Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04-10-01 Phosphoric Acid - Qualitative Method
Uploaded by
Muhammad Farhan HidayatOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04-10-01 Phosphoric Acid - Qualitative Method
Uploaded by
Muhammad Farhan HidayatCopyright:
Available Formats
Acids AACC International Method 04-10.
01
Page 1 of 1
Phosphoric Acid—Qualitative Method
Final approval May 5, 1960; Reapproval November 3, 1999
Objective
To determine the presence of phosphate salts in baking powders and baking
chemicals. The phosphates are present in baking powders as the acid
component, responsible for reacting with the bicarbonate source, causing carbon
dioxide to evolve. Typical phosphates used are monocalcium phosphate
(anhydrous and monohydrate), sodium acid pyrophosphate, sodium aluminum
phosphate, dicalcium phosphate, and dimagnesium phosphate. In baking
chemicals, such as dough conditioners and yeast foods, phosphates are used as
nutrient sources and pH/buffering agents. Dough conditioners may contain
calcium or ammonium phosphates.
Apparatus
1. Beaker, 150-ml
2. Litmus paper.
3. Filter paper.
Reagent
Ammonium molybdate solution (Method 04-11.01, reagent 2).
Procedure
1. To 1–2 g of sample in 150-ml beaker, add 10 ml water.
2. Make acid to litmus with 1N HNO3 and filter.
3. To volume of filtrate, add equal volume of ammonium molybdate solution
and warm at 40–50°. Yellow precipitate indicates presence of phosphate.
Reference
AOAC International. 1995. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed. Method
965.18D. The Association, Arlington, VA.
doi: 10.1094/AACCIntMethod-04-10.01
You might also like
- NPK FertilizerDocument11 pagesNPK FertilizerShivaniNo ratings yet
- Phytochemistry (Introduction, Plant Metabolites and PhytochemicalDocument48 pagesPhytochemistry (Introduction, Plant Metabolites and Phytochemicalanisahanifatinr100% (1)
- Phosphorus and Potassium AnalysisDocument9 pagesPhosphorus and Potassium AnalysisMatanda KatumbaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Phosphoric AcidDocument17 pages6 - Phosphoric AcidRohan GohilNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Phosphoric Acid SummaryDocument15 pagesPhosphoric Acid SummaryMarnel Roy Mayor100% (2)
- Content: The Determination of The Amount of Phosphate in A DetergentDocument20 pagesContent: The Determination of The Amount of Phosphate in A DetergentAditya jain100% (10)
- Phosphate Content PDFDocument5 pagesPhosphate Content PDFjuli_radNo ratings yet
- 10-05-01 Guidelines For Measurement of Volume by Rapeseed DisplacementDocument4 pages10-05-01 Guidelines For Measurement of Volume by Rapeseed DisplacementMuhammad Farhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- CMT 565 Experiment 6 Ltm-Phosphorus (P) : Name Student Id Group Name of PartnersDocument14 pagesCMT 565 Experiment 6 Ltm-Phosphorus (P) : Name Student Id Group Name of PartnersAiNo ratings yet
- 04-11-01 Phosphoric Acid - Quantitative MethodDocument2 pages04-11-01 Phosphoric Acid - Quantitative MethodMuhammad Farhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- 04-11-01 Phosphoric Acid - Quantitative MethodDocument2 pages04-11-01 Phosphoric Acid - Quantitative MethodMuhammad Farhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- Ex PhosphonatesDocument1 pageEx PhosphonatesBapu ReddyNo ratings yet
- CTA 61 PhosphatesDocument5 pagesCTA 61 PhosphatesrohitindiaNo ratings yet
- Standard Methods For The Examination of Water and WastewaterDocument9 pagesStandard Methods For The Examination of Water and WastewaterRuzy MohammadNo ratings yet
- Method 365.3: Phosphorous, All Forms (Colorimetric, Ascorbic Acid, Two Reagent)Document5 pagesMethod 365.3: Phosphorous, All Forms (Colorimetric, Ascorbic Acid, Two Reagent)Ahmed IsmailNo ratings yet
- The Colorimetric Determination of Total Phosphorous in Plant SolutionsDocument8 pagesThe Colorimetric Determination of Total Phosphorous in Plant SolutionsCahyo AjiNo ratings yet
- 365.3 Phosphorous, All Forms (Colorimetric, Ascorbic Acid, Two Reagent)Document4 pages365.3 Phosphorous, All Forms (Colorimetric, Ascorbic Acid, Two Reagent)moontrocNo ratings yet
- Exp5 The Green Minded 3735Document16 pagesExp5 The Green Minded 3735CyberR.DomingoNo ratings yet
- Determinare FosforDocument10 pagesDeterminare FosforDaniela CatanaNo ratings yet
- PapermineDocument6 pagesPaperminerikitasingh2706No ratings yet
- Catalytic Effect of Molybdate Hydrolysis of Organic Phosphate BondsDocument7 pagesCatalytic Effect of Molybdate Hydrolysis of Organic Phosphate BondsInda AlwanNo ratings yet
- MAss Balance of Phosphoric AcidDocument6 pagesMAss Balance of Phosphoric Acidwhãts brøNo ratings yet
- Phot.28.AUTO Phosphate LR v2WQDocument2 pagesPhot.28.AUTO Phosphate LR v2WQtcsconsultancyandserviceNo ratings yet
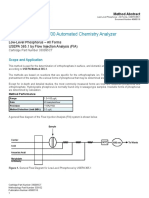
- Flow Solution FS 3700 Automated Chemistry AnalyzerDocument3 pagesFlow Solution FS 3700 Automated Chemistry AnalyzerAnonymous Z7Lx7q0RzNo ratings yet
- NPK FertilizerDocument11 pagesNPK FertilizermajidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Technology Phosphoric Acid Industry: Dr. Abhi Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Contai PolytechnicDocument2 pagesChemical Technology Phosphoric Acid Industry: Dr. Abhi Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Contai PolytechnicSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Vhemistry ProjectDocument16 pagesVhemistry Projectpriyankab7106No ratings yet
- Bikf3e3a9eb070full PDFDocument8 pagesBikf3e3a9eb070full PDFTri atikaNo ratings yet
- PapermineDocument6 pagesPapermineZaib Un NisaNo ratings yet
- Lampila-2013-Annals of The New York Academy of SciencesDocument8 pagesLampila-2013-Annals of The New York Academy of Sciencesdiagnoz7auto7carsvanNo ratings yet
- ApatitDocument9 pagesApatittrinh xuan hiepNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument34 pagesChemAaghash A SNo ratings yet
- WQV 07 COMP Ortho - Total - PhosphatesDocument11 pagesWQV 07 COMP Ortho - Total - Phosphatesagsan.algabh2718No ratings yet
- Phosphoric Acid H3Po4, Sulfuric Acid H2So4: ApplicationDocument2 pagesPhosphoric Acid H3Po4, Sulfuric Acid H2So4: ApplicationLaras SubektiNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction in The Phosphate Fertilizer IndustryDocument18 pagesSolvent Extraction in The Phosphate Fertilizer IndustryvzgscribdNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document11 pagesExperiment 7Anonymous YC6Sq5zNo ratings yet
- Phosphoric AcidDocument3 pagesPhosphoric AcidhussainNo ratings yet
- Introduction-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesIntroduction-WPS OfficeHIMANSHU VARDHANNo ratings yet
- Roy Amitava 197605 PHD 261183Document151 pagesRoy Amitava 197605 PHD 261183Oleg ShkolnikNo ratings yet
- Development and Application of A Novel UV Methodfor The Analysis of Ascorbic AcidDocument5 pagesDevelopment and Application of A Novel UV Methodfor The Analysis of Ascorbic Acidronahaniifah11No ratings yet
- 4500-P Phosphorus : 1. OccurrenceDocument16 pages4500-P Phosphorus : 1. OccurrenceOlgaNo ratings yet
- J. Biol. Chem.-1912-Folin-239-43Document6 pagesJ. Biol. Chem.-1912-Folin-239-43Сергей ГубскийNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 2020-2021Document23 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project 2020-2021S100% (1)
- Chemical Phosphorous Removal and Online AnalysisDocument31 pagesChemical Phosphorous Removal and Online AnalysisKrishna PedapatiNo ratings yet
- Research Project Phosphate DeterminationDocument4 pagesResearch Project Phosphate Determinationkunalkushwah4141No ratings yet
- Ullmanns Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates 58db177445fedDocument44 pagesUllmanns Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates 58db177445fedMuhammad FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Phosphoric Acid SummaryDocument15 pagesPhosphoric Acid SummaryamirNo ratings yet
- Partial Purification and Characterization of Polyphenol Oxidase From Sugarcane (Saccharum Officinarum L.)Document7 pagesPartial Purification and Characterization of Polyphenol Oxidase From Sugarcane (Saccharum Officinarum L.)Madelaine MaciasNo ratings yet
- Phosphate Det.Document4 pagesPhosphate Det.dafteri11No ratings yet
- 2007 WAS Fermentation PHsDocument7 pages2007 WAS Fermentation PHsQuỳnh PhươngNo ratings yet
- P 00405-p 00414Document10 pagesP 00405-p 00414elias_77No ratings yet
- Process Industries - Lecture Material 4Document30 pagesProcess Industries - Lecture Material 4Barnabas YohannesNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus in Oil. Production of Molybdenum Blue Derivative at Ambient Temperature Using Noncarcinogenic ReagentsDocument4 pagesPhosphorus in Oil. Production of Molybdenum Blue Derivative at Ambient Temperature Using Noncarcinogenic ReagentsAhmed IsmailNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus-To-Phospholipid Conversion Factors ForDocument4 pagesPhosphorus-To-Phospholipid Conversion Factors ForkartikkeyyanNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Method For The Determination of Phosphorus in Natural Waters Using The Bismuth-Phosphomolybdate ComplexDocument6 pagesSpectrophotometric Method For The Determination of Phosphorus in Natural Waters Using The Bismuth-Phosphomolybdate ComplexKartika AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- The Determination of The Amount of Phosphate in A DetergentDocument8 pagesThe Determination of The Amount of Phosphate in A DetergentHarish Parthasarathy0% (1)
- AIMDocument5 pagesAIMroshanjimaxoutNo ratings yet
- Iodized Salt Spec - Testing and Sampling MethodDocument9 pagesIodized Salt Spec - Testing and Sampling MethodHenok DireNo ratings yet
- Chem 28 Gravimetric Determination of PHDocument3 pagesChem 28 Gravimetric Determination of PHEdi HaryantoNo ratings yet
- 10 1007@bf00750564Document6 pages10 1007@bf00750564Jorge Alberto QuirogaFigueredoNo ratings yet
- 10-15-01 Baking Quality of Angel-Cake FlourDocument4 pages10-15-01 Baking Quality of Angel-Cake FlourMuhammad Farhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- Total Dietary Fiber (Codex Alimentarius Definition) : ObjectiveDocument12 pagesTotal Dietary Fiber (Codex Alimentarius Definition) : ObjectiveMuhammad Farhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- 04-22-01 Citric and Isocitric AcidsDocument5 pages04-22-01 Citric and Isocitric AcidsMuhammad Farhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- 04-27-01 Tartaric Acid - Quantitative MethodDocument2 pages04-27-01 Tartaric Acid - Quantitative MethodMuhammad Farhan Hidayat100% (1)