types of ledgers in front office accounting system:
Guest Ledger – It refers to the set of accounts related to the registered hotel guests. It is
also known as Transient ledger, Front Office ledger or Rooms ledger.
City Ledger – Also called the non-guest ledger, it is the collection of non-guest accounts.
It can contain credit card payment accounts, direct billing accounts, and accounts of past
guests due for collection by the hotel.
ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS
Non-Automated: Guest folios in a manual system contain a series of columns for listing
debit and credit entries accumulated during occupancy. At the end of the business day,
each column is totaled and the closing balance is carried forward as the opening balance
of the next day.
Semi-Automated – In this system, transactions are printed to a machine-posted folio.
Fully Automated – Computerized systems in which POS transactions are automatically
updated in the front office accounts.
CREDIT MONITORING
The front office accounting system must monitor guest and non-guest accounts to ensure
that they remain within acceptable credit limits.
Guests who present an acceptable credit card at registration may be extended credit
facility equal to the floor limit authorized by the issuing credit card company.
Guest and non-guest accounts with other approved credit arrangements are subject to
limitations established by the front office called house limit.
The night auditor is mainly responsible for identifying accounts which have reached or
exceeded the fixed credit limits. Such accounts are called high risk or high balance
accounts. The front office may deny additional charge purchase privileges to such
accounts.
This situation may be resolved by requesting the guest to make a partial payment or
requesting the credit card company to authorize additional credit.
Find latest hospitality resources at hmhub
|6
Front Office Accounting
FRONT OFFICE ACCOUNTING SYSTEM FORMULA
Transaction postings in the front office conform to a basic accounting formula, which
Previous Balance + Debits – Credits = Net Outstanding Balances
INTERNAL CONTROL IN THE FRONT OFFICE
Internal control in the front office involves:
Tracking transaction documentation
Verifying account entries and balances
Identifying vulnerabilities in the accounting system
Auditing is a process of verifying front office accounting records for accuracy. Certain
records are maintained to have a control in front office cash:
FRONT OFFICE CASH SHEET – The front office is responsible for a variety of cash
transactions affecting both guest and non-guest accounts. The front office cashiers have
to complete a front office cash sheet that lists each receipt or disbursement of cash.
CASH BANK – A cash bank is the amount of cash assigned to a cashier so that he/she can
handle the various transactions that occur during a particular work shift. Cashiers should
sign for their bank at the beginning of their shift and only the person who signs should
have access to it.
NET CASH RECEIPTS = Amount of Cash, Checks, Vouchers etc in the Cashier’s
Drawer – [Amount of Initial Cash Bank + Paid Outs]
OVERAGES – When the total of cash and checks in a cash drawer is greater than the initial
cash bank + net cash receipts
SHORTAGES – When the total of cash and checks in a cash drawer is less than the initial
cash bank + net cash receipts.
DUE BACK – A due back occurs when a cashier pays out more than he/she receives i.e.
there is not enough cash in the cash drawer to restore the initial cash bank. This may
happen when a cashier accepts many checks, or encashes large amount of foreign exchange
Find latest hospitality resources at hmhub
|7
Front Office Accounting
offered by a guest during shifts. These checks and bills are deposited with other receipts
and consequently the front office deposit may be greater than the cashier’s net cash
receipts, with the excess due back to the front office cashier’s bank.
AUDIT CONTROL – Internal auditors should make unannounced visits to the front office
cashier’s desk for auditing accounting records as well as conducting spot checks of the
cash bank of the cashier on duty. A report should be completed for management and
ownership review.
SETTLEMENT OF ACCOUNTS
The collection of payment for outstanding account balances is called account settlement
which involves bringing the account balance to zero. An account can be brought to zero
balance as a result of a cash payment in full or a transfer to an approved direct billing or
credit card account. All guest accounts must be settled at the time of check out.
Find latest hospitality resources at hmhub
|8
You might also like
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 13, Financial ManagementFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 13, Financial ManagementNo ratings yet
- Front Office Accounting Systems and ProcessesDocument5 pagesFront Office Accounting Systems and Processesmadhu anvekarNo ratings yet
- Front Office Accounting System TerminologyDocument6 pagesFront Office Accounting System TerminologypranithNo ratings yet
- Front Office Accounting ExplainedDocument10 pagesFront Office Accounting ExplainedpranithNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Guest Accounting - PT 2Document36 pagesBasic Concepts of Guest Accounting - PT 2Leonardo FloresNo ratings yet
- Front Office AccountingDocument13 pagesFront Office AccountingpranithNo ratings yet
- Front Office AccountingDocument7 pagesFront Office AccountingJaswinder SinghNo ratings yet
- 8.1669651497unit 8Document13 pages8.1669651497unit 8Riaz SardarNo ratings yet
- Front Office Accounting FundamentalsDocument11 pagesFront Office Accounting FundamentalsDawaNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY-SHEET-Q2-WEEK-1 (1)Document8 pagesACTIVITY-SHEET-Q2-WEEK-1 (1)Rochell Serranillo BanicoNo ratings yet
- Corporate Traveler Hotel Terms GuideDocument3 pagesCorporate Traveler Hotel Terms Guidevickie_sunnieNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Week 1 Hpc4Document13 pagesModule 1 Week 1 Hpc4Arvie Tejada100% (1)
- Front Office AccountingDocument6 pagesFront Office AccountingPreetyPriya100% (1)
- Front Office Management - AccountingDocument21 pagesFront Office Management - AccountingHunter KiranNo ratings yet
- Front Office Accounting FundamentalsDocument25 pagesFront Office Accounting Fundamentalsseemajaipuriar100% (1)
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledValentine Boco MontesNo ratings yet
- Notes On Frontoffice AccountingDocument38 pagesNotes On Frontoffice AccountingJaswinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Front office accounting basicsDocument5 pagesFront office accounting basicsGuneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Final LessonDocument8 pagesFinal LessonAngel Tabuena IINo ratings yet
- Hotel Accounting Chapter 01Document6 pagesHotel Accounting Chapter 01samaanNo ratings yet
- Night AuditDocument12 pagesNight AuditAshishDJosephNo ratings yet
- Front Office AccountingDocument9 pagesFront Office AccountingIga Asti AstriaNo ratings yet
- Front Office Cash Checkout and SettlementDocument21 pagesFront Office Cash Checkout and Settlementpranith100% (1)
- Cost Contro Ass2 - SemisDocument2 pagesCost Contro Ass2 - Semissamantha horlinaNo ratings yet
- Internal Control: Distinguish Between Floor Limit & House LimitDocument3 pagesInternal Control: Distinguish Between Floor Limit & House Limitsoundarya ReddyNo ratings yet
- HOTEL F&B INTERNAL CONTROLSDocument6 pagesHOTEL F&B INTERNAL CONTROLSJoydeep BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Front Office Services Night Audit From Other ReferenceDocument3 pagesFront Office Services Night Audit From Other ReferenceVicente VicenteNo ratings yet
- Night AuditDocument18 pagesNight AuditMandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- The Bank Account As A Tool For Controlling CashDocument11 pagesThe Bank Account As A Tool For Controlling CashJemal SeidNo ratings yet
- Hotel Accounting Procedures HS-3Document79 pagesHotel Accounting Procedures HS-3shivdas kaleNo ratings yet
- Front Office Department Training MaterialDocument52 pagesFront Office Department Training MaterialMurad Akmel HabibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 DUTYDocument19 pagesChapter 5 DUTYtemedebereNo ratings yet
- Night AuditDocument5 pagesNight AuditAshNo ratings yet
- Various Differentiation Between Front Office TerminologiesDocument3 pagesVarious Differentiation Between Front Office TerminologiesPritilata AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Notes Check Out and Settlement RC PDFDocument20 pagesNotes Check Out and Settlement RC PDFPrabir HalderNo ratings yet
- Night AuditDocument14 pagesNight AuditDinah Mae Alagao100% (1)
- Checkout and SettlementDocument19 pagesCheckout and Settlementmadhu anvekarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Acct - I, Lecture Note - Chapter 5-1Document13 pagesFundamentals of Acct - I, Lecture Note - Chapter 5-1Kiya GeremewNo ratings yet
- Front Office Voucher: Indrajit CDocument13 pagesFront Office Voucher: Indrajit CRuchi SongareNo ratings yet
- Front Office CashDocument4 pagesFront Office CashpranithNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledchef JamesNo ratings yet
- Applied Audititng Chapter-OneDocument39 pagesApplied Audititng Chapter-OneKumera Dinkisa ToleraNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Front Office AccountingDocument43 pagesUnit II - Front Office AccountingAdarsh ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Guest Charges, Payment and CHK OutDocument23 pagesGuest Charges, Payment and CHK OutDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Front Office (Accounting)Document9 pagesUnit 2 Front Office (Accounting)piyush agarwalNo ratings yet
- Cash and Marketable Securities-AuditDocument8 pagesCash and Marketable Securities-AuditFaruk H. IrmakNo ratings yet
- Front Office CashierDocument13 pagesFront Office CashierJen PequitNo ratings yet
- Front Office OperationsNotesDocument108 pagesFront Office OperationsNotesThomasJamesYodongNo ratings yet
- Front Office NC IIDocument24 pagesFront Office NC IIKathlyn AragonNo ratings yet
- Night Audit FunctionsDocument14 pagesNight Audit FunctionsKiran audinaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Ch-5 Cash & ReceivablesDocument97 pagesAccounting Ch-5 Cash & ReceivablesFeda EtefaNo ratings yet
- Cash Management in TBL Branches ID 1384Document8 pagesCash Management in TBL Branches ID 1384Saiful FaisalNo ratings yet
- Accommodation Unit-1,3Document25 pagesAccommodation Unit-1,3shikhaNo ratings yet
- Functions of Checkout and SettlementDocument4 pagesFunctions of Checkout and Settlementsoundarya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five CashDocument9 pagesChapter Five CashDawit TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Auditing, Hotel Front OfficeDocument22 pagesAuditing, Hotel Front OfficeVishnuNarayanan Viswanatha Pillai100% (1)
- Audit of CashDocument23 pagesAudit of CashmeseleNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping And Accountancy Made Simple: For Owner Managed Businesses, Students And Young EntrepreneursFrom EverandBookkeeping And Accountancy Made Simple: For Owner Managed Businesses, Students And Young EntrepreneursNo ratings yet
- Agent Banking Uganda Handbook: A simple guide to starting and running a profitable agent banking business in UgandaFrom EverandAgent Banking Uganda Handbook: A simple guide to starting and running a profitable agent banking business in UgandaNo ratings yet
- Urban GeographyDocument51 pagesUrban GeographyGuruKPO67% (3)
- Steps For Voluntary Winding Up Process of Company - Series 14Document9 pagesSteps For Voluntary Winding Up Process of Company - Series 14SHRINIDHINo ratings yet
- Business Regulations Cucbcss III Semester On29oct2015Document110 pagesBusiness Regulations Cucbcss III Semester On29oct2015akwadNo ratings yet
- 17 Course French Classical MenuDocument6 pages17 Course French Classical MenuJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Bansal (Definition and Scope of Urban Geo) PDFDocument10 pagesBansal (Definition and Scope of Urban Geo) PDFOwen NaldozaNo ratings yet
- MTTM C 202 Unit IDocument15 pagesMTTM C 202 Unit IJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- MTTM C 202 Unit IDocument15 pagesMTTM C 202 Unit IJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- MTTM C 204 Unit IDocument14 pagesMTTM C 204 Unit IJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Mba-C105Document48 pagesUnit-I Mba-C105Jeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Food Production NotesDocument42 pagesFood Production NotesRitika tiwari100% (3)
- MBA C 402 Unit IIDocument33 pagesMBA C 402 Unit IInaren mishraNo ratings yet
- MTTM C 204 Unit IDocument14 pagesMTTM C 204 Unit IJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- MTTM C 202 Unit IDocument15 pagesMTTM C 202 Unit IJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Draft Strategy For Medical and Wellness Tourism June 12Document29 pagesDraft Strategy For Medical and Wellness Tourism June 12Jeevesh Viswambharan100% (1)
- Steps For Voluntary Winding Up Process of Company - Series 14Document9 pagesSteps For Voluntary Winding Up Process of Company - Series 14SHRINIDHINo ratings yet
- 2) Classifi of HotelsDocument14 pages2) Classifi of HotelsAmit MondalNo ratings yet
- Information Request Under s.6 (1) of The Right To Information Act 2005Document3 pagesInformation Request Under s.6 (1) of The Right To Information Act 2005Jeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
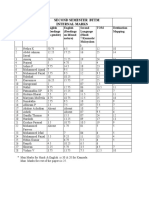
- Second Semester BTTM Internal MarksDocument3 pagesSecond Semester BTTM Internal MarksJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Unit-6, Keys and Key ControlDocument21 pagesUnit-6, Keys and Key ControlJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 GuestDocument3 pagesUNIT 2 GuestArj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Front Office AccountingDocument7 pagesFront Office AccountingJaswinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 During The Stay Activities: Mail HandlingDocument9 pagesUnit 6 During The Stay Activities: Mail HandlingKiran audinaNo ratings yet
- Staff Organization Structure: Assistant Front Office ManagerDocument9 pagesStaff Organization Structure: Assistant Front Office ManagerArun GautamNo ratings yet
- FRONT OFFICE MANAGEMENT SOFTWAREDocument47 pagesFRONT OFFICE MANAGEMENT SOFTWAREJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Concept of TeachingDocument7 pagesConcept of TeachingJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Hotel Front Office Guest Safety SecurityDocument15 pagesHotel Front Office Guest Safety SecurityJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Front Office Functions & OrganizationDocument9 pagesFront Office Functions & OrganizationJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Trip of Central India PDFDocument3 pagesTrip of Central India PDFJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Pilgrimage DestinationsDocument59 pagesPilgrimage DestinationsJeevesh ViswambharanNo ratings yet
- Warhammer Quest (Adventure) Priests of PleasureDocument8 pagesWarhammer Quest (Adventure) Priests of Pleasurefrankelee100% (1)
- The Bluest EyeDocument10 pagesThe Bluest EyeBethany0% (2)
- Trash Essay Emma LindheDocument2 pagesTrash Essay Emma Lindheapi-283879651No ratings yet
- "Wealth Builder": Mr. Rahul SharmaDocument5 pages"Wealth Builder": Mr. Rahul Sharmakrishna-almightyNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Generative AI Applications in Key IndustriesDocument2 pagesCase Study - Generative AI Applications in Key Industriessujankumar2308No ratings yet
- Varian9e LecturePPTs Ch38 PDFDocument76 pagesVarian9e LecturePPTs Ch38 PDF王琦No ratings yet
- Asobi CoinDocument37 pagesAsobi CoinVankokhNo ratings yet
- Inspired Love Presentation - Adam GiladDocument191 pagesInspired Love Presentation - Adam GiladJohn100% (1)
- SWOT On Philippine Port StateDocument7 pagesSWOT On Philippine Port StateLourisa LorenNo ratings yet
- FS Pimlico: Information GuideDocument11 pagesFS Pimlico: Information GuideGemma gladeNo ratings yet
- Attitudes and Behavior of Rural ConsumerDocument25 pagesAttitudes and Behavior of Rural ConsumerAlisha Bajpai67% (3)
- How to exploit insecure direct object references (IDOR) on Vimeo.comDocument4 pagesHow to exploit insecure direct object references (IDOR) on Vimeo.comSohel AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Cancer in The Army Identifying and Removing Toxic LeadersDocument47 pagesA Cancer in The Army Identifying and Removing Toxic LeadersFirebrand38No ratings yet
- Energy Management Systems Manual: (Company Name) AddressDocument48 pagesEnergy Management Systems Manual: (Company Name) AddressRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Bustos vs. Lucero, G.R. No. L-2068, October 20, 1948Document19 pagesBustos vs. Lucero, G.R. No. L-2068, October 20, 1948jam taumatorgoNo ratings yet
- Project Management - Harvard Management orDocument68 pagesProject Management - Harvard Management ortusharnbNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court of the Philippines upholds constitutionality of Act No. 2886Document338 pagesSupreme Court of the Philippines upholds constitutionality of Act No. 2886OlenFuerteNo ratings yet
- Top 7 Tips To Food Cost ControlDocument8 pagesTop 7 Tips To Food Cost ControlSubhasis BhaumikNo ratings yet
- DH 4012286Document5 pagesDH 4012286Edwin KurniawanNo ratings yet
- What Factors Affect Chinese Consumers Online Grocery Shopping Zhang 2020Document21 pagesWhat Factors Affect Chinese Consumers Online Grocery Shopping Zhang 2020Gus Mohammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- Doas LandDocument3 pagesDoas LandRudolfNo ratings yet
- 10 Basics of Ethical CommunicationDocument8 pages10 Basics of Ethical CommunicationsujzNo ratings yet
- Safety in PlantsDocument18 pagesSafety in PlantsVikas NigamNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of AUTOMOBILE COMPANIES (BMW & Daimler (Mercedes-Benz) )Document17 pagesFinancial Analysis of AUTOMOBILE COMPANIES (BMW & Daimler (Mercedes-Benz) )GUDDUNo ratings yet
- High Performance School Ancash Offers World of OpportunitiesDocument2 pagesHigh Performance School Ancash Offers World of OpportunitieswilliamNo ratings yet
- Intro to LCsDocument5 pagesIntro to LCsJara SadarNo ratings yet
- Vietnamese Rice Certificate DetailsDocument2 pagesVietnamese Rice Certificate DetailsNguyễn Thị Trà My100% (1)
- ISO Audit Findings ExplainedDocument4 pagesISO Audit Findings ExplainedJohn RajeshNo ratings yet
- Nike Inc Strategic Recommendation Report Part IDocument13 pagesNike Inc Strategic Recommendation Report Part IIkram Chakir100% (1)
- Mount ST Mary's CollegeDocument9 pagesMount ST Mary's CollegeIvan GutierrezNo ratings yet