Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set 1.1: Modeling
Uploaded by
Soumya AzxOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set 1.1: Modeling
Uploaded by
Soumya AzxCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAP.
1 First-Order ODEs
PROBLEM SET 1.1
CALCULUUs 1720 MODELING, APPLICATIONS
Solve the ODE by integration or by remenmbering a These problems will give you a first impression of modeling
differentiation fornnula. Many more problenms on modeling follow throughout this
I. 2 sin 2m -=0
chapter.
17. Half-life. The half-life measures exponential decay.
It is the time in which half of the given amount of
4. 1.Sr radioactive substance will disappear. What is the half-
5. v= 4t *cos N life of " Ra (in years) in Example 5?
18. Half-life. Radium Ra has a half-life of about
Y cosh 5.13 3.6 days.
0.2
(a) Given I gram, how much will still be present after
I day?
-15 VERIFICATION. INITIAL VALUE (b) After I year?
PROBLEM {IVP} 19. Free fall. In dropping a stone or an iron ball, air
(a) Verify that y is
solution of the ODE. (b) Determine
a resistance is practically negligible.
trom y the particular solution of the IVP.
Experiments
(c) Graph the show that the acceleration of the motion is constant
solution of the IVP. (equal to g = 9.80 m/sec = 32 ft/sec, called the
9. y+4y = 1.4. y ce +0.35, y(0) = ; acceleration of gravity). Model this as an ODE for
10. + 5 = 0. y0) = T
y(t), the distance fallen as a function of time t. If the
ce2.5a
motion starts at timet 0 from rest (i.e., with
=
11. y + e*, y= (x +t c)e, y0) = velocity
12. yy = 41, 2 4 2 = cy > 0), (1) =4
U
=y =
0), show that you obtain the familiar law of
free fall
13. y y- y1+ce MO)=0.25 y g2
14. tan x =
2y -8, y =
csin^x4, yT) =0
+ 20. Exponential decay. Subsonic flight. The efficiency
15. Find of the engines of subsonic
two constant solutions of the ODE in Prob. 13 by airplanes depends on air
inspection. pressure and is usually maximum near 35.000 ft.
Find the air pressure y(t) at this
16. Singular solution. An ODE may sometimes nave an height. Physical
additional solution that cannot be obtained from the information. The rate of change y' (x) is proportional
to the pressure. At 18,000 ft it is
general solution and is then called a singular solution. half its value
yo = y(0) at sea level. Hint. Remember from caleulus
The ODE y xy +y 0 is of this kind. Show
-
=
that if y e,
by differentiation and substitution that it has the
=
then y =
ke =
ky. Can you see
general solution y = cx - c and the singular solution
without calculation that the answer should be close
to yo/4?
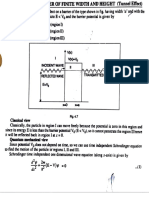
y =x/4. Explain Fig. 6.
4 4
Fig.6. Particular solutions and singular
solution in Problem 16
You might also like
- Lecture 1Document16 pagesLecture 1Anuj JhaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 3 PDFYashodhan JaltareNo ratings yet
- 2.16 EviDocument5 pages2.16 EviFitaNo ratings yet
- Review of Sdof Concepts: CEE490bDocument7 pagesReview of Sdof Concepts: CEE490bpedro sNo ratings yet
- Complex Variables and Partial Differential Equations 2019 Apr (2015 Ad)Document2 pagesComplex Variables and Partial Differential Equations 2019 Apr (2015 Ad)Aswin AswinNo ratings yet
- Recitation 2: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F)Document5 pagesRecitation 2: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F)cindy tatiana rodriguez marinNo ratings yet
- Functions of A Single VariableDocument113 pagesFunctions of A Single VariablegabrielNo ratings yet
- Kunci Jawaban: Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesKunci Jawaban: Bahasa InggrisNur Fahmi FauziatiNo ratings yet
- HW5 SolutionsDocument20 pagesHW5 Solutionsargoubi1984No ratings yet
- Time Response of Systems: 10.1 Some Standard Time ResponsesDocument8 pagesTime Response of Systems: 10.1 Some Standard Time ResponseskiranNo ratings yet
- TF2105 08 Rangkaian - ACDocument51 pagesTF2105 08 Rangkaian - ACGilbert SihombingNo ratings yet
- Ans&Sol JEE (Main)Document16 pagesAns&Sol JEE (Main)manoj jaiswalNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2024 Jan30 Shift2 Physics EveningDocument6 pagesJEE Main 2024 Jan30 Shift2 Physics Eveningjiniyapratihar01No ratings yet
- Year/Sem: III/VI Date: Time:3 Hrs Max. Marks:100Document2 pagesYear/Sem: III/VI Date: Time:3 Hrs Max. Marks:100Karthick DavoothNo ratings yet
- Year/Sem: III/VI Date: Time:3 Hrs Max. Marks:100Document2 pagesYear/Sem: III/VI Date: Time:3 Hrs Max. Marks:100Karthick DavoothNo ratings yet
- Year - M.Sc. (Mathematics) (New CBCS Pattern) Semester - III Subject - PSCMTH11 - Paper-I - Complex AnalysisDocument2 pagesYear - M.Sc. (Mathematics) (New CBCS Pattern) Semester - III Subject - PSCMTH11 - Paper-I - Complex AnalysisRamnareshNo ratings yet
- Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inDocument3 pagesDrttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - in Drttit - Gvet.edu - inrama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 SolutionDocument20 pagesTutorial 6 SolutionCKNo ratings yet
- 2-3 Complex AnalysisDocument12 pages2-3 Complex AnalysisQuickcureNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: X85762: Aeronautical EngineeringDocument3 pagesQuestion Paper Code: X85762: Aeronautical EngineeringSHANMUGARAJ MADASAMYNo ratings yet
- Module 02: Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis, Part 2Document53 pagesModule 02: Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis, Part 2Jos Hua MaNo ratings yet
- Pdes Iii (Hyperbolic Equations) : Phys 535Document53 pagesPdes Iii (Hyperbolic Equations) : Phys 535raul yondoNo ratings yet
- Single Degree of FreedomDocument29 pagesSingle Degree of Freedommm0493440No ratings yet
- TF2105-09-Sinusoids and PhasorsDocument26 pagesTF2105-09-Sinusoids and PhasorsGilbert SihombingNo ratings yet
- JHBVGV 656Document6 pagesJHBVGV 656Luis MancillaNo ratings yet
- The K Ahler Geometry of Toric Manifolds: E-Mail Address: Apostolov - Vestislav@uqam - CaDocument61 pagesThe K Ahler Geometry of Toric Manifolds: E-Mail Address: Apostolov - Vestislav@uqam - CaIvan Coronel MarthensNo ratings yet
- Rebounds in A Capillary TubeDocument4 pagesRebounds in A Capillary TubeSndy MahdiNo ratings yet
- MA3264CHAP1Document59 pagesMA3264CHAP1Nancy QNo ratings yet
- Ma5156 PDFDocument3 pagesMa5156 PDFJsvijay KumarNo ratings yet
- MA108 ODE: Basic Concepts and Examples Lecture 1 (D3 & D4) : Prachi Mahajan IIT BombayDocument26 pagesMA108 ODE: Basic Concepts and Examples Lecture 1 (D3 & D4) : Prachi Mahajan IIT BombayYash SaraogiNo ratings yet
- AE QP 2022Document25 pagesAE QP 2022Bharath ykNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Steady State AnalysisDocument7 pagesSinusoidal Steady State AnalysisMansi Arpit NanavatiNo ratings yet
- First-Order Odes Session 25-26: Course: Math6031 - Calculus Year: 2015Document40 pagesFirst-Order Odes Session 25-26: Course: Math6031 - Calculus Year: 2015bryan chandraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Academy: Branch: Civil Engineering ESE-Offline Test Series - 2015 (Mock I Paper 2) SolutionsDocument20 pagesEngineering Academy: Branch: Civil Engineering ESE-Offline Test Series - 2015 (Mock I Paper 2) Solutionssaxenaarpita41No ratings yet
- (@bohring - Bot) AITS 2324 FT III JEEA Paper 2 SolDocument12 pages(@bohring - Bot) AITS 2324 FT III JEEA Paper 2 Solrajkaran3765No ratings yet
- UPSC CSE Main 2023 Mathematics Optional Paper 1Document5 pagesUPSC CSE Main 2023 Mathematics Optional Paper 1sukutraoNo ratings yet
- EEE209 Online2Document28 pagesEEE209 Online2MeowNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument2 pagesBasic ElectronicsL.ABHISHEK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Ese 2022 Ode - MVCDocument4 pagesEse 2022 Ode - MVCirakool2014No ratings yet
- Review of Sdof Concepts: CEE490b Jan. 7, 2002Document7 pagesReview of Sdof Concepts: CEE490b Jan. 7, 2002stefanNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Apr 09, 2024Document14 pagesAdobe Scan Apr 09, 2024aadritadam2004No ratings yet
- Physics 2020 Cbse Marking SchemeDocument23 pagesPhysics 2020 Cbse Marking SchemeHARSH CHOUHANNo ratings yet
- Course 1assignment - 1 PDFDocument1 pageCourse 1assignment - 1 PDFSHUBHOJEET SINHANo ratings yet
- Free Vibrations of Simply Supported Beams Using Fourier SeriesDocument17 pagesFree Vibrations of Simply Supported Beams Using Fourier SeriesMauro GuerreiroNo ratings yet
- Final Exam SolutionsDocument31 pagesFinal Exam SolutionsSaswati BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Linear Differential Equations With Variable Coefficients: Fundamental Theorem of The Solving KernelDocument20 pagesLinear Differential Equations With Variable Coefficients: Fundamental Theorem of The Solving KernelJay acebedoNo ratings yet
- RevEx 3B04 AnsDocument5 pagesRevEx 3B04 Ans5E (12) LEE MAVISNo ratings yet
- MA 205 Complex Analysis: Lecture 6: U. K. Anandavardhanan IIT BombayDocument18 pagesMA 205 Complex Analysis: Lecture 6: U. K. Anandavardhanan IIT Bombayvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response Analysis: Karl D. Hammond January 2008Document14 pagesFrequency Response Analysis: Karl D. Hammond January 2008Trixie NuylesNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Solution Algorithm For Nonlinear Elasticity Problems by Domain Decomposition MethodDocument8 pagesFinite Element Solution Algorithm For Nonlinear Elasticity Problems by Domain Decomposition MethodsenthilcaeNo ratings yet
- 2022-II-UCV-EquationsDifferential (Exa-3) (03-11-2022)Document2 pages2022-II-UCV-EquationsDifferential (Exa-3) (03-11-2022)Gerson SosaNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration of ADocument12 pagesFree Vibration of AAlex oigara100% (1)
- Example Curl DivDocument4 pagesExample Curl DivHARSH GOYALNo ratings yet
- Sem IV Mathematics Partial Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesSem IV Mathematics Partial Differential Equationsankita kurwaleNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics HomeworkDocument3 pagesQuantum Mechanics HomeworkJuliana Marquez BustosNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Practice Test 1 Answer ExplanationsDocument15 pagesAP Physics 1 Practice Test 1 Answer ExplanationsMohamed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 9 - 3DSEDocument4 pagesProblem Set 9 - 3DSEJesseNo ratings yet
- Tunnel EffectDocument5 pagesTunnel EffectYashmeen KaurNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample (17th Nov 2023)Document8 pagesPhysics Sample (17th Nov 2023)shamimshafeb2005No ratings yet
- High Voltage - 2020 - Su - Electrical Tree Degradation in High Voltage Cable Insulation Progress and ChallengesDocument12 pagesHigh Voltage - 2020 - Su - Electrical Tree Degradation in High Voltage Cable Insulation Progress and ChallengesLuiz KowalskiNo ratings yet
- Pressure Screen Fundamentals 2020 2013.1.261Document43 pagesPressure Screen Fundamentals 2020 2013.1.261RajanbabuNo ratings yet
- Field2014 TheJournalofAsianStudiesDocument18 pagesField2014 TheJournalofAsianStudiesRevathi SakthiNo ratings yet
- R in Hydrology - EGUDocument25 pagesR in Hydrology - EGUJulio Montenegro GambiniNo ratings yet
- Tunnel EngineeringDocument53 pagesTunnel EngineeringshankaregowdaNo ratings yet
- ADAU1701Document12 pagesADAU1701onafetsNo ratings yet
- 1 - TorqueDocument9 pages1 - TorqueIvy GalamitonNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam Empowerment - TechnologiesDocument3 pages2nd Quarter Exam Empowerment - Technologieskathryn soriano100% (11)
- Nao Presentation - Robotics Lab, KCTDocument16 pagesNao Presentation - Robotics Lab, KCTRamkumar ANo ratings yet
- Treatment of LeprosyDocument11 pagesTreatment of LeprosyFajar YuniftiadiNo ratings yet
- Annotation in Indicator 2Document1 pageAnnotation in Indicator 2jon pantzNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term SyllabusDocument1 page2nd Term SyllabusBiplab233No ratings yet
- Fire Arson InvestigationDocument8 pagesFire Arson InvestigationJoshua D None-NoneNo ratings yet
- Sri Chaitanya Charitamrita PDFDocument3 pagesSri Chaitanya Charitamrita PDFAuther MerlinNo ratings yet
- PM For Ageing EquipmentDocument16 pagesPM For Ageing EquipmentAkhtar QuddusNo ratings yet
- NCPFORMATstudentcopy 2Document4 pagesNCPFORMATstudentcopy 2Reinhardt MostolesNo ratings yet
- S-CMT01 - Mechanical Training MCQ Screw Compressors - Presentations - EnglishDocument204 pagesS-CMT01 - Mechanical Training MCQ Screw Compressors - Presentations - Englishjmdc88% (8)
- Kuiz Minggu ICT Kelab Briged BestariDocument9 pagesKuiz Minggu ICT Kelab Briged Bestaribubblelicious_0701No ratings yet
- Social Media Strategy TemplateDocument11 pagesSocial Media Strategy TemplateCall Central USA ITNo ratings yet
- 7 Mobileye PDFDocument4 pages7 Mobileye PDFANDRES MORALESNo ratings yet
- Construction Issue: Qty. (Nos) AI DI AO DO Hvac System I Water Chilling Units 3Document11 pagesConstruction Issue: Qty. (Nos) AI DI AO DO Hvac System I Water Chilling Units 3Al Amin Hossain Srabon100% (1)
- Under Water Wind Mill ReportDocument13 pagesUnder Water Wind Mill ReportASHUTOSH SAHOOLME011 (LME011)No ratings yet
- Parliamentary Election Impact W14299-PDF-ENGDocument8 pagesParliamentary Election Impact W14299-PDF-ENGHarshit ShubhankarNo ratings yet
- Walls Sbu of UnileverDocument25 pagesWalls Sbu of Unilevermaham azizNo ratings yet
- Books Published in Goa 2007Document24 pagesBooks Published in Goa 2007Frederick NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Manual EQD Depths PDFDocument2 pagesManual EQD Depths PDFClaudio Villagra Revisor ArqNo ratings yet
- Mild Steel TMT BarDocument5 pagesMild Steel TMT BarEktaNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument4 pagesResumeapi-233282347No ratings yet
- Atlantic ComputersDocument16 pagesAtlantic ComputersNipun Duhan100% (1)
- Teachers English Proficiency Test 1Document13 pagesTeachers English Proficiency Test 1Vladimer Desuyo Pionilla100% (1)