Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The ASTM Website.: Standards Volume Information, Refer To The Standard's Document Summary Page On
Uploaded by
reiazhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The ASTM Website.: Standards Volume Information, Refer To The Standard's Document Summary Page On
Uploaded by
reiazhCopyright:
Available Formats
E1316 − 13d
2. Referenced Documents 3. Significance and Use
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: 3.1 The terms found in this standard are intended to be used
NOTE 1—This standard defines the terminology used in the standards uniformly and consistently in all nondestructive testing stan-
prepared by Committee E07 on Nondestructive Testing and published in dards. The purpose of this standard is to promote a clear
the Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Volume 03.03. understanding and interpretation of the NDT standards in
which they are used.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 4. Terminology
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Section A: Common NDT Terms
The terms defined in Section A are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.92, Editorial Review.
acceptable quality level—the maximum percent defective or flaw characterization, n—the process of quantifying the size,
the maximum number of units defective per hundred units shape, orientation, location, growth, or other properties, of a
that, for the purpose of sampling test, can be considered flaw based on NDT response.
satisfactory as a process average.
imperfection, n—a departure of a quality characteristic from
calibration, instrument, n—the comparison of an instrument its intended condition.
with, or the adjustment of an instrument to, a known
indication—the response or evidence from a nondestructive
reference(s) often traceable to the National Institute of
examination.
Standards and Technology (NIST). (See also DISCUSSION—An indication is determined by interpretation to be
standardization, instrument.) relevant, non-relevant, or false.
cognizant engineering organization—the company, govern- inspection, n—see preferred term examination.
ment agency or other authority responsible for the design, or
end use, of the material or component for which nondestruc- interpretation—the determination of whether indications are
tive testing is required. relevant or nonrelevant.
DISCUSSION—In addition to design personnel, the cognizant engineer- interpretation, n—the determination of whether indications
ing organization could include personnel from engineering, material are relevant, nonrelevant, or false.
and process engineering, stress analysis, nondestructive testing, quality
assurance and others, as appropriate. Nondestructive Evaluation—see Nondestructive Testing.
Nondestructive Examination—see Nondestructive Testing.
defect, n—one or more flaws whose aggregate size, shape,
Nondestructive Inspection—see Nondestructive Testing.
orientation, location, or properties do not meet specified
acceptance criteria and are rejectable. Nondestructive Testing (NDT), n—the development and ap-
plication of technical methods to examine materials or
discontinuity, n—a lack of continuity or cohesion; an inten- components in ways that do not impair future usefulness and
tional or unintentional interruption in the physical structure serviceability in order to detect, locate, measure and evaluate
or configuration of a material or component. flaws; to assess integrity, properties and composition; and to
measure geometrical characteristics.
evaluation—determination of whether a relevant indication is
cause to accept or to reject a material or component. nonrelevant indication, n—an NDT indication that is caused
by a condition or type of discontinuity that is not rejectable.
examination, n—a procedure for determining a property (or False indications are non-relevant.
properties) or other conditions or characteristics of a material
or component by direct or indirect means. reference standard, n—a material or object for which all
DISCUSSION—Examples include utilization of X-rays or ultrasonic relevant chemical and physical characteristics are known and
waves for the purpose of determining (directly or by calculation) flaw measurable, used as a comparison for, or standardization of,
content, density, or (for ultrasound) modulus; or detection of flaws by equipment or instruments used for nondestructive testing.
induction of eddy currents, observing thermal behavior, AE response, (See also standardization, instrument.)
or utilization of magnetic particles or liquid penetrants.
relevant indication, n—an NDT indication that is caused by a
false indication, n—an NDT indication that is interpreted to be condition or type of discontinuity that requires evaluation.
caused by a condition other than a discontinuity or imper-
fection. standard—(1) a physical reference used as a basis for com-
parison or calibration; (2) a concept that has been established
flaw, n—an imperfection or discontinuity that may be detect- by authority, custom, or agreement to serve as a model or
able by nondestructive testing and is not necessarily reject- rule in the measurement of quality or the establishment of a
able. practice or procedure.
Copyright by ASTM Int'l (all rights reserved); Tue Mar 18 09:11:19 EDT 2014
2
Downloaded/printed by
Reiaz Hosein (none) pursuant to License Agreement. No further reproductions authorized.
You might also like
- What Does NDT, NDE and NDI Stand For and Is There A Difference?Document6 pagesWhat Does NDT, NDE and NDI Stand For and Is There A Difference?reiazhNo ratings yet
- NDT Report TerminologyDocument1 pageNDT Report TerminologyreiazhNo ratings yet
- Inspection StepsDocument1 pageInspection StepsreiazhNo ratings yet
- NDT Report TerminologyDocument1 pageNDT Report TerminologyreiazhNo ratings yet
- Inspection StepsDocument1 pageInspection StepsreiazhNo ratings yet
- What Does NDT, NDE and NDI Stand For and Is There A Difference?Document6 pagesWhat Does NDT, NDE and NDI Stand For and Is There A Difference?reiazhNo ratings yet
- The ASTM Website.: Standards Volume Information, Refer To The Standard's Document Summary Page OnDocument1 pageThe ASTM Website.: Standards Volume Information, Refer To The Standard's Document Summary Page OnreiazhNo ratings yet
- DA62 Exterior Styling and Interior DesignDocument11 pagesDA62 Exterior Styling and Interior DesignreiazhNo ratings yet
- Paut Tofd Acfm Info-RDocument4 pagesPaut Tofd Acfm Info-RreiazhNo ratings yet
- ASNT L3 Renewal Required FormsDocument5 pagesASNT L3 Renewal Required FormsKeithNo ratings yet
- Paut Tofd Acfm Info PDFDocument16 pagesPaut Tofd Acfm Info PDFreiazhNo ratings yet
- TCG BlockDocument1 pageTCG BlockreiazhNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Testing Q&A Level IIDocument11 pagesMagnetic Particle Testing Q&A Level IIreiazhNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Testing Level 2 GuideDocument22 pagesMagnetic Particle Testing Level 2 GuidereiazhNo ratings yet
- ASTM E824 Light Meter CalibrationDocument6 pagesASTM E824 Light Meter CalibrationreiazhNo ratings yet
- Facts and Specifications: More of The BestDocument2 pagesFacts and Specifications: More of The BestreiazhNo ratings yet
- Reiaz Hosein Resume September 2017Document6 pagesReiaz Hosein Resume September 2017reiazhNo ratings yet
- Ilt1000 Instruction Manual PDFDocument11 pagesIlt1000 Instruction Manual PDFreiazhNo ratings yet
- Scan Plans PautDocument32 pagesScan Plans Pautreiazh100% (2)
- ASTM Nondestructive-Testing-Standards PDFDocument9 pagesASTM Nondestructive-Testing-Standards PDFreiazhNo ratings yet
- Radiometer Calibration ProcedureDocument1 pageRadiometer Calibration ProcedurereiazhNo ratings yet
- UT of TKY Connections PDFDocument14 pagesUT of TKY Connections PDFreiazh0% (1)
- Phased Array in Lieu of RadiographyDocument4 pagesPhased Array in Lieu of RadiographyreiazhNo ratings yet
- NDT Training BrochureDocument4 pagesNDT Training BrochureSafiq UddinNo ratings yet
- Phased Array Pipework Inspection A4Document2 pagesPhased Array Pipework Inspection A4reiazhNo ratings yet
- NDT Training BrochureDocument4 pagesNDT Training BrochureSafiq UddinNo ratings yet
- Scan Plans PautDocument32 pagesScan Plans Pautreiazh100% (2)
- Visual Acuity FormDocument1 pageVisual Acuity FormreiazhNo ratings yet
- Phased Array in Lieu of RadiographyDocument4 pagesPhased Array in Lieu of RadiographyreiazhNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Quot - Leak Tester BP Ridwan - PTI Cosmetics - 08apr21Document6 pagesQuot - Leak Tester BP Ridwan - PTI Cosmetics - 08apr21mario gultomNo ratings yet
- Draft Nokia MSC O&M Daily and Weekly ProcessesDocument17 pagesDraft Nokia MSC O&M Daily and Weekly Processestest321yNo ratings yet
- General Tables & Fields Primavera P6Document54 pagesGeneral Tables & Fields Primavera P6José Antonio Ferrer GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Computer Animation and Gaming Industry Strategies for PakistanDocument23 pagesComputer Animation and Gaming Industry Strategies for PakistanMustafa KhanNo ratings yet
- "Fiberglass!", "Why Does It Always Have To Be Fiberglass?": Fiberglass Work in Seven Easy StepsDocument15 pages"Fiberglass!", "Why Does It Always Have To Be Fiberglass?": Fiberglass Work in Seven Easy StepsEsnayder Nova CastellanosNo ratings yet
- TLC Online Learning Packs Brochure 2020Document20 pagesTLC Online Learning Packs Brochure 2020trongnvtNo ratings yet
- Sessions 3 and 4: Business Process Re-EngineeringDocument48 pagesSessions 3 and 4: Business Process Re-Engineeringpick YourpetNo ratings yet
- GNSS Processing Report for TDTV MarkerDocument9 pagesGNSS Processing Report for TDTV MarkerJoshua Paskah NugrahaNo ratings yet
- SBI Online Registration Form for CINB SaralDocument1 pageSBI Online Registration Form for CINB Saralamitjainis60% (5)
- Detailed Seismic Assessment Assessment Objectives PrinciplesDocument71 pagesDetailed Seismic Assessment Assessment Objectives Principlesyoshdog@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- CPK Guide 0211 TECH1Document11 pagesCPK Guide 0211 TECH1Mark LacroNo ratings yet
- Mdaemon enDocument865 pagesMdaemon enYadi RachmanNo ratings yet
- 3 - MT 103 - 202 Base Procedure For Receiver Review and Comments AoDocument4 pages3 - MT 103 - 202 Base Procedure For Receiver Review and Comments Aouink wowNo ratings yet
- Client Contract1Document4 pagesClient Contract1Jeysi MartinezNo ratings yet
- In Southeast Asia Poised For Rapid Growth: AUGUST 2019Document8 pagesIn Southeast Asia Poised For Rapid Growth: AUGUST 2019Nguyễn Vũ HoàngNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE - Module 1 - Welcome To TenableDocument2 pagesLAB EXERCISE - Module 1 - Welcome To Tenablenet flixNo ratings yet
- Lec4-5 QDocument4 pagesLec4-5 QBashir Emad kadimNo ratings yet
- ODJMS Project ReportDocument40 pagesODJMS Project ReportBALACHANDAR R (RA2031005010056)No ratings yet
- APCOB Recruitment for 35 Staff Assistant PostsDocument17 pagesAPCOB Recruitment for 35 Staff Assistant Postsgowthami ravinuthalaNo ratings yet
- Science: Modul E 1 Lesson 1: General ConceptsDocument6 pagesScience: Modul E 1 Lesson 1: General ConceptsORTILE, IVAN H.No ratings yet
- 4 CP NS-01 BD Draft Part 2 Vol.2 EM Version 11 FINAL REV ADocument1,357 pages4 CP NS-01 BD Draft Part 2 Vol.2 EM Version 11 FINAL REV Asamarendra parida100% (1)
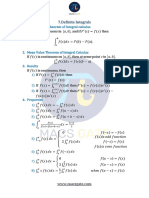
- Definite Integrals and Trigonometric FunctionsDocument4 pagesDefinite Integrals and Trigonometric Functionskartikey papnoiNo ratings yet
- Rainvue SeriesDocument50 pagesRainvue Seriesradicall8No ratings yet
- Microscope 101: How To Safely Use A Microscope: Preparing A Wet-Mount SlideDocument2 pagesMicroscope 101: How To Safely Use A Microscope: Preparing A Wet-Mount SlideClara AbegãoNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller To Sensor Interfacing TechniquesDocument13 pagesMicrocontroller To Sensor Interfacing TechniquesSantosh Martha100% (1)
- Iso 19731-2017Document6 pagesIso 19731-2017Borja Arrizabalaga UriarteNo ratings yet
- Shell Brake Fluids Bring Safety and PerformanceDocument3 pagesShell Brake Fluids Bring Safety and Performancebrojokishor700No ratings yet
- Catalogo VPFT 4535Document91 pagesCatalogo VPFT 4535PRISCILA FAGUNDESNo ratings yet
- CSC 222 - Lecture 1Document30 pagesCSC 222 - Lecture 1trenches4446No ratings yet