Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Two Marks WC
Uploaded by
baby yoda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesFrequency borrowing involves congested cells using frequencies from adjacent cells. Cell splitting subdivides congested cells into smaller cells with reduced antenna height and transmitter power to increase capacity. Sectoring uses directional antennas to decrease co-channel interference and improve performance. Coherence time is the maximum duration the channel can be assumed constant, while coherence bandwidth is the frequency separation of two samples in the frequency domain.
Original Description:
.
Original Title
Two marks WC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFrequency borrowing involves congested cells using frequencies from adjacent cells. Cell splitting subdivides congested cells into smaller cells with reduced antenna height and transmitter power to increase capacity. Sectoring uses directional antennas to decrease co-channel interference and improve performance. Coherence time is the maximum duration the channel can be assumed constant, while coherence bandwidth is the frequency separation of two samples in the frequency domain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesTwo Marks WC
Uploaded by
baby yodaFrequency borrowing involves congested cells using frequencies from adjacent cells. Cell splitting subdivides congested cells into smaller cells with reduced antenna height and transmitter power to increase capacity. Sectoring uses directional antennas to decrease co-channel interference and improve performance. Coherence time is the maximum duration the channel can be assumed constant, while coherence bandwidth is the frequency separation of two samples in the frequency domain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Two marks 6.
Define Frequency borrowing
UNIT- I Frequency borrowing: In the simplest case, frequencies are taken from
1. Write some examples for wireless communication system adjacent cells by congested cells. The frequencies can also be assigned
Cordless phones, handheld walkie-talkies, pagers, mobiles, remote to cells dynamically.
controllers for home entertainment. 7. Define cell splitting.
2. Define Small scale fading Cell splitting is the process of subdividing congested cells into smaller
Small scale fading is the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio cells each with its own base stations and a corresponding reduction in
signal over a short period of time or distance. antenna height and transmitter power. It increases the capacity of
3. Define Large scale fading cellular system.
Large scale fading is the fading associated with a larger coverage area 8. What is sectoring?
for a long amount of time. Sectoring is a technique for decreasing co-channel interference and thus
4. Define ISI? increasing the system performance by using directional antennas.
The major consequence of multipath component is signal dispersion. 9. What are the types of Channels in cellular systems
The impulse response of the channel is not a single delta pulse but Two types of channels are available between the mobile unit and the
rather a sequence of pulses (different MPCs), each of which has a base station (BS): control channels and traffic channels.
distinct arrival time in addition to having a different amplitude and Control channels are used to exchange information having to do with
phase. This signal dispersion leads to InterSymbol Interference (ISI) setting up and maintaining calls and with establishing a relationship
at the RX between a mobile unit and the nearest BS.
5. What are the approaches for Increasing the Capacity? Traffic channels carry a voice or data connection between users.
A number of approaches have been used to cope with this situation, 10. What is hand off?
including the following: When a mobile moves into a different cell while conversation in
a. Adding new channels: progress, the MSC automatically transfers the call from one cell to other
b. Frequency borrowing cell without any interference. This is called as hand off.
c. cell splitting 11. What is meant by frequency reuse?
d. sectoring If an area is served by a single Base Station, then the available spectrum
e. Microcell can be divided into N frequency channels that can serve N users
simultaneously. If more than N users are to be served, multiple BSs are required. For this channel assignment is used. The types of channel
required, and frequency channels have to be reused in different assignment are:
locations. Since spectrum is limited, the same spectrum has to be used i. Fixed channel assignment
for different wireless connections in different locations. This method of ii. Dynamic channel assignment.
reusing the frequency is called as frequency reuse
12. Define FDMA, TDMA and CDMA. UNIT II
FDMA - the total bandwidth is divided into non-overlapping frequency 1. What are the propagation mechanisms of EM waves?
subbands. TDMA – divides the radio spectrum into time slots and in The four propagation mechanisms of EM waves are
each slot only one user is allowed to either transmit or receive. CDMA i. Free space propagation
– many users share the same frequency same tome with different coding. ii. Reflection
13. What are the features of TDMA? iii. Diffraction
Features of TDMA are: iv. Scattering
i. TDMA shares a single carrier frequency with several users, 2. What is the significance of propagation model?
where each user makes use of non-overlapping time slots. The major significance of propagation model are:
ii. Data transmission occurs in bursts. i. Propagation model predicts the parameter of receiver.
iii. Handoff process is much simpler ii. It predicts the average received signal strength at a given
iv. Duplexers are not required, since transmission and reception distance from the transmitter.
occurs at different time slots. 3. What do you mean by small scale fading?
14. What are the features of FDMA? Features of FDMA are: Rapid fluctuations of the amplitude, phase as multipath delays of a radio
i. FDMA channel carries only one phone circuit at a time signal over a short period of time is called small scale fading.
ii. The bandwidth of FDMA channels are relatively narrow as each 4. What are the factors influencing small scale fading?
channel supports only one circuit per carrier. The factors which influence small scale fading are: Multipath
15. What is channel assignment? What are the types? propagation, Speed of the mobile, Speed of surrounding objects and the
For efficient utilization of radio spectrum a frequency reuse transmission bandwidth of the signal.
scheme with increasing capacity and minimizing interference is 5. When does large scale propagation occur?
Large scale propagation occurs due to general terrain and the density Coherence time is the maximum duration for which the channel can be
and height of buildings and vegetation, large scale propagation occurs. assumed to be approximately constant. It is the time separation of the
6. Differentiate the propagation effects with mobile radio. two time domain samples. Coherence bandwidth is the frequency
Slow Fading Fast Fading Slow variations in the signal strength. Rapid separation of the two frequency domain samples.
variations in the signal strength. Mobile station (MS) moves slowly. 10. Define EIRP.
Local objects reflect the signal causes fast fading. It occurs when the EIRP (Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power) of a transmitting
large reflectors and diffracting objects along the transmission paths are system in a given direction is defined as the transmitter power that
distant from the terminal. Eg. Rayleigh fading, Rician fading and would be needed, with an isotropic radiator, to produce the same power
Doppler shift It occurs when the user terminal (MS) moves for short density in the given direction. EIRP=PtGt Where Pt-transmitted power
distances. in W Gt-transmitting antenna gain.
7. Define Doppler shift. 11. Explain path loss.
If the receiver is moving towards the source, then the zero crossings of The path loss is defined as the difference (in dB) between the effective
the signal appear faster and the received frequency is higher.The transmitted power and the received power. Path loss may or may not
opposite effect occurs if the receiver is moving away from the source. include the effect of the antenna gains.
The resulting chance in frequency is known as the Doppler shift (fD). PL(dB)=10log Pt/Pr
FD = fr – f0 = -f0V/C Where f0 -> transmission frequency fr -> received 12. What is scattering?
frequency When a radio wave impinges on a rough surface, the reflected energy is
8. Differentiate time selective and frequency selective channel. spread out in all directions due to scattering.
The gain and the signal strength of the received signal are time varying 13. Name some of the outdoor propagation models?
means then the channel is described as time selective channel. The Some of the commonly used outdoor propagation models are i.
frequency response of the time selective channel is constant so that Longely-Rice model ii. Durkin’s model iii. Okumura model.
frequency flat channel. The channel is time invariant but the impulse 14. Define indoor propagation models.
response of the channel show a frequency-dependent response so called The indoor propagation models are used to characterizing radio
frequency selective channel. propagation inside the buildings. The distances covered are much
9. Define coherence time and coherence bandwidth. smaller, and the variability of the environment is much greater for
smaller range of Transmitter and receiver separation distances. Features
such as lay-out of the building, the construction materials, and the 6. Define temporal diversity.
building type strongly influence the propagation within the building. Wireless propagation channel is time variant, so for sufficient
15. Mention some indoor propagation models? decorrelation, the temporal distance between antennas must be atleast
Some of the indoor propagation models are: the half of maximum Doppler frequency.
i. Long –distance path loss model 7. What is meant by frequency diversity?
ii. Ericession multiple break point model Correlation is increased by transmitting information on more than one
iii. Attenuation factor model. carrier frequency. Frequencies are separated by more than one
UNIT III coherence bandwidth of the channel. So the signals will not experience
1. How the link performance can be improved? same fades.
Link performance can be improved by various techniques such as 8. What is transmit diversity?
i. Equalization Diversity effect is achieved by transmitting signals from several
ii. Diversity transmit antenna.
iii. Channel coding 9. What is an equalizer?
2. Why diversity and equalization techniques are used? Equalizer is a linear pulse shaping circuit which is used to reduce ISI.
To reduce ISI, Equalization technique is used. Diversity is used to 10. What is diversity?
reduce fading effects. Diversity is used to compensate the fading channel impairments and is
3. What is diversity? usually implemented by using two or more receiving antennas.
Signal is transmitted by more than one antenna via channel. It ensures Diversity improves transmission performance by making use of more
that the same information reaches the receiver on statistically than one independently faded version of the transmitted signal.
independent channels. 11. Define spatial diversity.
4. Define Switched Diversity The most common diversity technique is spatial diversity, whereby
If the signal level falls below the threshold, then the receiver switches multiple antennas are strategically spaced and connected to a common
to a new antenna which is called as switched diversity. receiving system. While one antenna sees a signal null, one of the other
5. Define feedback or scanning diversity. antenna may sees a signal peak, and the receiver is able to select the
All the signals are scanned in a fixed sequence until one signal is found antenna with the best signals at any time.
to be above a predetermined threshold.
UNIT IV 6. What is W-CDMA?
1. State the principles of CDMA. It is a 3G wireless standard for cellular telephony. It provides better
Principles of CDMA: efficiency, higher peak rates upto 2 Mbps. Bandwidth of 5 MHz.
i. Many users share the same frequency. Supports multimedia applications.
ii. Each user is assigned a different spreading code. 7. What are the services offered by GSM?
2. How the capacity can be increased in CDMA? Services offered by GSM are:
Capacity in CDMA can be increased by i. Telephone services
i. Quiet periods during speech transmission are shared by many ii. Bearer or Data services
users. iii. Supplementary services
ii. Flexible data rate. 8. List the advantages and disadvantages of FH-SS.
iii. Soft capacity. Advantages of FH-SS:
iv. Error Correction coding used. i. High processing gain than DS-SS.
3. Write short notes on OFDM. ii. Shorter acquisition time makes the system fast.
OFDM splits the information into N parallel streams which are Disadvantages of FH-SS:
modulated by N distinct carriers and then transmitted. In order to i. FH-SS requires large bandwidth.
separate the subcarriers by the receiver, they have to be orthogonal. ii. Circuit used for FH-SS is complex. Expensive frequency
4. Why cyclic prefix? synthesizers are required.
In delay dispersive channel, inter carrier interference occur. To 9. List the types of FH-SS.
overcome the effect of inter carrier interference and ISI, cyclic prefix is Types of FH-SS are:
introduced. i. Slow frequency hopping
It is a cyclically extended guard interval whereby each symbol sequence ii. Fast frequency hopping
is preceded by a periodic extension of the sequence itself. 10. Write the two types of spread spectrum?
5. Write the goals of GSM standard. Types of spread spectrum are: Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DS-
Better and more efficient technical solution for wireless SS) Frequency hop spread spectrum (FH-SS)
communication. Single standard was to be realized all over Europe 11. What do you mean by spread spectrum?
enabling roaming across borders.
Spread spectrum multiple access uses signals which have a transmission standard offers the time bounded and asynchronous services. The data
bandwidth whose magnitude is greater than the minimum required RF rate of this standard is 54 Mbits/s at 5 GHZ.
bandwidth. A pseudo noise (PN) sequence converts a narrowband signal 5. Define Basic Service Set?
to a wideband noise like signal before transmission. IEEE 802.11 defines the BSS as the building block of a wireless
12. What is the frequency range of uplink and downlink in GSM LAN. It consists of stationary or mobile stations and a possible central
network? base station known as Access Point.
The frequency range of uplink in GSM network is 890-960 MHz.
The frequency range of downlink in GSM network is 935-960 MHz.
UNIT V
1. List the type of architecture used in IEEE 802.11
• Infrastructure based
• Ad-Hoc based
2. What is Bluetooth? Give its data rate.
Bluetooth is an open specification for short range wireless voice and
data communications that was developed for cable replacement in PAN
(Personal Area Network). The maximum data rate is 721 for asymmetric
mode.
3. What are IEEE 802.11 Services?
- Association
- Reassociation
- Disassociation - Authentication
- Privacy
4. What is IEEE 802.11 standard?
The IEEE 802.11 standard specifies the physical and medium access
layer adapted to the special requirements of wireless LANs. This
You might also like
- Wireless Communication Cellular ArchitectureDocument15 pagesWireless Communication Cellular ArchitectureTECH FROM ASHNo ratings yet
- EC 6801 - Wireless Communication QB (New One)Document20 pagesEC 6801 - Wireless Communication QB (New One)SamuelHericNo ratings yet
- K. RAMAKRISHNAN COLLEGE EC6801 Wireless Communication Question Bank Part ADocument14 pagesK. RAMAKRISHNAN COLLEGE EC6801 Wireless Communication Question Bank Part Aهيثم محمد عبده قائد المخلافيNo ratings yet
- Wireless CommunicationDocument15 pagesWireless CommunicationShahzebKhurshidNo ratings yet
- Fifth Semester Wireless Communication Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013Document12 pagesFifth Semester Wireless Communication Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJI78% (9)
- Mobile CommunicationDocument16 pagesMobile CommunicationArun SampathNo ratings yet
- Ec2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit IDocument10 pagesEc2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit ITrishul SampathNo ratings yet
- Ec 71 QBDocument16 pagesEc 71 QBepregithaNo ratings yet
- EC 3501 Wireless CommunicationDocument20 pagesEC 3501 Wireless CommunicationParanthaman GNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Key ConceptsDocument11 pagesWireless Communication Key ConceptsNupoor BombNo ratings yet
- EC1451 - Mobile CommunicationDocument18 pagesEC1451 - Mobile Communicationarivurp67% (3)
- Mobile Communication 2-MARK Questions and AnswersDocument16 pagesMobile Communication 2-MARK Questions and Answersnoblelion92% (12)
- 2 How Mobile WorksDocument84 pages2 How Mobile Workspnlinh28No ratings yet
- Ec2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit IDocument10 pagesEc2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit Inazareth621No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument184 pagesUntitledKathiravan ReddyNo ratings yet
- It1403 Mobile ComputingDocument15 pagesIt1403 Mobile Computingappsectesting3No ratings yet
- WC Cellular ArchitectureDocument4 pagesWC Cellular ArchitectureJagan GcNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Fundamentals ExplainedDocument25 pagesWireless Communication Fundamentals ExplainedAbirami ManiNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument6 pagesUnit IimanoprabhaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication 2 MarksDocument14 pagesWireless Communication 2 MarksBala Subramani100% (2)
- MC Module1 MU Questions With SolutionsDocument8 pagesMC Module1 MU Questions With Solutionskhanvilkarshruti6No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Multiplexing: StructureDocument15 pagesUnit 8 Multiplexing: StructurelandNo ratings yet
- Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of TechnologyDocument33 pagesSns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of Technology Sns College of TechnologyakttripathiNo ratings yet
- EC2401-Wireless Communication Notes VII Semester ECEDocument94 pagesEC2401-Wireless Communication Notes VII Semester ECEsplouvrosNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topics With Material: UNIT-1Document69 pagesAssignment Topics With Material: UNIT-1Prabhakara RaoNo ratings yet
- CST64Document16 pagesCST64Thiagu RajivNo ratings yet
- What Are Different Categories of Antenna and Give An Example of Each?Document8 pagesWhat Are Different Categories of Antenna and Give An Example of Each?Anonymous qYuxgojGe3No ratings yet
- MCC-Assignment 1Document4 pagesMCC-Assignment 1Saif ChogleNo ratings yet
- cs2402 2 Marks Question Bank-With AnswerDocument26 pagescs2402 2 Marks Question Bank-With AnswerFrousper29No ratings yet
- Ec1451 Mobile CommunicationDocument12 pagesEc1451 Mobile CommunicationainugiriNo ratings yet
- Communications Interview Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesCommunications Interview Questions and Answersshiv389No ratings yet
- What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Wireless Communication?Document31 pagesWhat Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of Wireless Communication?Kanishk JainNo ratings yet
- Mcqbanksem 7Document15 pagesMcqbanksem 7jaskaran31No ratings yet
- Wireless Mobile Communication Unit 3Document28 pagesWireless Mobile Communication Unit 3Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- SR - No Topic Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8: Celluler Network Technology GSMDocument36 pagesSR - No Topic Name 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8: Celluler Network Technology GSMMahavir JadavNo ratings yet
- Adhoc and Sensor Networks CharacteristicsDocument25 pagesAdhoc and Sensor Networks CharacteristicsMohammed AkilNo ratings yet
- ECE Interview Questions With AnswersDocument7 pagesECE Interview Questions With AnswersRohit Xavier100% (1)
- Mobile Computing Sample Ques AnsDocument6 pagesMobile Computing Sample Ques AnsAmirtharaj SelvamohanNo ratings yet
- CMC (2marks)Document9 pagesCMC (2marks)Prabhu PkNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Small Scale FadingDocument43 pagesChapter Two Small Scale FadingGuta MekesaNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing Techniques and Cellular SystemsDocument5 pagesMultiplexing Techniques and Cellular SystemsSaif ChogleNo ratings yet
- Define Soft Hand Off and Hard Hand OffDocument3 pagesDefine Soft Hand Off and Hard Hand OffJagan GcNo ratings yet
- Mobile CommunicationDocument27 pagesMobile CommunicationUmamageswari KumaresanNo ratings yet
- TN 424: OFDM techniques for wireless channelsDocument34 pagesTN 424: OFDM techniques for wireless channelsJoakim NgatungaNo ratings yet
- WC UNIT 1 Two Marks2021 22Document5 pagesWC UNIT 1 Two Marks2021 22r jeyanthiNo ratings yet
- Coverage and Size of The RadiosDocument22 pagesCoverage and Size of The RadiosAalaa Hussein HamidNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing and App Development SyllabusDocument112 pagesMobile Computing and App Development SyllabusAbbhinav JaiinNo ratings yet
- Win, Scholtz - 1998 - Impulse Radio How It WorksDocument3 pagesWin, Scholtz - 1998 - Impulse Radio How It WorksAhmed AbdelraheemNo ratings yet
- My WaveDocument8 pagesMy WaveFrancis LubangoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Wireless Networks OverviewDocument5 pagesCellular Wireless Networks OverviewMarufa Kamal LabonnoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Mobile Computing and Wireless TechnologiesDocument33 pagesBasics of Mobile Computing and Wireless TechnologiesDinesh CNo ratings yet
- TELECOMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING: CELLULAR CONCEPTSDocument31 pagesTELECOMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING: CELLULAR CONCEPTSAbid SagorNo ratings yet
- Wireless AssignDocument3 pagesWireless AssignPankia Mer AmunNo ratings yet
- Frequency ReuseDocument8 pagesFrequency ReuseiamhannielynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1Document40 pagesChapter 3 Part 1Behailu AsmareNo ratings yet
- Cellular Networks, Satellite Communication 1 Satellite CommunicationDocument9 pagesCellular Networks, Satellite Communication 1 Satellite CommunicationSsk TempNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication: Cellular Systems and SDMADocument7 pagesWireless Communication: Cellular Systems and SDMAمجيد علاء خضيرNo ratings yet
- WC02-Celluar Concept and Analysis (Part 1)Document45 pagesWC02-Celluar Concept and Analysis (Part 1)Nguyễn Thái NguyênNo ratings yet
- Ps2 Mobile CommunicationDocument10 pagesPs2 Mobile Communicationchikku090700No ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Malayalam Handwriting StudyDocument6 pagesMalayalam Handwriting Studybaby yodaNo ratings yet
- ALL IN ONE COURSE FOR CENTRAL GOVT JOBSDocument1 pageALL IN ONE COURSE FOR CENTRAL GOVT JOBSA.VengadeshNo ratings yet
- 100 English Nouns That Are Plural OnlyDocument1 page100 English Nouns That Are Plural Onlybaby yodaNo ratings yet
- Trains AptitudeDocument19 pagesTrains Aptitudebaby yodaNo ratings yet
- By-Product of Fishing IndustryDocument6 pagesBy-Product of Fishing Industrybaby yodaNo ratings yet
- If You Are Wondering How To Get To Visayas and Mindanao by LandDocument7 pagesIf You Are Wondering How To Get To Visayas and Mindanao by LandHisoka HillingtonNo ratings yet
- Due Diligence InvestmentsDocument6 pagesDue Diligence InvestmentselinzolaNo ratings yet
- NHBC Standards 2011 Bre SD 1 SRCDocument5 pagesNHBC Standards 2011 Bre SD 1 SRCSuresh RaoNo ratings yet
- Ulliensb PDF 1516040087Document30 pagesUlliensb PDF 1516040087Jose Daniel ArangoNo ratings yet
- Dhaka Epz Factory List & List of Inspected Factories by EIMS For AllianceDocument12 pagesDhaka Epz Factory List & List of Inspected Factories by EIMS For Alliancearman chowdhury100% (4)
- Proximate Cause ExplainedDocument3 pagesProximate Cause ExplainedJoanne BayyaNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument13 pagesHistoryMuhamed Zimić ZimaNo ratings yet
- ) (Significant Digits Are Bounded To 1 Due To 500m. However I Will Use 2SD To Make More Sense of The Answers)Document4 pages) (Significant Digits Are Bounded To 1 Due To 500m. However I Will Use 2SD To Make More Sense of The Answers)JeevikaGoyalNo ratings yet
- TUTO 4 PU Sol PDFDocument21 pagesTUTO 4 PU Sol PDFVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesNo ratings yet
- GPU, A Gnutella Processing UnitDocument27 pagesGPU, A Gnutella Processing UnitMengotti Tiziano FlavioNo ratings yet
- Joint Ventures Synergies and BenefitsDocument5 pagesJoint Ventures Synergies and BenefitsleeashleeNo ratings yet
- Mode D'emploi 2-43 Operating Instructions 44-85 Manual de Instrucciones 86-127Document43 pagesMode D'emploi 2-43 Operating Instructions 44-85 Manual de Instrucciones 86-127Oleksii_ServiceNo ratings yet
- Manual Flowpet 5GDocument56 pagesManual Flowpet 5GRahkmat DanizarNo ratings yet
- California Evaluation Procedures For New Aftermarket Catalytic ConvertersDocument27 pagesCalifornia Evaluation Procedures For New Aftermarket Catalytic Convertersferio252No ratings yet
- Case Study of Vietinbank Dao Hoang NamDocument14 pagesCase Study of Vietinbank Dao Hoang NamNam ĐàoNo ratings yet
- How Nokia Failed to Adapt to Market ChangesDocument5 pagesHow Nokia Failed to Adapt to Market ChangesRiangelli ExcondeNo ratings yet
- AarDocument2 pagesAarkomar agusNo ratings yet
- LeCroy 1996 Catalog (Reduced Size) PDFDocument196 pagesLeCroy 1996 Catalog (Reduced Size) PDFpetrocelliNo ratings yet
- Operation Manuals HCWA10NEGQ - Wired ControllerDocument2 pagesOperation Manuals HCWA10NEGQ - Wired Controllerchamara wijesuriyaNo ratings yet
- Sources of Finance ExplainedDocument114 pagesSources of Finance Explained7229 VivekNo ratings yet
- TMA2 12 09 2021 UploadDocument3 pagesTMA2 12 09 2021 UploadG.G. PRABHATH CHINTHAKANo ratings yet
- W3. The Relational ModelDocument21 pagesW3. The Relational ModelSABOOR UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Balcony AnalysysDocument4 pagesBalcony AnalysysKory EstesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document21 pagesAssignment 2api-445531772No ratings yet
- Design Thinking ReflectionDocument3 pagesDesign Thinking ReflectionNeil PerlasNo ratings yet
- Ram SAP MM Class StatuscssDocument15 pagesRam SAP MM Class StatuscssAll rounderzNo ratings yet
- Table 141: India'S Overall Balance of Payments - RupeesDocument2 pagesTable 141: India'S Overall Balance of Payments - Rupeesmahbobullah rahmaniNo ratings yet
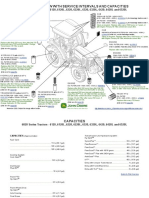
- SE John Deere 6020 Series Filter Overview and Capacities 6120 6120L 6220 6220L 6320 6320L 6420 6420L 6520L NOV20Document2 pagesSE John Deere 6020 Series Filter Overview and Capacities 6120 6120L 6220 6220L 6320 6320L 6420 6420L 6520L NOV20marianNo ratings yet
- 04 Greeting Card Activity RubricDocument1 page04 Greeting Card Activity RubricJon Jon Marcos100% (2)
- Analysis and Design of BeamsDocument12 pagesAnalysis and Design of BeamsHasanain AlmusawiNo ratings yet